-
摘要:
水平-先进接收机自主完好性监测(H-ARAIM)属欧美大力发展的新型机载自主卫星导航完好性监测技术。从H-ARAIM的基于性能的导航(PBN)和广播式自动相关监视(ADS-B)应用方法出发,基于美国全球卫星导航系统(GPS)和中国自主北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)组合系统,综合考虑不同卫星故障概率、不同星座故障概率、不同星钟星历误差配置以及不同星座配置,全面仿真评估了H-ARAIM的PBN和ADS-B应用全球可用性,结果表明:卫星和星座故障概率变化,对水平保护级(HPL)结果的影响不足0.1%,PBN和ADS-B均可实现全球100%可用性;星钟星历误差变化,会导致较大幅度的HPL变化,最大值可达20 m,但对PBN和ADS-B应用可用性没有显著影响;不同星座配置会对全球和亚太区域平均99.9%HPL结果及PBN和ADS-B应用可用性产生显著影响,HPL变化幅度达到32 m,可用性随星座配置不同而变化,最差可降低到96%。所取成果可为北斗民航应用提供坚实的理论参考和可靠的技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 水平-先进接收机自主完好性监视(H-ARAIM) /
- 水平保护级(HPL) /
- 基于性能的导航(PBN) /
- 广播式自动相关监视(ADS-B) /
- 可用性
Abstract:Horizontal-advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (H-ARAIM) is a new type of airborne autonomous satellite navigation integrity monitoring technology developed in the United States and Europe. In view of performance based navigation (PBN) and automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) application methods of H-ARAIM and based on the global position system (GPS) and our own BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) combination system, different constellation/satellite failure probabilities, different satellite clock and ephemeris error configurations and different constellation configurations have been considered, and then the availability of PBN and ADS-B of H-ARAIM was assessed. The results show that the change of constellation/satellite failure probability has little impact on the results of horizontal protection level (HPL), which is less than 0.1%. Both PBN and ADS-B can achieve 100% availability globally. The change of satellite clock and ephemeris configuration can lead to large variation of HPL with the maximum reaching 20 m. But there is no significant influence on PBN and ADS-B availability. Different constellation configurations have significant impact on average 99.9%HPL of the Asia-Pacific region and the world, as well as PBN and ADS-B availability. Variations in HPL reach 32 m. Availability varies with different constellation configurations, and the worst can be reduced to 96%. The results obtained can provide a solid theoretical reference and reliable technical support for the application of BeiDou civil aviation.
-
表 1 导航完好性类别
Table 1. Navigation integrity category
NIC 水平与垂直范围边界 描述 0 Rc≥37.04 km(20 n mile) 未定义完好性 1 Rc<37.04 km(20 n mile) RNP-10包含范围 2 Rc<14.816 km(8 n mile) RNP-4包含范围 3 Rc<7.408 km(4 n mile) RNP-2包含范围 4 Rc<3.704 km(2 n mile) RNP-1包含范围 5 Rc<1 852 m(1 n mile) RNP-0.5包含范围 6 Rc<1 111.2 m(0.6 n mile) RNP-0.3包含范围 7 Rc<370.4 m(0.2 n mile) RNP-0.1包含范围 8 Rc<185.2 m(0.1 n mile) RNP-0.05包含范围 9 Rc<75 m且VPL<112 m 例如WAAS HPL, VPL 10 Rc<25 m且VPL<37.5 m 例如WAAS HPL, VPL 11 Rc<7.5 m且VPL<11 m 例如LAAS HPL, VPL 表 2 导航位置精度类别
Table 2. Navigation accuracy category-position
NACp 水平与垂直范围边界 描述 0 EPU≥18.52 km(10 n mile) 未定义完好性 1 EPU<18.52 km(10 n mile) RNP-10包含范围 2 EPU<7.408 km(4 n mile) RNP-4包含范围 3 EPU<3.704 km(2 n mile) RNP-2包含范围 4 EPU<1 852 m(1 n mile) RNP-1包含范围 5 EPU<1 111.2 m(0.6 n mile) RNP-0.5包含范围 6 EPU<370.4 km(0.2 n mile) RNP-0.3包含范围 7 EPU<185.2 m(0.1 n mile) RNP-0.1包含范围 8 EPU<92.6 m(0.05 n mile) 例如带SA的GPS 9 EPU<30 m且VEPU<45 m 例如不带SA的GPS 10 EPU<10 m且VEPU<15 m 例如WAAS 11 EPU<3 m且VEPU<4 m 例如LAAS 表 3 不同飞行阶段对导航和监视系统的性能需求
Table 3. Performance requirements of navigation and monitoring system at different stages of flight
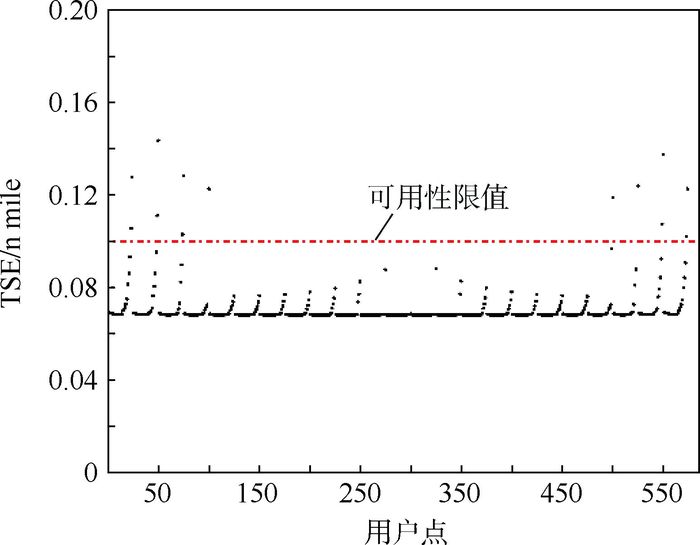
需求标准 导航(可用性>99.0%) 监视(可用性>99.9%) 精度(95%) 限值/10-7 间隔 NACp(95%) NIC/10-7 航路 *10 n mile 20 n mile 5 n mile 308 m(7) 1 n mile(5) *4 n mile 8 n mile *2 n mile 4 n mile 终端区 *1 n mile 2 n mile 3 n mile 171 m(8) 0.6 n mile(6) LNAV *0.3 n mile 0.6 n mile RNP(AR) *0.1 n mile **0.1 n mile 2.5 n mile DPA 171 m(8) 0.2 n mile(7) LPV 16 m/4 m 40 m/50 m 2.5 n mile DPA 171 m(8) 0.2 n mile(7) LPV-200 16 m/4 m 40 m/35 m GLS Cat-Ⅰ 16 m/4 m 40 m/10 m 2.0 n mile IPA 121 m(8) 0.2 n mile(7) GLS Cat-Ⅲ 16 m/2 m 40 m/10 m 注:*—运行需求由总系统精度定义,主要为飞行技术误差,这些运行的定位精度可以忽略; **—RNP AR的容限定义为全系统需求,所给值基于当前的运行批准;表格中()内的数字5,6,7,8表示对应的NACp级别。 表 4 基本仿真参数设置
Table 4. Basic simulation parameter setting
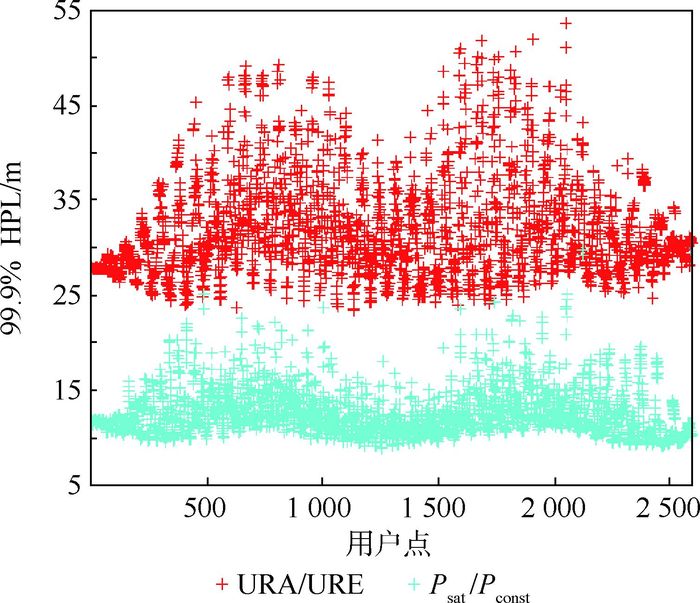
参数 设置 星座 24+35 信号 L1/E1+B1/B2 URA/URE(GPS) 1/0.5 URA/URE(BDS) 1.5/0.75 bnom 0.75 PsatBDS/PsatGPS 10-5 PconstBDS/PconstGPS 10-5 表 5 不同Psat/Pconst情景仿真参数设置
Table 5. Simulation parameter setting for different Psat/Pconst cases
参数 设置 星座 24+35 信号 L1/E1+B1/B2 URA/URE(GPS) 1/0.5 URA/URE(BDS) 1.5/0.75 bnom 0.75 情景描述 基础情景 PsatBDS/PsatGPS:10-5 PconstBDS/PconstGPS:10-5 退化Pconst情景 PsatBDS/PsatGPS:10-5 PconstBDS/PconstGPS:10-4 退化BDS情景 PconstGPS/PsatGPS:10-5 PconstBDS/PsatBDS:10-4 现实情景 PsatBDS/PsatGPS:10-5 PconstBDS:10-3 PconstGPS:10-8 表 6 不同Psat/Pconst情景仿真结果
Table 6. Simulation result for different Psat/Pconst cases
运行情景 99.9%
HPL/mRNP 0.1
可用性/%全球ADS-B
可用性/%基础情景 13.34 100 100 退化Pconst情景 13.53 100 100 退化BDS情景 13.81 100 100 现实情景 14.93 100 100 表 7 不同URA/URE情景仿真参数设置
Table 7. Simulation parameter setting for different URA/URE cases
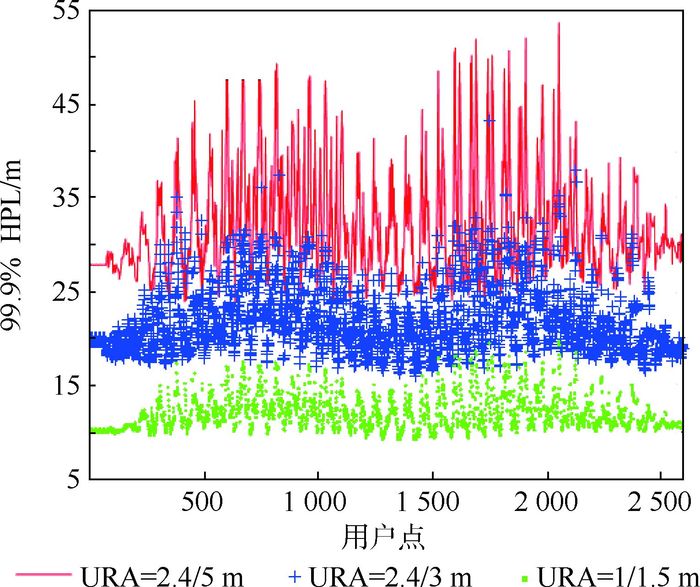
参数 设置 星座 24+35 信号 L1/L5+B1/B2 bnom 0.75 PsatBDS/PsatGPS 10-5 PconstBDS/PconstGPS 10-5 情景描述 基础情景 URA=1 m/URE=0.5 m(GPS) URA=1.5 m/URE=0.75 m(BDS) 现实情景 URA=2.4 m/URE=2 m(GPS) URA=3 m/URE=1.5 m(BDS) 退化情景 URA=2.4 m/URE=2 m(GPS) URA=6 m/URE=3 m(BDS) 表 8 不同URA/URE情景仿真结果
Table 8. Simulation results for differentURA/URE cases
运行情景 99.9%
HPL/mRNP 0.1
可用性/%全球ADS-B
可用性/%乐观情景 13.34 100 100 现实情景 23.71 100 100 退化BDS情景 36.43 100 100 表 9 不同星座配置仿真结果
Table 9. Simulation results for different constellation configuration
运行情景 99.9%
HPL/mRNP 0.1
可用性/%全球ADS-B
可用性/%亚太ADS-B
可用性/%亚太 24GPS+14BDS 34.18 100 100 31GPS+14BDS 34.02 100 100 23GPS+13BDS 移除MEO 34.61 100 100 移除GEO1 46.41 98.35 99.96 移除GEO3 40.62 100 100 移除GEO5 50.94 97.39 98.65 移除IGSO1 43.01 99.83 99.65 移除IGSO2 44.64 99.65 99.65 全球 24GPS+35BDS 13.21 100 100 31GPS+35BDS 13.19 100 100 23GPS+34BDS 移除GEO5 14.22 100 100 移除MEO 14.86 100 100 表 10 移除关键星时仿真结果
Table 10. Simulation results when removes key satellites
运行情景 99.9%
HPL/mRNP 0.1
可用性/%亚太ADS-B
可用性/%24GPS+14BDS 34.18 100 100 31GPS+14BDS 34.02 100 100 GPS+BDS:GDOP
方式移除2颗星65.51 96 97.74 -
[1] ICAO. Global air navigation plan 2013-2028:Doc9750AN[S].Montreal:ICAO, 2013:1-32[2016-06-01]. [2] GEAS.GNSS evolutionary architecture study:PhaseⅠ-Panel report[S/OL].Washington, D.C.:FAA, 2008:2-9[2016-06-01]. [3] GEAS.GNSS evolutionary architecture study:PhaseⅡ-Panel report[S/OL].Washington, D.C.:FAA, 2010:42-45[2016-06-01]. [4] WG-C.EU-U.S.Cooperation on satellite navigation:Interim report issue 1.0[S/OL]. [5] WG-C.EU-U.S.Cooperation on satellite navigation:Milestone 2 report[S/OL].Washington, D.C.:FAA, 2015:28-33[2016-06-01]. [6] WG-C.EU-U.S.Cooperation on satellite navigation:Milestone 3 report[S/OL].Washington, D.C.:FAA, 2016:37-42[2016-06-01]. [7] ICAO. Performance-based navigation(PBN) manual:Doc9613AN[S].Montreal:ICAO, 2013:I-A-1-1-I-A-1-7. [8] RTCA. Minimum operational performance standards for 1090 MHz automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B):DO-242A[S].Washington, D.C.:RTCA, Inc., 2000:37-41. [9] 中国民用航空局. 中国民用航空ADS-B实施规划[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空局空管行业管理办公室, 2016: 5-20.Civil Aviation Administration of China.China civil aviation ADS-B implementation planning[S].Beijing:Air Traffic Control Industry Management Office, Civil Aviation Administration of China, 2016:5-20(in Chinese). [10] BLANCH J, WALTER T, ENGE P.Advanced RAIM user algorithm description:Integrity support message processing, fault detection, exclusion, and protection level calculation[C]//Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2012.Nashville:Curran Associates, Inc, 2012:2818-2828. [11] BLANCH J, WALTER T, ENGE P.RAIM with optimal integrity and continuity allocations under multiple failures[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic System.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2003:1020-1023. [12] RTCA.Minimum aviation system performance standards for airborne supplemental navigation equipment using global positioning system:DO-208[S].Washington, D.C.:RTCA, Inc., 1991:87-96. [13] ICAO.Manual on required navigation performance(RNP):[S].Montreal:ICAO, 1999:12-29. [14] 张青竹. TIS-B数据精度与完好性研究及应用[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2008: 1-16.ZHANG Q Z.Research and application of data accuracy and integrity for traffic information service-broadcast[D].Beijing:Beihang University, 2008:1-16(in Chinese). [15] RTCA.Minimum aviation system performance standards for aircraft surveillance applications (ASA):DO-289[S].Washington, D.C.:RTCA, Inc., 2000:37-41. [16] LTER T, ENGE P.Statistical characterization of GPS signal-in-space errors[C]//Proceedings of the International Technical Meeting of the ION.San Diego, CA:Curran Associates, Inc., 2012:312-319. [17] RTCA.Minimum aviation system performance standards for GPS local area augmentation system airborne equipment:DO-253A[S].Washington, D.C.:RTCA, Inc., 2001. [18] RTCA. Minimum aviation system performance standards for global positioning system/wide area augmentation system airborne equipment:DO-229D[S].Washington, D.C.:RTCA, Inc., 2008:223-327. [19] 中国卫星导航系统管理办公室. 北斗卫星导航系统公开服务性能规范: BDS-OS-1. 0[S]. 北京: 中国卫星导航系统管理办公室, 2013: 4-14.China Satellite Navigation Office.Beidou satellite navigation system in public service performance specifications:BDS-OS-1.0[S].Beijing:China Satellite Navigation Office, 2013:4-14(in Chinese). [20] TONG H, ZHAO J W, ZHANG G Z, et al.Performance analysis of two RAIM methods for multiple faults[C]//The 3rd China Satellite Navigation Electronic Corpus Academic Conference.Beijing:China Academic Journal Electronic Magazine Co., Ltd, 2012:5-15. [21] 胡志刚. 北斗卫星导航系统性能评估理论与试验验证[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2013: 96-102.HU Z G.BeiDou navigation satellite system performance assessment theory and experimental verification[D].Wuhan:Wuhan University, 2013:96-102(in Chinese). [22] 从丽, AHMED I A, 谈展中.卫星导航几何因子的分析和仿真[J].电子学报, 2006, 34(12):2206-2207. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU200612016.htmCONG L, AHMED I A, TAN Z Z.Analysis and simulation of the GDOP of satellite navigation[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(12):2206-2207(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU200612016.htm -








 下载:
下载: