-
摘要:
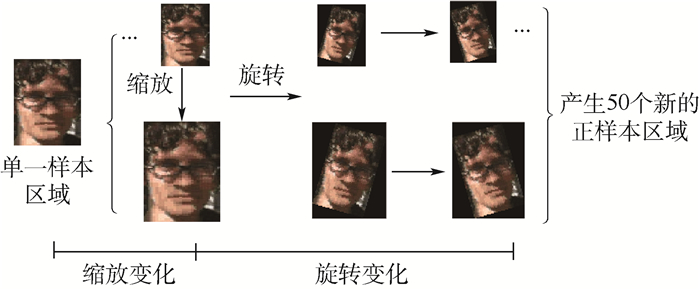
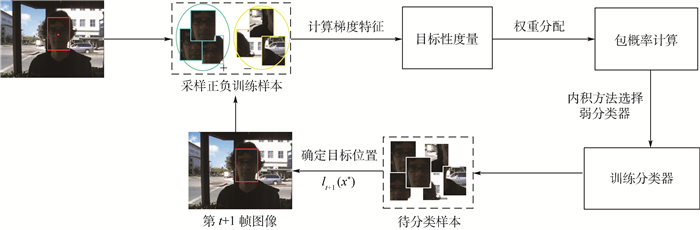
针对多示例学习(MIL)跟踪算法在包概率计算过程中对示例样本不加以区分导致分类器性能下降,及采用最大化似然函数选择相应的弱分类构造强分类增加了算法复杂度的问题,提出了一种基于目标性权值学习的多示例目标跟踪算法,该算法利用目标性测量每个示例样本对包概率的重要性,根据其目标性测量结果对每个正示例样本赋予相应的权值,从而判别性地计算包概率,提高跟踪精度。同时在弱分类器选择过程中,采用最大化弱分类器与似然函数概率内积的方法从弱分类器池中选择弱分器构造强分类器,减少算法的计算复杂度。通过对不同复杂场景下视频序列的跟踪,实验结果表明,本文所提出的目标性权值学习的多示例目标跟踪算法优于其对比算法,表现出较好的跟踪精度和鲁棒性能。
-
关键词:
- 多示例学习(MIL) /
- 目标性测量 /
- 弱分类器选择 /
- 包概率计算 /
- 目标跟踪
Abstract:For the problems that the multiple instance learning (MIL) tracking algorithm does not distinguish the differences of each sample when computing the bag probability and selects the weak classifiers by maximizing the log likelihood function, which reduce the performance of classifier and increase the complexity of the algorithm, this paper proposes a tracking algorithm based on objectness weighted multiple instance learning. First, the importance of each sample is measured by the objectness, which is also used to assign the weight for each instance. Then the weighted value is utilized for computing the final bag probability. In the phase of weak classifier selection, a maximized inner product between weak classifier and log likelihood function is adopted to select weak classifiers from weak classifier pool, and then these weak classifiers are combined into a strong classifier. All these strategies are beneficial for improving the tracking accuracy and reducing the computational complexity. By tracking the video sequences under different complex scenes, experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has strong robustness and high tracking accuracy compared with competing method.
-
磁悬浮控制敏感陀螺(Magnetically Suspended Control and Sensing Gyroscope, MSCSG)是一种新概念陀螺[1-2],其融合了磁悬浮控制力矩陀螺(Magnetically Suspended Control Momentum Gyroscope, MSCMG)对载体输出控制力矩[3-4]以及转子式速率陀螺仪对载体进行姿态测量[5-6]的功能,将航天器姿态控制系统的执行机构与敏感器合二为一,不仅继承了MSCMG转子系统无接触、无摩擦、寿命长、精度高[7]的优点,还明显降低了航天器姿态控制系统的体积、质量、功耗和成本。MSCSG转子系统采用五自由度全主动控制,具有一定小角度的微框架效应,能够瞬间输出较大的陀螺力矩,实现姿态控制;载体姿态变化时,磁轴承对转子沿径向施加二自由度控制力矩,通过测量偏转磁轴承的控制力矩间接实现姿态敏感。然而,受转子质量分布不平衡因素的影响,磁轴承-转子系统产生的扰动力矩传递到载体上,影响力矩输出精度和姿态测量精度。因此,对MSCSG转子系统进行不平衡振动控制是实现其测控一体化的必然要求,而对不平衡振动机理进行分析及动力学建模是实现不平衡振动控制的前提条件。
转子不平衡是磁悬浮转子系统产生振动的最主要因素[8]。目前,国内外学者对各类磁悬浮转子不平衡振动的原理及建模研究取得了一系列成果。文献[9-12]分析了质量分布不平衡条件下杆状磁悬浮电机转子的振动机理,并在此基础上建立了磁轴承-转子系统动力学模型;文献[13-14]基于模态平衡理论分析了挠性转速下杆状磁悬浮电机转子的运动特性,推导了柔性转子不平衡振动模型;文献[15-17]针对基于磁阻力磁轴承支承的MSCMG转子系统存在不平衡扰动以及转子检测轴与旋转轴不重合2种不同角度,分别建立转子系统动力学模型;文献[18-20]分析了基于混合磁轴承支承的MSCMG转子系统不平衡振动机理,针对混合磁轴承对转子扭转自由度不存在主动可控电流的特殊性,在分析主被动通道磁力非线性的基础上,建立了混合磁轴承支承的磁悬浮转子动力学模型;文献[21-22]在建立包含动不平衡的磁悬浮转子系统动力学模型基础上,分析了模型中不平衡量对转子控制系统的影响。
由于MSCSG是一种新概念陀螺,采用双球形转子结构,通过具有线性特性的洛伦兹力磁轴承(Lorentz Force Magnetic Bearing,LFMB)支承,其支承原理与上述磁悬浮电机、MSCMG有较大区别,因此上述不平衡振动分析方法无法直接应用于MSCSG转子系统。而对这类新型陀螺转子的不平衡振动机理尚未开展系统的理论研究,关于其扰动量能观性的解析性分析也未见报道。因此,本文在对MSCSG转子系统工作机理进行分析的基础上,对转子不平衡问题进行了几何描述,推导了高速转子质量不平衡产生的扰动力矩数学模型,并在此基础上对扰动量的可观测性进行了解析性分析;建立了不平衡振动条件下磁轴承-转子控制系统模型,分析了闭环控制系统不平衡振动的产生机理,并对不平衡振动的响应特性进行仿真,验证了所建立模型的正确性;根据不平衡振动的特点提出了对其进行主动振动控制的要求。
1. MSCSG工作原理
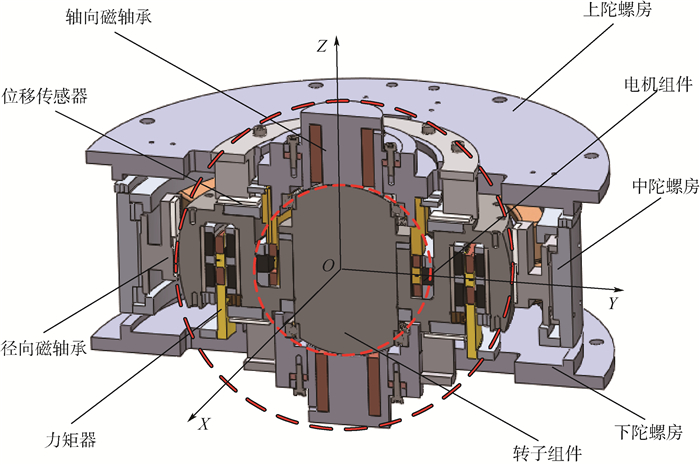
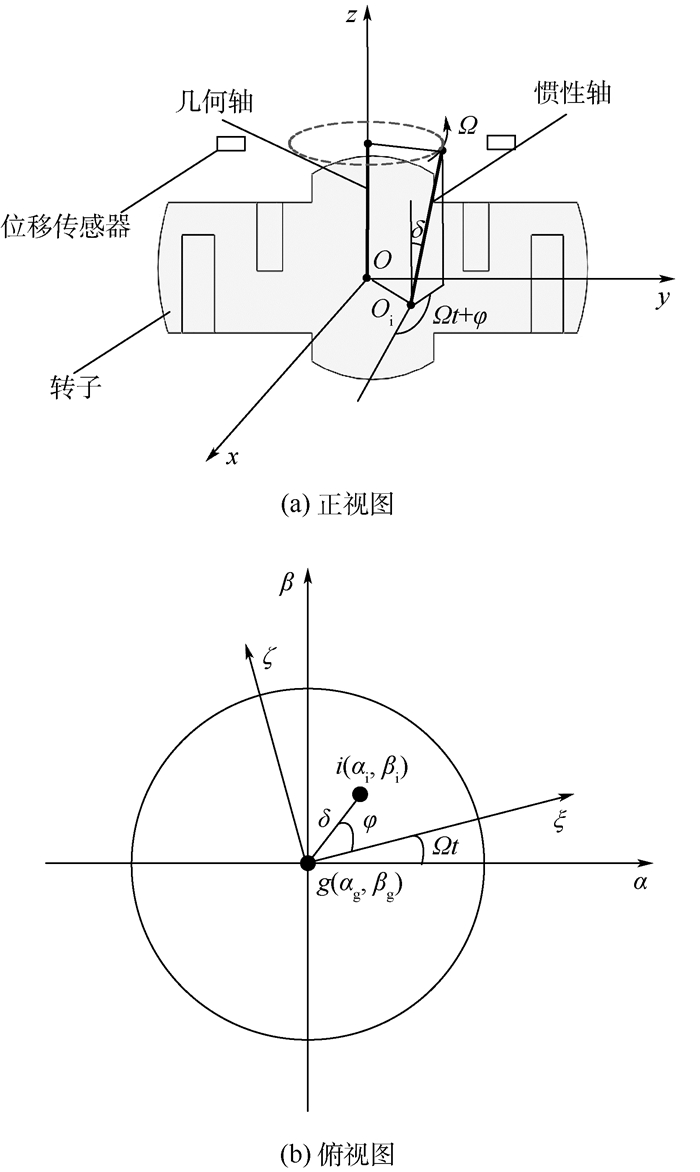
MSCSG结构如图 1所示,主要由陀螺房、陀螺转子、轴向磁轴承、力矩器、径向磁轴承、旋转电机、位移传感器构成。其中,旋转电机驱动转子绕轴向高速旋转,力矩器驱动转子绕径向偏转,径向磁轴承驱动转子沿径向平动,轴向磁轴承驱动转子沿轴向平动。
图 1中,MSCSG的转子组件为双球形包络面结构,由位于转子轴向和径向的2个共球心球缺组成,其中轴向球缺构成轴向磁轴承的转子部分,径向球缺构成径向磁轴承的转子部分。由于径向磁轴承及轴向磁轴承的磁极都呈球状,球面磁极产生的电磁力始终经过磁极球心,无论转子在磁间隙内处于什么位置,都不会产生扭转力矩,从而实现了平动自由度对径向转动自由度的解耦。因此,转子径向偏转只受力矩器控制。
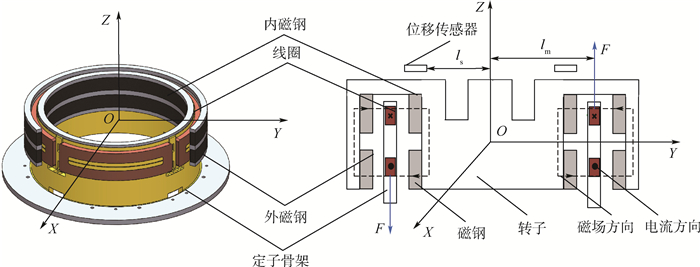
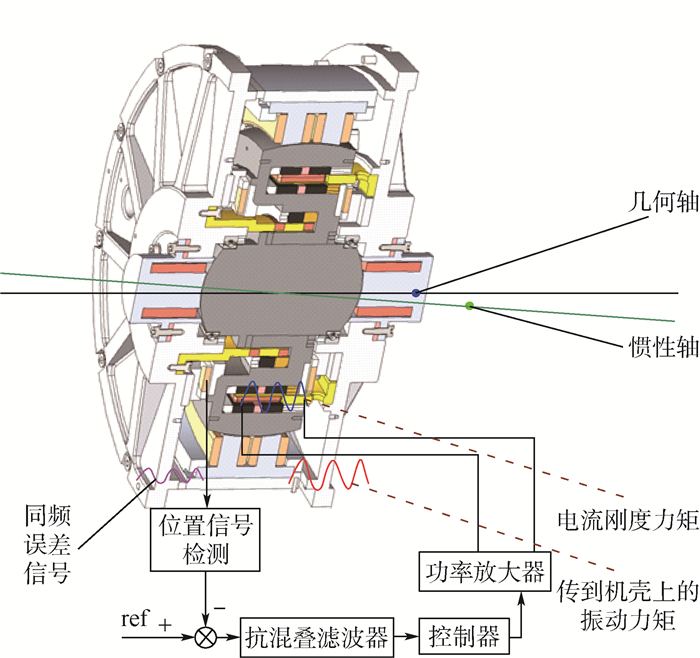
MSCSG采用LFMB为力矩器驱动转子偏转,LFMB产生的电磁力依据安培力定律,即磁感应强度为B的磁场中沿与磁场垂直方向放置长度为L的线圈,当流经线圈中电流为I时,线圈将受到大小为BIL的安培力作用。LFMB组件结构如图 2所示。转子外沿一周的狭长内壁上放置着上、下2层磁钢,2层磁钢的内、外磁钢间充磁方向相反,因此形成了如图 2中虚线所示的闭合磁场。LFMB的定子部分由4组匝数相同的线圈构成,位于内、外磁钢间的狭缝中,沿LFMB周向均匀分布,4组线圈成对使用,正对的2组线圈为一对,用于实现转子的二自由度偏转控制。
以LFMB几何中心O为原点定义定子坐标系O-XYZ,其中X轴与Y轴分别与相对方向2组线圈中心线重合,Z轴方向根据右手定则确定。当与磁场垂直方向放置的线圈通入电流时,线圈的上下两部分将分别产生垂直于线圈及磁场方向的安培力,合力大小为

(1) 式中:n为线圈匝数。
根据如图 2所示的LFMB工作原理图,LFMB提供的X、Y方向偏转力矩分别为

(2) 式中:iX+、iX-分别为X轴正、负方向上的线圈驱动电流;iY+、iY-分别为Y轴正、负方向上线圈驱动电流;lm为LFMB定子半径。令iY+=iα,iX-=iβ,当相对方向线圈通入大小相等、方向相同的电流时,线圈将产生大小相等、方向相反的安培力,形成力偶驱动转子径向偏转,此时,根据式(2)可知偏转力矩pX、pY表达式分别为

(3) 2. MSCSG转子不平衡问题几何分析
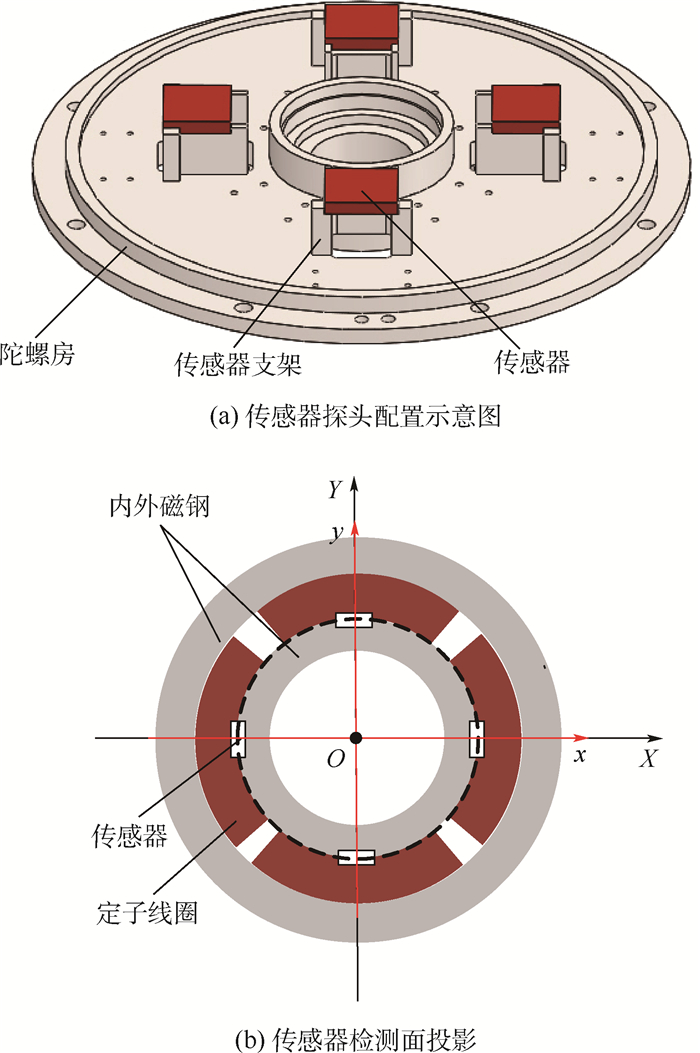
MSCSG转子除轴向旋转自由度由电机驱动控制,其余5个由磁轴承悬浮的自由度均需通过传感器来获得转子位置信息。该位置信息既提供给闭环控制器进行反馈控制,也作为转子悬浮工作状态的判定依据。转子偏转自由度为LFMB控制的自由度,需要位移传感器测量转子的位置信息来实现偏转通道的偏转角信息反馈。MSCSG偏转通道4个位移传感器安装在上陀螺房的传感器支架上,配置方式如图 3(a)所示,4个传感器在同一平面上,过定子坐标系原点O对检测面投影,如图 3(b)中黑色虚线所示。
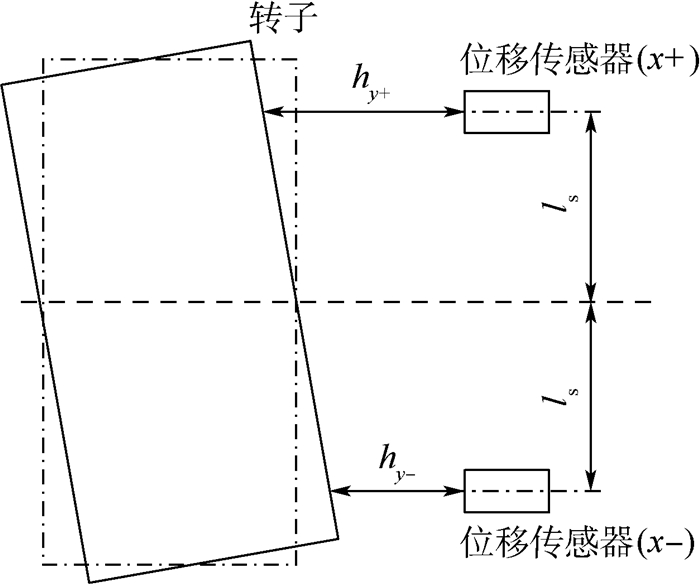
以定子坐标系原点O为原点定义几何坐标系O-xyz,其中x轴与y轴分别与相对方向2组线圈中心线重合,z轴方向根据右手定则确定。由于线圈对向中心线与几何坐标系的x轴、y轴重合,因此定子坐标系与几何坐标系重合。hy+、hy-、hx+、hx-分别为投影在y轴正、负方向以及x轴正、负方向上的轴向传感器测得的转子轴向位移。转子偏转角可以通过同一条直线上2个传感器位置差获得。以转子绕x轴偏转的α通道为例,如图 4所示,转子的偏转角可以通过转子在该通道两端的位置差与对应传感器间跨距比值获取。计算公式为

(4) 同理,转子绕y轴偏转的β通道偏转角计算公式为

(5) 定义转子惯性轴为高速转子旋转自由度所对应的惯性主轴。转子质量分布均匀的情况下,惯性轴与几何轴相一致。然而,转子材料不均匀和加工、装配等误差会使转子质量分布不平衡,导致转子的惯性轴与几何轴不再一致,从而使转子惯性轴相对于几何轴产生如图 5(a)所示的偏转。质量分布不平衡条件下,MSCSG转子惯性轴与几何轴的角位置关系如图 5(b)所示,(αg, βg)为几何轴的角坐标,(αi, βi)为惯性轴的角坐标,g(ξ, ζ)为与转子固连的旋转角坐标系,转子惯性主轴在g(ξ, ζ)中的幅值和相位分别为δ和φ。
由图 5中的转子惯性轴与几何轴间关系可知,惯性坐标系下转子偏转角信息αi、βi表达式为

(6) 式中,α、β分别由式(4)和式(5)得到;Ω为转子轴向转速;Δα、Δβ分别为径向两偏转角在惯性坐标系与几何坐标系下的偏差。
3. 磁轴承-转子控制系统不平衡振动建模
3.1 不平衡扰动项能观性分析
根据欧拉定理写出陀螺技术方程[23]:

(7) 式中:Jx、Jy分别为转子在x、y方向的转动惯量,且Jx、Jy数值上与转子径向转动惯量Jr相等;Jz为转子在z方向的转动惯量。
由于控制系统中各测量值都是在几何坐标系中获取,而陀螺技术方程是在惯性坐标系下定义。因此,将式(6)中转子惯性坐标系与几何坐标系间的关系表达式代入式(7),得到惯性坐标系下转子信息表达式为

(8) 根据式(8)可知,不平衡扰动力矩表达式分别为

(9) 式中:

(10) 根据以上分析可知,当转子质量分布不均匀时,转子的几何轴与惯性轴不再一致,此时转子系统将产生不平衡扰动力矩,作用于与定子固连的基座,引起载体航天器的振动。
将式(3)、式(9)代入式(8),得

(11) 令


(12) 式中:

(13) 
(14) 
(15) 对扰动项d列写状态方程,取状态变量T=[Tx Ty]T,则扰动项pd=[pdx pdy]T可用如下模型表述:

(16) 对于式(16)表述的扰动模型,其能观性矩阵N表达式为

(17) 从式(17)表达式可知,转速Ω不等于0时,能观性矩阵的秩rank(N)=2,式(16)能观,因此系统的不平衡扰动可测。
3.2 含振动源的磁轴承-转子控制系统动力学建模
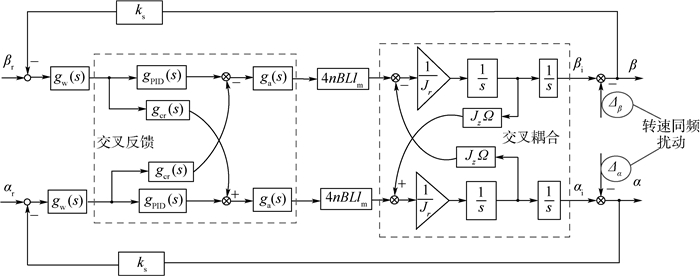
转子不平衡条件下,MSCSG转子偏转控制系统闭环结构如图 6所示。控制通道主要包括传感器、抗混叠滤波器、控制器和功率放大器构成。闭合回路中,传感器检测到转子偏转信息并通过抗混叠滤波器进行降噪处理,控制器根据偏转信息确定偏转指令,随后功率放大器将偏转指令转化为控制电流,驱动LFMB产生控制力矩,使转子偏转至指定参考位置。
由式(7)可知,转子偏转通道间存在耦合,因此为抑制陀螺耦合效应,控制器采用基于交叉滤波的PID控制算法,其中的PID控制器和交叉滤波器传递函数表达式分别为

(18) 
(19) 式中:kp、ki、kd分别为比例、积分、微分系数;ωD为不完全微分系数;kl和kh分别为低通和高通滤波器增益;a1l、a2l为低通滤波器系数;a1h、a2h为高通滤波器系数。
由如图 4所示的控制系统框图可知,根据转子偏转角可确定控制电流为

(20) 式中:ks为传感器比例增益;gw、ga、gPID和gcr分别为抗混叠滤波器、功率放大器、PID控制器和交叉滤波器的输入-输出传递函数变换算子,对其进行拉普拉斯变换,满足关系式




将式(3)、式(6)、式(20)代入式(7),得到MSCSG转子偏转动力学方程组:

(21) 将式(21)进行拉普拉斯变换得

(22) 对式(22)进行化简,得到

(23) 式(23)的等效闭环控制系统框图如图 7所示,αr、βr为偏转指令信号。对图 7中的转子不平衡条件下MSCSG转子系统模型进行分析可知,转子不平衡量经过磁轴承控制器和功率放大器进入闭环控制系统,通过LFMB产生电流刚度力矩,引起转子产生不平衡振动。
4. 仿真分析
根据本文所建立的MSCSG磁轴承-转子控制系统不平衡振动模型,对惯性轴与几何轴不一致条件下磁轴承-转子控制系统产生的不平衡振动力矩进行仿真分析。仿真参数如表 1所示,其中,转子参数根据MSCSG设计指标确定,控制器相关参数依照文献[23]设定。表 1中:ka为功率放大器增益;ωa为功率放大器截止频率;ωf为抗混叠滤波器截止频率。
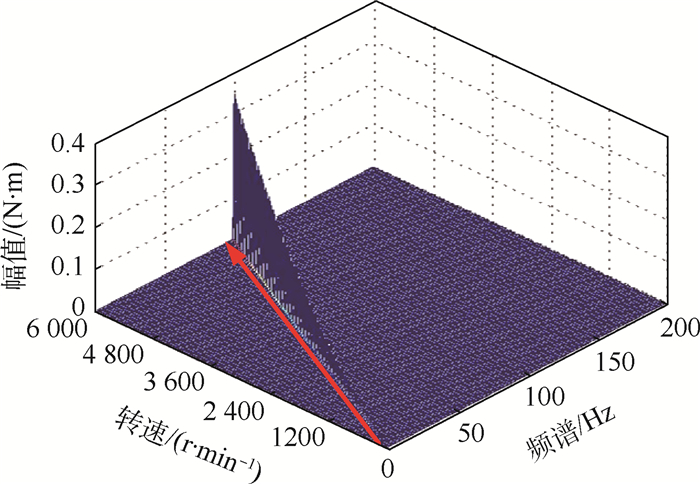
表 1 MSCSG系统参数Table 1. Parameters of MSCSG system参数 数值 Jz/(kg·m2) 0.016 6 Jy/(kg·m2) 0.009 7 ki 0.001 ωD 240 kh 0.001 5 n 200 l/m 0.115 8 a2l 2 200 000 a2h 92 100 ls/m 0.078 ka/(V·A-1) 0.22 ωf/Hz 310 Jx/(kg·m2) 0.009 7 kp 15.1 kd 3.2 kl 0.001 5 B/T 0.4 lm/m 0.059 a1l 2 400 a1h 370 ks/(V·m-1) 10 300 δ/(°) 0.009 ωa/Hz 240 φ/(°) 10 转子转速由0升至6 000 r/min时,不平衡振动力矩的响应仿真结果如图 8所示。可知,瀑布图中包含了明显的转速同频成分,不平衡振动频率随转子转速升高而增加,不平衡振动幅值与转子转速呈递增的趋势。因此,不平衡振动仿真结果与动力学模型所描述不平衡因素的频率特性相一致,验证了本文所建立模型的正确性。根据以上分析可知,要想实现MSCSG转子系统的主动振动控制,必须对转子不平衡引起的转速同频扰动量进行抑制。
5. 结论
1) MSCSG转子质量分布不平衡条件下,转子惯性主轴与几何主轴不一致,导致转子系统产生不平衡振动力矩。
2) MSCSG转子转速不为零的条件下,转子质量分布不平衡产生的振动力矩可观测。
3) MSCSG转子不平衡量经过磁轴承-转子控制系统产生电流刚度力矩,引起的振动与转子转速同频,为实现对转子的主动振动控制,必须对转速同频扰动量进行抑制。
-
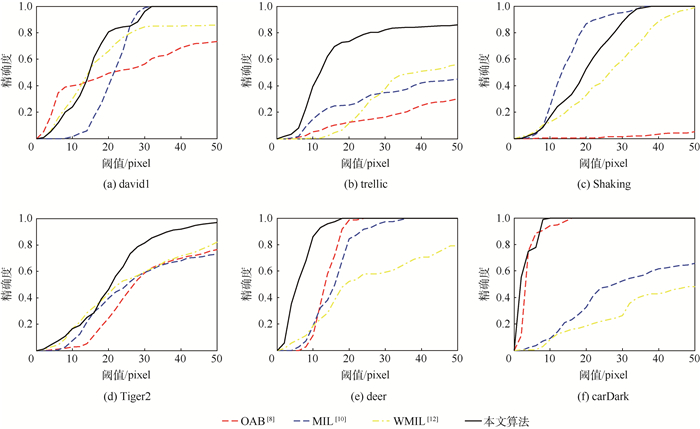
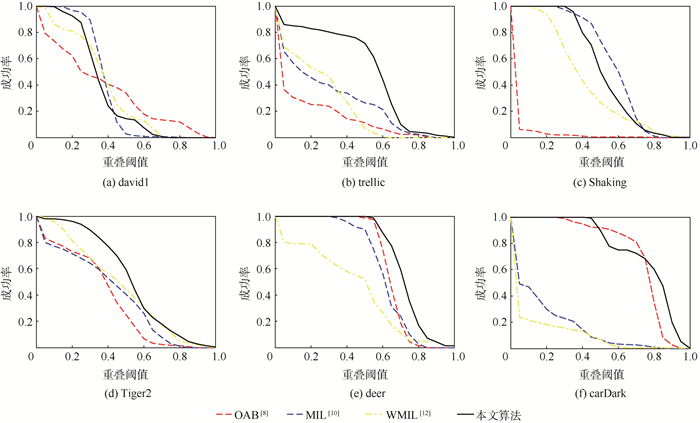
表 1 测试视频序列的特点
Table 1. Characteristics of test video sequences
视频序列 帧数 主要特点 david1 471 遮挡、尺度、旋转及光照变化 trellic 569 旋转、尺度及光照变化,复杂背景 Shaking 365 光照、尺度变化,旋转及复杂背景 Tiger2 365 遮挡,快速运动,复杂背景 deer 71 运动模糊、形变、旋转及复杂背景 carDark 393 光照变化及复杂背景 表 2 平均中心位置误差
Table 2. Average center position error
-
[1] WU Y, LIM J, YANG M H.Online object tracking:A benchmark[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2013:2411-2418. [2] ZHANG K, ZHANG L, YANG M H.Fast compressive tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(10):2002-2015. [3] ZHONG W, LU H, YANG M H.Robust object tracking via sparse collaborative appearance model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(5):2356-2368. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2313227 [4] ROSS D A, LIM J, LIN R S, et al.Incremental learning for robust visual tracking[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1-3):125-141. doi: 10.1007/s11263-007-0075-7 [5] ADAM A, RIVLIN E, SHIMSHONI I.Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram[C]//2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2006:798-805. [6] KWON J, LEE K M.Visual tracking decomposition[C]//2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2010:1269-1276. [7] KALAL Z, MIKOLAJCZYK, MATAS J.Tracking-learning-detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2011, 34(7):1409-1422. [8] GRABNER H, BISCHOF H.On-line boosting and vision[C]//2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2006:260-267. [9] GRABNER H, LEISTNER C, BISCHOF H.Semi-supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2008, European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin:Springer, 2008:234-247. [10] BABENKO B, YANG M H, BELONGIE S.Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(8):1619-1632. [11] ZHANG K, ZHANG L, LIU Q, et al.Fast visual tracking via dense spatio-temporal context learning[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2014:127-141. [12] ZHANG K, SONG H.Real-time visual tracking via online weighted multiple instance learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(1):397-411. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.07.013 [13] 丁建睿, 黄剑华, 刘家锋, 等.局部特征与多示例学习结合的超声图像分类方法[J].自动化学报, 2013, 39(6):861-867. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201306020.htmDING J R, HUANG J H, LIU J F, et al.Combining local features and multi-instance learning for ultrasound image classification[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6):861-867(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201306020.htm [14] VIOLA P, JONES M.Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features[C]//Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2001.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2001:511. [15] CHENG M M, ZHANG Z, LIN W Y, et al.BING:Binarized normed gradients for objectness estimation at 300fps[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2014:3286-3293. [16] LIANG P, LIAO C, MEI X, et al.Adaptive objectness for object tracking[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(7):949-953. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2556706 [17] YUAN G X, CHANG K W, HSIEH C J, et al.A comparison of optimization methods and software for large-scale L1-regularized linear classification[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11(2):3183-3234. [18] XU X, FRANK E.Logistic regression and boosting for labeled bags of instances[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2004, 3056(3):272-281. [19] EVERINGHAM M, GOOL L V, WILLIAMS C K I, et al.The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2):303-338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张成龙,索继东,麻智雄. 基于非等维状态交互的并行IMM转移概率自适应算法. 现代电子技术. 2022(05): 14-18 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(4)
-








 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术