-
摘要:
针对现有动态故障树分析方法存在的状态空间爆炸、计算效率低、适用范围有限等缺点,提出一种基于顺序二元决策图的动态故障树分析方法。在将动态逻辑门转化为含顺序事件的逻辑门的基础上,给出了顺序二元决策图的模型以及含有顺序事件的布尔运算规则,利用顺序二元决策图和扩展的布尔运算获取动态故障树的失效路径,并给出多单元顺序事件的发生概率。以某弹药为实例,考虑不完全覆盖问题,针对指数分布与非指数分布2种情形进行了动态故障树分析,结果表明该方法具有计算高效、精度高、适用性广泛等优点,为复杂动态系统的可靠性分析提供了理论基础。
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of the existing dynamic fault tree analysis method, such as state space explosion, low computational efficiency and limited application range, a method for dynamic fault tree analysis based on sequential binary decision diagram is proposed. First, dynamic logic gates are transformed into logic gates with sequential events. Next, sequential binary decision diagram model and Boolean operation with sequential events are presented. Then, failure paths of dynamic fault tree are obtained by sequential binary decision diagram and extensional Boolean operation. Finally, probability calculations for sequential events with multi-unit are deduced. With a certain ammunition as an example, considering the imperfect coverage problem, the dynamic fault tree is analyzed under the situations of exponential and non-exponential distribution. The results show that this method has the advantages of high efficiency, high accuracy and wide applicability, which provides a theoretical basis for the reliability analysis of complex dynamic systems.
-
故障树分析作为一种重要的系统可靠性分析方法,已成功应用于核工业、航空航天、电子通信等众多领域,为提高产品的安全性与可靠性发挥了巨大作用[1-2]。然而,传统的故障树分析方法把系统失效看作部件失效的组合,而忽视了部件间的优先关系、顺序关系、功能相关性等动态失效特性,因此,在分析具有动态失效特征的系统可靠性时存在较大误差。为解决系统的动态行为建模问题,Dugan 等[3-4]提出了动态故障树分析方法,定义一组动态逻辑门来描述部件的动态特征,弥补了传统故障树分析方法的不足。早期的动态故障树分析方法采用马尔可夫模型[5-6],该模型只适用于部件寿命服从指数分布的情形,同时面临着状态空间爆炸的风险。1997年,Gulati和Dugan[7]提出模块化方法进行动态故障树分析,该方法只是在一定程度上缓解了马尔可夫模型面临的状态爆炸问题而未能从根本上解决。马尔可夫模型和模块化方法存在的缺陷限制了动态故障树定量分析的发展,众多研究者开始探索动态故障树分析的新方法。2003年,Amari等[8]提出一种基于复合梯形积分的数值方法,该方法求解动态故障树时不需要转化为马尔可夫模型,然而难以处理含重复单元的故障树。2005年,Boudali和Dugan[9]将动态故障树转化为贝叶斯网络进行分析,避免了状态爆炸问题的发生,但在处理部件寿命为非指数分布时,计算精度较低。2009年,Rao等[10]提出一种基于蒙特卡罗仿真方法,该方法适用于部件寿命服从任意分布类型,具备较高的计算精度,但需要大量的计算时间。
随着研究者对动态故障树定量分析方法的不断深入,顺序二元决策图作为一种高效、高精度、适用范围广的方法得到了广泛的关注。2011年,Xing等[11]利用顺序二元决策图对只含优先与门的动态系统进行了可靠性分析,但文中方法得到的失效路径含有不可能发生的伪失效路径。同时,文献[12-13]采用顺序二元决策图对不可修冷备份系统和温备份系统进行了可靠性分析,但未考虑备份结构的不完全覆盖问题。不完全覆盖问题指系统不能及时监测、定位并调整失效组件,进而导致整个系统发生故障的现象[14]。目前,基于顺序二元决策图的分析方法主要对含单一动态逻辑门的系统进行可靠性分析,而对多种动态逻辑门混合的系统缺乏研究。
本文采用顺序二元决策图对含有优先与门、备份门等多种逻辑门的动态故障树进行分析,给出了考虑不完全覆盖时系统的可靠性计算方法,并实例论证方法的可行性,同时与传统方法进行比较,结果显示该方法具有较高的计算效率、良好的计算精度和广泛的适用性等优点,为复杂动态系统的可靠性分析奠定了基础。
1. 动态故障树基础
1.1 动态逻辑门
随着系统复杂程度的增加,系统部件通常存在动态失效特征。为解决系统动态行为的建模问题,在传统的故障树分析基础上引入动态逻辑门而构成动态故障树的方法被提出。这些动态逻辑门包括优先与门(PAND)、顺序相关门(SEQ)、功能相关门(FDEP)以及备份门(SPARE)。系统失效由部件基本事件状态以及它们的相互关系决定,这个相互关系源于系统的拓扑学。动态故障树分析依赖于与门、或门、k/n门等静态逻辑门和优先与门、顺序相关门、备份门、功能相关门等动态逻辑门。备份门和优先与门是系统设计中应用最广泛的动态逻辑门,下面对其进行重点介绍。
1) 优先与门
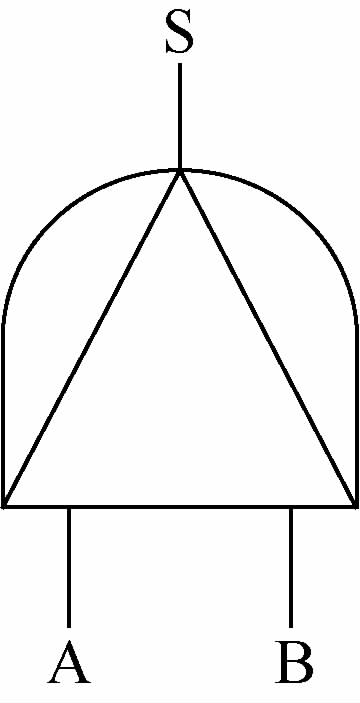
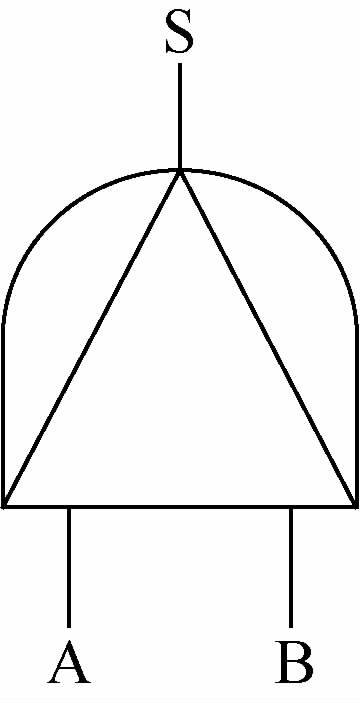
在容错系统的可靠性分析中,系统的失效可能与部件的失效顺序有关,优先与门相比于与门增加了一个附加条件,即部件的失效必须按照特定的顺序发生。如图 1所示,优先与门有2个输入事件A、B,当A、B均失效,且A先于B失效,其输出S才失效。优先与门的输入可以是基本事件,也可以是逻辑门的输出端。
2) 备份门
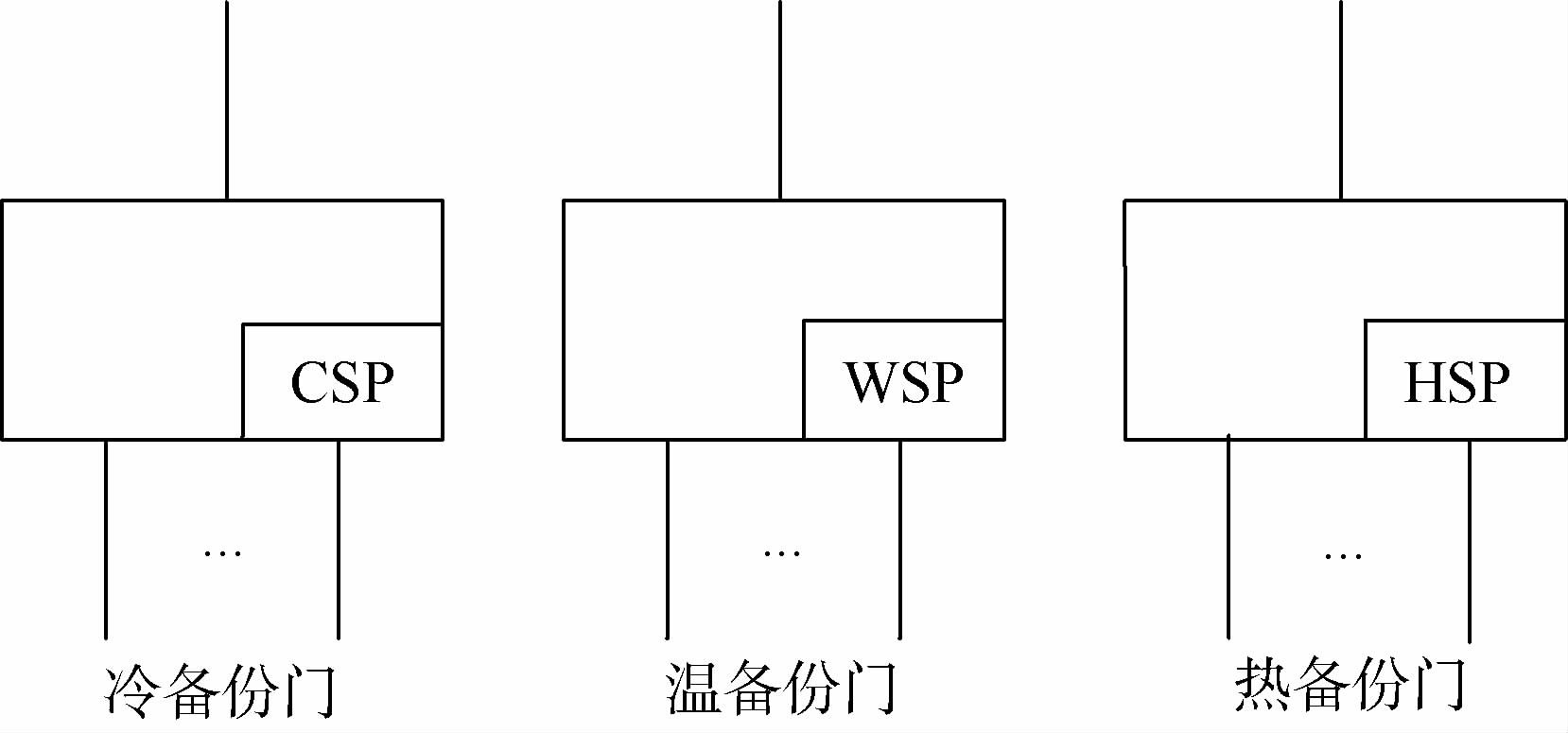
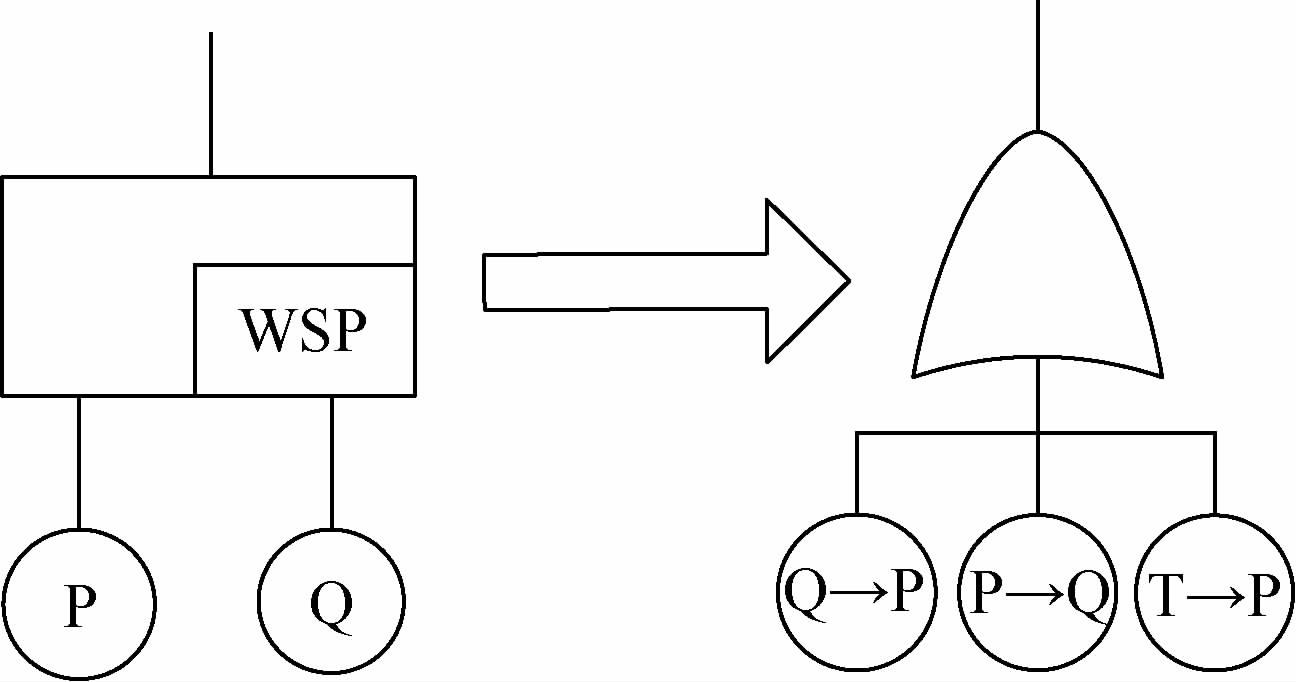
根据备份单元处于储备状态与工作状态下失效率的大小关系,备份门可分为冷备份(CSP)、温备份(WSP)和热备份(HSP),其图形符号如图 2所示。
在备份门中,主件处于工作状态,而备份件处于储备状态,当主件发生失效后,备份单元才进入工作状态。冷备份门在进入工作状态前视为无耗损,即失效率为零。温备份门指备份件在储备状态下失效率小于工作状态下的失效率,因此,当其进入工作状态时,可能已经失效。而热备份门中备份件在储备状态下与工作状态下失效率相同,当不考虑备份结构的覆盖问题时,热备份门等同于并联结构。温备份门是最接近于实际工程的备份结构。
1.2 二元决策图
二元决策图是一种布尔运算的图的表现,在函数的逐层展开过程中对各变量进行0或者1的赋值,直到函数的终值。二元决策图是一个具有有限节点的有向无环图,其节点包含终节点和非终节点。终节点没有输出边,且只能用0和1表示,每个非终节点用一个输入变量表示,且有2条0和1的输出边,其中0和1表示这个节点变量分别取0和1时对应的分支。每个二元决策图只有一个根节点,从根节点到终节点为1的路径即为系统的失效路径。二元决策图的运算基于香农分解法则,其数学表达式为

(1) 式中:f为变量X布尔逻辑表达式;x为变量X的变量值,x=1和x=0分别表示变量X失效和完好2种状态;ite为if-then-else法则的简写;F1和F2分别表示fx=1和fx=0。f发生概率表达式为

(2) 系统的故障树自下而上可通过以下运算规则转化为系统的二元决策图[15]。

(3) 式中:g表示布尔表达式;◇表示与、或逻辑关系;index表示输入变量列表中布尔变量的顺序,合理的变量顺序有利于得到结构简单的二元决策图。
1.3 顺序二元决策图
传统的二元决策图只适用于静态故障树,而无法处理顺序相关等动态行为。在动态故障树中,动态逻辑门输入事件的失效顺序关系对系统失效具有重大的影响,因此本文采用→表示部件失效的顺序关系。例如,在温备份中,P为主件,Q为备份件,P →Q 表示P、Q均发生失效,且P先于Q失效,备份件Q在P失效前处于储备状态,其故障率为αQ,当P失效后,备份件Q进入工作状态,其失效率变为λQ。Q →P 表示P、Q均发生失效,且Q先于P失效,意味着Q在储备状态下发生失效,其失效率为αQ。顺序二元决策图是二元决策图的扩展,弥补了传统二元决策图无法分析动态逻辑门的缺陷。基于顺序二元决策图的动态故障树分析方法包括以下3个过程:动态故障树的转化、顺序二元决策图模型的建立和顺序二元决策图的分析评估。
2. 基于顺序二元决策图的分析方法
2.1 动态故障树的转化
动态逻辑门是动态故障树分析的难点,对动态逻辑门进行适当的转化有利于动态故障树的求解。例如,动态逻辑门可转化为马尔可夫链和贝叶斯网络以便进一步的研究。本文将动态逻辑门转化为顺序事件或者含有顺序事件的逻辑门。优先与门和备份门是实际工程中最常见的动态逻辑门,而温备份门又是备份门中最符合实际情况的,因此,本文重点介绍优先与门和温备份门的转化方法。
1) 优先与门的转化
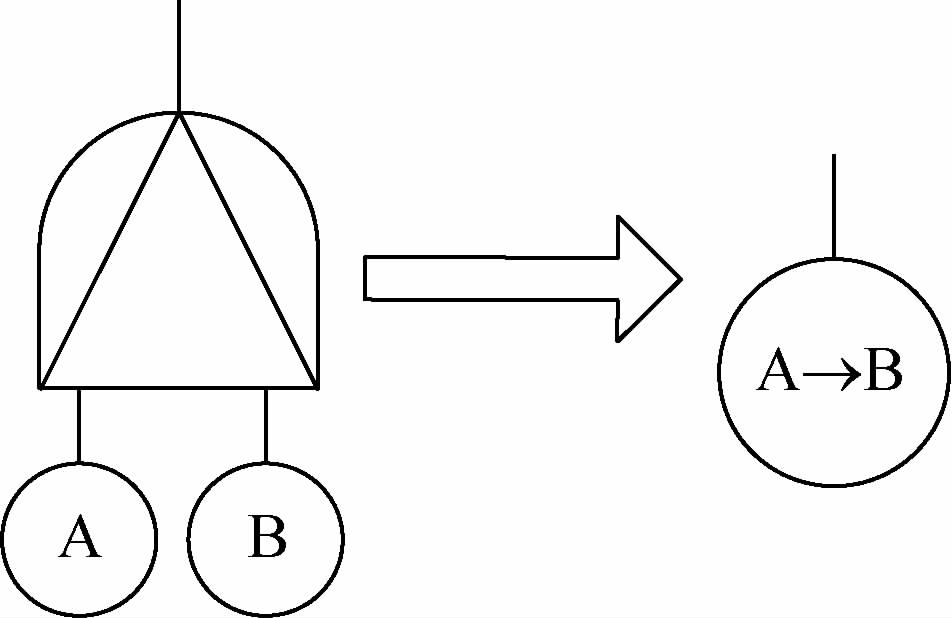
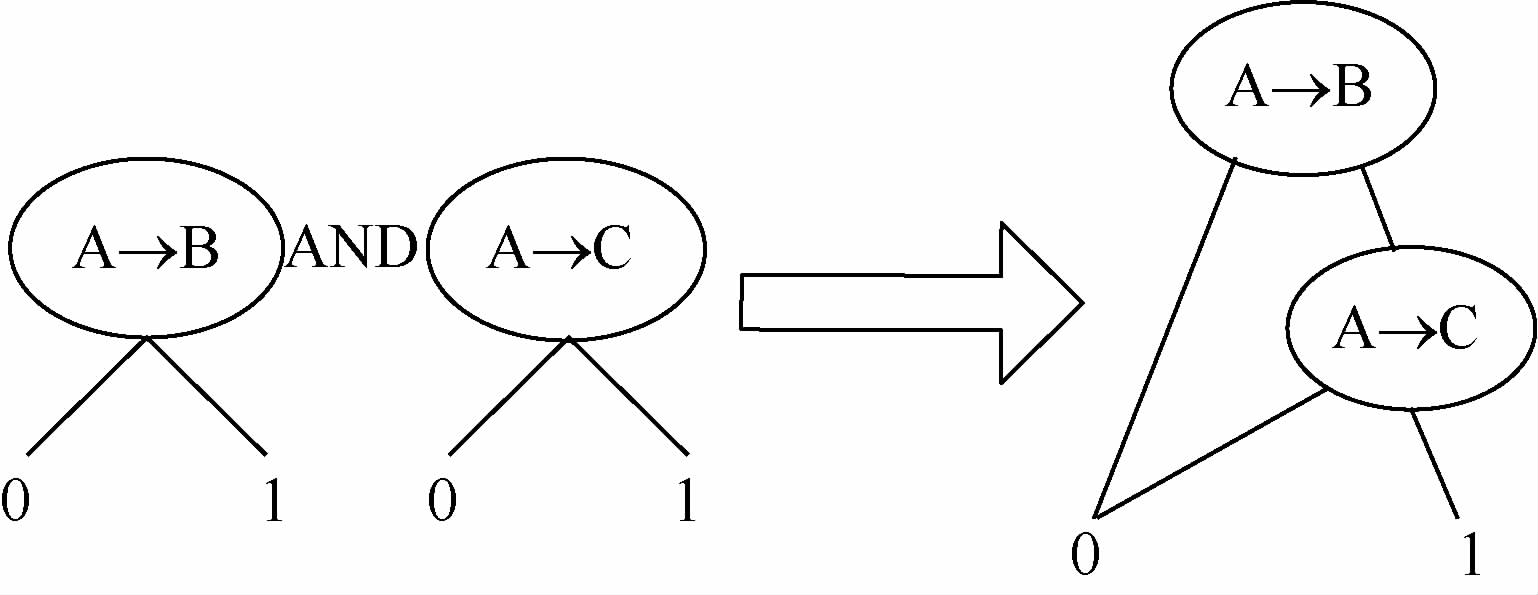
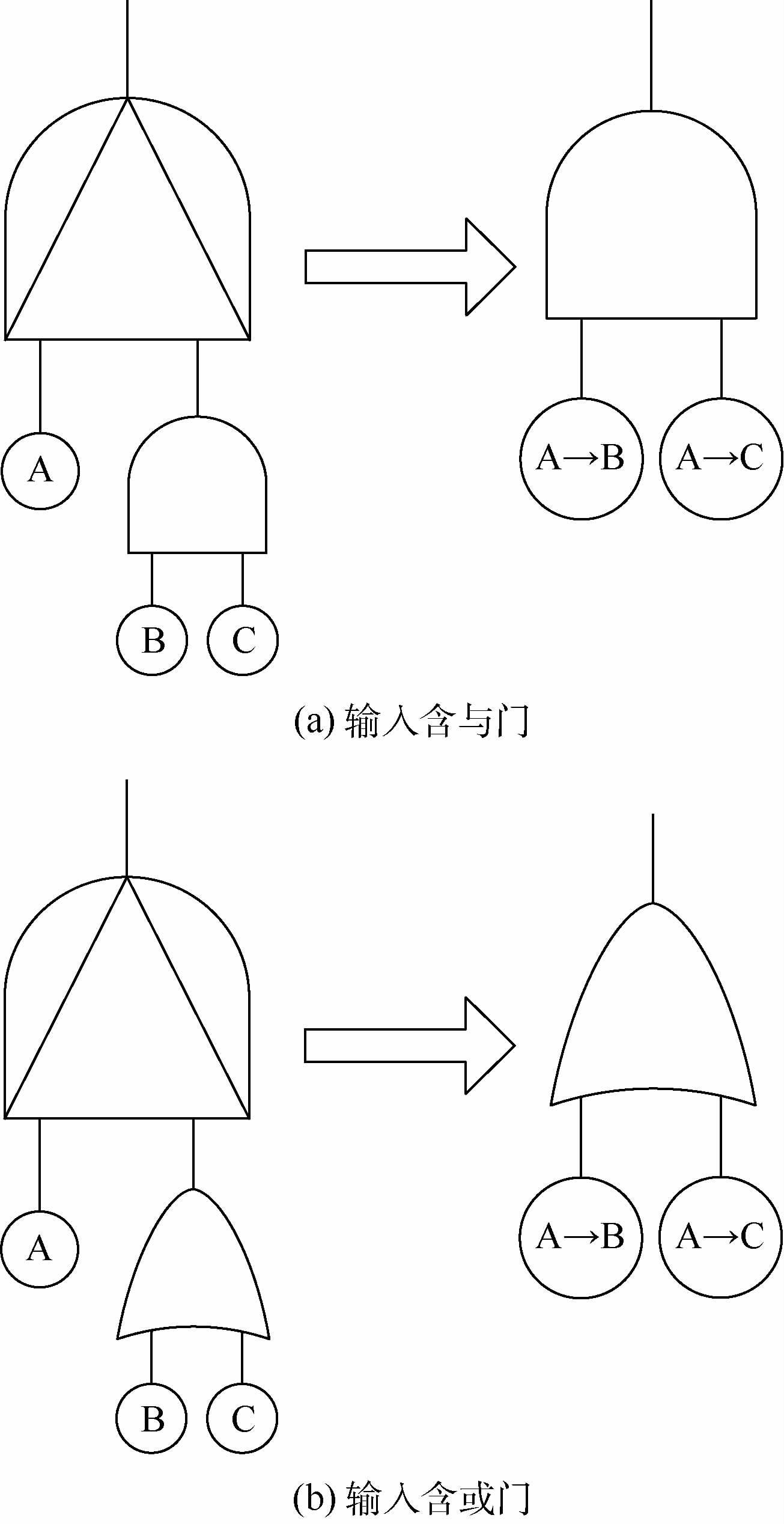
当优先与门的输入均为基本事件时,优先与门可转化为顺序事件,其转化方法如图 3所示。图中A→B为顺序事件,其含义为A、B均发生,且A先于B发生。
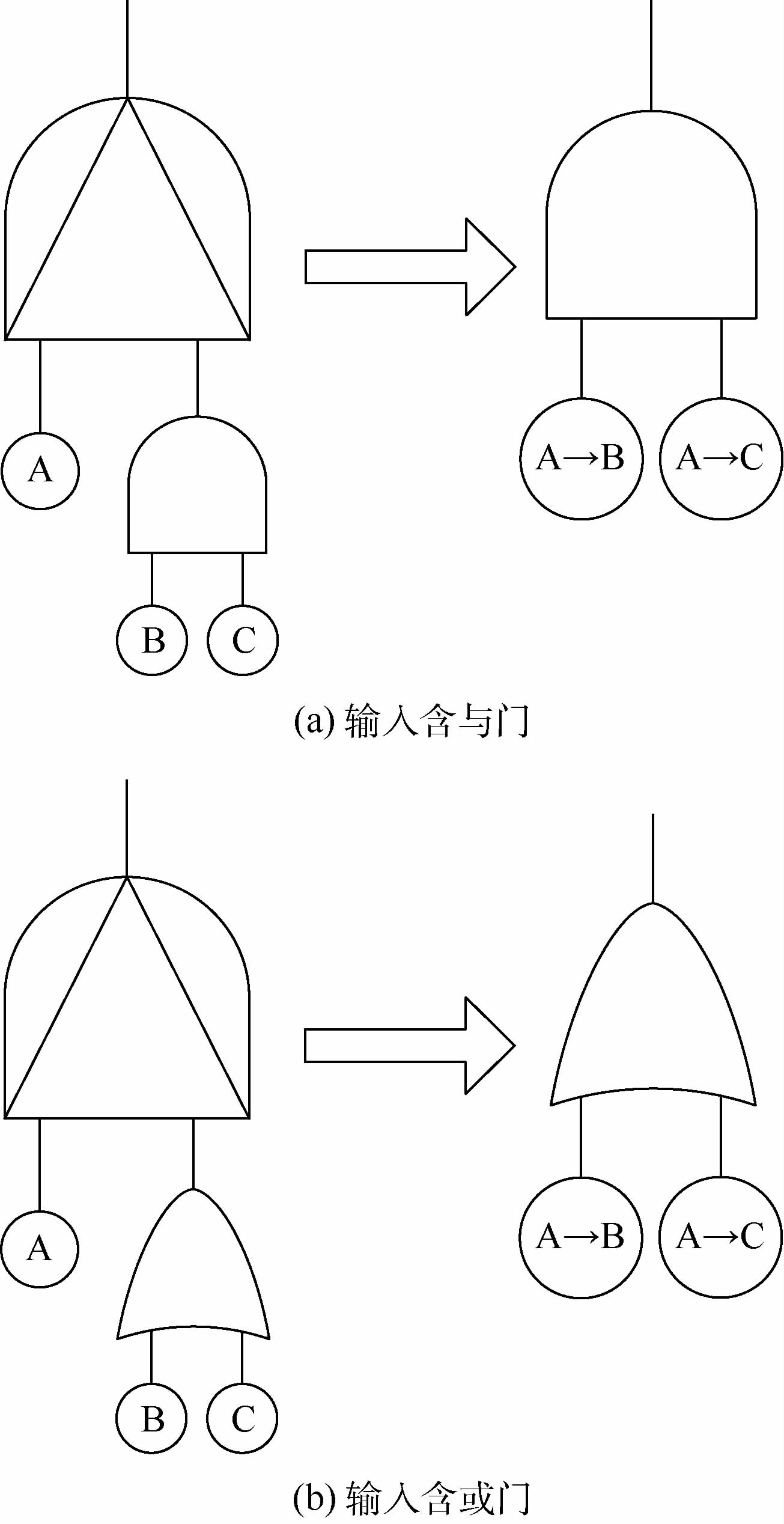
当优先与门的输入含有逻辑门时,优先与门可转化为含顺序事件的逻辑门,其转化方法如图 4所示。图中A→C也是顺序事件,其含义与A→B类似。
2) 温备份门的转化
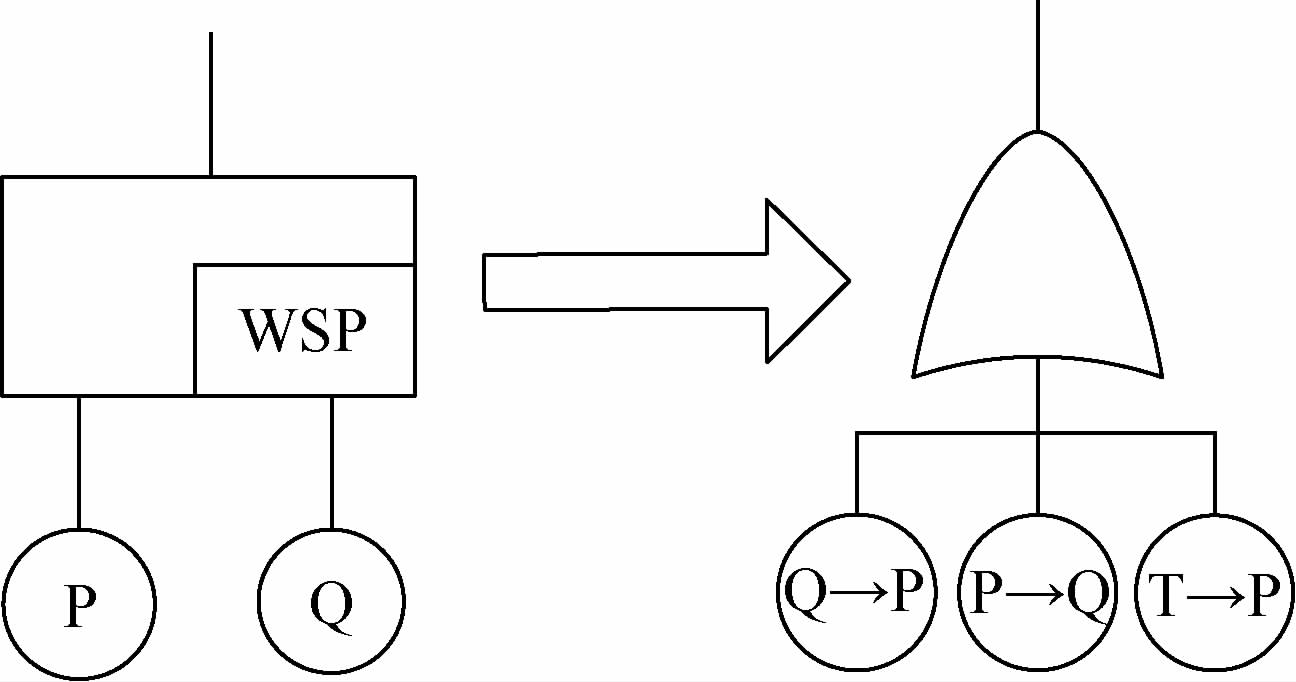
当考虑备份结构的不完全覆盖时,系统的不完全覆盖是由于系统不能及时监测定位故障的发生并成功切换到备份单元而引起的。假定监测、定位、转换装置为基本事件T,此时备份门可转化为含顺序事件的逻辑门,其转化方法如图 5所示。
2.2 顺序二元决策图模型的建立
在建立系统的顺序二元决策图模型时,假设所有的事件都相互独立,即使对于含有相同单元的2个事件也认定为相互独立,如事件A→B和事件A→C,事件的相关性将在顺序二元决策图的分析评估中考虑。系统的顺序二元决策图建模方法与传统的二元决策图方法类似,其具体方法参考式(3),下面举例说明。
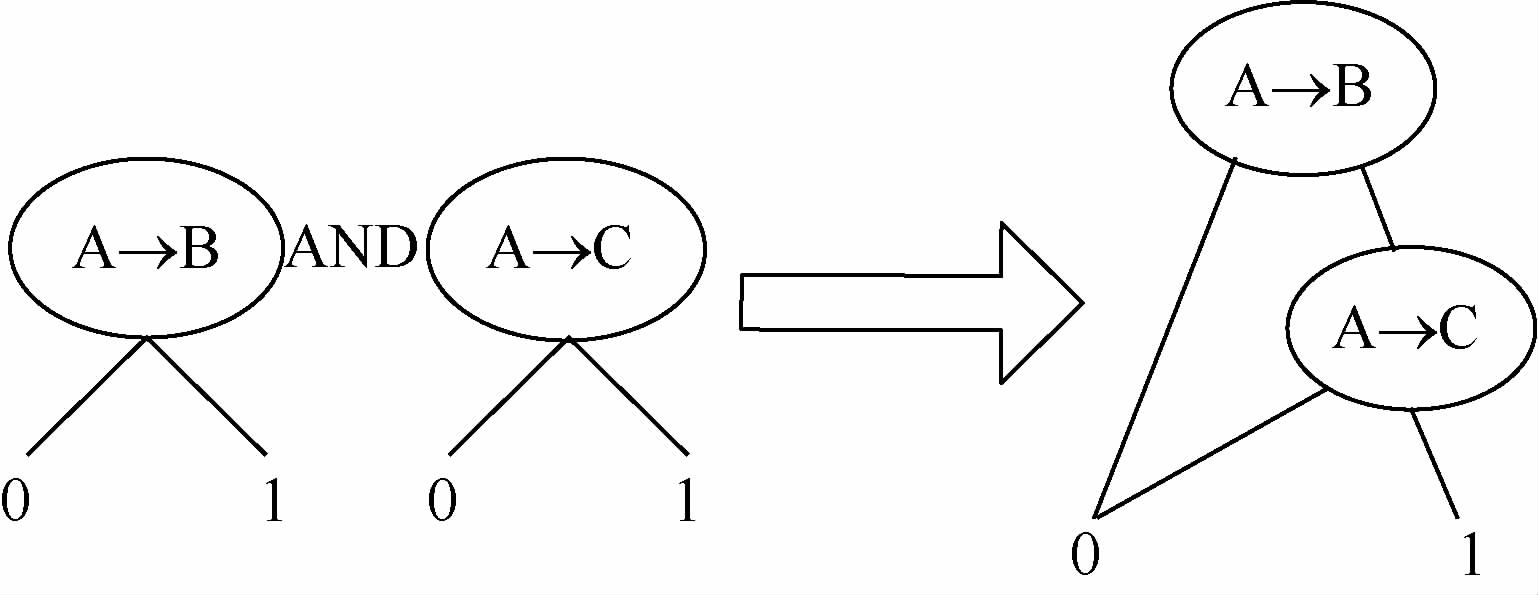
对于图 4(a)中的2个顺序事件的与门,若假定index(A →B)<index(A →C),则建立的顺序二元决策图如图 6所示。
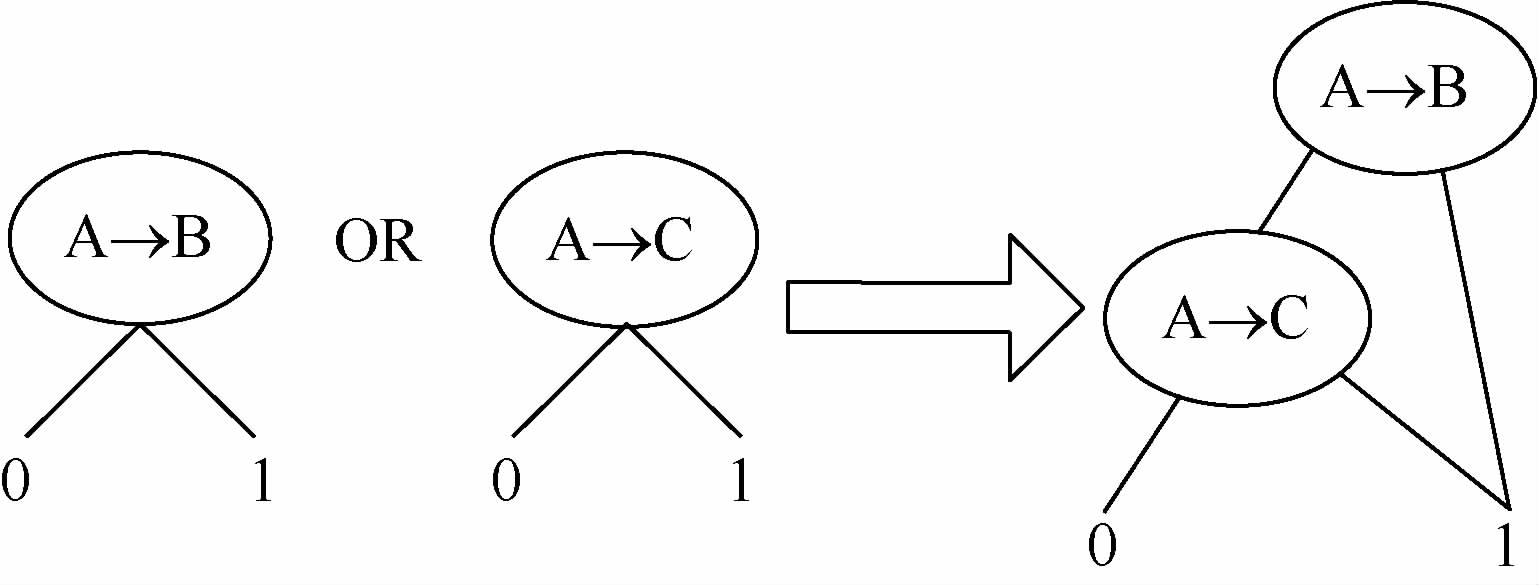
对于图 4(b)中的2个顺序事件的或门,同样假定index(A →B)<index(A→C),得到的顺序二元决策图如图 7所示。
从图 7的二元决策图可以得到其失效路径为A→B和A→B·(A→C),其中A→B代表顺序事件A→B不发生;显然二元决策图得到的失效路径是不交化的,相比于传统的最小割集方法,二元决策图不需利用容斥原理进行不交化运算,提高了计算效率。
2.3 顺序二元决策图的分析评估
顺序二元决策图的分析评估是顺序二元决策图进行动态故障树分析的关键,主要包括失效路径的化简以及顺序事件的发生概率计算。
2.3.1 失效路径化简规则
失效路径的化简采用扩展的布尔运算,传统的布尔运算用于处理基本事件之间的与、或等逻辑运算,而扩展的布尔运算则可以处理基本事件与顺序事件、顺序事件与顺序事件之间的逻辑运算。对失效路径化简前,对顺序事件的补集进行化简,如A→B,化简公式如下:

(4) 式中:∪代表逻辑关系“或”。
失效路径的化简主要涉及基本事件、顺序事件以及基本事件补集的与、或运算。在文献[16]的基础上,本文给出了相关的运算法则。
将失效路径中基本事件、顺序事件以及基本事件的补集分别用Ci(或Cj)、ˆCi(或ˆCi)、Ci(或Cj)表示。其定义如下:

同理:

在此只讨论含有顺序事件的运算规则,对于不含顺序事件的运算规则可参考传统的布尔运算法则。
1)Ci∩Cj (∩表示逻辑关系“与”)
① 当Ci∩Cj=∅时,Ci∩Cj的发生概率:

(5) 式中:Pr{·}为·的发生概率。
② 当Ci∩Cj≠∅时,令Ci∩Cj=Dij,Di/j=Ci/Dij,其意义是Ci中元素除去Dij中元素剩下的集合。此时Ci∩ˆCj的发生概率:

(6) 2)Ci∩Cj
① 当Ci∩Cj=∅时,Ci∩Cj的发生概率:

(7) ② 当Ci∩Cj≠∅时,Ci∩Cj的发生概率:

(8) 3) ˆCi∩ˆCj
① 当Ci∩Cj=∅时,Ci∩Cj的发生概率:

(9) ② 当Ci∩Cj≠∅时,令Ci∩Cj=Dij,Dij={f1,f2,…,fk},其中Dij的元素顺序与其在Ci内的顺序一致,Dij=〈f1,f2,…,fk〉。
若Dij≠Dji,Ci∩Cj的发生概率:

(10) 若ˆDij=ˆDji,假定:
P0={Ci中从ei1到f1的前一个元素};
Q0={Cj中从ej1到f1的前一个元素};
Pl={Ci中从fl的后一个元素到fl+1的前一个元素} (l=1,2,…,k-1);
Ql={Cj中从fl的后一个元素到fl+1的前一个元素} (l=1,2,…,k-1);
Pk={Ci中从fk的后一个元素到ein};
Qk={Cj中从fk的后一个元素到ejm}。
令Pi∩Qi=Ei=Ei1∪E
i2∪…∪Eixi(i=1,2,…,k),其中Ei表示所有符合Pi和Qi元素顺序的排列,则Ci∩Cj=〈E0,f1,E1,…,Ek-1,fk,Ek 〉=Gij1∪Gij2∪…∪Gijx,其中Gijm(m=1,2,…,x)为Ci∩Cj的不交化序列。 因此,Ci∩Cj的发生概率:

(11) 2.3.2 顺序事件发生概率计算
1) 对于两单元的顺序事件A →B (或B →A)
若A、B为优先与门的输入事件,A、B的失效密度函数分别为fA(t)和fB(t)。假设A在t1时刻发生失效,则在任务时间t内,顺序事件A→B发生的概率为

(12) 特别地,当A、B均服从指数分布时,即fA(t)=λ1e-λ1t,fB(t)=λ2e-λ2t。式(12)变为

(13) 若A、B为温备份门的输入事件,其中B为备份件。A的失效密度函数为fA(t);B工作状态下的失效密度函数为fB(t),B贮备状态下的失效密度函数为fB,α(t)。假设A在t1时刻发生失效,B在t2时刻发生失效,则在任务时间t内,顺序事件A→B发生的概率为

(14) 顺序事件B→A 发生的概率为

(15) 特别地,当fA(t)=λ1e-λ1t,fB(t)=λ2e-λ2t,fB,α(t)=λαe-λαt时,式(14)、式(15)可化简为

(16) 
(17) 2) 对于n单元的顺序事件A1→A2→…→An
若A1,A2,…,An中不包括温备份件,其失效密度函数分别为fi(t)(i=1,2,…,n),则在任务时间t内,顺序事件A1→A2→…→An发生的概率为

(18) 若A1,A2,…,An中包括温备份件Ai。Ai工作状态下的失效密度函数为fi(t),贮备状态下的失效密度函数为fi,α(t)、单元Ai所处备份结构的主件是Aj。
当i<j时,顺序事件发生的概率:

(19) 当i>j时,顺序事件发生的概率:

(20) 3. 实例分析
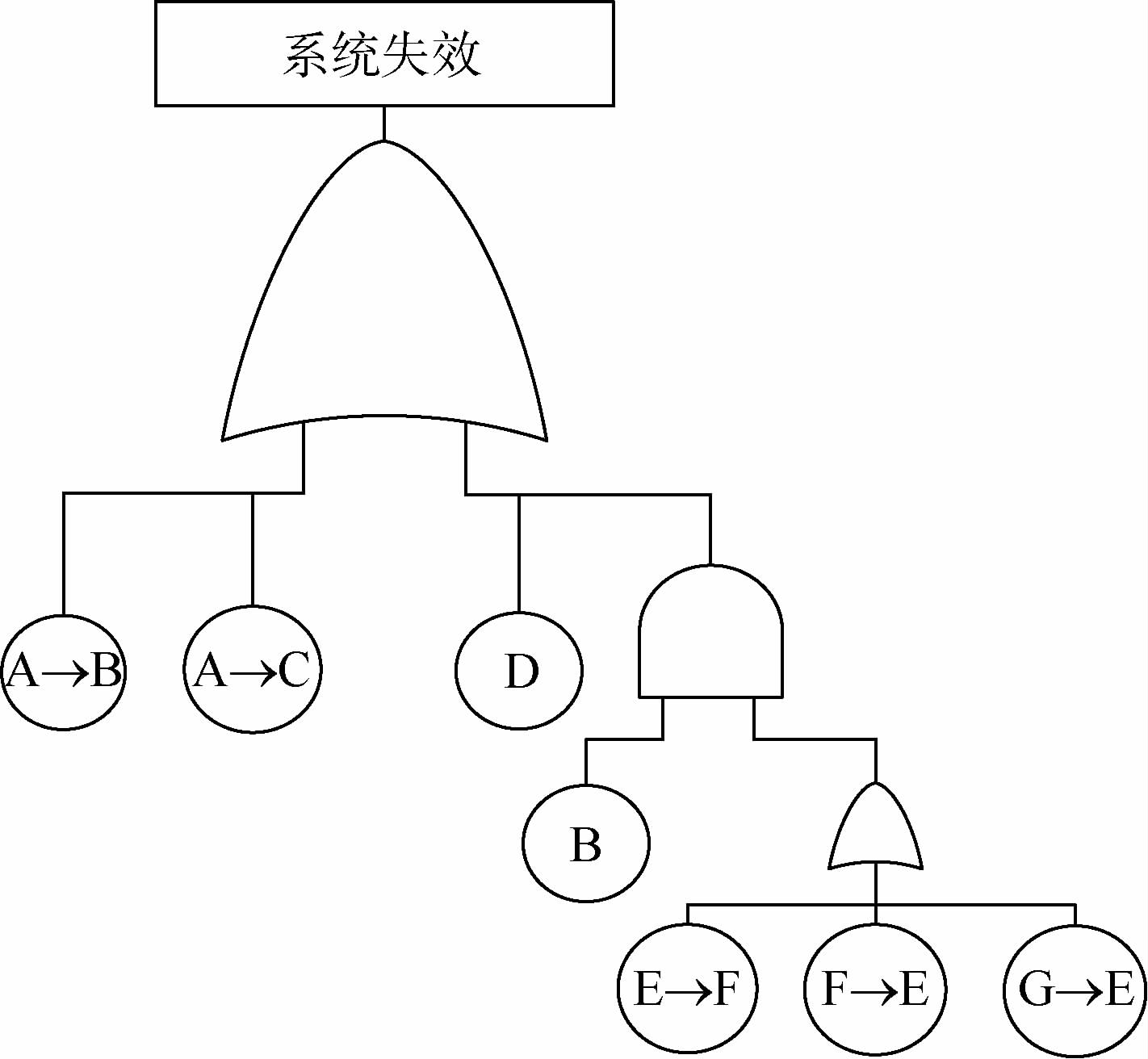
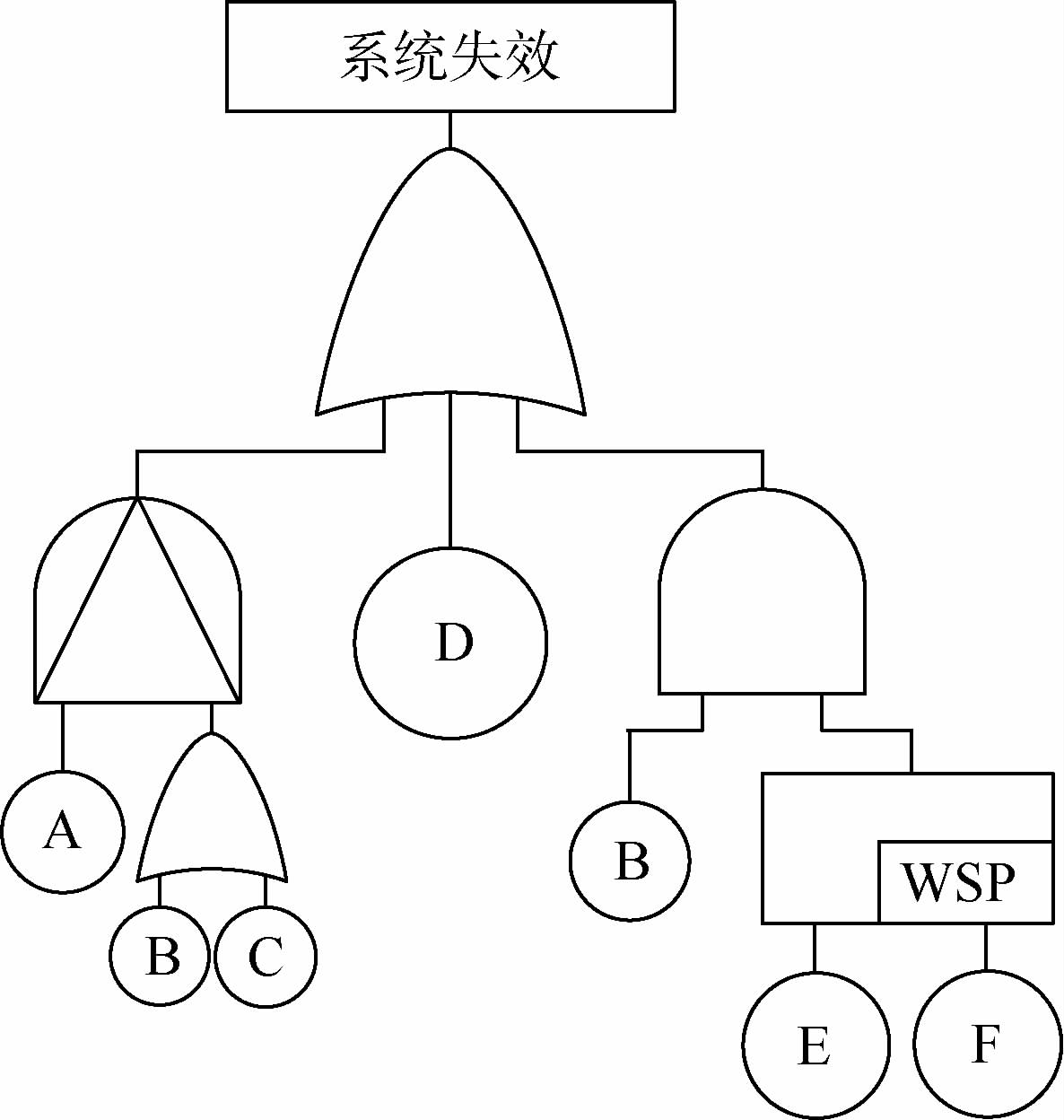
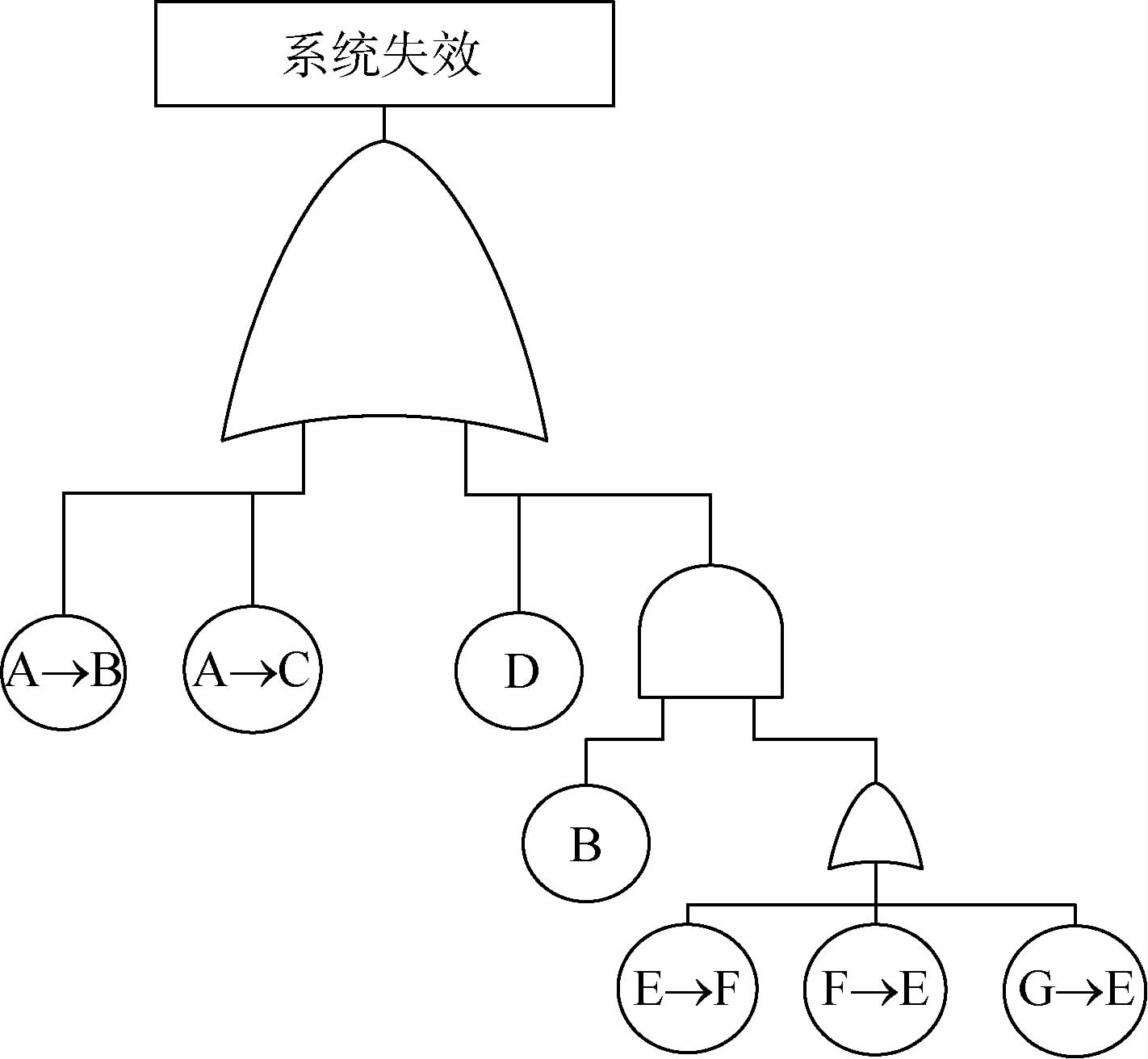
以某弹药系统为例,验证本文方法的有效性。通过对弹药进行故障模式影响及危害性分析,并结合相关的失效数据,得到了系统容易发生失效的部件,分析其结构功能以及系统的动态失效特征,建立了系统的动态故障树,见图 8。其中A为密封件,B为火工品,C为关键电子器件,D为激光探测器,E为陀螺仪驱动装置,F为其备用装置。
1) 动态故障树的转化
考虑到陀螺仪驱动装置及其备用装置组成的备份结构工作过程中可能存在的不完全覆盖问题,为方便系统不完全覆盖问题的定量计算,以其故障监测、定位、转化装置G来衡量系统的覆盖问题。装置G的可靠度即为不完全覆盖系统的覆盖系数。采用本文的动态故障树转化方法,得到含顺序事件的故障树,如图 9所示。
2) 顺序二元决策图模型的建立
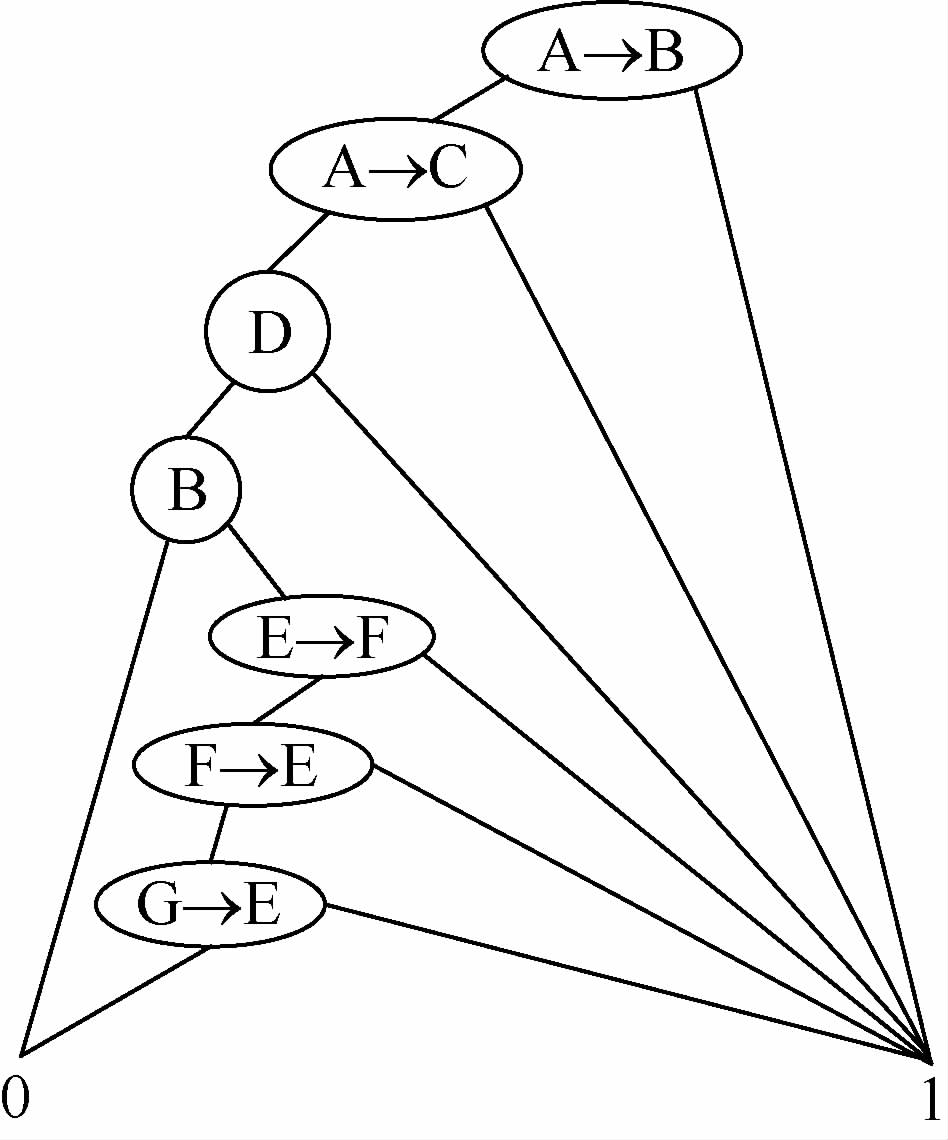
针对图 9中的故障树,利用顺序二元决策图相关分析方法,得到了系统的顺序二元决策图,如图 10所示。
3) 顺序二元决策图的分析评估
分析图 10中得到的系统顺序二元决策图,可知系统不交化的失效路径有6条,分别为:
① A →B
② A →B·(A→C)
③ A →B·A→C·D
④ A →B·A→C·D·B·(E→F)
⑤ A →B·A→C·D·B·E→F·(F→E)
⑥ A →B·A→C·D·B·E→F·F→E·
(G→E)
采用扩展的布尔运算对失效路径进行化简,得到各路径的发生概率Pi(i=1,2,…,6),其中P(·)表示事件·失效的概率。

因此,系统的可靠度函数为

(21) 3.1 指数分布情形
当所有部件工作状态下的密度函数服从指数分布时,其分布参数分别为:λA=3×10-6h-1,λB=5×10-6h-1,λC=10-6h-1,λD=10-5h-1,λE=10-5h-1,λF=5×10-6h-1,λG=10-5h-1。温备份件F储备状态下也服从指数分布,其失效率为αF=2×10-6 h-1。
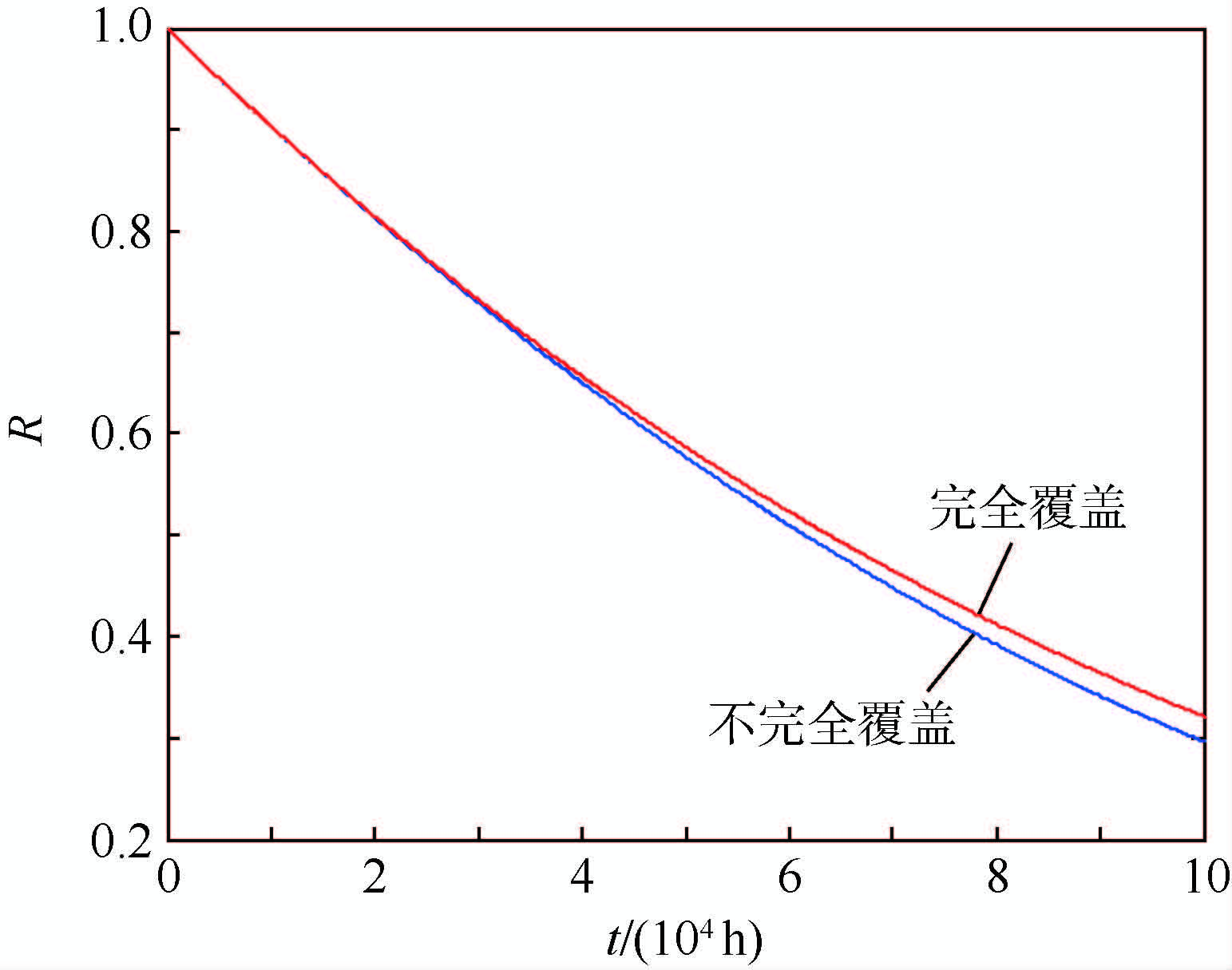
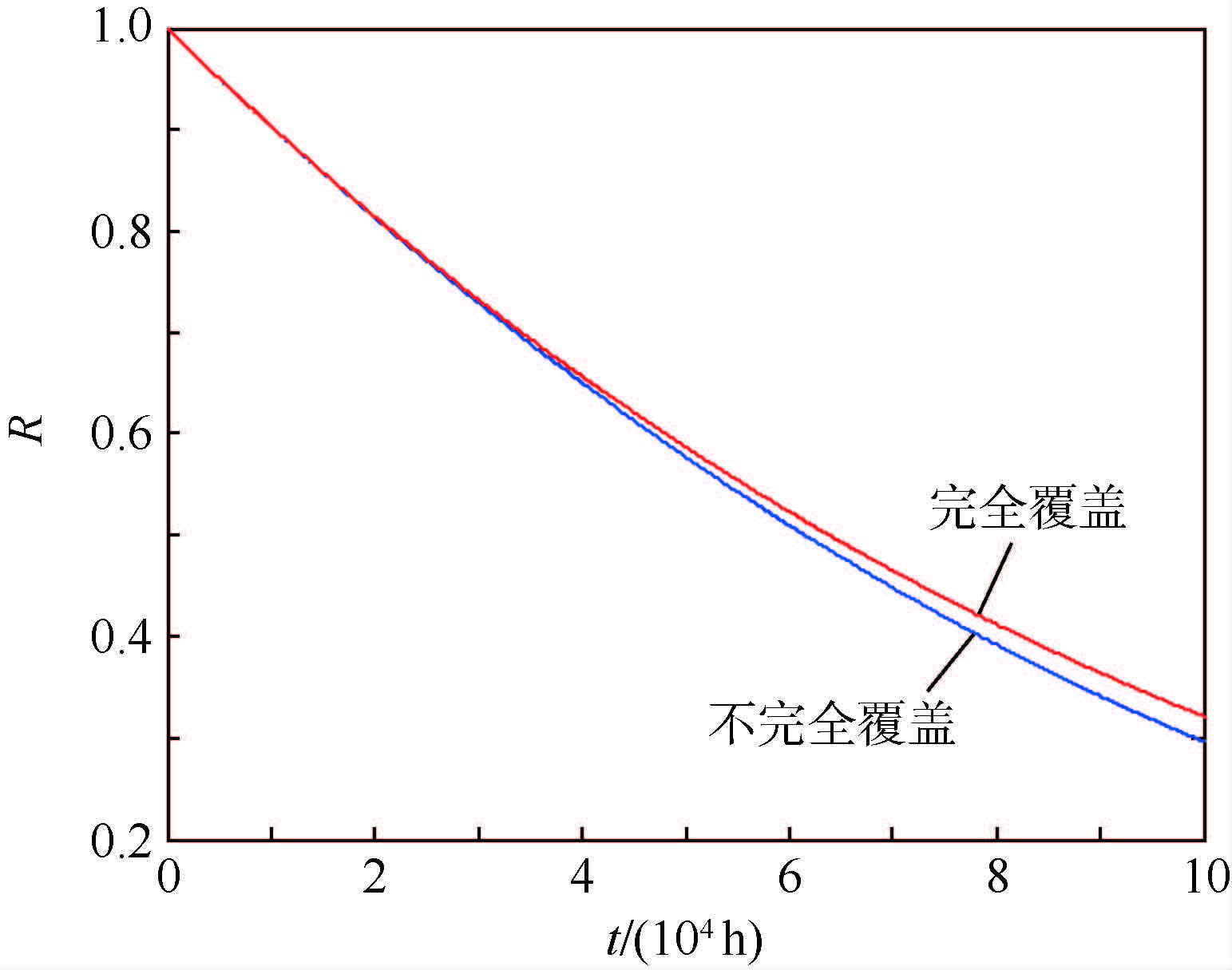
将相关数据代入式(21),并根据顺序事件发生概率计算公式,利用MATLAB软件,得到指数分布情形下不完全覆盖系统的可靠度R随时间变化曲线,如图 11所示;并与不考虑温备份的不完全覆盖,即完全覆盖时系统可靠度进行对比。
马尔可夫模型是一种处理部件服从指数分布情形的动态故障树分析的有效方法。考虑系统的不完全覆盖,选取不同任务时间,对比本文方法与马尔可夫模型方法得到的系统可靠度R(t),其结果如表 1所示。
表 1 本文方法与基于马尔可夫模型方法的系统可靠度Table 1. Reliability of the system by proposedmethod and Markov-based methodt/h R(t) 本文方法 马尔可夫模型方法 5 000 0.951 0 0.951 0 10 000 0.903 7 0.903 7 30 000 0.729 6 0.729 6 50 000 0.577 8 0.577 8 100 000 0.321 6 0.321 6 由表 1结果可知,本文方法和基于马尔可夫模型方法均可处理系统部件服从指数分布情形,且具备相同的计算精度。
3.2 非指数分布情形
当部件A、D、E的失效分布函数服从两参数威布尔分布,其分布参数分别为:mA=0.85,ηA=3×105h;mD=1.1,ηD=1.5×105h;mE=0.9,ηE=105h。部件B、C、F、G工作状态下的密度函数服从指数分布时,其分布参数分别为:λB=5×10-6h-1,λC=10-6h-1,λF=5×10-6h-1,λG=10-5h-1。温备份件F储备状态下也服从指数分布,其失效率为αF=2×10-6 h-1。
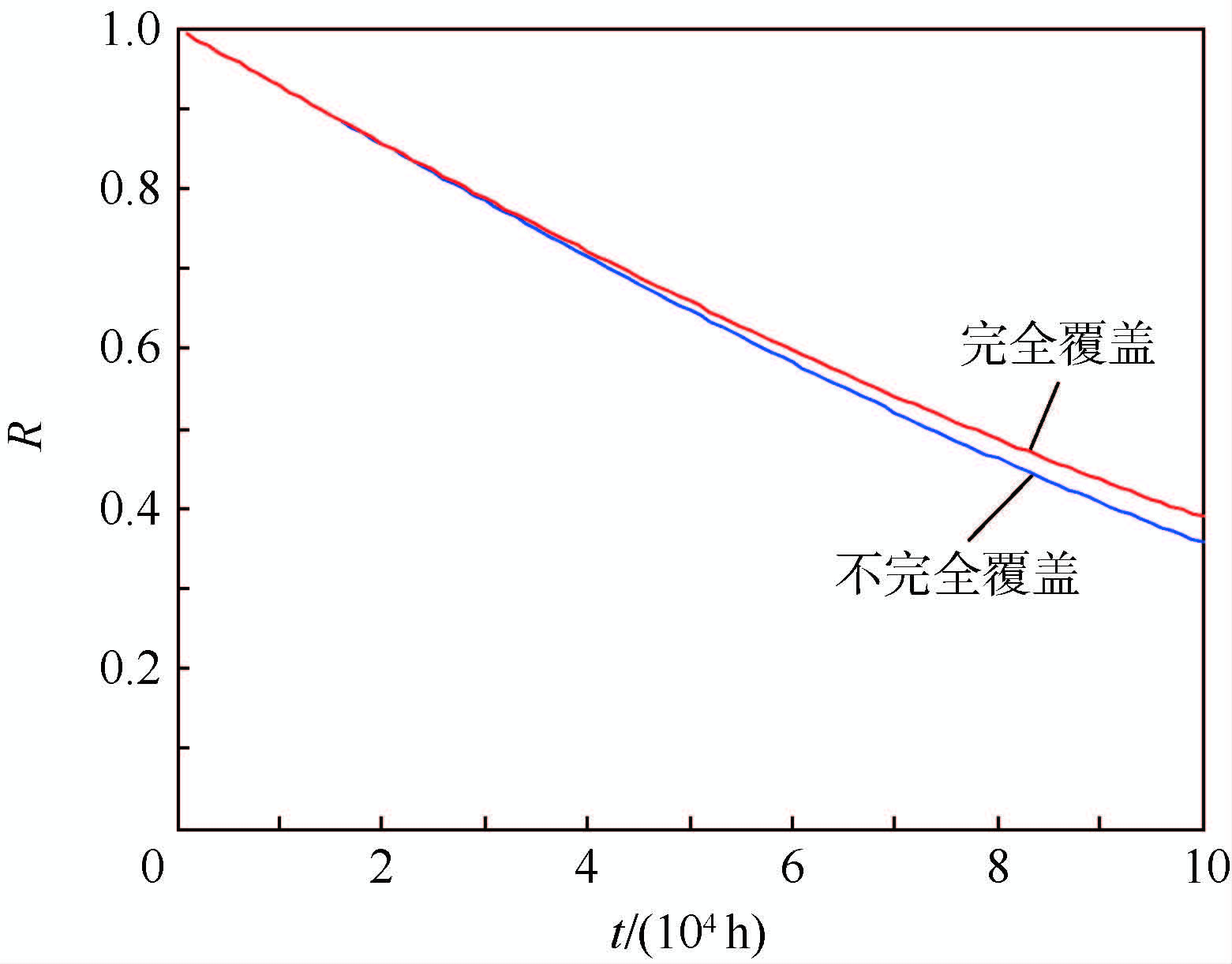
根据顺序事件发生概率计算公式以及式(21),代入相关数据,得到非指数分布情形下不完全覆盖系统的可靠度随时间变化曲线,如图 12所示,并与不考虑温备份的不完全覆盖时系统可靠度进行对比。
蒙特卡罗仿真方法作为动态故障树分析的重要方法,其适用于部件寿命服从任意分布类型,同时也是评价其他方法的标杆。为验证本文方法处理非指数分布情形的有效性,将本文方法与蒙特卡罗仿真方法进行对比,选取不同任务时间,在蒙特卡罗方法仿真次数为106时,得到2种方法下系统可靠度计算结果,如表 2所示。采用CPU型号为E5-2640 v3的计算机进行计算分析,其运算时间如表 3所示(注:不同任务时间下的运算时间基本一致)。
表 2 本文方法与基于蒙特卡罗仿真方法的系统可靠度Table 2. Reliability of the system by proposedmethod and Monte Carlo simulation methodt/h R(t) 相对误差/% 本文方法 蒙特卡罗仿真方法 5 000 0.963 4 0.963 4 0 10 000 0.927 2 0.927 2 0 30 000 0.784 3 0.784 4 0.01 50 000 0.647 2 0.647 4 0.03 100 000 0.357 2 0.357 5 0.08 表 3 本文方法与基于蒙特卡罗仿真方法的运算时间Table 3. Computation time by proposed method andMonte Carlo simulation method方法 本文方法 蒙特卡罗仿真方法 运算时间/s 24.894 0 48.093 7 分析图 11和图 12可知,考虑不完全覆盖情形的系统可靠性计算结果更符合实际情况;对于任务时间较长的产品,必须考虑系统的不完全覆盖问题。
综合分析表 1和表 2的结果,本文方法适用于部件服从各种分布类型的系统动态故障树分析,突破了马尔可夫模型等传统动态故障树分析方法仅限于指数分布的局限,具有广泛的适用性和良好的计算精度。表 3的结果表明本文方法计算高效,大大节省了运算时间,相比于蒙特卡罗仿真方法,更适用于基本事件众多的复杂动态故障树分析。
4. 结 论
1) 方法考虑备份结构的不完全覆盖问题,对含优先与门和温备份门的复杂动态故障树进行了建模分析。
2) 方法对比了完全覆盖和非完全覆盖情形的可靠度计算,说明了失效覆盖问题对于系统可靠性的影响。
3) 方法通过指数分布和非指数分布2种情形的实例分析,并与马尔可夫模型和蒙特卡罗仿真方法进行了对比,显示了其具备计算精度高、计算效率高、适用性广泛的优点。
因此,对于实际工程中存在动态失效特征的系统,基于顺序二元决策图的动态故障树分析方法是系统可靠性分析的有效方法。同时,对于冗余系统,提高失效检测与定位技术对于保障系统安全可靠运行具有重大意义。
-
表 1 本文方法与基于马尔可夫模型方法的系统可靠度
Table 1. Reliability of the system by proposedmethod and Markov-based method
t/h R(t) 本文方法 马尔可夫模型方法 5 000 0.951 0 0.951 0 10 000 0.903 7 0.903 7 30 000 0.729 6 0.729 6 50 000 0.577 8 0.577 8 100 000 0.321 6 0.321 6 表 2 本文方法与基于蒙特卡罗仿真方法的系统可靠度
Table 2. Reliability of the system by proposedmethod and Monte Carlo simulation method
t/h R(t) 相对误差/% 本文方法 蒙特卡罗仿真方法 5 000 0.963 4 0.963 4 0 10 000 0.927 2 0.927 2 0 30 000 0.784 3 0.784 4 0.01 50 000 0.647 2 0.647 4 0.03 100 000 0.357 2 0.357 5 0.08 表 3 本文方法与基于蒙特卡罗仿真方法的运算时间
Table 3. Computation time by proposed method andMonte Carlo simulation method
方法 本文方法 蒙特卡罗仿真方法 运算时间/s 24.894 0 48.093 7 -
[1] LENG L,LIU Y.Fault tree reliability analysis for passive medium pressure safety injection system in nuclear power plant[J].Energy and Power Engineering,2013,5(4):264-268. doi: 10.4236/epe.2013.54B051 [2] NYSTROM B,AUSTRIN L,ANKARBACK N,et al.Fault tree analysis of an aircraft electric power supply system to electrical actuators[C]//Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems,2006.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2006:1-7. [3] DUGAN J B,BAVUSO S J,BOYD M A.Dynamic fault-tree for fault-tolerant computer systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Reliability,1992,41(3):363-376. doi: 10.1109/24.159800 [4] DUGAN J B,SULLIVAN K J,COPPIT D.Developing a low-cost high-quality software tool for dynamic fault-tree analysis[J].IEEE Transactions on Reliability,2000,49(1):49-59. doi: 10.1109/24.855536 [5] SMOTHERMAN M K,ZEMIUDEH K.A non-homogenedous Makrov model for phased-mission reliability analysis[J].IEEE Transaciton on Reliability,1989,38(5):585-590. doi: 10.1109/24.46486 [6] DUGAN J B.Galileo:A tool for dynamic fault tree analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Performance Evaluation:Modelling Techniques and Tools.Berlin:Springer-Verlag,2000:328-331. [7] GULATI R,DUGAN J B.A modular approach for analyzing static and dynamic fault trees[C]//Reliability and Maintainability Symposium.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,1997:57-63. [8] AMARI S,DILL G,HOWALD E.A new approach to solve dynamic fault trees[C]//Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2003:374-379. [9] BOUDALI H,DUGAN J B.A new Bayesian network approach to solve dynamic fault trees[C]//Reliability and Maintainability Symposium.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2005:451-456. [10] RAO K D,GOPIKA V,RAO V V S S,et al.Dynamic fault tree analysis using Monte Carlo simulation in probabilistic safety assessment[J].Reliability Engineering and System Safety,2009,94(4):872-883. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2008.09.007 [11] XING L D,SHRESTHA A,DAI Y.Exact combinatorial reliability analysis of dynamic systems with sequence-dependent failures[J].Reliability Engineering and System Safety,2011,96(10):1375-1385. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2011.05.007 [12] XING L D,TANNOUS O,BECHTA DUGAN J.Reliability analysis of nonrepairable cold-standby systems using sequential binary decision diagrams[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics,2012,42(3):715-726. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2011.2170415 [13] TANNOUS O, XING L,DUGAN J B.Reliability analysis of warm standby systems using sequential BDD[C]//Reliability and Maintainability Symposium.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2011:1-7. [14] DUGAN J B. Fault trees and imperfect coverage[J].IEEE Transactions on Reliability,1989,38(2):177-185. doi: 10.1109/24.31102 [15] BRYANT R E. Graph-based algorithms for boolean function manipulation[J].IEEE Transactions on Computers,1986,35(8):677-691. [16] YUGE T, YANAGI S.Quantitative analysis of a fault tree with priority AND gates[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety,2008,93(11):1577-1583. 期刊类型引用(16)
1. 钟志成,徐封杰,李超超,武恪,方菱. 基于动态故障树的汽车系统故障诊断方法. 电子测量技术. 2023(14): 131-137 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 柯倩云,涂志琦,刘亚奇. 基于动态故障树的故障隔离程序分析方法. 航空工程进展. 2023(06): 133-142 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 魏文涛,李美福,朱大欢,钟明君,郭永晋,杜政瑀,蒋孝蔚. 基于动态贝叶斯网络的核能系统可靠性评估方法研究. 核动力工程. 2023(S2): 109-114 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 王康,齐金平,周亚辉,李少雄,赵睿虎,郭浩. 基于离散时间贝叶斯网络的列控中心可靠性分析. 中国机械工程. 2021(04): 390-398 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 秦清,徐晓理. 基于Huffman树的雷达故障分析优化技术. 电子技术. 2021(02): 25-27 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 钟尚染,叶强,杨迁. 电动汽车充电桩常见故障及其诊断研究. 中国设备工程. 2021(13): 44-45 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 姚成玉,王传路,陈东宁,魏星,吕世君. 连续时间T-S动态故障树分析方法. 机械工程学报. 2020(10): 244-256 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 吴勇,陶军. 基于T-S模型的装载机液压系统动态故障树分析. 液压与气动. 2020(11): 171-176 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 陈东宁,魏星,姚成玉,王传路,吕世君. 连续时间T-S动态故障树重要度分析方法. 仪器仪表学报. 2020(09): 232-241 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 高德欣,梁珂,侯俊杰,杨清. 电动汽车充电桩移动监控与故障诊断系统设计. 青岛科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(03): 107-113 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 海宁,张彩珍,孙国营,于洋. 基于动态故障树的新型区间占检系统可用性分析. 计算机应用与软件. 2019(06): 47-53 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 姚成玉,饶乐庆,陈东宁,侯鑫,吕世君,于传宇. T-S动态故障树分析方法. 机械工程学报. 2019(16): 17-32 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 高德欣,梁珂. 基于云平台的电动汽车充电站远程设备监控系统. 青岛科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(05): 93-100 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 孙超勇,张永进,张燕军,石坤. 基于故障树方法的汽车追尾事故分析. 机械研究与应用. 2018(04): 29-33 .  百度学术
百度学术15. 齐金平,李兴运,蒋兆远,郭济鸣. 动车组空气供给系统动态可靠性分析. 兰州交通大学学报. 2018(02): 92-97 .  百度学术
百度学术16. 李莉,刘翠杰,王政,任逸飞. 动态故障树的边值多值决策图分析. 计算机系统应用. 2018(12): 123-128 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(29)
-








 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术