-
摘要:
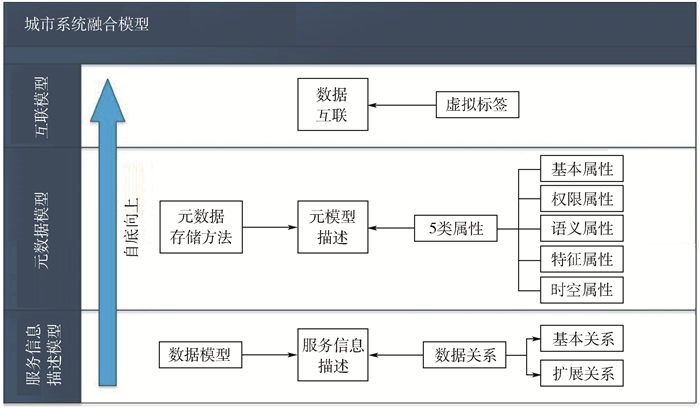
随着云计算和大数据等技术的发展及城市发展的迫切需求,智慧城市已成为近年来国内外研究的热点之一。随着城市中摄像头、监测传感器等采集设备数量的增加,城市数据种类也越来越多。所获取的城市数据具有多源、异构、时变、高维等多模式特性。如何让这些多模式的城市数据关联起来,实现它们的互通互联,挖掘出更丰富多样的信息,从而能更好地指导智慧城市的构建,是本领域的难点。本文提出了一个城市多模式数据融合模型,即多模式互联生长(MICROS)模型,并从3个层面对该模型进行了描述。首先,针对多模式数据的特点,重点描述了多模式数据多源、异构、时变、高维等特点。其次,针对多模式数据的特点,自底向上构建实现针对多模式数据的融合过程的3层基础模型,分别是服务信息描述模型、元数据模型和数据互联模型。最后,在这3层模型的基础上,本文提出了一个适用于智慧城市建设的多模式数据融合模型。
-
关键词:
- 智慧城市 /
- 多模式数据 /
- 数据挖掘 /
- 数据融合 /
- 多模式互联生长(MICROS)模型
Abstract:With the rapid growth of cloud computing and big data, in addition to the urgent demand for city development, smart city construction has become one of the hot topics of domestic and international computer science researches. With the increasing number of closed-circuit televisions and sensor devices in urban city, types of data that people can obtain in city increase as well. The city data has multimodal properties like time dependent, heterogeneous, multi-source and high-dimension. How to make the multimodal city data connected, related to each other, and interconnected to each other, and how to mine better and various information for city construction become the key in this area. In this paper, we propose a multimodal data fusion model for smart city:the multimodal connecting growing fusion (MICROS) model. We present our model in three directions. First, targeting at multimodal data, we describe four features:multisource, heterogeneous, time-dependent and high-dimension. Second, we construct the three-layer fundamental model structure for multimodal fusion from bottom to top, including service-information description model, meta-data model and data-connection model. Finally, based on this three-layer fundamental model, we propose a multimodal data fusion model suitable for smart city construction.
-
表 1 基本数据关系
Table 1. Basic data relationship
关系定义 释义(A关系名B) defined by A由B定义 contains A包含了B subconcept of A是B的子概念 has state A具有B状态 has role in A是B的一个角色 at A在B takes A作用于B implements B由A实施 for A为了B used by A被B所用 responsibility of A对B有责任关系 provided by A由B提供 owned by A为B所有 data links A和B是互联 has outcome A能产出B derived from A由B驱动 applies A使用B for outcome A是B的产出 influenced by A被B影响 planned A由B计划 has A具有B about 关于关系 records A记录B members of A是B的成员 raised from A产生于B data activation 数据A活化B cause A引发B 表 2 扩展数据关系
Table 2. Expansion data relationship
关系定义 释义(A关系名B) co-ordination A协调关系 monitoring A监控B integration A集成B procurement A采购B supply chain A供应链 configuration A配置B broadband connection A连接B operation A操作B 表 3 元数据属性的描述方法
Table 3. Method for meta-data property description
描述项 释义 编号 按一定规则排列的属性项的顺序号 中文名称 该属性项的中文标识 英文名称 该属性项的英文标识 目的 描述该属性项的必要性和作用 约束性 说明采用该属性项的强制性程度 值域 可以分配给该属性项的值 缺省值 该属性项的默认值 注释 对该属性项的进一步说明 表 4 “性别”这一基本属性的描述方法
Table 4. Method for basic property "gender" description
描述项 释义 编号 101016001 中文名称 性别 英文名称 gender 目的 描述人员的性别特征 约束性 非必填项 值域 1(男),0(女) 缺省值 无 注释 无 -
[1] WANG L, JING C, ZHOU P.Security structure study of city management platform based on cloud computing under the conception of smart city[C]//20124th International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security (MINES).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2012:91-94. [2] LI H, XUE L, ZHU Y, et al.The application and implementation research of smart city in China[C]//2012 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2012:288-292. [3] COLLINS J P.Sailing on an ocean of 0 s and 1s[J].Science, 2010, 327(5972):1455-1456. doi: 10.1126/science.1186123 [4] NIELSEN M.A guide to the day of big data[J].Nature, 2009, 462(7274):722-723. doi: 10.1038/462722a [5] WICKER J, KRAUTER N, DERSTORFF B, et al.Cinema data mining:The smell of fear[C]//Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.New York:ACM, 2015:1295-1304. [6] WANG J P, CONG G, ZHAO X W, et al.Mining user intents in twitter:A semi-supervised approach to inferring intent categories for tweets[C]//29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2015 and the 27th Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference.Palo Alto, CA:AAAI, 2015:318-324. [7] GRBOVIC M, RADOSAVLJEVIC V, DJURIC N, et al.E-commerce in your inbox:Product recommendations at scale[C]//21st ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2015.New York:ACM, 2015:1809-1818. [8] GROVES A R, BECKMANN C F, SMITH S M, et al.Linked independent component analysis for multimodal data fusion[J].Neuroimage, 2011, 54(3):2198-2217. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.073 [9] SRIVASTAVA N, SALAKHUTDINOV R.Multimodal learning with deep Boltzmann machines[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(8):1967-2006. http://jmlr.org/papers/volume15/srivastava14b/srivastava14b.pdf [10] STATHOPOULOS A, TSEKERIS T.The athens dynamic traffic map for multimodal travel information services[J].Journal of Maps, 2008, 4(1):119-133. doi: 10.4113/jom.2008.1001 [11] LINDEN G, SMITH B, YORK J.Amazon.com recommendations:Item-to-item collaborative filtering[J].Internet Computing IEEE, 2003, 7(1):76-80. doi: 10.1109/MIC.2003.1167344 [12] O'GRADY M, O'HARE G.Computer science.How smart is your city [J].Science, 2012, 335(6076):1581-1582. doi: 10.1126/science.1217637 [13] NAM T, PARDO T A.Conceptualizing smart city with dimensions of technology, people, and institutions[C]//International Digital Government Research Conference:Digital Government Innovation in Challenging Times.New York:ACM, 2011:282-291. [14] SCHOEPFLIN T N, DAILEY D J.Dynamic camera calibration of roadside traffic management cameras for vehicle speed estimation[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2003, 4(2):90-98. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2003.821213 [15] PORIKLI F, LI X.Traffic congestion estimation using hmm models without vehicle tracking[C]//Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2004.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2004:188-193. [16] FAN W, CHEN Z, XIONG Z, et al.The Internet of data:A new idea to extend the IOT in the digital world[J].Frontiers of Computer Science, 2012, 6(6):660-667. http://www.docin.com/p-884155272.html [17] PORIA S, CAMBRIA E, HUSSAIN A, et al.Towards an intelligent framework for multimodal affective data analysis[J].Neural Networks, 2015, 63:104-116. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.10.005 [18] ZHENG L Y, MA H, WU B, et al.Estimation of travel time of different vehicle types at urban streets based on data fusion of multisource data[C]//14th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals:Safe, Smart, and Sustainable Multimodal Transportation Systems, CICTP 2014.Panama:ASCE, 2014:452-466. -







 下载:
下载: