-
摘要:
常用实验手段测得单节锂离子电池热释放速率无法真实反映航空运输包装件内大量锂离子电池因发生多米诺效应导致热量散失及传递过程间歇性变化。本文提出一种基于多米诺效应的锂离子电池热释放速率等效分析方法,即通过自主设计的实验平台对3×3排布的典型18650型锂离子电池热失控后发生的多米诺效应及各节电池表面温度进行分析。利用FLUENT使用标准18650型锂离子电池热释放速率曲线用于同等实验条件下的锂离子电池热失控传播仿真模拟,采用二分法逐次修正标准热释放速率、使仿真和实验的锂离子电池表面温度相符。将获得等效的锂离子电池热释放速率曲线再次应用于仿真,得到各电池的最高温度及达到最高温度的时间和实验数据相吻合,验证了修正后的等效热释放速率模型可靠性。该方法可适用于各型号及不同数量包装件内锂离子电池热释放速率获取,指导航空运输锂离子电池火灾防控工程实际。
Abstract:The heat release rate of single lithium-ion battery measured by the commonly used experimental method is not able to reflect the heat losses caused by the domino effect and the intermittent changes during the transfer process of a large number of lithium-ion batteries within the air transport package. This paper, instead, proposes a method of equivalent analysis for the heat release rate of lithium-ion battery based on domino effect. Namely, the domino effect and the surface temperature of each battery after the thermal runaway of typical 18650 lithium-ion battery in 3×3 configuration were analyzed with the help of independently designed experimental platform. Using FLUENT to use the standard 18650 lithium-ion battery heat release rate curve for the same experimental conditions of lithium-ion battery thermal runaway simulation. Then dichotomy was used to revise the standard heat release rate to accord the surface temperature of the lithium-ion battery in simulation and in experiment to obtain equivalent heat release rate curve of lithium-ion battery to apply to further simulation. It turned out that the maximum temperature of each battery and the time to reach maximum temperature coincided with the experimental data, verifying the reliability of the revised equivalent heat release rate model. This method can be applied to obtain heat release rate of various types of lithium-ion batteries in different amount of package, therefore guiding the fire prevention and control project in the air transport of lithium-ion battery in practice.
-
Key words:
- heat release rate /
- domino effect /
- thermal runaway /
- lithium-ion battery /
- air transport
-
表 1 不同网格数量下温度随时间变化
Table 1. Temperature changes over time under different numbers of grid
网格数量 温度/K t=25s t=50s t=100s t=150s t=200s 14 752 408 505 670 788 862 100 740 405 504 672 784 869 224 268 404 502 677 784 863 表 2 各节电池表面温度参数的实验与仿真结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental and simulation results of temperature parameters of cell surface
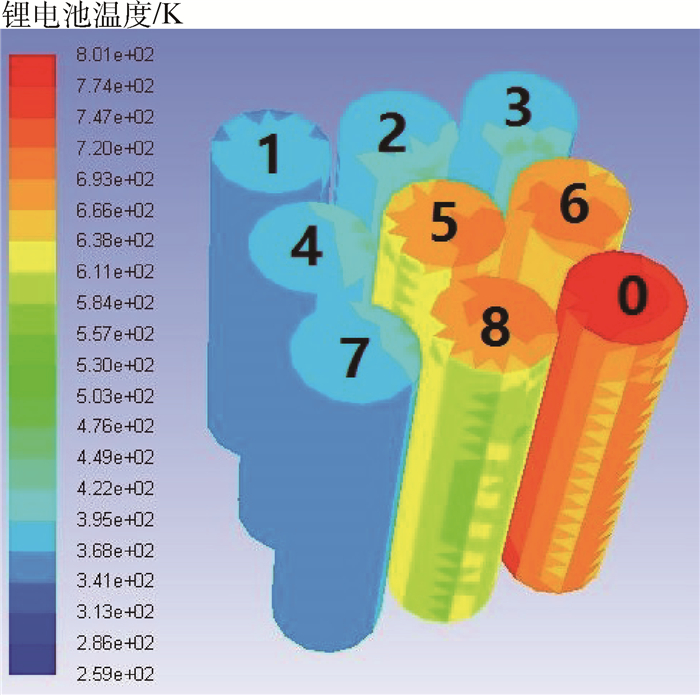
电池编号 初爆时间/s 达到最高温度时间/s 最高温度/℃ 实验 仿真 实验 仿真 实验 仿真 8 160 95 231 160 652.6 1 386.4 6 170 95 245 160 681.4 1 386.4 7 196 125 244 144 656.7 1 311.5 3 199 125 243 144 593.6 1 311.5 5 209 115 254 158 846.5 1 701.9 4 218 130 250 166 620.5 1 322.7 1 218 138 261 176 737.1 1 459.3 2 218 130 259 166 699.4 1 322.7 表 3 各节电池表面温度参数的实验与修正后仿真结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental and simulation after correction results of temperature parameters of cell surface
电池编号 初爆时间/s 达到最高温度时间/s 最高温度/℃ 实验 仿真 实验 仿真 实验 仿真 8 160 175 231 233 652.6 679.5 6 170 175 245 233 681.4 679.5 7 196 204 244 256 656.7 652.6 3 199 204 243 256 593.6 652.6 5 209 198 254 257 846.5 849.1 4 218 217 250 252 620.5 684.5 1 218 221 261 260 737.1 716.4 2 218 217 259 252 699.4 684.5 -
[1] WEBSTER H.Fire protection for the shipment of lithium batteries in aircraft cargo compartments:DOT/FAA/AR-09/55[R]. Washington, D.C.:Federal Aviation Administration, 2010:1-4. [2] FENG X, SUN J, OUYANG M, et al.Characterization of penetration induced thermal runaway propagation process within a large format lithium ion battery module[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275:261-273 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.11.017 [3] SPINNER N S, FIELD C R, HAMMOND M H, et al.Physical and chemical analysis of lithium-ion battery cell-to-cell failure events inside custom fire chamber[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 279:713-721 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.068 [4] 罗星娜, 张青松, 戚瀚鹏, 等.基于计算流体动力学的锂离子电池热失控多米诺效应研究[J].科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(33):327-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.33.062LUO X N, ZHANG Q S, QI H P, et al.Lithium-ion battery thermal runaway domino effect analysis based on the CFD[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(33):327-332(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.33.062 [5] 张青松, 姜乃文, 罗星娜, 等.锂离子电池热失控多米诺效应实证研究[J].科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(10):252-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.10.050ZHANG Q S, JIANG N W, LUO X N, et al.Lithium-ion battery thermal runaway domino effect experimental verification research[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(10):252-256(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.10.050 [6] Standards Policy and Strategy Committee.Reaction-to-fire tests-Heat release, smoke production and mass loss rate:BS ISO 5660-1[S]. London:British Standard Institution, 2015:16-17. [7] FU Y, LU S, LI K, et al.An experimental study on burning behaviors of 18650 lithium ion batteries using a cone calorimeter[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 273:216-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.09.039 [8] HUANG P, WANG Q, LI K, et al.The combustion behavior of large scale lithium titanate battery[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:77-88. [9] PING P, WANG Q, HUANG P, et al.Thermal behaviour analysis of lithium-ion battery at elevated temperature using deconvolution method[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 129:261-273. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.092 [10] FINEGAN D P, SCHEEL M, ROBINSON J B, et al.In-operando high-speed tomography of lithium-ion batteries during thermal runaway[J/OL]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6:2-4[2016-03-15]. [11] FENG X, FANG M, HE X, et al.Thermal runaway features of large format prismatic lithium ion battery using extended volume accelerating rate calorimetry[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 255:294-301. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.01.005 [12] JHU C Y, WANG Y W, WEN C Y, et al.Self-reactive rating of thermal runaway hazards on 18650 lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2011, 106(1):159-163. doi: 10.1007/s10973-011-1452-6 [13] 戚瀚鹏, 张青松, 宋广韬.非稳态火源热释放速率等效合成模型研究[J].安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(4):131-134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201504029.htmQI H P, ZHANG Q S, SONG G T.Innovated synthesis model of the heat releasing rate for the non-steady state fires[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(4):131-134(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201504029.htm [14] LIU X, STOLIAROV S I, DENLINGER M, et al.Comprehensive calorimetry of the thermally-induced failure of a lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 280:516-525. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.125 [15] 张雯霞. 锂离子电池电解液的锥形量热仪研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2015.ZHANG W X.Experimental study of electrolytes of lithium ion batteries by cone calorimeter[D]. Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China, 2015(in Chinese). [16] 胡棋威. 锂离子电池热失控传播特性及阻断技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国舰船研究院, 2015.HU Q W.Study on lithium-ion batteries thermal runaway propagation characteristics and blocking techniques[D]. Beijing:China Ship Research and Development Academy, 2015(in Chinese). [17] WU P, ROMBERG J, FENG X, et al.Thermal runaway propagation within module consists of large format li-ion cells[C]//Proceedings of SAE-China Congress 2015:Selected Papers.Beijing:Springer, 2015:127-133. [18] LAMB J, ORENDORFF C J, STEELE L A M, et al.Failure propagation in multi-cell lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 283:517-5230. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.10.081 [19] HATCHARD T D, MACNEIL D D, STEVENS D A, et al.Importance of heat transfer by radiation in Li-ion batteries during thermal abuse[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2000, 3(7):305-308. [20] WANG Q, PING P, ZHAO X, et al.Thermal runaway caused fire and explosion of lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 208:210-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.02.038 -








 下载:
下载: