-
摘要:
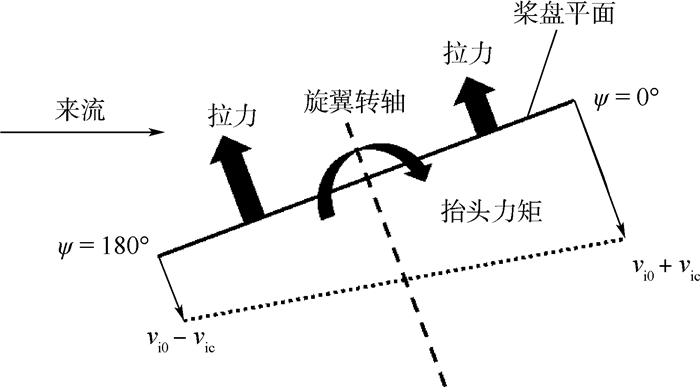
近年来多旋翼无人飞行器(UAV)成为了小型无人飞行器发展的热门领域,而学界对于多旋翼飞行器飞行力学建模与飞行力学特性分析的研究还相对较少。针对相关研究需求,基于传统旋翼模型,建立了适用于多旋翼无人飞行器的飞行力学模型,并利用此模型对多旋翼无人飞行器悬停模态特性进行了初步分析,结果显示多旋翼飞行器模态稳定性明显弱于传统直升机,且横向Phugoid模态取代了荷兰滚模态。随后利用弱耦合系统理论与纵向模态简化模型,对多旋翼建模过程中的旋翼旋转自由度(DOF)动态特性、入流模型和旋翼气动力矩的建模必要性进行了研究。分析表明,旋翼旋转自由度的动态特性在飞控增稳条件下对全机特性有着重要影响,入流分布对刚性旋翼的俯仰、滚转气动力矩有着决定性作用,而旋翼气动力矩是决定多旋翼悬停模态的重要因素,这三者在多旋翼建模分析中不能忽略。
Abstract:The multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is one of the popular configurations in the UAV industry for small UAVs. However, research on the modeling of multi-rotor vehicles and its characteristics regarding flight mechanics is still limited. A flight mechanics model for multi-rotor UAV is developed based on a classical helicopter model, and is used for the initial analyses of the hovering modes of a multi-rotor UAV. The results show that the dynamic stability of a multi-rotor vehicle is lower than that of a conventional helicopter, and the Dutch-roll mode is replaced by the lateral Phugoid mode. Based on the weakly-coupled system theory and simplified longitudinal equation of motion, the impacts of different modeling elements on multi-rotor modeling are analyzed, including the rotor rotation degree of freedom (DOF), the rotor inflow model and the rotor aerodynamic moments. It is shown that the rotor rotation DOF has large impacts on the flight mechanics characteristics of a multi-rotor vehicle with stability augmentation system. For a rigid rotor, the inflow distribution is one of the definitive factors for the rotor pitch and roll aerodynamic moments, which play an important role in the hovering modes of a multi-rotor vehicle. Therefore, all these three elements should be considered in the modeling and flight mechanics analyses for multi-rotor vehicles.
-
Key words:
- rotor vehicle /
- mode characteristics /
- modeling /
- rotor inflow /
- system coupling
-
表 1 四旋翼无人飞行器总体参数
Table 1. Main parameters of quad-rotor UAV
设计参数 数值 起飞质量/kg 5 布局形式 X4布局 总功率/W 2 000 旋翼直径/m 0.457 2 旋翼轴距/m 0.85 最大速度/(m·s-1) 20 表 2 算例悬停模态对比
Table 2. Comparison of hovering modes between two study cases
四旋翼无人飞行器 Bo-105 模态 特征值 模态 特征值 俯仰收敛 -1.699 俯仰收敛 -5.449 滚转收敛 -1.699 滚转收敛 -17.14 Phugoid 0.550 6+1.259 2i Phugoid 0.264 9+0.474 9i 横向Phugoid 0.550 6+1.259 2i 荷兰滚 -0.274 8+0.559 4i 沉浮收敛 -0.500 2 沉浮收敛 -0.419 3 螺旋 -0.033 5 螺旋 -0.284 0 表 3 无增稳全系统与近似系统部分模态对比
Table 3. Comparison of some modes between entire system and approximate system without stability augmentation
模态 特征值 全系统 近似系统 俯仰收敛 -1.725 9 -1.698 9 Phugoid 0.553 9+1.266i 0.550 6+1.259i 沉浮收敛 -0.513 7 -0.500 2 螺旋 -0.033 52 -0.033 52 表 4 有增稳全系统与近似系统部分模态对比
Table 4. Comparison of some modes between entire system and approximate system with stability augmentation
模态 特征值 全系统 近似系统 俯仰收敛 -2.168+0.901 6i -1.978 Phugoid -0.094 19+1.540i -0.095 52+1.283i 沉浮收敛 -2.209+0.299 2i -1.239 螺旋 -0.117 7 -0.115 4 表 5 算例俯仰模态与稳定性导数
Table 5. Pitch mode and stability derivatives of study case
气动导数/模态 特征值 四旋翼无人飞行器 Bo-105 Xu -0.032 71 -0.024 29 Mu 0.327 5 0.130 5 Mq -0.564 9 -4.763 Phugoid模态 0.550 6+1.259i 0.015 48+0.514 4i -
[1] 王史春.四旋翼飞行器力学模型与控制系统设计[J].中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(2):218-224.WANG S C.Design of mechanical model and control system of quadrotor[J].Journal of North University of China(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 35(2):218-224(in Chinese). [2] 杨成顺. 多旋翼飞行器建模与飞行控制技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.YANG C S.Research on modeling and flight controltechnology of multi-rotor aircraft[D].Nanjing:Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013(in Chinese). [3] 韩志凤, 李荣冰, 刘建业, 等.小型四旋翼飞行器动力学模型优化[J].控制工程, 2013(S1):158-162. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZDF2013S1045.htmHAN Z F, LI R B, LIU J Y, et al.Model optimization of small quad-rotor in the case of center of mass offset[J].Control Engineering of China, 2013(S1):158-162(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZDF2013S1045.htm [4] 李俊, 李运堂.四旋翼飞行器的动力学建模及PID控制[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 31(1):114-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKY201201028.htmLI J, LI Y T.Modeling and PID control for a quadrotor[J].Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science), 2012, 31(1):114-117(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKY201201028.htm [5] 聂博文, 马宏绪, 王剑, 等.微小型四旋翼飞行器的研究现状与关键技术[J].电光与控制, 2007, 14(6):113-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGKQ200706030.htmNIE B W, MA H X, WANG J, et al.Study on actualities and critical technologies of micro/mini quadrotor[J].Electronics Optics & Control, 2007, 14(6):113-117(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGKQ200706030.htm [6] BOUABDALLAH S, MURRIERI P, SIEGWART R.Design and control of an indoor micro quadrotor[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2004:4393-4398. [7] MOKHTARI A, BENALLEGUE A.Dynamic feedback controller of Euler angles and wind parameters estimation for a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2004:2359-2366. [8] MISTLER V, BENALLEGUE A, M'SIRDI N K.Exact linearization and noninteracting control of a 4 rotors helicopter via dynamic feedback[C]//Proceedings of 10th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive Communication.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2001:586-593. [9] 曾小勇, 彭辉, 吴军.四旋翼飞行器的建模与姿态控制[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(9):3693-3700.ZENG X Y, PENG H, WU J.Modeling and attitude control for a quad-rotor aircraft[J].Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2013, 44(9):3693-3700(in Chinese). [10] NAIDOO Y, STOPFORTH R, BRIGHT G.Quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle helicopter modelling & control[J].International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2011, 8(4):139-149. [11] PROUTY R.Helicopter aerodynamics[M].Lebanon:Eagle Eye Solutions, LLC, 2007. [12] LEISHMAN J G.Principles of helicopter aerodynamics[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2006. [13] PETERS D A, NINH H.Dynamic inflow for practical applications[J].Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 1988, 33(4):64-68. doi: 10.4050/JAHS.33.64 [14] 姜军, 齐俊桐, 韩建达.面向机动飞行的多旋翼飞行器设计和建模与控制[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(S2):135-144. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2013S2018.htmJIANG J, QI J T, HAN J D.Aggressive maneuver oriented multi-rotor aircraft design, modeling and control[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(S2):135-144(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2013S2018.htm [15] WAN J. Ornicopter multidisciplinary analyses and conceptual design[D].Delft:Delft University of Technology, 2014. [16] PADFIELD G D.Helicopter flight dynamics[M].Chichester:John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2007. [17] MILNE R D.The analysis of weakly coupled dynamical systems[J].International Journal of Control, 1965, 2(2):171-199. doi: 10.1080/00207176508905535 -








 下载:
下载: