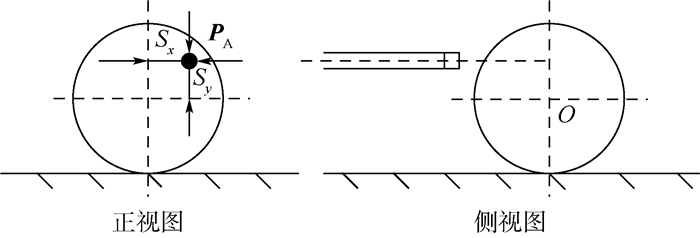
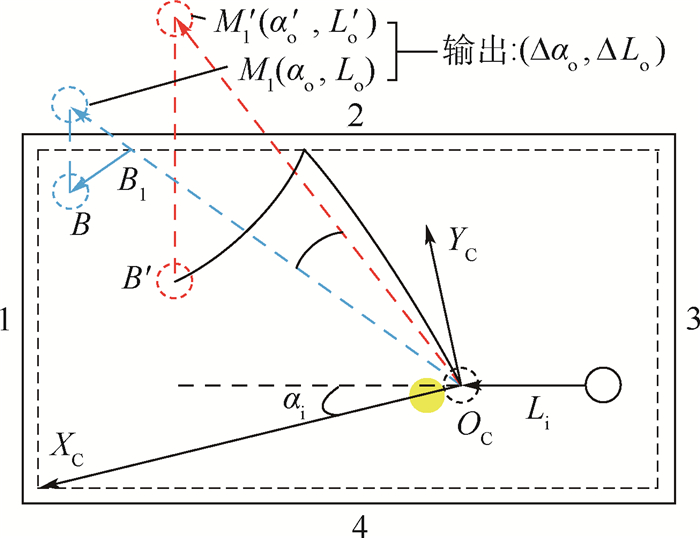
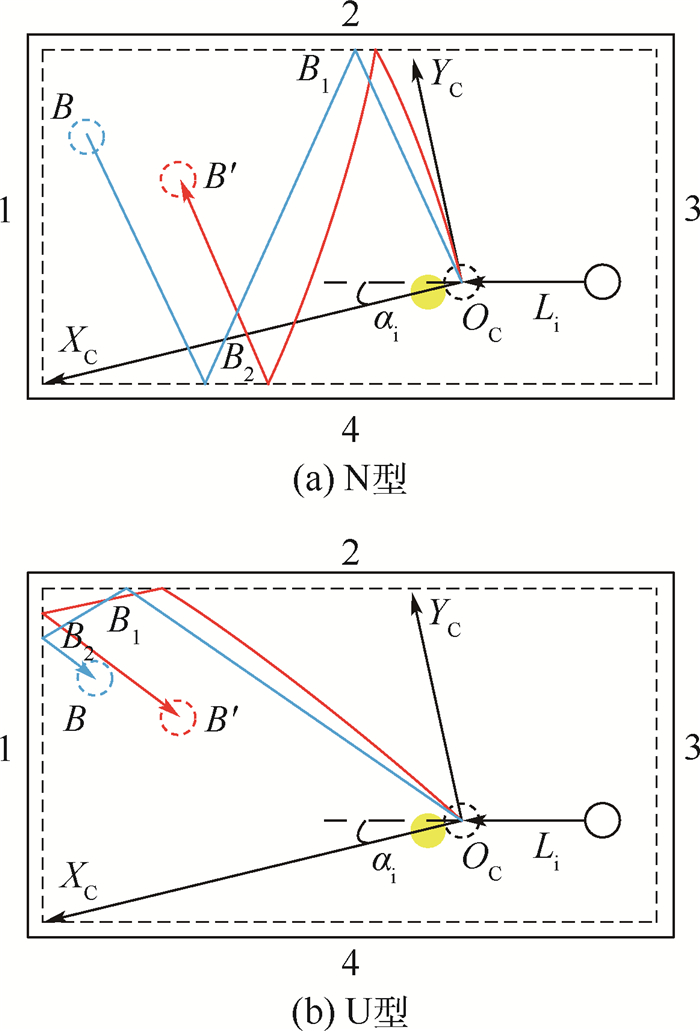
Design of neural network controller for a billiard robot
-
摘要:
对撞球机器人的母球控制问题展开研究,设计了一种基于神经网络(NN)的控制器,使机器人能够控制母球在击打目标球后按照预定的模式运动至目标点——即完成走位。针对该问题非线性且非光滑的特点,对坐标系进行阐述并给出机器人击球的模型;在光滑的假设下使用理论分析的方法建立母球的运动学模型与边库反弹的理想镜像模型;进而使用神经网络方法对理想模型进行修正,并对不同的轨迹模式进行分析与分类。测试结果表明:经过训练的机器人能够掌握各种模式的走位,统计结果与模型分析结果相吻合;相比于单一使用神经网络方法,本文使用理论分析与神经网络相结合的方法能够有效地提升网络的品质,降低训练的误差。
Abstract:This paper focuses on the cue ball controlling problem for a billiard robot. A neural network (NN) controller is designed, and the trained robot is able to stroke the cue ball moving to the target point after colliding with objective ball and cushions. Since the problem is non-linear and non-smooth, the solution is divided into several steps. First, the stroking model and the coordinate definition are described. Second, the kinematic model for cue ball motion and the mirror model for cushion rebounds are established under the ideal smooth assumption. Then, the neural network method is used to modify the ideal models, and the pattern recognition method for trajectories is presented. In the verification test, the trained robot is able to master the cue ball controlling with each pattern. The statistic results tally with the model analysis. Compared with simply adopting neural network method, the method combined with theoretical kinematic analysis will effectively improve the network quality and reduce the training error.
-
表 1 模式0神经网络模型
Table 1. Neural network model for Pattern 0
输入 (5维) 输出 (2维) 控制量FI, Sx, Sy 位置偏差Δαo, ΔLo 几何特征量αi, Li 表 2 模式EASY神经网络模型
Table 2. Neural network model for Pattern EASY
输入 (7维) 输出 (2维) 控制量FI,Sx,Sy 位置偏差Δαo,ΔLo 几何特征αi,Li, 
旋转分类参数β 表 3 N型轨迹模式的神经网络模型
Table 3. Neural network model for pattern N
输入 (7维) 输出 (2维) 控制量FI,Sx,Sy 位置偏差Δαo,ΔLo 几何特征αi,Li, 
旋转分类参数β 表 4 U型轨迹模式的神经网络模型
Table 4. Neural network model for pattern U
输入 (8维) 输出 (2维) 控制量FI,Sx,Sy 位置偏差Δαo,ΔLo 几何特征αi,Li, 

旋转分类参数β 表 5 部分轨迹模式的平均走位成功率统计结果
Table 5. Statistical results of average controlling rate for some trajectory patterns
模式 数据量 成功率/% 0 5611 90 EASY 4786 80 c 2566 74 u 2609 73 n 2048 78 z 2367 76 0 10423 96 EASY 9387 90 c 5872 83 u 5163 82 n 4759 85 z 4821 86 -
[1] HO K H L, MARTIN T, BALDWIN J.Snooker robot player-20 years on[C]//IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Games, 2007.(CIG 2007).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2007:1-8. [2] YANG J S, CHEN Y M.The design of jump shot decision-making system for a billiard robot[C]//2010 IEEE Conference on Robotics Automation and Mechatronics (RAM).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2010:409-413. [3] CHENG B R, LI J T, YANG J S.Design of the neural-fuzzy compensator for a billiard robot[C]//2004 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2004:909-913. [4] LEGG P A, PARRY M L, CHUNG D H S, et al.Intelligent filtering by semantic importance for single-view 3D reconstruction from Snooker video[C]//IEEE International Conference on Image Processing.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2011:2385-2388. [5] LECKIE W, GREENSPAN M A.Pool physics simulation by event prediction 1:Motion transitions[J].ICGA Journal, 2005, 28(4):214-222. [6] LANDRY J F, DUSSAULT J P, MAHEY P.A heuristic-based planner and improved controller for a two-layered approach for the game of billiards[J].IEEE Transactions on Computational Intelligence & AI in Games, 2013, 5(4):325-336. [7] DOMÉNECH A.Non-smooth modelling of billiard-and superbilliard-ball collisions[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2008, 50(4):752-763. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2007.11.006 [8] MATHAVAN S, JACKSON M R, PARKIN R M.Numerical simulations of the frictional collisions of solid balls on a rough surface[J].Sports Engineering, 2014, 17(4):227-237. doi: 10.1007/s12283-014-0158-y [9] MATHAVAN S, PARKIN R M, JACKSON M R.A theoretical analysis of billiard ball dynamics under cushion impacts[J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2010, 224(9):1863-1873. doi: 10.1243/09544062JMES1964 [10] GAO J, HE Q, ZHAN Z, et al.Dynamic modeling based on fuzzy neural network for a billiard robot[C]//IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2016:1-4. [11] ZUO Z, WANG C.Adaptive trajectory tracking control of output constrained multi-rotors systems[J].IET Control Theory & Applications, 2014, 8(13):1163-1174. [12] LOU W, GUO X.Adaptive trajectory tracking control using reinforcement learning for quadrotor[J/OL].International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2016, 13(38).[2016-03-09].OI:105772/62128. [13] LECKIE W, GREENSPAN M A.Pool physics simulation by event prediction 2:Collisions[J].ICGA Journal, 2006, 29(1):24-31. -








 下载:
下载: