-
摘要:
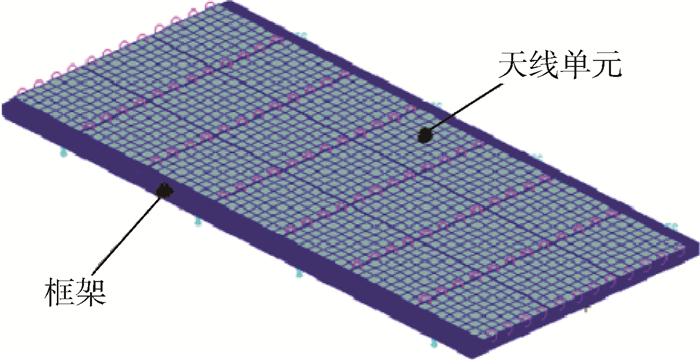
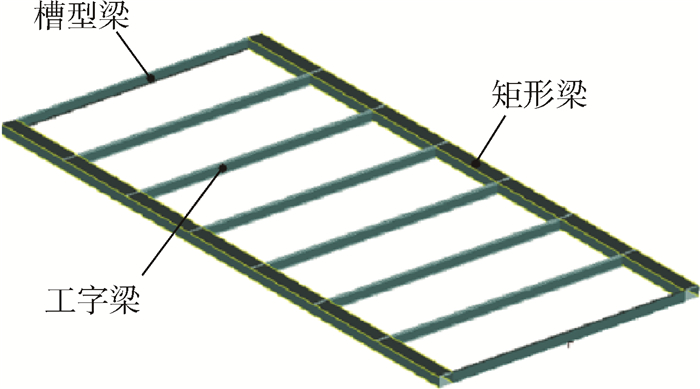
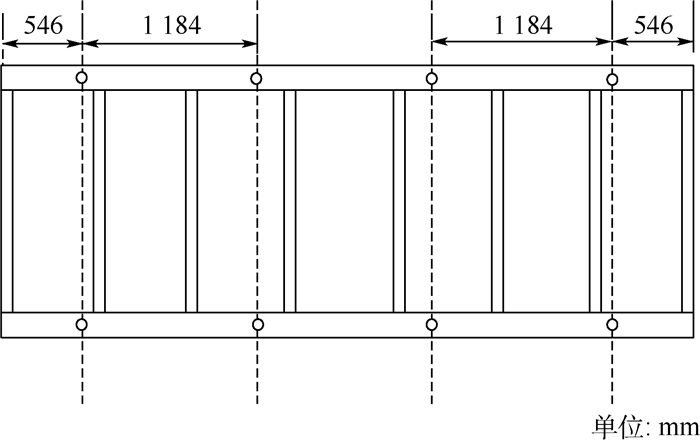
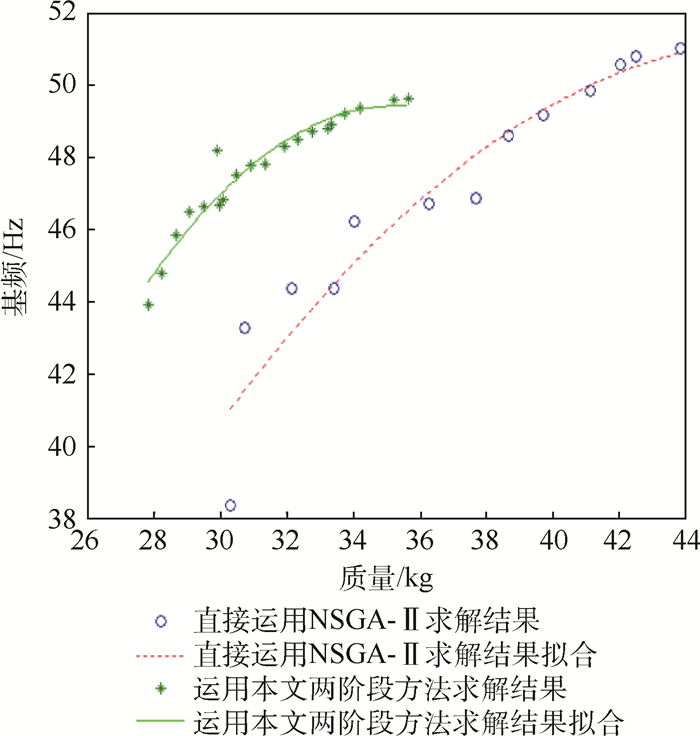
为了改善卫星天线复合材料框架的结构动力学性能,提出了一种针对卫星天线框架复合材料铺层的两阶段优化设计方法。阶段Ⅰ以各铺层的角度为设计变量进行铺层顺序优化,框架基频的最大化为优化目标,铺层数的最大值为约束条件。其中设计变量用一种多进制码来表示,并将多进制码映射为连续变量,应用粒子群优化(PSO)算法对阶段Ⅰ优化模型进行求解。在阶段Ⅰ优化结果的基础上,阶段Ⅱ主要是优化复合材料的层数,以基频最大化与质量最小化为优化目标建立多目标拓扑优化模型,应用第2代非劣排序遗传算法(NSGA-Ⅱ)进行求解。为了验证该方法的有效性,对某大型卫星天线复合材料框架进行优化设计,结果表明:该方法能有效地减小天线板复合材料框架的质量,并提高基频。
Abstract:A two-phase optimization method for layup design of composite frame for satellite antenna is introduced to improve the structural dynamics performance of the composite frame. Phase Ⅰ focused on generating a new ply layout by optimizing the ply orientation angle and stacking sequences, while the number of plies is the upper bound of the constraints. The objective of the first phase was to maximize the fundamental frequency of the frame. Design variables were n-nary codes which were mapped to continuous variables. The optimization model of phase Ⅰ was solved by the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Phase Ⅱ aimed to reduce the number of plies for the ply layout optimized in phase Ⅰ. A multi-objective topology optimization model was built to minimize the mass of the frame and maximize the fundamental frequency. The optimization model was solved by the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm Ⅱ (NSGA-Ⅱ). To verify the feasibility of optimization method, the example of a frame of large satellite antenna was conducted. The result shows that the two-phase optimization can effectively reduce the mass of the frame of large satellite antenna and also improve the fundamental frequency.
-
Key words:
- composite frame /
- satellite antenna /
- two-phase optimization /
- structural dynamics performance /
- mapping
-
表 1 PSO参数设置
Table 1. Parameters setting of PSO
参数 最大迭代次数 粒子数 惯性权重 全局增量 粒子增量 最大搜索速度 数值 20 12 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.1 表 2 阶段Ⅰ求解结果
Table 2. Solving results of phase Ⅰ
变量类型 x1(铺层序列) x2(铺层序列) x3(铺层序列) 基频/Hz 质量/kg 迭代次数 连续变量 [33122210101021033203] [21111311111131111111] [11112212012202301102] 53.93 45.71 20 离散变量 [21031003122122102102] [13131113131112111110] [13101011220213222221] 52.49 45.71 20 表 3 NSGA-Ⅱ参数设置
Table 3. Parameters setting of NSGA-Ⅱ
参数 种群大小 迭代次数 交叉概率 交叉分布指数 变异分布指数 数值 12 30 0.9 10 20 表 4 阶段Ⅱ的Pareto最优解集
Table 4. Pareto optimal solution set of phase Ⅱ
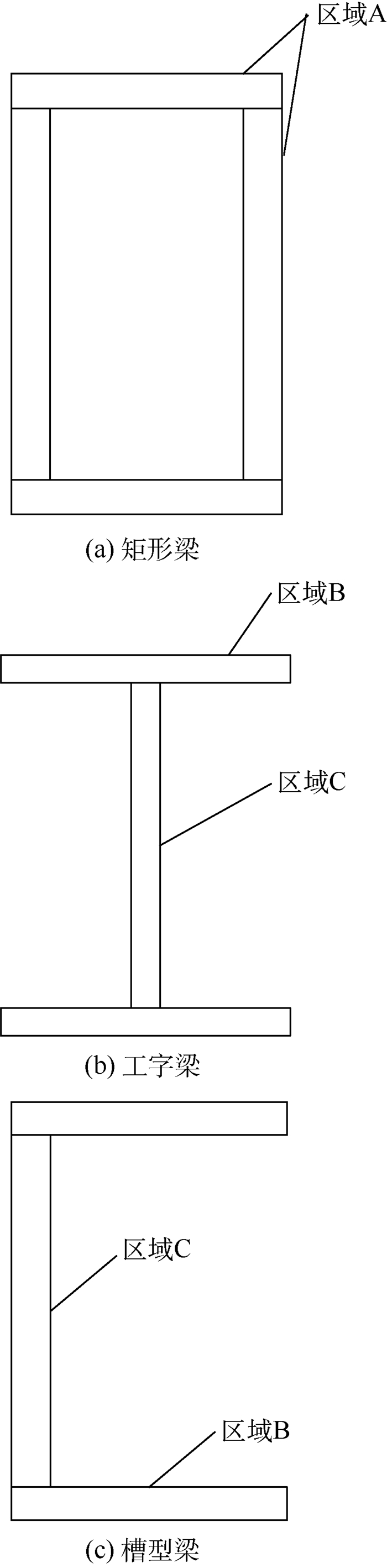
方案 区域A(铺层序列) 区域B(铺层序列) 区域C(铺层序列) 基频/Hz 质量/kg 原始方案 [1023102310231023] [1023102310231023] [1023102310231023] 41.421 38.37 1 [332210012032] [1113111111111111] [11221212030102] 46.657 29.97 2 [33221001020320] [21113111111111111] [112121203102] 48.460 32.32 3 [332201020323] [11131111111111] [112122031102] 44.791 28.24 4 [332210002032] [1113111111111111] [112121200102] 46.479 29.06 5 [332210002032] [111311111111111] [112121200102] 45.816 28.65 6 [3322100102032] [111311111111111] [112121200102] 46.807 30.08 7 [332210101020320] [21113111111111111] [112121203102] 49.171 33.75 8 [3322101010203203] [1113111111111111] [1121212031102] 49.549 35.21 9 [33221001020320] [1113111111111111] [112121200102] 48.277 31.91 10 [33220101021020] [111131111111111111] [112212010011] 48.169 29.89 11 [3322100102032] [1113111111111111] [112121200102] 47.481 30.49 12 [33221001020320] [21113111111111111] [11212120301102] 48.761 33.22 13 [3322100102032] [21113111111111111] [112121200102] 47.748 30.90 14 [332210002032] [21113111111111111] [112212120102] 46.630 29.48 15 [332210101020320] [1113111111111111] [121220301102] 48.887 33.33 16 [3322100102032] [21113111111111111] [1121212030102] 47.799 31.35 17 [33221001020320] [21113111111111111] [1121212001102] 48.712 32.77 18 [332210101020320] [21113111111111111] [1121212030102] 49.326 34.20 19 [3322101010203203] [1113111111111111] [11212120231102] 49.613 35.66 20 [332201020323] [1113111111111] [112220231102] 43.912 27.83 -
[1] 孙士平, 张卫红.基于改进模拟退火算法的复合材料层合板频率优化[J].复合材料学报, 2015, 32(3):902-910. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FUHE201503037.htmSUN S P, ZHANG W H.Frequency optimization of composite laminates using an improved simulated annealing algorithm[J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2015, 32(3):902-910(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FUHE201503037.htm [2] 晏飞, 李为吉.基于改进遗传算法的复合材料层合板自振频率优化设计[J].机械科学与技术, 2000, 19(增刊):91-96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXKX2000S1038.htmYAN F, LI W J.Optimal design of composite laminates subject to natural frequency constraint using an improved genetic algorithm[J].Mechanical Science and Technology, 2000, 19(Suppl.):91-96(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXKX2000S1038.htm [3] 柯俊, 史文库, 钱琛, 等.采用遗传算法的复合材料板簧多目标优化方法[J].西安交通大学学报, 2015, 49(8):102-108. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201508017KE J, SHI W K, QIAN C, et al.A multiobjective optimization for composite leaf springs using genetic algorithm[J].Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(8):102-108(in Chinese). doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201508017 [4] HONDA S, NARITA Y, SASAKI K.Discrete optimization for vibration design of composite plates by using lamination parameters[J].Advanced Composite Materials, 2009, 18(4):297-314. doi: 10.1163/156855109X434739 [5] NARITA Y.Layerwise optimization for the maxi-mum fundamental frequency of laminated composite plates[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2003, 263(5):1005-1016. doi: 10.1016/S0022-460X(03)00270-0 [6] GHIASI H, FAYAZBAKHSH K, PASINI D, et al.Optimum stacking sequence design of composite materials Part Ⅱ:Variable stiffness design[J].Composite Structures, 2010, 93(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2010.06.001 [7] ABDALLA M M, SETOODEH S, GURDAL Z.Design of variable stiffness composite panels for maxi-mum fundamental frequency using lamination parameters[J].Composite Structures, 2007, 81(2):283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2006.08.018 [8] STEGMAN J, LUND E.Discrete material optimization of general composite shell structures[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2005, 62(14):2009-2027. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0207 [9] 冯消冰, 黄海, 王伟.基于遗传算法的大型风机复合材料叶片根部强度优化设计[J].复合材料学报, 2012, 29(5):196-202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FUHE201205033.htmFENG X B, HUANG H, WANG W.Strength optimization of large wind turbine blade root on the genetic algorithm[J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2012, 29(5):196-202(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FUHE201205033.htm [10] 穆朋刚, 赵美英, 陈鹏飞, 等.基于蚁群算法的复合材料层合板的铺层顺序优化[J].玻璃钢/复合材料, 2007, 11(6):14-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BLGF200706003.htmMU P G, ZHAO M Y, CHEN P F, et al.Ply stacking-sequence optimization of composite laminate plates by ant colony system[J].Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites, 2007, 11(6):14-17(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BLGF200706003.htm [11] 顾元宪, 亢战, 赵国忠, 等.卫星承力筒复合材料结构的优化设计[J].宇航学报, 2003, 24(1):88-91. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB200301016.htmGU Y X, KANG Z, ZHAO G Z, et al.Optimal design of composite structure of satellite bearing cylinder[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2003, 24(1):88-91(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB200301016.htm [12] 陈烈民, 杨宝宁.复合材料的力学分析[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社, 2006:98-101.CHEN L M, YANG B N.Mechanical analysis for composite materials[M].Beijing:Science and Technology of China Press, 2006:98-101(in Chinese). [13] 陈烈民.航天器结构与机构[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社, 2005:102-103.CHEN L M.Spacecraft structures and mechanisms[M].Beijing:Science and Technology of China Press, 2005:102-103(in Chinese). [14] 唐俊.PSO算法原理及应用[J].计算机技术与发展, 2010, 20(2):213-216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFZ201002057.htmTANG J.Principle and application of PSO algorithm[J].Computer Technology and Development, 2010, 20(2):213-216(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFZ201002057.htm [15] MARLE R T, ARORA J S.Survey of multi-objective optimization methods for engineering[J].Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2004, 26(6):369-395. doi: 10.1007/s00158-003-0368-6 [16] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al.A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2):182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 -








 下载:
下载: