-
摘要:
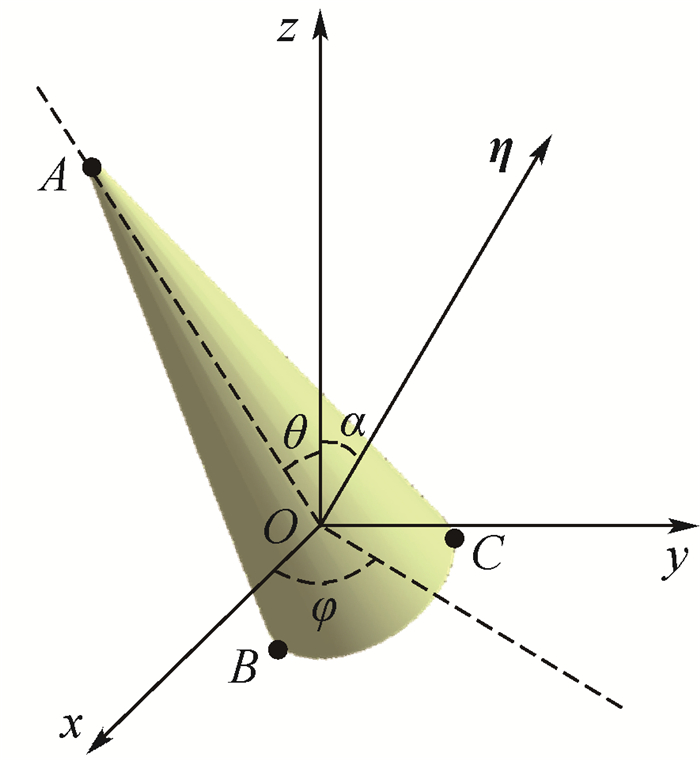
空间锥体目标在飞行时存在多种微动,具体可分为章动、进动及自旋,准确获取目标微动形式是弹道目标微动及结构参数估算的前提。首先分析了3种微动形式下锥体目标锥顶及锥底滑动型散射源微多普勒及其频谱分布特性,发现自旋锥体目标散射源微多普勒为0 Hz,章动锥体目标任意散射源微多普勒谱的峰值非等间距分布,进动锥体目标任意散射源微多普勒谱的峰值等间距分布。据此提出利用微多普勒阈值识别自旋、利用微多普勒谱峰值是否等间距分布识别章动和进动的分类方法。最后通过仿真说明了本文分类方法的有效性,可为空间锥体目标微动分类提供一定的参考。
Abstract:There are many kinds of micro-motion in the spatial cone target in flight, which can be divided into nutation, precession and spinning. Accurate acquisition of the target's micro-motion form is the premise for the estimation of the micro-motion and the structural parameters of the ballistic target. First, the micro-Doppler distribution characteristics and the spectrum distribution characteristics of the cone target's cone node and cone bottom slip-type scattering source under the three micro-motions are analyzed, and it is found out that the micro-Doppler of spinning cone target's scattering source is 0 Hz, the micro-Doppler spectrum's peak value of nutation cone target's arbitrary scattering source is non-equidistantly distributed, and the micro-Doppler spectrum's peak value of precession cone target's arbitrary scattering source is equidistantly distributed. Base on this, the paper proposes the classification method, which recognizes the spinning cone target by the threshold of micro-Doppler and recognizes the nutation or precession cone target by judging whether micro-Doppler spectrum's peak value is equidistantly distributed or non-equidistantly distributed. Finally, the validity of the classification method is illustrated by simulation, which can provide reference for the micro-motion classification of spatial cone target.
-
表 1 不同微动下锥体目标强散射源微多普勒谱谱线峰值位置
Table 1. Micro-Doppler spectrum's peak position of strong scattering source of cone target under different micro-motions
微动形式 谱线峰值位置/Hz 锥顶散射源 锥底滑动型散射源 自旋 无峰值 无峰值 进动 fφ nfφ 章动 nfθ±fφ, nfθ mfθ±nfφ 表 2 微动仿真参数设置范围
Table 2. Micro-motion simulation parameter setting range
微动形式 fφ/Hz φ/(°) fθ/Hz θ0/(°) θ1/(°) θ2/(°) α/(°) 自旋 0~360 5~20 0~180 进动 0.3~1.5 0~360 5~20 0~180 章动 0.3~1.5 0~360 0.4~1.2 5~20 0~360 0~180 0~180 -
[1] 韩勋, 杜兰, 刘宏伟, 等.窄带雷达观测下的锥体目标参数估计方法[J].西安电子科技大学学报, 2015, 42(6):43-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD201506012.htmHAN X, DU L, LIU H W, et al.Parameter estimation method for the cone-shaped target under narrow-band radar observation[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2015, 42(6):43-48(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD201506012.htm [2] 杨有春, 童宁宁, 冯存前, 等.利用最强散射点信息的平动补偿与微多普勒提取[J].西安电子科技大学学报, 2012, 39(6):147-153. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD201206024.htmYANG Y C, TONG N N, FENG C Q, et al.Translation compensation and micro-Doppler extraction by using the information on the strongest scatter[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2012, 39(6):147-153(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD201206024.htm [3] 宁超, 黄璟, 黄培康.基于HRRP的进动锥体目标特征参数求解方法[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(4):650-655. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201404008.htmNING C, HUANG J, HUANG P K.Solution for characteristic parameters of precession cone-shaped target using HRRP[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(4):650-655(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201404008.htm [4] 黄璟, 宁超, 朱勇.基于最优路径的弹道目标径向长度提取方法[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(7):1499-1503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.07.06HUANG J, NING C, ZHU Y.Estimation method for ballistic target range profile length based on the optimal route algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(7):1499-1503(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.07.06 [5] 邵长宇, 杜兰, 韩勋, 等.基于双视角距离像序列的空间锥体目标参数估计方法[J].电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(11):2735-2741. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201511028.htmSHAO C Y, DU L, HAN X, et al.Estimation method for space coning target parameters based on two-aspect range profile sequences[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(11):2735-2741(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201511028.htm [6] 洪灵, 戴奉周, 刘宏伟.基于三维重构的空间目标进动参数估计方法[J].电波科学学报, 2015, 30(2):237-243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201502007.htmHONG L, DAI F Z, LIU H W.Precession parameters estimation for space target based on 3D reconstruction[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2015, 30(2):237-243(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201502007.htm [7] WANG Z L, YAN F X, HE F, et al.Missile target automatic recognition from its decoys based on image time-series[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(6):2157-2164. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.12.016 [8] 金光虎, 高勋章, 黎湘, 等.基于ISAR像序列的弹道目标进动特征提取[J].电子学报, 2010, 6(6):1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU201006001.htmJIN G H, GAO X Z, LI X, et al.Precession feature extraction of ballistic targets based on dynamic image sequence[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 6(6):1-6(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU201006001.htm [9] 高红卫, 谢良贵, 文树梁, 等.弹道导弹目标微动特性的微多普勒分析与仿真研究[J].系统仿真学报, 2009, 21(4):954-961. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200904009.htmGAO H W, XIE L G, WEN S L, et al.Micro-Doppler analysis and simulation study of micro-motion performance of ballistic missile targets[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(4):954-961(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200904009.htm [10] 高红卫, 谢良贵, 文树梁, 等.基于微多普勒特征的真假目标雷达识别研究[J].电波科学学报, 2008, 23(4):775-780. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX200804042.htmGAO H W, XIE L G, WEN S L, et al.Research on radar target identification of warhead and decoys based on micro-Doppler signature[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2008, 23(4):775-780(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX200804042.htm [11] 韩勋, 杜兰, 刘宏伟, 等.基于时频分布的空间锥体目标微动形式分类[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(4):684-691. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201304004.htmHAN X, DU L, LIU H W, et al.Classification of micro-motion form of space cone-shaped objects based on time-frequency distribution[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(4):684-691(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD201304004.htm [12] 关永胜, 左群声, 刘宏伟, 等.空间锥体目标微动特性分析与识别方法[J].西安电子科技大学学报, 2011, 38(2):105-111. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10701-1013114413.htmGUAN Y S, ZUO Q S, LIU H W, et al.Micro-motion characteristic analysis and recognition of cone-shaped targets[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2011, 38(2):105-111(in Chinese). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10701-1013114413.htm [13] 关永胜, 左群声, 刘宏伟.基于微多普勒特征的空间锥体目标识别[J].电波科学学报, 2011, 26(2):209-215. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201102001.htmGUAN Y S, ZUO Q S, LIU H W.Micro-Doppler signature based cone-shaped target recognition[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2011, 26(2):209-215(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201102001.htm [14] 关永胜, 左群声.基于特征谱的空间锥体目标识别方法[J].中国电子科学研究院学报, 2014, 9(2):161-168. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJPL201402011.htmGUAN Y S, ZUO Q S.Eigenvalue spectrum signature based cone-shaped target recognition[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2014, 9(2):161-168(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJPL201402011.htm [15] 王竹溪, 郭敦仁.特殊函数概论[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 2012:260-264.WANG Z X, GUO D R.Introduction to special function[M]. Beijing:Peking University Press, 2012:260-264(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: