-
摘要:
针对机载对地观测载机长时间匀速直线飞行时分布式位置姿态测量系统(POS)姿态误差随时间积累的问题,基于载机有效机动能够提高分布式POS系统可观测度进而提高系统估计精度的思想,设计并对比多种机动方式下分布式POS系统的估计精度,并对机动后分布式POS系统进入测区前的滤波估计稳定时间、直线飞行成像时长和全球定位系统(GPS)基线长度进行了测试。仿真结果表明,设计的飞行轨迹能够提高成像段运动参数的测量精度,可为机载对地观测最优飞行轨迹的选择和设计提供理论指导。
-
关键词:
- 惯性/卫星组合导航 /
- 飞行轨迹 /
- 机动 /
- 传递对准 /
- 位置姿态测量系统(POS)
Abstract:Aimed at the problem of attitude errors of distributed position and orientation system (POS) accumulate over time when airborne earth observation aircraft moves along a straight line at a constant velocity, a variety of maneuver modes were designed. Not only the estimation accuracy of distributed POS was compared, but also the time of system reaching stability after maneuver and the time of straight flight in imaging segment and baseline length of global position system (GPS) were tested. The method was based on the concept that the effective maneuver can improve the observability of distributed POS. Simulation results show that the designed flight trajectory can improve the measurement accuracy of the imaging segment motion parameters and can provide theoretical guidance for the selection and design of optimal flight trajectory for airborne earth observation.
-
表 1 惯性器件性能参数
Table 1. Performance parameters of inertial sensors
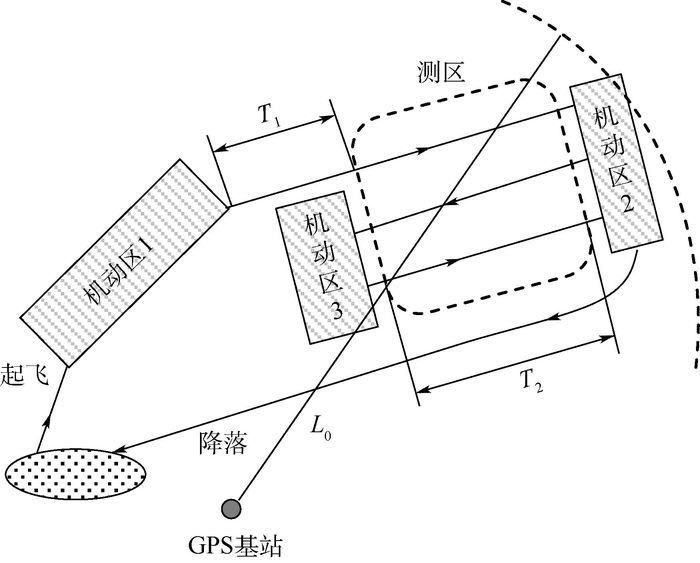
器件水平 陀螺仪漂移/((°)·h-1) 加速度计偏置/μg 高精度 0.01 10 中精度 0.05 50 低精度 0.1 100 表 2 飞行轨迹影响因素与参数选取
Table 2. Influencing factors and parameter selection of flight trajectory
子IMU惯性器件水平 测区前机动方式 测区前飞行时长/s 直线段飞行时长/s GPS基线长度/km 高精度 无机动 0 100 20 中精度 S型 100 200 40 低精度 O型 200 400 60 8字型 300 曲线爬升 400 表 3 5种运动方式的轨迹参数
Table 3. Trajectory parameters of five modes of motion
运动方式 时间/s 运动状态 1 0~400 匀速直线 400~600 顺时针转180° 600~1 000 匀速直线 2 0~100 匀速直线 100~800 S型机动 800~1 200 匀速直线 1 200~1 400 顺时针转180° 1 400~1 800 匀速直线 3 0~100 匀速直线 100~500 O型机动 500~900 匀速直线 900~1 100 顺时针转180° 1 100~1 500 匀速直线 4 0~100 匀速直线 100~1 000 8字型机动 1 000~1 400 匀速直线 1 400~1 600 顺时针转180° 1 600~2 000 匀速直线 5 0~500 曲线爬升 500~900 匀速直线 900~1 100 顺时针转180° 1 100~1 500 匀速直线 表 4 不同机动方式下成像段姿态误差统计(STD)
Table 4. Statistics of imaging segment attitude error under different maneuvering modes (STD)
机动方式 航向角估计误差/(°) 俯仰角估计误差/(°) 横滚角估计误差/(°) 无机动 0.248 3 0.037 6 0.040 4 S型 0.012 0 0.008 2 0.004 1 O型 0.020 9 0.008 2 0.004 1 8字型 0.011 6 0.008 4 0.004 0 曲线爬升 0.152 1 0.009 2 0.003 8 表 5 不同T1下成像段姿态误差统计(STD)
Table 5. Statistics of imaging segment attitude error with different T1 (STD)
T1/s 航向角估计误差/(°) 俯仰角估计误差/(°) 横滚角估计误差/(°) 0 0.011 6 0.008 4 0.004 0 100 0.011 6 0.008 3 0.004 0 200 0.009 1 0.008 5 0.003 8 300 0.009 3 0.008 2 0.003 8 400 0.009 9 0.008 1 0.003 8 500 0.010 2 0.008 2 0. 0038 表 6 不同T2下成像段姿态误差统计(STD)
Table 6. Statistics of imaging segment attitude error with different T2 (STD)
T2/s 航向角估计误差/(°) 俯仰角估计误差/(°) 横滚角估计误差/(°) 100 0.008 3 0.007 6 0.003 8 200 0.008 6 0.007 7 0.003 9 400 0.009 1 0.008 5 0.003 8 表 7 不同GPS基线长度下GPS定位精度
Table 7. GPS positioning accuracy under different baseline lengths of GPS
GPS基线长度/km 水平定位精度/m 高度定位精度/m 20 0.1 0.2 40 0.5 1 60 1 2 表 8 不同GPS基线长度下成像段子系统运动参数误差统计(STD)
Table 8. Statistics of motion parameter error of imaging segment subsystem under different baseline lengths of GPS (STD)
运动参数 GPS基线长度/km 20 40 60 航向角/(°) 0.010 1 0.009 8 0.009 8 俯仰角/(°) 0.008 0 0.008 0 0.008 1 横滚角/(°) 0.003 7 0.003 8 0.003 8 东向速度/(m·s-1) 0.013 7 0.016 2 0.018 1 北向速度/(m·s-1) 0.016 2 0.017 1 0.018 9 天向速度/(m·s-1) 0.019 4 0.019 4 0.020 1 纬度/m 0.205 7 0.244 5 0.246 5 经度/m 0.168 8 0.230 8 0.278 2 高度/m 0.494 2 0.484 9 0. 519 2 基线长度/m 0.218 0 0.597 2 1.275 7 -
[1] ZUFFADA C,LI Z,NGHIEM S V,et al.The rise of GNSS reflectometry for Earth remote sensing[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2015. [2] 韦立登,向茂生,吴一戎. POS数据在机载干涉SAR运动补偿中的应用[J].遥感技术与应用,2007,22(2):188-194. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2007.2.188WEI L D,XIANG M S,WU Y R.The application of POS data in airborne interferometric SAR imaging processing[J].Remote Sensing Technology and Application,2007,22(2):188-194(in Chinese). doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2007.2.188 [3] LI S S,ZHONG M Y,QIN J.The internal model control design of three-axis inertially stabilized platform for airborne remote sensing[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Instrumentation and Control Technology.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2012:1-9. [4] GONG X L,ZHANG R,FANG J C.Application of unscented R-T-S smoothing on INS/GPS integration system post processing for airborn earth observation[J].Measurement,2013,46(3):1074-1083. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2012.11.028 [5] KIM T J.Motion measurement for high-accuracy real-time airborne SAR[C]//Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering.Bellingham,WA:SPIE,2004:36-44. [6] GROVES P D.Principles of GNSS,inertial,and multisensor integrated navigation systems[M].London:Artech House,2013. [7] FANG J C,CHEN L,YAO J F.An accurate gravity compensation method for high-precision airborne POS[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing,2014,52(8):4564-4573. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/27/9/095103 [8] FANG J C,GONG X L.Predictive iterated Kalman filter for INS/GPS integration and its application to SAR motion compensation[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement,2010,59(4):909-915. doi: 10.1007/s12555-013-0048-2 [9] CHATTARAJ S,MUKHERJEE A,CHAUDHURI S K.Transfer alignment problem:Algorithms and design issues[J].Gyroscopy and Navigation,2013,4(3):130-146. doi: 10.1134/S2075108713030036 [10] 李四海,王珏,刘镇波,等.快速传递对准中机翼弹性变形估计方法比较[J].中国惯性技术学报,2014,22(1):38-44. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXJ201401009.htmLI S H,WANG J,LIU Z B,et al.Comparison of wing distortion estimation methods in transfer alignment[J].Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology,2014,22(1):38-44(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGXJ201401009.htm [11] GROVES P D.Optimising the transfer alignment of weapon INS[J].Journal of Pediatric Psychology,2003,56(2):323-335. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22879-2_9 [12] 王新龙,申亮亮,马闪.摇摆基座SINS快速精确传递对准方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2009,35(6):728-731. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8819.shtmlWANG X L,SHEN L L,MA S.Transfer alignment of strapdown inertial navigation system on rolling bases[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2009,35(6):728-731(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8819.shtml [13] Technical reference manual IPAS10[EB/OL].[2016-07-01].http://www.leica.com. [14] 万德钧,房建成.惯性导航初始对准[M].南京:东南大学出版社,1998:152-155.WAN D J,FANG J C.Initial alignment of inertial navigation[M].Nanjing:Publishing House of Southeast University,1998:152-155(in Chinese). [15] 姜军,杨亚非.SINS/GPS组合导航系统初始对准的可观测度分析[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报,2007,39(7):1025-1027. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200707004.htmJIANG J,YANG Y F.The analysis on the degree of observability to initial alignment of SINS/GPS integrated navigation system[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2007,39(7):1025-1027(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200707004.htm [16] 宫晓琳,房建成.一种机载遥感成像用分布式POS传递对准方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2012,38(4):491-496. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12257.shtmlGONG X L,FANG J C.Method of transfer alignment of distributed POS for airborne remote imaging[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2012,38(4):491-496(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12257.shtml [17] AKCA T,DEMIREKLER M.An adaptive unscented Kalman filter for tightly coupled INS/GPS integration[C]//IEEE Position Location & Navigation Symposium.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2012:389-395. [18] ZHOU N X,WANG S,DENG Z L.Comparison of three transfer alignment methods in marine missile SINS[C]//Proceeding of the 25th Chinese Control Conference.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,2006:27-31. [19] 李端昌,钟麦英,郭丁飞.分布式POS传递对准中的误差检测与补偿[C]//第25届中国控制与决策会议论文集.沈阳:东北大学出版社,2013.LI D C,ZHONG M Y,GUO D F.Error detection and compensation in transfer alignment for the distributed POS[C]//Proceeding of the 25th Chinese Control and Decision Conference.Shenyang:Northeasten University Press,2013. [20] JONES D,ROBERTS C,TARRANT D,et al.Transfer alignment design and evaluation environment[C]//Proceeding of the IEEE Regional Conference on Aerospace Control Systems.Piscataway,NJ:IEEE Press,1993:753-757. [21] 吴北平.GPS网络RTK定位原理与数学模型研究[D].武汉:中国地质大学,2003.WU B P.Principle and mathematical model research for GPS network RTK[D].Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2003. -







 下载:
下载: