Measurement for back-reflection of photonic crystal fiber fusion splicing point based on low-coherence light
-
摘要:
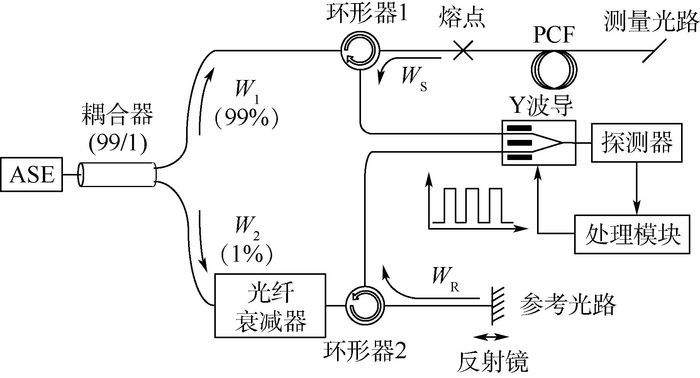
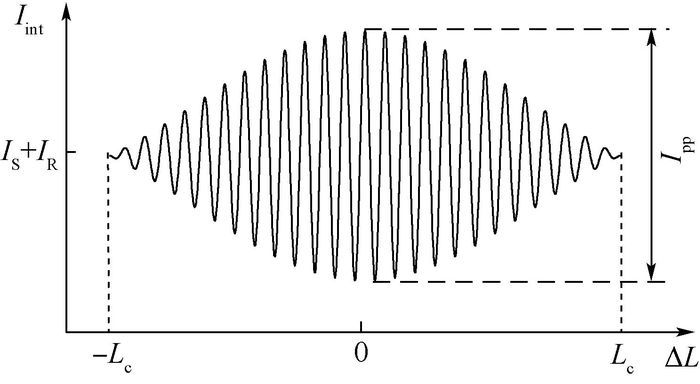
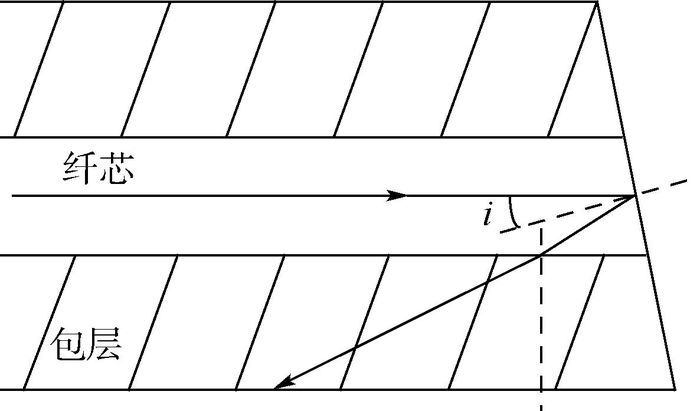
光子晶体光纤(PCF)与传统单模光纤熔接时斜切熔接可以大大减小熔点处反射,但是仍然存在微弱的残余背向反射,为了精确测量该残余背向反射大小,本文基于低相干光干涉测量原理提出了一种Mach-Zehnder与Michelson混合型干涉仪。基于该干涉仪,对包层直径125 μm实芯光子晶体光纤与传统单模光纤斜8°熔点,以及包层直径100 μm实芯光子晶体光纤与传统单模光纤斜8°熔点处的背向反射进行了测量,得到背向反射率分别为-52.12 dB和-49.35 dB,并获得了熔点的位置信息。该干涉仪为光子晶体光纤斜切熔点残余背向反射的精确定位和测量提供了工具和手段,为熔点质量的改善奠定了基础。
-
关键词:
- 光子晶体光纤(PCF) /
- 斜切熔接 /
- 背向反射 /
- 低相干光 /
- 干涉测量
Abstract:Although angle-cleaved fusion splice can greatly reduce the reflection of the fusion splicing point between photonic crystal fiber (PCF) and conventional single mode fiber, a weak residual back-reflection still exists at the fusion splicing point. A Mach-Zehnder and Michelson hybrid interferometer based on the principle of low-coherence interferometry was designed to achieve accurate positioning measurement of the residual back-reflection.Utilizing the interferometer, a -52.12 dB back reflectance of the 8° oblique splicing point between 125 μm cladding diameter solid-core PCF and conventional single mode fiber and a -49.35 dB back reflectance of the 8° oblique splicing point between 100 μm cladding diameter solid-core PCF and conventional single mode fiber were obtained.The locations of the two fusion splicing points were also acquired. The interferometer provides tools and means for precise positioning and measurement of the residual back-reflection of PCF angle-cleaved fusion splicing point, and lays a foundation for the quality improvement of the fusion splicing point.
-
-
[1] KNIGHT J C, BIRKS T A, RUSSELL P S J, et al.Properties of photonic crystal fiber and the effective index model[J].Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1998, 15(3):748-752. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.15.000748 [2] 丁文慧. 光子晶体光纤传感技术的研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2015: 2-4.DING W H.Investigation of photonic crystal fiber sensor[D].Beijing:Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015:2-4(in Chinese). [3] DONG L, MCKAY H A, FU L.All-glass endless single-mode photonic crystal fibers[J].Optics Letters, 2008, 33(21):2440-2442. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.002440 [4] SAITOH K, FLOROUS N, KOSHIBA M.Ultra-flattened chromatic dispersion controllability using a defected-core photonic crystal fiber with low confinement losses[J].Optics Express, 2005, 13(21):8365-8371. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.008365 [5] HENSLEY C J, OUZOUNOV D G, GAETA A L, et al.Silica-glass contribution to the effective nonlinearity of hollow-core photonic band-gap fibers[J].Optics Express, 2007, 15(6):3507-3512. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.003507 [6] XU Q, MIAO R, ZHANG Y.High birefringence low-dispersion of nonlinear photonic crystal fiber[J].Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2013, 124(15):2269-2272. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.06.088 [7] LIMPERT J, SCHREIBER T, NOLTE S, et al.High-power air-clad large-mode-area photonic crystal fiber laser[J].Optics Express, 2003, 11(7):818-823. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.000818 [8] TIAN L, WEI L, FENG G.Numerical simulation of supercontinuum generation in liquid-filled photonic crystal fibers with a normal flat dispersion profile[J].Optics Communications, 2015, 334(1):196-202. [9] WU D K C, KUHLMEY B T, EGGLETON B J.Ultrasensitive photonic crystal fiber refractive index sensor[J].Optics Letters, 2009, 34(3):322-324. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.000322 [10] XU X B, ZHANG Z H, ZHANG Z C, et al.Method for measurement of fusion-splicing-induced reflection in a photonic band gap fiber-optical gyro[J].Chinese Optics Letters, 2015, 13(3):030601. doi: 10.3788/COL [11] COUNY F, BENABID F, LIGHT P S.Reduction of fresnel back-reflection at splice interface between hollow core PCF and single-mode fiber[J].IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2007, 19(13):1020-1022. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2007.898770 [12] WANG C, BRADLEY T, WANG Y, et al.Angle splice of large-core kagome hollow-core photonic crystal fiber for gas-filled microcells[C]//CLEO:Science and Innovations.Washington, D.C.:Optical Society of America, 2013:1-2. [13] SORIN W V, BANEY D M.A simple intensity noise reduction technique for optical low-coherence reflectometry[J].IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 1992, 4(12):1404-1406. doi: 10.1109/68.180591 [14] 黄延毅. 低相干度光学反射测量技术的应用研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2005: 13-20.HUANG Y Y.Study on the low coherence reflectometrytechnique[D].Guangzhou:Sun Yat-Sen University, 2005:13-20(in Chinese). [15] THOMAS J.Low-coherence, high-resolution optical reflectometry for fiber length measurement[D].Lawrence:University of Kansas, 2002:5-7. [16] 郁道银.工程光学[M].3版.北京:机械工业出版社, 2011:83-84.YU D Y.Engineering optics[M].3rd ed.Beijing:China Machine Press, 2011:83-84(in Chinese). [17] 王素芹, 阮玉, 殷东亮, 等.C-lens准直器回波损耗的理论计算与分析[J].光电子技术与信息, 2003, 16(1):24-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDJY200301004.htmWANG S Q, RUAN Y, YIN D L, et al.The calculation and analizing of the RL of C-lens collimator[J].Optoelectronic Technology & Information, 2003, 16(1):24-28(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDJY200301004.htm 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 邢志伟,阚犇,朱书杰,刘子硕,李彪,罗谦. 基于双价值驱动的到港旅客动力学模型. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2024(12): 3645-3653 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 邢志伟,何川,罗谦,蒋祥枫,刘畅,丛婉. 基于双层K近邻算法航站楼短时客流量预测. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2019(01): 26-34 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(9)
-








 下载:
下载: