-
摘要:
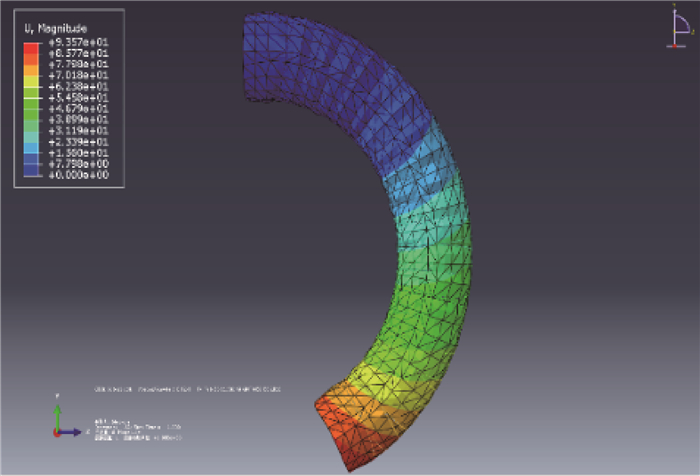
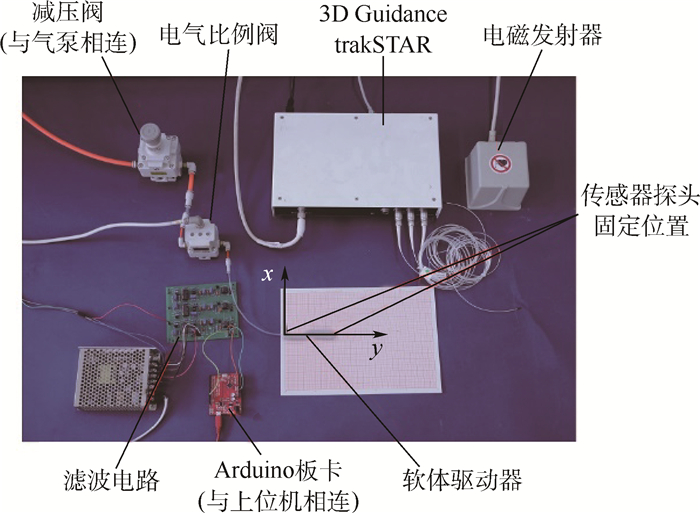
与传统的“刚性”机器人相比,基于仿生学启发的软体机器人由于其与生俱来的柔顺性和安全性受到广泛关注。然而,此类软体机器人驱动器的设计与控制目前仍缺少理论指导。针对这些问题,设计了一种由气压驱动的可实现弯曲运动的新型软体驱动器,在系统分析其结构和弯曲原理的基础上,利用几何方法和虚功原理建立了其数学模型,并且通过有限元模型和原理样机实验验证了数学模型的有效性,为软体机器人驱动器的优化设计和控制提供了依据。
Abstract:Compared with traditional "rigid" robots, soft robots inspired by biology have been of particular interest to the robotic communities due to their inherent compliance and safety. However, the actuation and control of the soft actuators for such soft robotics are still lacking of theoretical investigation. For these issues, a pneumatic actuator was designed to achieve compliant motions for use in soft robots. The mathematical model was then developed based on the analysis of its structure and bending principle utilizing the geometric analysis and the principle of virtual work. The model were finally validated by finite element model and prototype experiments, and can be used for the future design and control of soft robotic actuators.
-
Key words:
- soft actuator /
- pneumatic actuation /
- bending deformation /
- mathematical model /
- finite element analysis
-
近年来, 基于无线信道本身固有的稀疏性, 压缩感知(Compressed Sensing, CS)[1]技术被应用于稀疏信道估计并得到了广泛的研究, 相比最小二乘(Least Square, LS)和最小均方误差(Minimum Mean Square Error, MMSE)等传统信道估计方法, 利用压缩感知方法的信道估计器能够以较少的导频准确地估计稀疏信道, 降低正交频分复用(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing, OFDM)系统的导频开销[2]。许多压缩感知恢复算法已被应用于稀疏信道的估计, 如正交匹配追踪(Orthogonal Matching Pursuit, OMP)、压缩采样匹配追踪(Compressive Sampling Matching Pursuit, CoSaMP)算法、基追踪(Basis Pursuit, BP)算法等[3-4]。
然而, 与LS和MMSE估计方法达到最优的信道估计性能要求导频均匀分布不同, 非均匀分布导频的压缩感知信道估计才具有较好的信道估计性能。稀疏信号重建的准确性不仅取决于压缩感知算法, 也与采样矩阵有关, 压缩感知高概率重建稀疏信道要求采样矩阵满足有限等距特性或互相关准则[5]。由于没有已知的方法在多项式时间内验证一个矩阵是否满足有限等距特性(Restricted Isometry Property, RIP), 可行的方法是计算采样矩阵的互相关且互相关越小采样矩阵的重建概率越高[6], 因此可以通过采样矩阵设计提高压缩感知信道估计准确性。
现有的导频设计方法都是最小化测量矩阵的互相关设计导频[7-12]。文献[7]提出随机搜索方法, 通过先随机生成一定数量的导频, 再计算导频所确定采样矩阵的互相关值, 选择具有最小互相关的导频作为最优导频, 尽管该方法简单, 但是搜索算法具有随机性且导频的搜索结果依赖于随机生成的导频数。文献[8-9]将互相关作为目标函数, 分别使用进化算法中的分布式估计算法和遗传算法求解最优导频, 但是进化算法的性能受参数设置影响较大且收敛时间难以保证。文献[10]提出一种修改的统计随机近似方法通过计算导频的占用概率搜索最优导频, 但是该方法性能取决于备选导频数量的大小。文献[11]提出SSS(Stochastic Search Schemes)算法, 通过先随机生成一定数量的导频, 再对各导频进行逐位优化, 选择具有最小互相关的导频输出, 然而该算法受限于随机生成的导频数量。文献[12]提出使用并行树结构的循环替换导频搜索算法, 采用并行树选择最优的导频, 但是该搜索算法性能受限于替换步长, 容易陷入局部最小值解。
此外, 互相关仅反映采样矩阵2列之间相关的极端情况, 不能反映采样矩阵的整体重建性能, 如何较准确评价采样矩阵的重建性能仍是一个需要进一步研究的问题[13]。文献[12]认为最优采样矩阵的任意不同列之间应该正交, 提出采用互相关矩阵和单位矩阵的欧氏距离作为新的互相关定义评价采样矩阵的性能。然而, 最优傅里叶采样矩阵为循环差集确定的等角紧框架, 该矩阵任意2列互相关相等, 因此互相关矩阵和单位矩阵的欧氏距离不能准确反映采样矩阵的重建性能。文献[14]提出基于阈值的相关矩阵元素的立方和评价采样矩阵, 但是该方法仅考虑相关矩阵中元素较大的值, 不能全面反映采样矩阵重建性能, 并且该方法中的阈值难以选择。
本文首先提出一种新的评价采样矩阵重建性能方法, 针对导频设计的组合优化问题, 提出一种新的导频搜索算法。然后对所提出的新准则及导频搜索算法与现有的准则及导频搜索算法进行仿真比较, 仿真结果验证了所提出新方法的优越性。
1. 系统模型
考虑一个子载波数为N的OFDM系统, 其中导频数为Np, 导频位置集合表示为P={p1, p2, …, pNp}。不失一般性, 假设1≤p1 < p2 < … < pNp≤N, 对应的频域发送导频符号表示为x(p1), x(p2), …, x(pNp)。假设信道的最大长度为L, h(1), h(2), …, h(L)为信道冲击响应的采样值。接收端接收到的导频载波处的信号可表示为

(1) 式中:η(i)~(0, ση2)(i=1, 2, …, Np)为满足独立同分布的高斯白噪声, ση2为噪声的方差; FNp×L为从一个大小为N×N的傅里叶变换矩阵中抽取P所在的Np行和前L列所构成的部分傅里叶变换矩阵,

(2) 定义

则式(1)可以表示为

(3) 在实际的无线通信中, 无线信道通常呈现出稀疏性即离散采样信道h中的绝大部分抽头为零值, 仅有少数采样点为非零值。传统LS等信道估计方法要求Np≥L, 考虑导频数小于信道长度的情况即Np < L, 此时式(3)为标准的压缩感知采样, 可以利用压缩感知算法求解稀疏信道。
2. 导频设计方法
2.1 采样矩阵性能评价方法
定义1[15] 有限等矩性质(Restricted Isometry Property, RIP), 如果存在常数δs(0 < δs < 1)对任意最多有s个非零值的稀疏信号z都能使式(4)成立, 则称矩阵Φ满足有限等距特性, 其中最小的δs称为有限等距常数。

(4) 压缩感知指出, 在无噪声的情况下, 当式(3)中的采样矩阵A满足RIP时, 压缩感知重建算法利用y和A能够高概率地重建稀疏信道h。然而, 目前没有任何已知的方法能在多项式时间内验证给定的采样矩阵A是否满足RIP[11], 可以选择的方法是计算采样矩阵的互相关。文献[16]指出采样矩阵的互相关强于RIP且互相关越小越好, 因此可以通过最小化互相关设计导频。
互相关定义为采样矩阵A任意2列之间最大的归一化绝对值内积, 即

(5) 式中:〈·, ·〉表示内积; A(i)(0≤i≤L-1)为矩阵A的第i列。
假设Np个导频功率相同, 即

(6) 将式(2)代入式(5)可得

(7) 对矩阵A按列进行归一化, 互相关矩阵G=abs(AHA)的第i行j列元素gi, j(0≤i, j≤L-1)即为采样矩阵A的第i列和第j列的互相关, G的对角线元素gi, j=1(i=j)为第i列的自相关, 其中abs(·)表示对矩阵的元素取模。G为对称矩阵, 因此式(7)也可以表示为G上三角元素最大值, 即

(8) 由式(7)可以看出, μ(A)仅取决于导频集合P。因此, 导频设计就是找到Np个导频位置使式(7)尽可能小即式(9)最优化问题。

(9) 然而, 使用式(7)设计的采样矩阵不一定具有较好的重建性能, 文献[5]指出这是因为μ(A)仅反映采样矩阵A 2列之间相关的最极端的情况。文献[12]认为最优的A任意2列应正交, 提出以G和单位矩阵I之间的欧氏距离评价采样矩阵性能。因为G是对称矩阵, 以欧氏距离作为相关性定义的准则可以表示为

(10) 然而, 由循环差集确定的采样矩阵才是最优傅里叶采样矩阵, 此时任意2列之间的相关值相等即G中所有元素都相等且不等于零[11]。因此, G和单位矩阵的欧氏距离不能准确反映测量矩阵的重建性能。
文献[14]考虑矩阵G中较大值, 提出基于阈值的式(11)计算矩阵G上三角元素值大于阈值t的三次方和评价采样矩阵性能, 其中t为预先设置的非零值, 并通过仿真得出t=0.15时性能较好并以最小化γt(A)为目标函数设计导频。

(11) 然而, 该方法没有考虑G中gi, j < t的值, 部分的反映了采样矩阵的重建性能。而且文献[14]中t=0.15是针对N=512, Np=24, L=50一种情况, 并没有对具体的(Np, L, N)确定阈值t的方法。采样矩阵具有好的重建性能是压缩感知算法能够重建稀疏信号的前提条件, 因此是否能够准确地评价采样矩阵并构建采样矩阵关系到压缩感知算法能否重建稀疏信号。
2.2 新导频设计准则
为后文分析, 首先给出以下推论。
推论1 设N、Np和L分别为IFFT大小、导频数和信道长度, 导频集合为P={p1, p2, …, pNp}, A为由N×N的傅里叶变换矩阵对应P所在的行和前L列构成采样矩阵, G=abs(AHA)为按列归一化矩阵A的互相关矩阵, 则与G主对角线平行的对角线上的值相等且第r(0≤r≤L-1)个对角线上的值为

证明 考虑G的第1行, 由式(7)可得第1行的第r(0≤r≤L-1)列的值为

(12) 令G的第i行第j列(0≤i, j≤L-1)的值为gi, j, 为证明对角线上的值相等, 只需要证明gi, j=gi+1, j+1。

(13) 因此, G的值取决于第1行且与主对角线平行的对角线上的元素相等。 证毕
由推论1可知, G仅有L个不同值且L个值取决于N、P和L, 不恰当的阈值t会导致式(11)的结果差别较大。为准确地评价采样矩阵的重建性能, 应考虑采样矩阵任意2列之间的相关对稀疏信号重建的贡献。考虑所有列之间的相关对稀疏信号重建性能的贡献, 提出式(14)以G所有元素的三次方和为准则衡量A的重建性能。

(14) 因为G是对称矩阵, 所以可以仅计算矩阵G的上三角元素。式(14)也可表示为

(15) 导频设计问题为求解以下最优化问题:

(16) 由式(15)可以得出, 问题式(16)为仅与导频位置集合P有关的离散组合优化问题, 计算所有可能的组合并选择满足式(16)的最小集合Popt不可行, 因此只能通过搜索算法计算其次最优解。
3. 并行完全树分组替换导频搜索算法
基于2.2节提出的导频设计准则, 提出一种并行完全树分组替换导频搜索算法, 该算法使用分组替换以实现更多的导频组合。算法主要包括初始化、外循环、内循环和导频更新, 具体步骤如下:
步骤1 初始化。设外循环次数为U, 树和树枝的个数分别为T和V, 分组大小为b, OFDM系统的载波数和导频数分别为N和Np, 信道长度为L, 所有可用的索引集Ω={1, 2, …, N}。从Ω中随机选择Np个位置索引构成一个导频, 共生成T个导频P10, P20, …, PT0, 导频集合的上标表示外循环次数。
步骤2 外循环。算法进行第r(1≤r≤U)次外循环, 分别将T个导频分为每组包含b个索引的

步骤3 内循环。设第s-1次内循环结果的T个导频为P1r, s-1, P2r, s-1, …, PTr, s-1, 按步骤4更新T个导频得到第s(s≤c)次内循环结果P1r, s, P2r, s, …, PTr, s。执行完c次内循环后转到步骤2进行下一次外循环。
步骤4 导频更新。设第i个导频Pir, s-1={Q1, Q2, …, Qc}的第k(1≤k≤c)组为Qk={Qk(1), Qk(2), …, Qk(b)}。当替换第k组的第1个索引Qk(1)时, 固定Λ={Q1, …, Qk-1, Qk(2), …, Qk(b), Qk+1, …, Qc}不变, 将Ω\Λ的位置索引逐一添加到Λ中的Qk(1)位置并按照式(15)计算对应的λm=κ(A)(1≤m≤N-Np+1), 从中选出对应最小V个κ(A)的V个导频Pk, 1r, s-1, Pk, 2r, s-1, …, Pk, Vr, s-1作为V个导频子节点, 因此第i个导频第k组替换第l个索引位置时, 对第k组第l-1个索引位置替换结果Pk, 1r, s-1, Pk, 2r, s-1, …, Pk, Vl-1r, s-1的每一个导频用同样的方法替换并选择V个导频子节点作为结果, 第k组导频经过b次替换后产生Vb个导频子节点, b次迭代过程构成一个V叉树且是完全树。同时并行替换T个导频第k组的b个索引, 共产生TVb个导频, 从TVb个导频中选择T个最优导频作为本步骤结果P1r, s, P2r, s, …, PTr, s, 转到步骤3进行下一次内循环。
步骤5 输出结果。经过U次外循环后, 从T个备选结点P1U, P2U, …, PTU中选择具有最小κ(A)的导频输出。
考虑时间复杂度, 从N个索引中选择Np个位置的计算复杂度为O(CNpN), 本节提出的算法的计算复杂度为O(UTVbbcNL2Np)。
4. 仿真结果
为验证提出的评价采样矩阵重建性能方法的优越性, 本文从信道估计的误码率和均方误差验证新准则的性能, 并对提出的导频搜索算法性能与已有导频搜索算法的性能进行了仿真比较。
4.1 信道估计均方误差和误码率比较
同文献[14]仿真参数设置和仿真方法相同, 考虑载波数N=512的OFDM系统, 设定导频数Np=24, L=60。随机产生5×105个导频, 分别根据互相关准则式(7)、文献[12]提出的导频设计准则式(10)、文献[14]提出的准则式(11)和本文提出的导频设计准则式(15)从随机产生的导频中选择最优的导频。
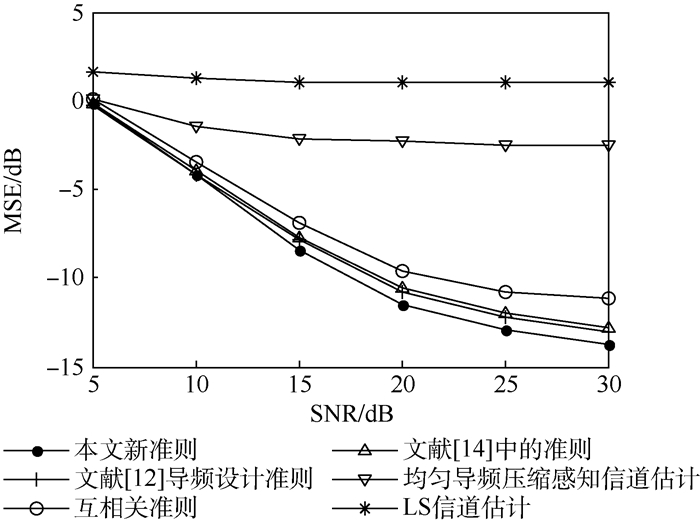
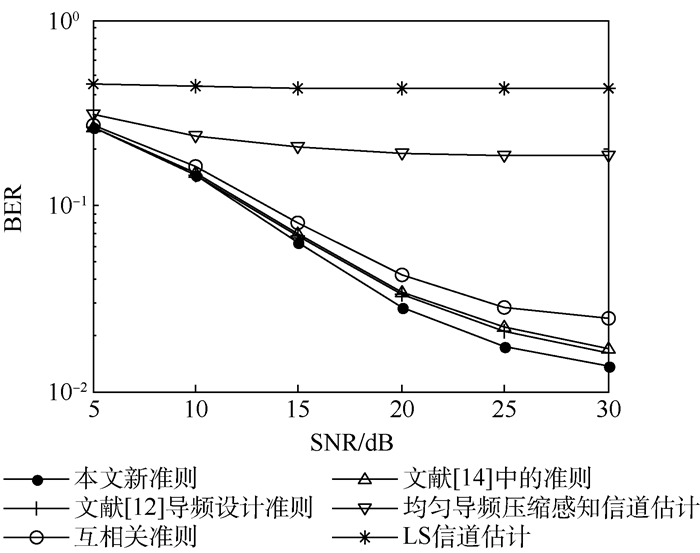
用得到的4种导频按照式(2)构成采样矩阵采样稀疏信道以验证不同导频设计准则的准确性。稀疏信道非零位置均匀分布于[1, 60], 非零系数服从(0, 1)的高斯分布。稀疏度即非零系数的个数为12, 每个信噪比(SNR)仿真3 000次, 压缩采样重建算法使用OMP算法, 信道估计均方误差(MSE)和误码率(BER)曲线如图 1和图 2所示。同时, 本文仿真了Np=24均匀导频LS信道估计和均匀导频压缩感知信道估计。
由仿真结果可以得出, 由于导频太少, 传统的LS算法无法估计信道, 而使用等间隔导频分布的压缩感知信道估计性能要远好于LS算法。因为均匀导频确定的采样矩阵具有较大的互相关, 均匀导频压缩感知信道估计相比非均匀导频压缩感知信道估计具有最差的信道估计性能, 因而通过导频的设计可以减小采样矩阵的互相关, 提高信道估计的准确性。与互相关准则、文献[12]提出的导频设计准则相比, 根据提出的新准则设计的导频信道估计均方误差分别减小约3 dB和1 dB。和文献[14]准则相比, 信道估计均方误差可减小约0.8 dB, 在相同的误码率时, 最大可节省约5 dB信噪比。与等间隔导频压缩感知信道估计相比, 信道估计均方误差减小约12 dB。仿真结果表明, 在所有的评价采样矩阵重建性能的准则中, 根据本文提出的评价准则设计的导频具有最小的均方误差和误码率。
由于互相关、文献[12]和文献[14]提出的准则仅部分的反映了采样矩阵的重建性能, 而本文提出的准则考虑了采样矩阵任意2列之间的互相关, 能较准确的衡量采样矩阵的重建性能, 因此根据本文的新准则设计的导频具有最优的稀疏信号重建性能, 使用本文提出准则设计的导频具有最优的信道估计性能。
4.2 导频搜索算法性能比较
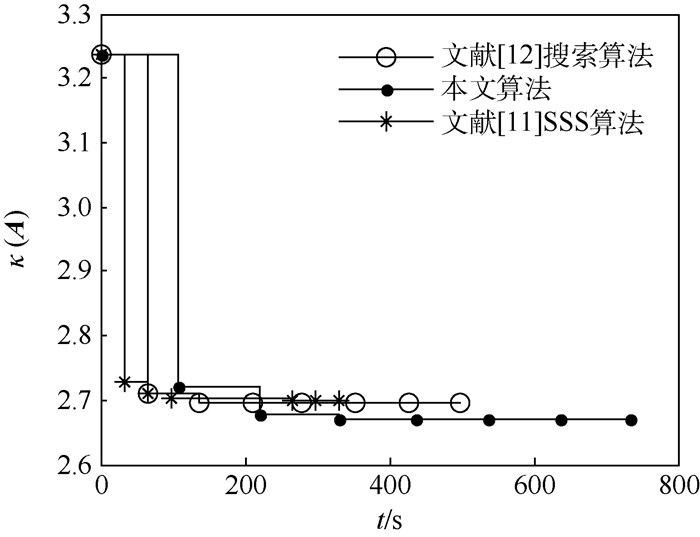
在现有的导频搜索算法中, 文献[11]的SSS算法和文献[12]的搜索算法有较好的导频搜索性能。为了比较的公平性, 3种算法设置相同的随机初始导频, 仿真中的导频数Np=16, 信道长度L=60, N=512。本文算法设置b=2, T=2, 文献[12]算法设置T=2。3种算法均设置初始导频数为2, SSS算法内循环次数、本文算法外循环次数和文献[12]算法外循环次数均为5。用提出的新准则式(15)设计导频, κ(A)随时间t的变化如图 3所示。
由仿真结果可以看出, 本文提出的算法能够持续收敛而文献[12]中的算法κ(A)在3次迭代之后不再减小, 2种算法均优于SSS算法。尽管本文算法的运行时间均比文献[12]算法长, 本文算法收敛时间360 s约是文献[12]算法200 s的1.8倍, 但是求解的目标是获取最优的导频而且导频在设计系统前离线设计, 因此在可接受的运行时间内可以忽略算法的运行时间。仿真结果表明提出算法可获得更优的导频, 这是因为本文提出的算法采用分组替换而非单个索引位置替换, 在相同的导频初始值可以实现更多的导频组合, 得到更优的导频。
5. 结论
1) 考虑相关矩阵所有元素对稀疏信号重建的贡献, 提出一种新的评价采样矩阵重建性能的方法, 可以准确的衡量采样矩阵的重建性能。
2) 提出一种新的导频搜索算法求解最优导频, 算法能够快速收敛且具有较好的导频搜索性能。
本文的采样矩阵是傅里叶采样矩阵, 下一步将研究高斯矩阵、伯努利矩阵等作为采样矩阵时如何准确评价采样矩阵的重建性能的问题。
-
表 1 软体驱动器设计参数
Table 1. Parameters for soft actuator design
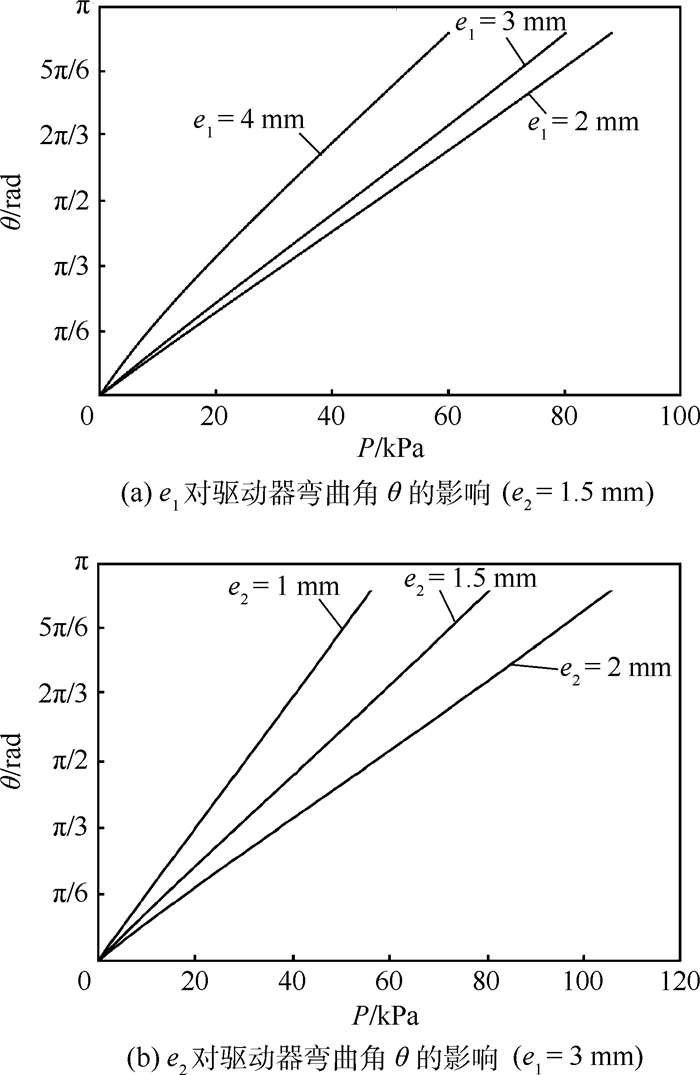
参数 数值 长度l0/mm 80 驱动器半径R0/mm 6.5 空腔内径r0/mm 1.5 空腔圆心偏离驱动器中心距离e1/mm 3 不可伸长面与驱动器中心间距离e2/mm 1.5 绕线圈数N 28 绕线螺旋角/(°) 5 质量/kg 0.017 -
[1] ROBINSON G, DAVIES J B C. Continuum robots-A state of the art [C]//1999 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 1999, 4:2849-2854. [2] TRIVEDI D, RAHN C D, KIER W M, et al. Soft robotics:Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research [J].Applied Bionics and Biomechanics, 2008, 5(3):99-117. doi: 10.1155/2008/520417 [3] KIM S, LASCHI C, TRIMMER B.Soft robotics:A bioinspired evolution in robotics [J].Trends in Biotechnology, 2013, 31(5):287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.03.002 [4] RUS D, TOLLEY M T.Design, fabrication and control of soft robots [J].Nature, 2015, 521(7553):467-475. doi: 10.1038/nature14543 [5] 曹玉君, 尚建忠, 梁科山, 等.软体机器人研究现状综述[J].机械工程学报, 2012, 48(3):25-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201203005.htmCAO Y J, SHANG J Z, LIANG K S, et al.Review of soft-bodied robots [J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(3):25-33(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201203005.htm [6] ILIEVSKI F, MAZZEO A D, SHEPHERD R F, et al.Soft robotics for chemists[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(8):1890-1895. doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.8 [7] SEOK S, ONAL C D, CHO K J, et al.Meshworm:A peristaltic soft robot with antagonistic nickel titanium coil actuators [J].IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013, 18(5):1485-1497. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2012.2204070 [8] CAMARILLO D B, MILNE C F, CARLSON C R, et al.Mechanics modeling of tendon-driven continuum manipulators[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(6):1262-1273. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2002311 [9] CIANCHETTI M, MATTOLI V, MAZZOLAI B, et al.A new design methodology of electrostrictive actuators for bio-inspired robotics[J].Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2009, 142(1):288-297. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2009.08.039 [10] BARTOW A, KAPADIA A, WALKER I D.A novel continuum trunk robot based on contractor muscles[C]//Proceedings of the 12th WSEAS International Conference on Signal Processing, Robotics, and Automation.Cambridge:WSEAS Press, 2013:181-186. [11] MOSADEGH B, POLYGERINOS P, KEPLINGER C, et al.Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly[J].Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(15):2163-2170. doi: 10.1002/adfm.v24.15 [12] JONES B A, WALKER I D.Kinematics for multisection continuum robots[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2006, 22(1):43-55. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2005.861458 [13] POLYGERINOS P, WANG Z, OVERVELDE J T B, et al.Modeling of soft fiber-reinforced bending actuators [J].IEEE Transa-ctions on Robotics, 2015, 31(3):778-789. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2428504 [14] 马建旭, 李明东, 包志军, 等.仿蚯蚓蠕动微机器人及控制系统[J].上海交通大学学报, 1999, 33(7):855-857. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT907.019.htmMA J X, LI M D, BAO Z J, et al.Microperistaltic robot simulating earthworm and its control system[J].Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 1999, 33(7):855-857(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT907.019.htm [15] 王振龙, 杭观荣, 李健, 等.面向水下无声推进的形状记忆合金丝驱动柔性鳍单元[J].机械工程学报, 2009, 45(2):126-131. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB200902024.htmWANG Z L, HANG G R, LI J, et al.Shape memory alloy wire actuated flexible biomimetic fin for quiet underwater propulsion [J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(2):126-131 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB200902024.htm [16] KANG R, BRANSON D T, ZHENG T, et al.Design, modeling and control of a pneumatically actuated manipulator inspired by biological continuum structures [J].Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2013, 8(3):036008. [17] BISHOP-MOSER J, KRISHNAN G, KIM C, et al.Design of soft robotic actuators using fluid-filled fiber-reinforced elastomeric enclosures in parallel combinations [C]//2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2012:4264-4269. [18] YEOH O H.Some forms of the strain energy function for rubber [J].Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 1993, 66(5):754-771. doi: 10.5254/1.3538343 [19] KOTHERA C S, JANGID M, SIROHI J, et al.Experimental characterization and static modeling of McKibben actuators [J].Journal of Mechanical Design, 2009, 131(9):091010. doi: 10.1115/1.3158982 [20] 黄建龙, 解广娟, 刘正伟.基于Mooney-Rivlin和Yeoh模型的超弹性橡胶材料有限元分析[J].橡胶工业, 2008, 55(8):467-470. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJJZ200812005.htmHUANG J L, XIE G J, LIU Z W.FEA of hyperelastic rubber material based on Mooney-Rivlin model and Yeoh model [J].China Rubber Industry, 2008, 55(8):467-470(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJJZ200812005.htm [21] American Society for Testing and Materials.Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics:ASTM D638 [S].[S.l.]:ASTM, 2003. 期刊类型引用(48)
1. 王玲,张驻军,吴鑫,田辉,李慧琴,张红梅. 硬度耦合刚度增强型软体夹持器设计研究. 机械设计. 2024(02): 22-31 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 方海峰,黄希,范纪华,陈立威,谷通顺. 仿鸟喙微型气动软体机械手爪的设计及优化. 机械科学与技术. 2022(01): 67-74 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 刘卓群,张翔,黄奕勇,陈小前,赵勇. 气控软体驱动器结构分析与优化设计. 国防科技大学学报. 2022(02): 150-161 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 张珂,魏洪涛,苏凯伦,李青松. 多气腔软体致动器的弯曲特性分析和试验验证. 机床与液压. 2022(10): 63-69 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 李明鑫,宁萌,陈海卫. 一种新型软体驱动器的设计与研究. 机械科学与技术. 2021(01): 33-39 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 田德宝,毕学文,张欣欣,刘晓敏,赵云伟. 变腔室气动软体机械手结构设计与实验. 机床与液压. 2021(11): 109-112 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 张浩. 考虑通信连通性的输电线路巡检无人机群动态调度方法. 电气自动化. 2021(06): 42-45 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 张志远,王松涛,王学谦,孟得山,梁斌. 螺线型气动软体致动器设计与建模. 机器人. 2020(01): 10-20 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 陆兴华,明仲,邱子琪,曾凌锋. 无人机低空滑翔抗攻击突防控制律优化设计. 计算机技术与发展. 2020(02): 183-187 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 余莎. 足球机器人腿部机构设计与步态规划研究. 机械设计与制造工程. 2020(02): 110-114 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 施明泰,胡全贵,郭翔,贾伟昭,苏彦龙. 数据中心智能巡检机器人管理平台自主控制方法. 工业仪表与自动化装置. 2020(02): 65-69 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 董虎,王保兴,李巍,曹毅. 基于单向气动驱动器的软体手变形机理. 东华大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(02): 288-296+303 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 冯超. 基于粒子滤波的篮球旋转投射最优角度分析研究. 宜春学院学报. 2020(03): 118-121 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 樊国根,蒙芳. 基于粒子群智能优化的机器人路径全局规划算法. 电子测量技术. 2020(07): 41-45 .  百度学术
百度学术15. 范需,戴宁,王宏涛,丁龙伟,谢绍辉. 气动网格软体驱动器弯曲变形预测方法. 中国机械工程. 2020(09): 1108-1114 .  百度学术
百度学术16. 李祥伟,何彦霖,孙广开,孟凡勇,宋言明. 软体心脏固定器柔性支撑臂变刚度性能分析与测试. 中国测试. 2020(06): 140-146 .  百度学术
百度学术17. 谢荣臻,黄东煜,苏满佳,管贻生,朱海飞. 三维气动软体驱动器弯曲建模与分析. 机械工程学报. 2020(15): 157-169 .  百度学术
百度学术18. 魏琼,张永梁,游颖,汪泉. 基于多腔软体驱动器的柔性手指设计. 工程设计学报. 2020(04): 425-432+532 .  百度学术
百度学术19. 刘飞. 高负荷赛前训练下游泳姿势轨迹跟踪方法分析. 商丘师范学院学报. 2020(12): 88-92 .  百度学术
百度学术20. 甄冒发,徐振峰,谢宇. 多自由度机器人惯性误差反馈融合闭环控制. 微电子学与计算机. 2020(12): 77-80 .  百度学术
百度学术21. 田德宝,郝思琦,赵云伟,陈芳芳,孙国栋. 网络式气动软体驱动器设计、制造与实验. 吉林化工学院学报. 2020(11): 61-64 .  百度学术
百度学术22. 李文朔,弓永军,陈英龙,赵佳莹. 基于Neo-Hookean模型的软体机械臂变曲率运动学建模研究. 组合机床与自动化加工技术. 2020(12): 31-34 .  百度学术
百度学术23. 陈刚,邬元富,李伟,李缘春,王依涛. 面向结肠镜软体机器人设计与建模仿真. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学). 2020(12): 157-162 .  百度学术
百度学术24. 任彦朋. 舰载对空导弹的自动装载控制系统优化设计. 智能计算机与应用. 2019(01): 248-251 .  百度学术
百度学术25. 高东,孟凡勇,宋言明,孙广开,祝连庆. 植入光纤光栅的软体驱动器形状传感研究. 仪器仪表学报. 2019(02): 155-163 .  百度学术
百度学术26. 王炜华,张全洋. 足球机器人运动中的动态激光定位方法. 激光杂志. 2019(05): 183-187 .  百度学术
百度学术27. 杨振兴. 蹴鞠训练中落球点轨迹跟踪方法研究. 太原师范学院学报(自然科学版). 2019(01): 93-97 .  百度学术
百度学术28. 鲍官军,张亚琪,许宗贵,蔡世波,胥芳,杨庆华,张立彬. 软体机器人气压驱动结构研究综述. 高技术通讯. 2019(05): 467-479 .  百度学术
百度学术29. 涂琴,岳东海,王延杰,刘光新. 果蔬侧立采摘柔性手爪设计与变形特性研究. 机床与液压. 2019(09): 51-57 .  百度学术
百度学术30. 刘炜. 基于多维谱峰联合搜索的无人机控制抗扰动算法. 电子测量技术. 2019(09): 19-23 .  百度学术
百度学术31. 田小玲. 基于末端圆周标定的软体机器人刚度独立控制研究. 国外电子测量技术. 2019(06): 135-139 .  百度学术
百度学术32. 田小玲. 基于末端圆周标定的软体机器人刚度独立控制研究. 电子测量技术. 2019(10): 105-109 .  百度学术
百度学术33. 丁响林,阚玉锦,苏进. 基于自适应模糊PID的连铸机电液伺服控制系统设计. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版). 2019(02): 89-93 .  百度学术
百度学术34. 陈晓生. 轮式机器人的末端位姿测量与误差补偿控制. 智能计算机与应用. 2019(04): 274-277 .  百度学术
百度学术35. 黄智勇. 基于毫米波雷达的汽车自动避障控制系统研究. 佳木斯大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(04): 580-584 .  百度学术
百度学术36. 颜慧佳. 基于激光测距的智慧停车管理系统研究与设计. 激光杂志. 2019(08): 150-154 .  百度学术
百度学术37. 陆兴华,明仲,吴宏裕,刘文林. 基于动态基元轨迹跟踪的无人机低空突防控制. 国外电子测量技术. 2019(08): 92-96 .  百度学术
百度学术38. 吴正,李凤芝. 基于解耦控制的跨栏跑步点轨迹跟踪方法研究. 赤峰学院学报(自然科学版). 2019(08): 8-10 .  百度学术
百度学术39. 刘夏瑜,牛哲斌. 短距离游泳身体机能疲劳极限监控方法研究. 赤峰学院学报(自然科学版). 2019(08): 101-104 .  百度学术
百度学术40. 董虎,林苗,顾苏程,曹毅,李巍. 多向气动驱动器软体仿生舌弯曲状态的研究. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2019(09): 1882-1893 .  本站查看
本站查看41. 刘飞. 田径运动员腿部爆发力长时效应建模分析. 湘南学院学报. 2019(05): 88-93 .  百度学术
百度学术42. 刘晓刚,张斌. 基于神经网络的机器人激光传感定位技术. 激光杂志. 2019(11): 127-130 .  百度学术
百度学术43. 龙卓群,高平,段超. 外力干扰下光纤式机器人移动路径优化控制. 激光杂志. 2019(11): 195-199 .  百度学术
百度学术44. 涂琴,岳东海,王延杰,刘光新. 多腔体软体驱动器负载抓持变形特性研究. 液压与气动. 2019(12): 68-74 .  百度学术
百度学术45. 黄二辉,王瑷珲,王东云,李继朋,郭光复. 智能软体驱动器的跟踪控制器设计. 中原工学院学报. 2018(01): 78-82 .  百度学术
百度学术46. 樊继壮,于庆国,袁博文,赵杰. 软体仿蛙游动机器人关节式气动致动器研制. 机器人. 2018(05): 578-586 .  百度学术
百度学术47. 许宗贵,方醒,陈凌峰,潘鲁锋,鲍官军. 一种仿生软体驱动器的设计与弯曲建模研究. 机电工程. 2018(11): 1190-1194 .  百度学术
百度学术48. 孙沂琳,张秋菊,陈宵燕. 气动软体驱动器设计与建模. 食品与机械. 2018(11): 101-105 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(42)
-








 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术