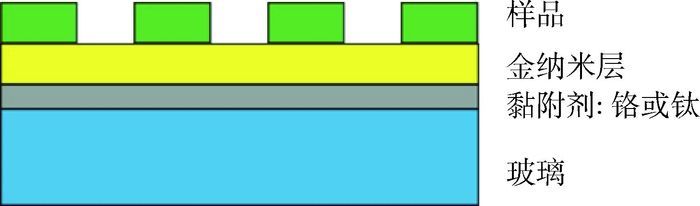
-
摘要:
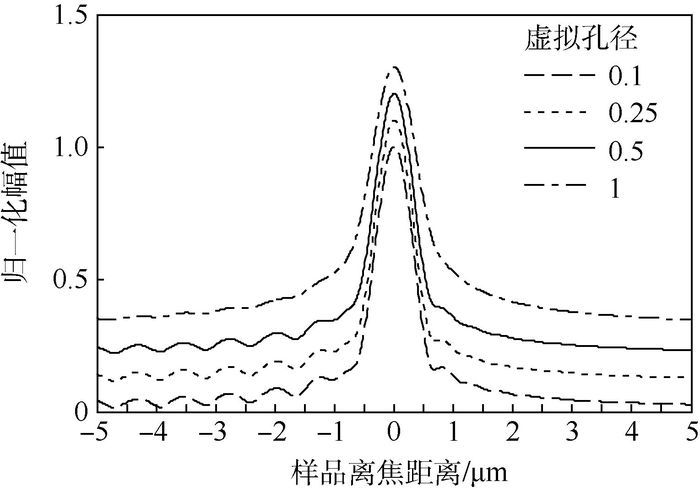
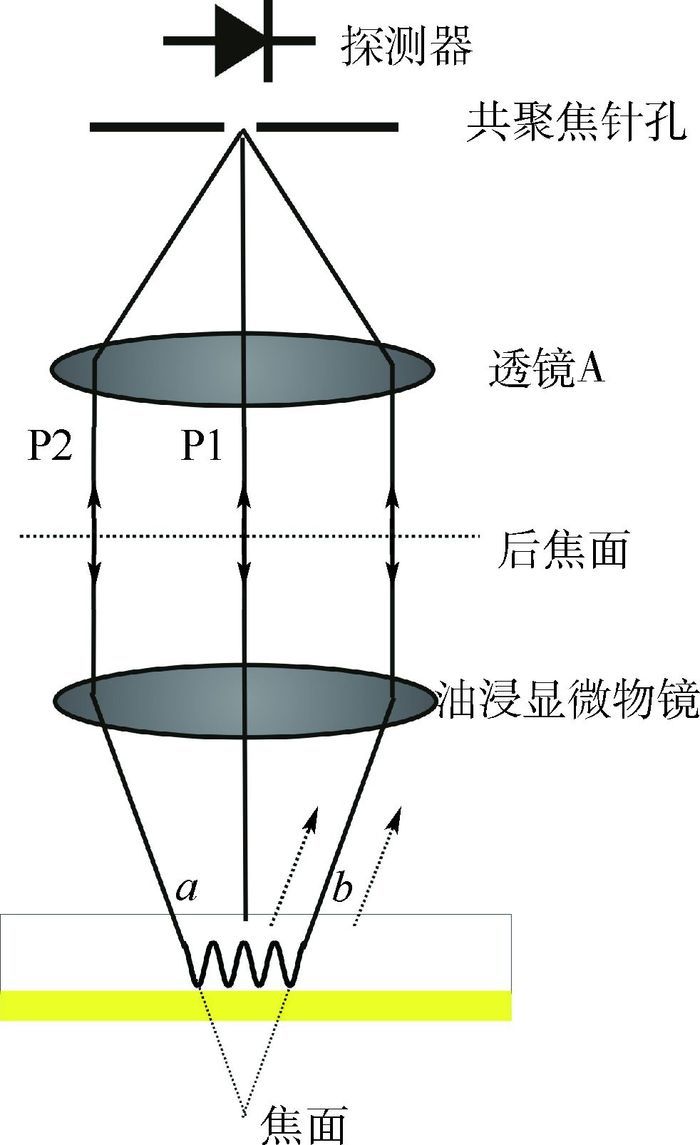
表面等离子体(SPs)显微成像技术能够在纳米尺度上对材料折射率的局部变化以及材料的表面形貌进行检测,这一特性使其在生物医疗及半导体材料等领域有很多的应用。提出一种新型共轴共聚焦干涉式表面等离子体显微成像技术,该技术可以定量地对折射率变化进行检测,而且具有实现简单、成本低、对环境条件要求低、信噪比高等优点。采用压电陶瓷微纳米移动平台在显微物镜的焦面附近对样品进行扫描,SPs信号与参考光的相对相位会改变从而产生一个周期性的振荡信号即
V (z )曲线。同时该技术能够通过控制样品的离焦距离来实现图像对比度的可控,而且这一举措不会显著地降低图像的分辨率及对比度。也分别从理论仿真和实验结果上证明了该技术的可行性。Abstract:Surface plasmon (SPs) microscopy can measure local changes of refractive index on the nano scale and has been successfully applied in biomedical or semiconductor material fields. Here, we propose and develop a novel common-path confocal interferometric SPs microscopy. This technique delivers quantitative high spatial resolution sensitive to refractive index and offers the advantages of simplicitye, low cost, low environmental requirements, and high signal-to-noise ratio. The so-called
V (z ) effect is the period oscillation by the relative phase between the reference and the SPs signal and obtained by scanning the sample along the optical axis (z direction) with a Piezo-electric stage. We demonstrate that the image contrast can be controlled by varying the sample defocus without substantially degrading spatial resolution. We also verify the technique theoretically and experimentally.-
Key words:
- microscopy /
- confocal interference /
- surface plasmon /
- imaging systems /
- nano-measurement
-
表 1 3种成像技术的参数比较
Table 1. Comparison of parameters among three imaging techniques
成像技术 轴向分辨率 横向分辨率 频率调制器件 系统架构 振动隔离平台 灰度式 Sub-nm >1 μm × 单轴 × 双臂干涉式 Sub-nm λ/2 √ 双轴 √ 本文 Sub-nm λ/2 × 单轴 × -
[1] BERGER C E H, KOOYMAN R P H, GREVE J.Resolution in surface-plasmon microscopy[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 1994, 65(9):2829-2836. doi: 10.1063/1.1144623 [2] KANO H, MIZUGUCHI S, KAWATA S.Excitation of surface-plasmon polantons by a focused laser beam[J].Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 1998, 15(4):1381-1386. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.15.001381 [3] EATMAN E, ASH E A.Surface-plasmon microscopy[J].Electronics Letters, 1987, 23(20):1091-1092. doi: 10.1049/el:19870762 [4] MOH K J, YUAN X C, BU J, et al.Surface plasmon resonance imaging of cell-substrate contacts with radially polarized beams[J].Optical Society of America, 2008, 16(25):20734-20741. [5] SOMEKH M G, LIU S G, VELINOV T S, et al.Optical V(z) for high-resolution 2 pi surface plasmon microscopy[J].Optics Letters, 2000, 25(11):823-825. doi: 10.1364/OL.25.000823 [6] BERGUIGA L, BOYER-PROVERA E, ELEZGARAY J, et al.Sensing nanometer depth of focused optical fields with scanning surface plasmon microscopy[J].Plasmonics, 2013, 8(2):715-722. doi: 10.1007/s11468-012-9462-1 [7] BOYER-PROVERA E, ROSSI A, ORIOL L, et al.Wavelet-based decomposition of high resolution surface plasmon microscopy V(z) curves at visible and near infrared wavelengths[J].Optics Express, 2013, 21(6):7456-7477. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.007456 [8] SOMEKH M G, LIU S G, VELINOV T S, et al.High-resolution scanning surface-plasmon microscopy[J].Applied Optics, 2000, 39(34):6279-6287. doi: 10.1364/AO.39.006279 [9] ZHOU H, SHEPPARD R.Aberration measurement in confocal microscopy:Phase retrieval from a single intensity measurement[J].Journal of Modern Optics, 1997, 44(8):1553-1561. doi: 10.1080/09500349708230757 [10] MATTHEWS H J, HAMILTON D K, SHEPPARD C J R.Aberration measurement by confocal interferometry[J].Journal of Modern Optics, 1989, 36(2):233-250. doi: 10.1080/09500348914550281 [11] SOMEKH M G, STABLER G, LIU S, et al.Wide-field high-resolution surface-plasmon interference microscopy[J].Optics Letters, 2009, 34(20):3110-3112. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.003110 [12] BERGUIGA L, ZHANG S J, ARGOUL F, et al.High-resolution surface-plasmon imaging in air and in water:V(z) curve and operating conditions[J].Optics Letters, 2007, 32(5):509-511. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.000509 [13] BAO Y J, PENG R W, SHU D J, et al.Role of interference between localized and propagating surface waves on the extraordinary optical transmission through a subwavelength-aperture array[J].Physical Review Letters, 2008, 101(8):087401 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.087401 [14] WONG C L, OLIVO M.Surface plasmon resonance imaging sensors:A review[J].Plasmonics, 2014, 9(4):809-824. doi: 10.1007/s11468-013-9662-3 [15] LIU X, QIU B, CHEN Q, et al.Characterization of graphene layers using super resolution polarization parameter indirect microscopic imaging[J].Optics Express, 2014, 22(17):20446-20456. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.020446 -







 下载:
下载: