-
摘要:
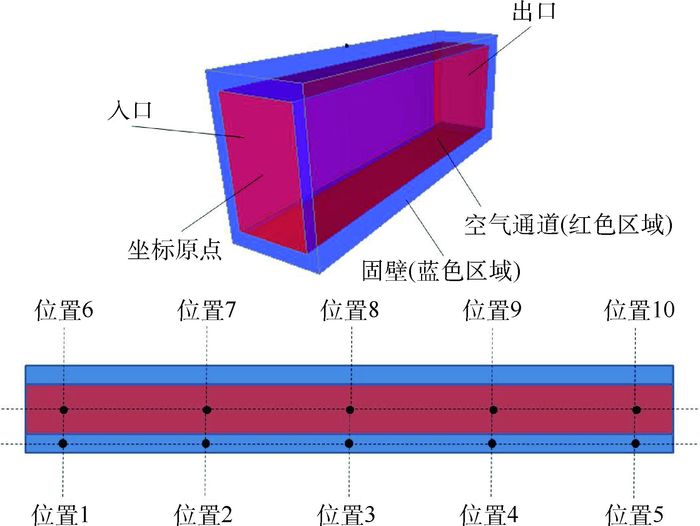
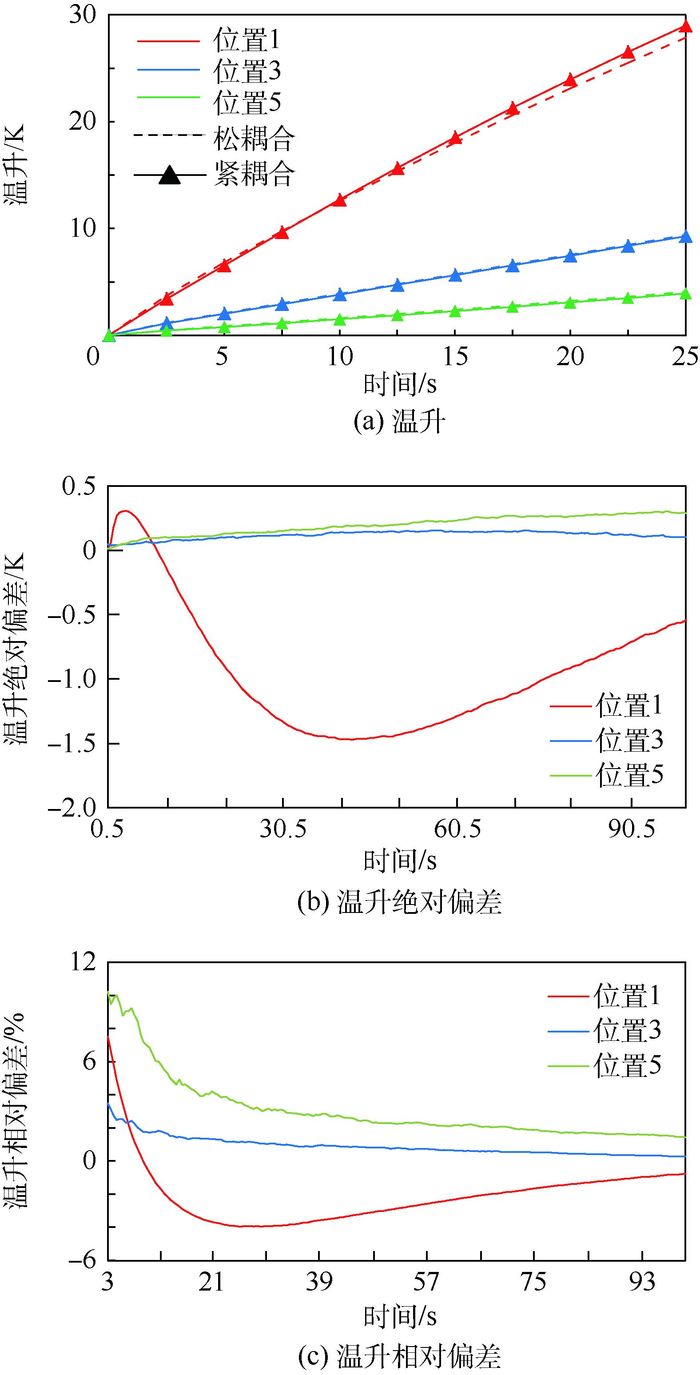
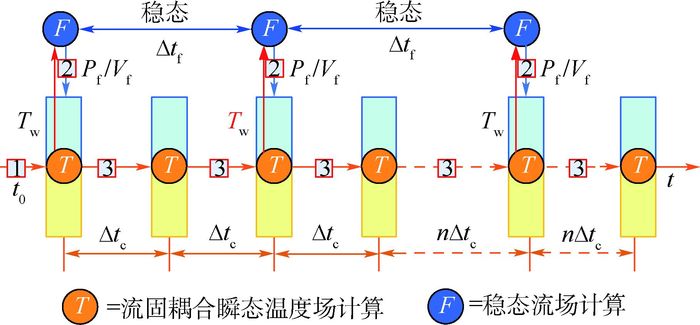
针对千秒级长时间流固耦合传热(CHT)过程求解问题,进一步提出一种基于准稳态流场的全局瞬态紧耦合传热的新型松耦合算法。交替使用单独对流体区域进行稳态流场求解的算法更新流场,以及同时对流固区域进行瞬态传热求解的算法计算瞬态温度场。该算法相对于传统流固松耦合算法,可以大大减小流场更新频率,进一步显著提高计算效率。以管内定来流速度空气连续300 s的强制对流瞬态加热过程为例,利用Fluent软件证明了该算法相对于瞬态紧耦合算法获得的管体结构温升最大偏差为5%,而计算耗时减小到14.8%。
-
关键词:
- 流固耦合传热 /
- 松耦合 /
- 准稳态 /
- 计算流体力学(CFD) /
- 强制对流
Abstract:Concerning the specific demands for solving problems of the long-term conjugate heat transfer (CHT) problem at the kilosecond level, a new loosely coupled algorithm of the global tightly transient coupled heat transfer based on the quasi-steady flow field is put forward. The flow field is updated alone by steady algorithm and the transient temperature field of the fluid and solid regions are solved by transient heat transfer algorithm alternately. Compared to the traditional loosely coupled algorithm, the computational efficiency is further improved with the greatly reduced update frequency of the flow field. Taking a tube heated by inner forced air flow heating process for 300 s as an example, the results by Fluent software show that, compared to the tightly transient coupled calculation, the maximum wall temperature rise deviation is 5% while the computing time is reduced to 14.8%.
-
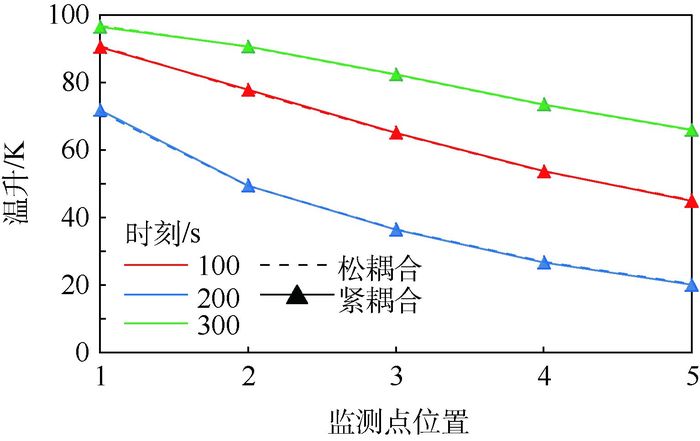
表 1 2种算法所得不同时刻管体温升分布情况
Table 1. Wall temperature rise distribution at different moments by two algorithms
K 时刻/s 位置1 位置2 位置3 位置4 位置5 紧耦合 松耦合 偏差 紧耦合 松耦合 偏差 紧耦合 松耦合 偏差 紧耦合 松耦合 偏差 紧耦合 松耦合 偏差 100 71.79 71.24 -0.55 49.43 49.38 -0.05 36.43 36.53 0.10 26.72 26.84 0.12 20.09 20.37 0.28 200 90.41 90.78 0.37 77.80 77.46 -0.34 65.10 64.89 -0.21 53.68 53.61 -0.07 44.95 45.08 0.13 300 96.45 96.79 0.34 90.62 90.57 -0.05 82.36 82.20 -0.16 73.44 73.28 -0.16 65.93 65.80 -0.13 -
[1] STOKOS K, VRAHLIOTIS S, PAPPOU T, et al.Development and validation of an incompressible Navier-Stokes solver including convective heat transfer[J].International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2015, 25(4):861-886. [2] HOOPER R W, SMITH T M, OBER C C.Enabling fluid-structural strong thermal coupling within a multi-physics environment[C]//44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit.Reston:AIAA, 2006:1-10. [3] KAZEMI-KAMYAB V, VAN ZUIJLEN A H, BIJL H.Analysis and application of high order implicit Runge-Kutta schemes for unsteady conjugate heat transfer:A strongly-coupled approach[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2014, 272:471-486. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.04.016 [4] 曾大文, 黄开金.非交错网格下三维准稳态激光重熔熔池数值模拟[J].计算物理, 1999, 16(6):616-623. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSWL199906010.htmZENG D W, HUANG K J.Numerical simulation of three dimensional quasi-steady state laser melted pools on the non-staggered grids[J].Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 1999, 16(6):616-623(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSWL199906010.htm [5] 殷鹏飞, 张蓉, 熊江涛, 等.搅拌摩擦焊准稳态温度场数值模拟[J].西北工业大学学报, 2012, 30(4):622-627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBGD201204031.htmYIN P F, ZHANG R, XIONG J T, et al.An effective numerical simulation of temperature distribution of friction stir welding in quasi-steady-state[J].Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2012, 30(4):622-627(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBGD201204031.htm [6] BAUMAN P T, STOGNER R, CAREY G F, et al.Loose-coupling algorithm for simulating hypersonic flows with radiation and ablation[J].Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2011, 48(1):72-80. doi: 10.2514/1.50588 [7] KAZEMI-KAMYAB V, VAN ZUIJLEN A H, BIJL H.A high order time-accurate loosely-coupled solution algorithm for unsteady conjugate heat transfer problems[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 264:205-217. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2013.05.021 [8] KAZEMI-KAMYAB V, VAN ZUIJLEN A H, BIJL H.Accuracy and stability analysis of a second-order time-accurate loosely coupled partitioned algorithm for transient conjugate heat transfer problems[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2014, 74(2):113-133. doi: 10.1002/fld.v74.2 [9] LOHNER R, YANG C, CEBRAL J, et al.Fluid-structure-thermal interaction using a loose coupling algorithm and adaptive unstructured grids[C]//Proceedings of 29th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference.Reston:AIAA, 1998:1-16. [10] LI Q, LIU P, HE G.Fluid-solid coupled simulation of the ignition transient of solid rocket motor[J].Acta Astronautica, 2015, 110:180-190. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.01.017 [11] MILLER B A, CROWELL A R, MCNAMARA J J.Loosely coupled time-marching of fluid-thermal-structural interactions:AIAA-2013-1666[R].Reston:AIAA, 2013. [12] KONTINOS D.Coupled thermal analysis method with application to metallic thermal protection panels[J].Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 1997, 11(2):173-181. doi: 10.2514/2.6249 [13] CHEN Y K, MILOS F S, GOKCEN T.Loosely coupled simulation for two-dimensional ablation and shape change[J].Journal of Spacecraft & Rockets, 2010, 47(5):775-785. [14] ZHANG S, CHEN F, LIU H.Time-adaptive, loosely coupled strategy for conjugate heat transfer problems in hypersonic flows[J].Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 2014, 28(4):1-12. [15] AMES W F.Numerical methods for partial differential equations[M].2nd ed. New York:Academic Press, 1977:114, 116-117, 145-151. -







 下载:
下载: