Numerical simulation of droplet motion on glass surface driven by ultrasonic travelling wave
-
摘要:
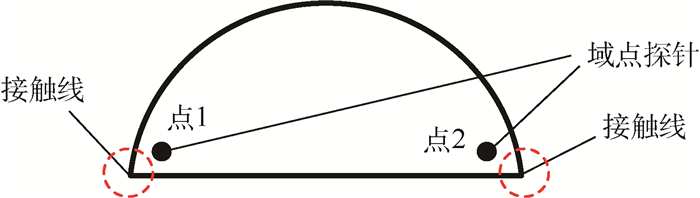
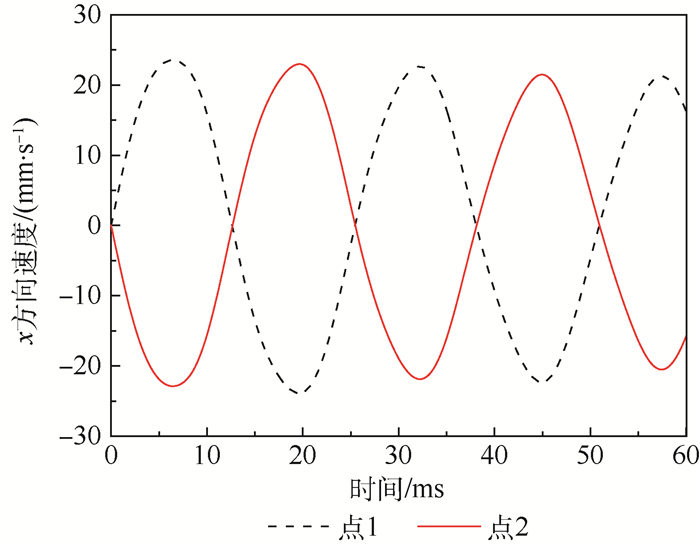
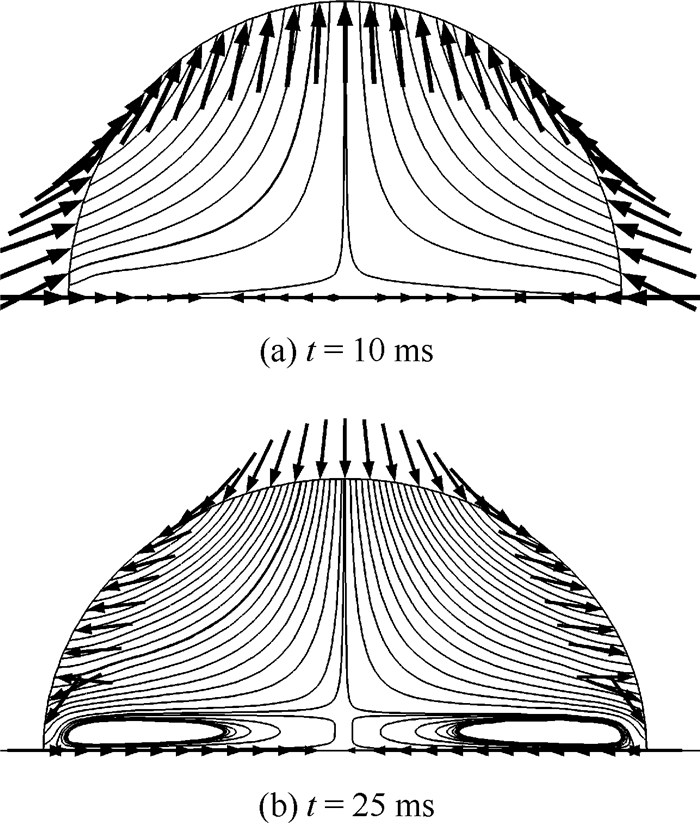
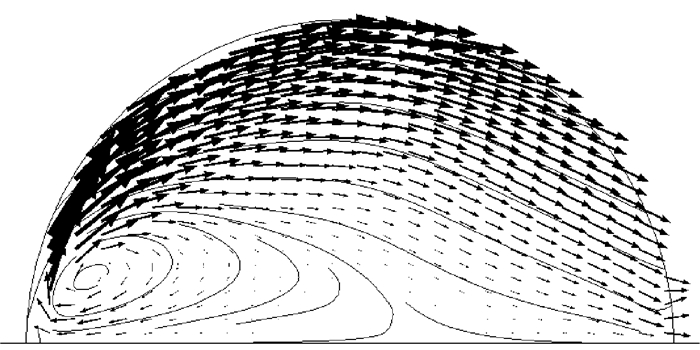
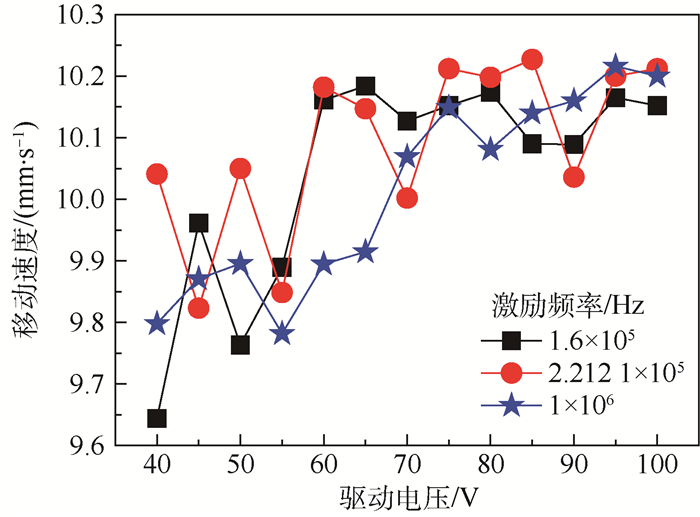
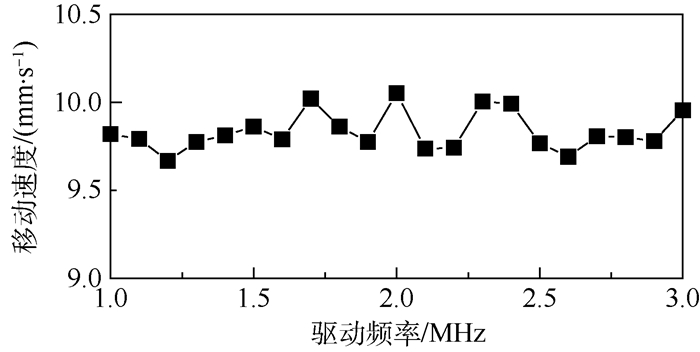
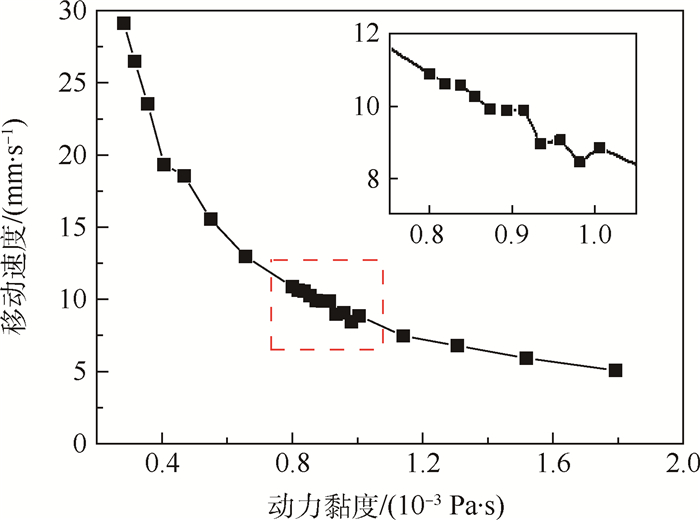
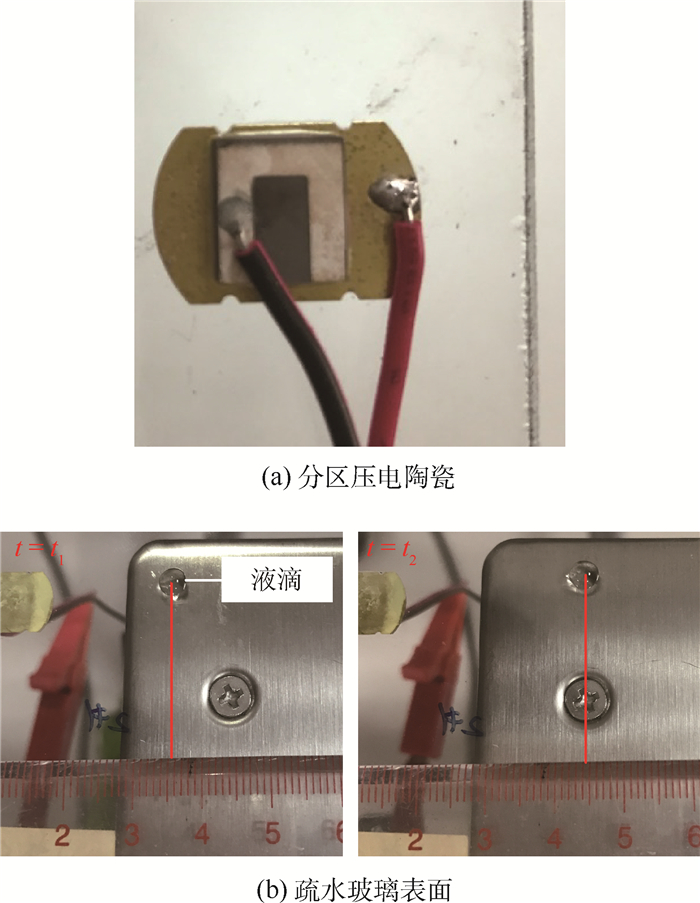
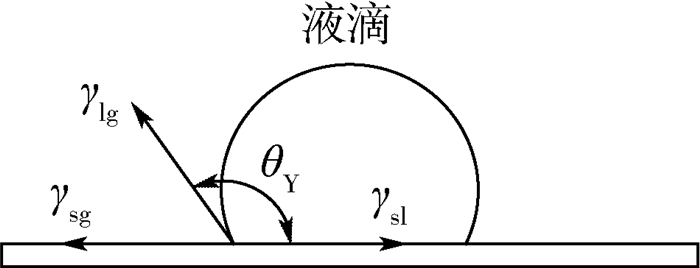
针对液滴铺展和移动的动力学行为在工业生产和微流控芯片等领域有着重要作用,提出了一种基于超声行波理论的弹性体平板驱动模型,利用压电陶瓷的逆压电效应在弹性体玻璃产生超声行波从而驱动液滴运动。借助多物理场软件COMSOL建立液滴模型,首先进行行波分析,验证了驱动液滴的可行性。在0~60 ms中,液滴在超声行波的驱动下进行收缩-铺展的正弦振荡运动。然后通过液滴内部流场结构分析发现,当液滴半径铺展到最大后开始收缩时,液滴与基底接触面处的速度首先发生变化,表明液滴内部速度场的变化对接触线是否发生移动有着重要作用。液滴内部流场存在一个类似于椭圆形的漩涡,说明液滴运动不是单纯由于收缩-铺展而引起的平动,而是滚动着朝前运动。最后分别探讨了液滴移动速度与驱动电压、驱动频率以及动力黏度的关系,结果表明液滴移动速度受动力黏度影响较为显著。
Abstract:Aimed at the situations of the spreading and moving dynamics behavior of the droplet that plays an important role in industrial production and microfluidic chips, an elastic planar model based on the theory of ultrasonic travelling wave was proposed. The droplet on the elastic glass surface was driven by ultrasonic travelling wave generated by the inverse piezoelectric effect of piezoelectric ceramic. The droplet model was built with multi-physics field software COMSOL. Firstly, through the analysis of the ultrasonic travelling wave, the feasibility of the model was verified. During the period of 0 to 60 ms, the droplet behaves a shrinking-spreading sinusoidal oscillation motion driven by ultrasonic travelling wave. Then, the internal flow structure inside the droplet was also investigated. When the droplet radius spreads to the maximum and begins to shrink, the velocity inside the contact surface between the droplet and the substrate changes first. It shows that the change of the velocity field inside the droplet plays an important role in the motion of the contact line. There is a similar elliptic vortex in the flow field inside the droplet, which illustrates that the droplet motion is not a simple translation induced by shrinking-spreading, but a forward movement with rolling. Finally, we studied the dependency of the moving velocity of the droplet on the parameters (driving voltage, driving frequency and dynamic viscosity) via simulations. The results show that the moving velocity of the droplet is significantly influenced by the dynamic viscosity.
-
Key words:
- ultrasonic travelling wave /
- droplet /
- contact line motion /
- droplet oscillations /
- piezoelectric
-
表 1 几何模型的结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of geometric model
类型 长度/mm 厚度/mm 玻璃平板 150 3 压电陶瓷 5π/4 1 表 2 玻璃的材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of glass
参数 弹性模量/Pa 密度/(kg·m-3) 泊松比 数值 7×1010 2 210 0.24 表 3 质点的瞬时位移
Table 3. Instantaneous displacement of particle
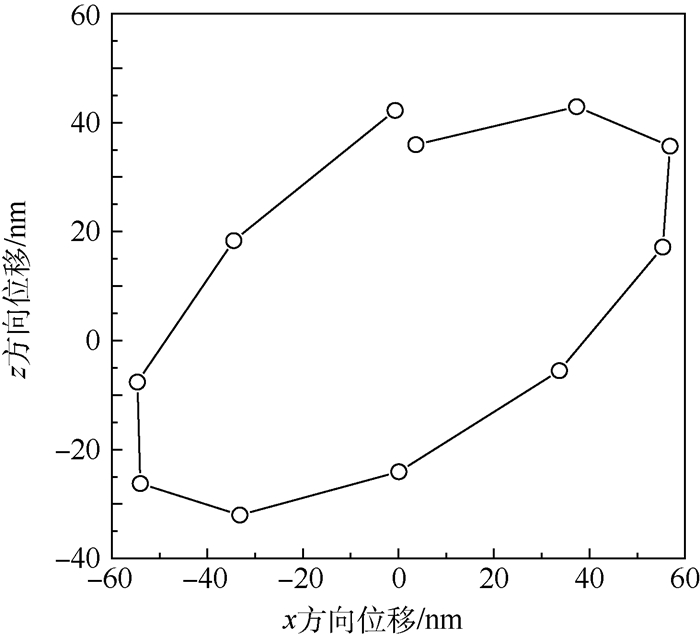
时间/ms x方向位移/nm z方向位移/nm 30.085880 3.654254 35.945566 30.086332 37.307580 42.905864 30.086784 56.858371 35.665642 30.087236 55.340976 17.141958 30.087688 33.690540 -5.537054 30.088140 0.086644 -24.081458 30.088592 -33.196754 -32.023728 30.089044 -54.042325 -26.239285 30.089496 -54.650676 -7.623552 30.089948 -34.476498 18.330271 30.090400 -0.687655 42.223590 -
[1] BECKER J, GRUN G.The thin-film equation:Recent advances and some new perspectives[J]. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 2005, 17(9):S291-S307. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/17/9/002 [2] SINGHAL V, GARIMELLA S V, RAMAN A.Microscale pumping technologies for microchannel cooling systems[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2004, 57(3):191. doi: 10.1115/1.1695401 [3] 魏长智, 魏守水, 张冲.超声行波微流体驱动的流动特性分析[J].应用基础与工程科学学报, 2013, 21(1):97-106. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX201301012.htmWEI C Z, WEI S S, ZHANG C.Flow characteristics analysis of ultrasonic traveling wave micro-fluid driving[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2013, 21(1):97-106 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX201301012.htm [4] SHI W, QIN J, YE N, et al.Droplet-based microfluidic system for individual Caenorhabditis elegans assay[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2008, 8(9):1432-1435. doi: 10.1039/b808753a [5] ABDELGAWAD M, WATSON M W, WHEELER A R.Hybrid microfluidics:A digital-to-channel interface for in-line sample processing and chemical separations[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(8):1046-1051. doi: 10.1039/b820682a [6] YOUNG T.An essay on the cohesion of fluids[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1805, 95:65-87. doi: 10.1098/rstl.1805.0005 [7] WENZEL R N.Resistance of solid surface to wetting by water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28(8):988-994. [8] CASSIE A B D, BAXTER S.Wettability of porous surfaces[J]. Transactions of Faraday Society, 1944, 40:546-551. doi: 10.1039/tf9444000546 [9] CHAUDHURY M K, WHITESIDES G M.How to make water run uphill[J]. Science, 1992, 256(5063):1939-1541. [10] DANIEL S, CHAUDHURY M K.Rectified motion of liquid drops on gradient surfaces induced by vibration[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(9):3404-3407. doi: 10.1021/la025505c [11] DANIEL S, SIRCAR S, GLIEM J, et al.Ratcheting motion of liquid drops on gradient surfaces[J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(10):4085-4092. doi: 10.1021/la036221a [12] 王晓东, 彭晓峰, 陆建峰, 等.粗糙表面接触角滞后现象分析[J].热科学与技术, 2003, 2(3):230-234. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RKXS200303008.htmWANG X D, PENG X F, LU J F, et al.Analysis of contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology, 2003, 2(3):230-234(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RKXS200303008.htm [13] 石自媛, 胡国辉, 周哲玮.润湿性梯度驱动液滴运动的格子Bolzmann模拟[J].物理学报, 2010, 59(4):2595-2600. doi: 10.7498/aps.59.2595SHI Z Y, HU G H, ZHOU Z W.Lattice Boltzmann simulation of droplet motion driven by gradient of wettability[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2010, 59(4):2595-2600(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.59.2595 [14] DAS A K, DAS P K.Multimode dynamics of a liquid drop over an inclined surface with a wettability gradient[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(12):9547-9555. doi: 10.1021/la100145e [15] 周建臣, 耿兴国, 林可君, 等.微液滴在超疏水表面的受迫振动及其接触线的固着-移动转变[J].物理学报, 2014, 63(21):216801. doi: 10.7498/aps.63.216801ZHOU J C, GENG X G, LIN K J, et al.Stick-slip transition of a water droplet vibrated on a superhydrophobic surface[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(21):216801(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.63.216801 [16] WALKER S W, SHAPIRO B.A control method for steering individual particles inside liquid droplets actuated by electrowetting[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2005, 5(12):1404-1407. doi: 10.1039/b513373b [17] WALKER S W, SHAPIRO B.Modeling the fluid dynamics of electrowetting on dielectric (EWOD)[J]. Journal of Microelectro-mechanical Systems, 2006, 15(4):986-1000. doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2006.878876 [18] WALKER S W, SHAPIRO B, NOCHETTO R H.Electrowetting with contact line pinning:Computational modeling and comparisons with experiments[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2009, 21(10):443-451. [19] LI F, MUGELE F.How to make sticky surface slippery:Contact angle hysteresis in electrowetting with alternating voltage[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(24):244108. doi: 10.1063/1.2945803 [20] GAO Y, LI Y G, ZHANG J F.Two-dimensional actuation of liquid using surface acoustic wave[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2009, 17(7):1548-1552. [21] BATCHELOR G K.An introduction to fluid dynamics[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2000:73-79. [22] BAL G, BEKIROGLU E.Servo speed control of travelling-wave ultrasonic motor using digital signal processor[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2004, 109(3):212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2003.10.019 [23] NETO C, EVANS D R, BONACCURSO E, et al.Boundary slip in Newtonian liquids:A review of experimental studies[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2005, 68(12):2859-2897. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/68/12/R05 [24] BLAKE T D, HAYNES J M.Kinetics of liquid/liquid displacement[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1969, 30(3):421-423. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(69)90411-1 [25] LAMB H.Hydrodynamics[J]. Hydrodynamics New York Dover, 1932, 6(4):181-185. [26] DONG L, CHAUDHURY A, CHAUDHURY M K.Lateral vibration of water drop and its motion on a vibrating surface[J]. European Physical Journal E, 2006, 21(3):231-242. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2006-10063-7 -







 下载:
下载: