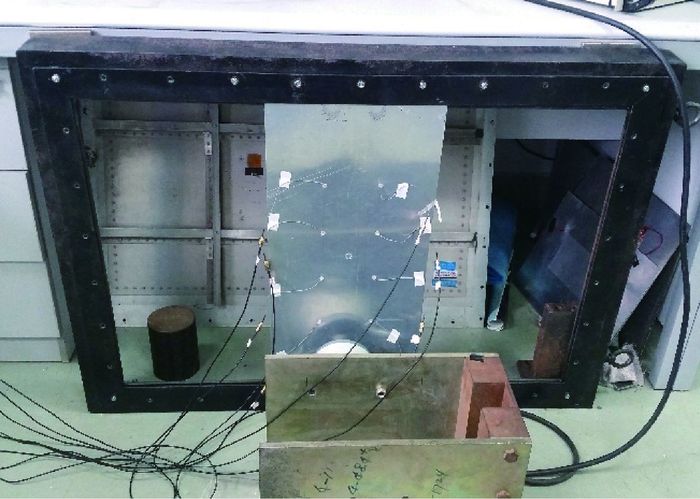
Localization and imaging of crack damage in plate-like structures based on vibro-acousic modulation
-
摘要:
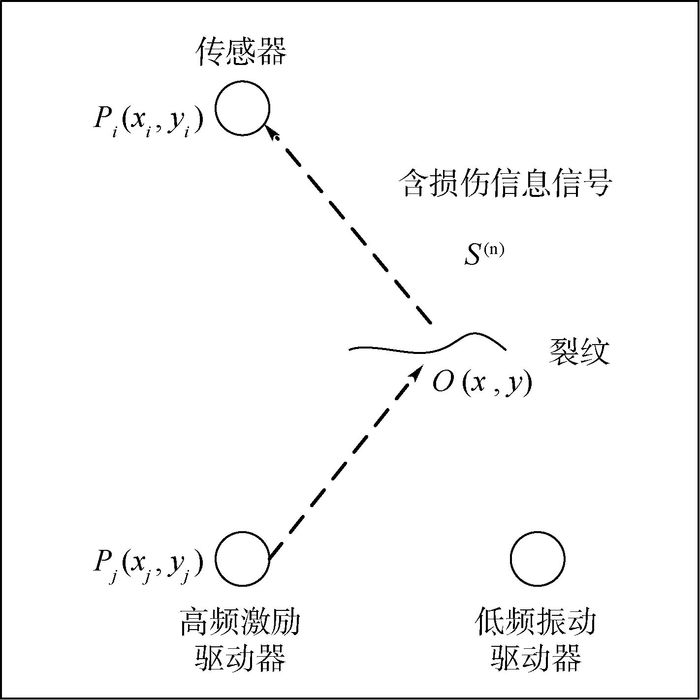
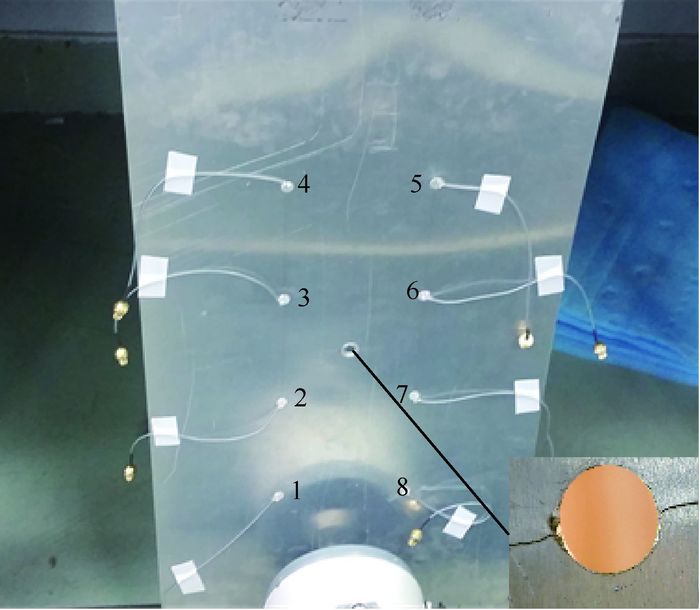
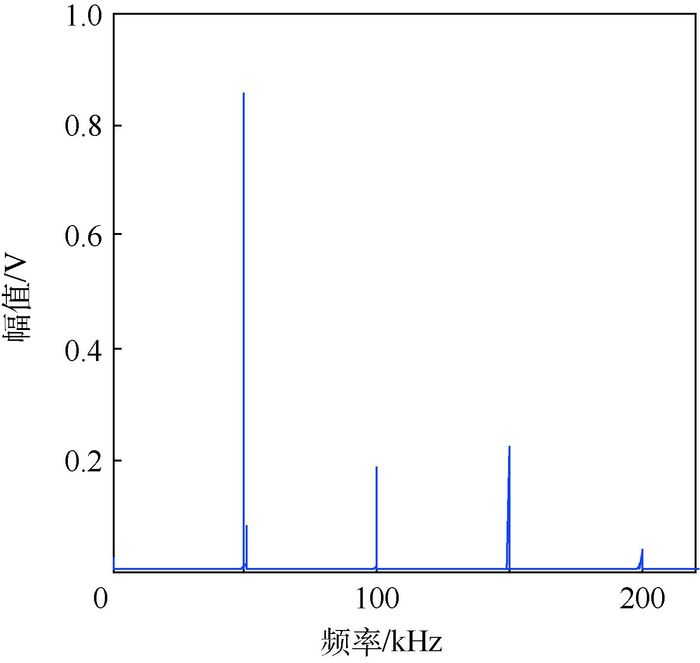
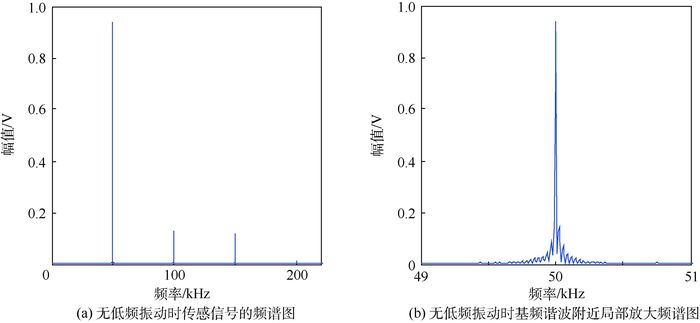
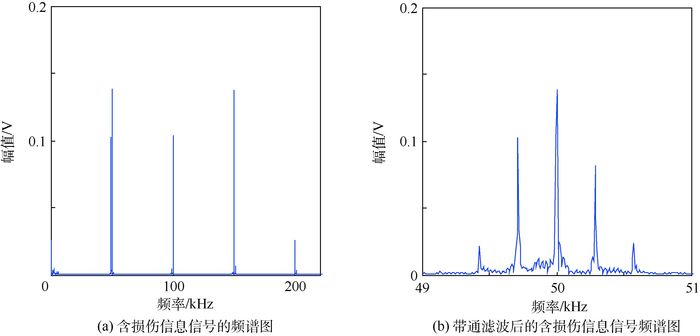
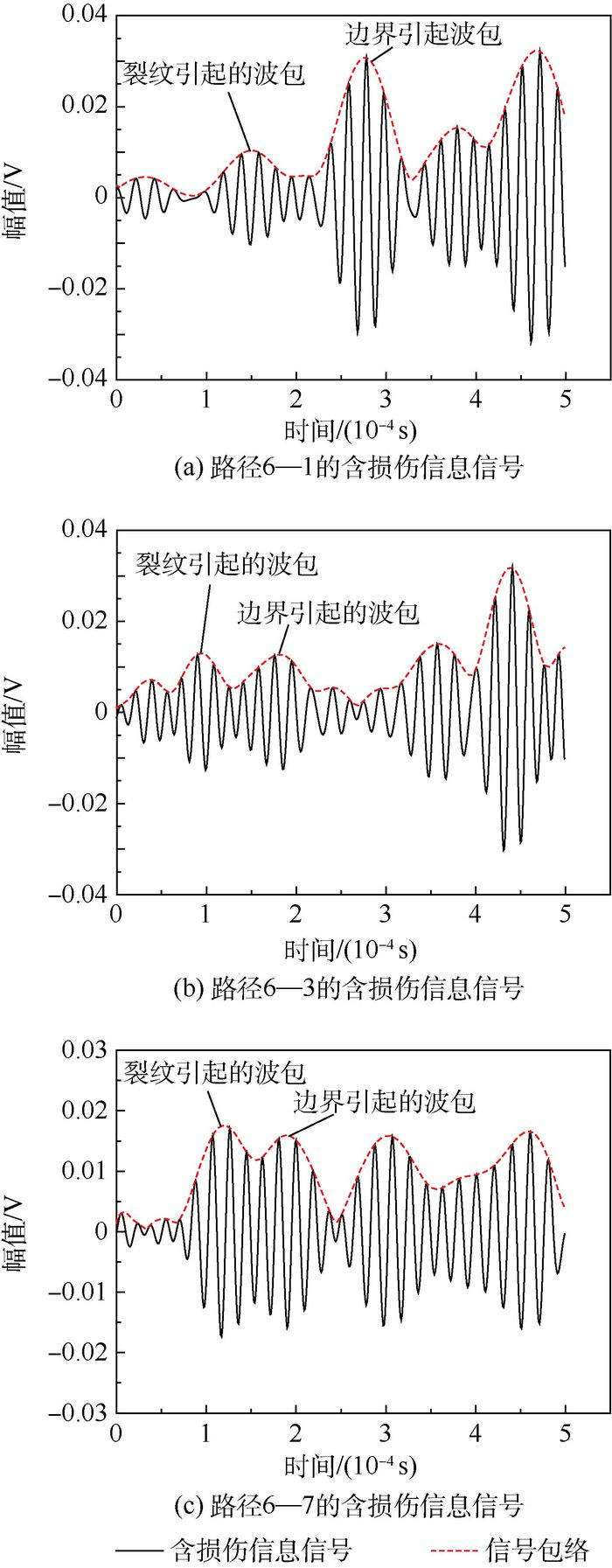
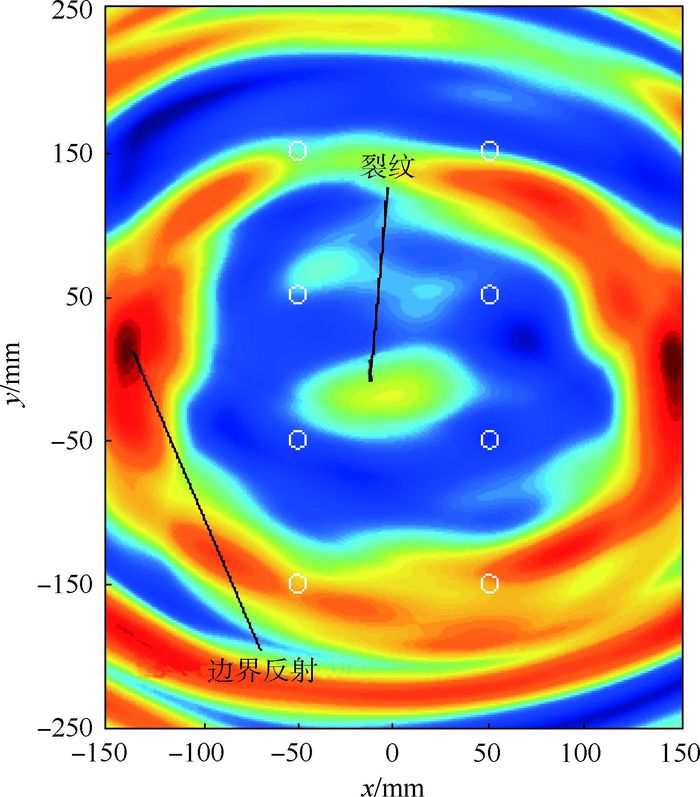
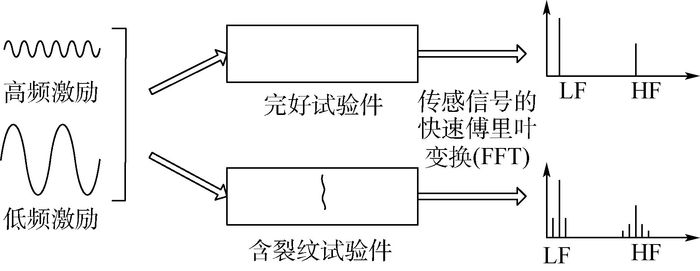
针对线性Lamb波在监测闭合裂纹及微裂纹方面的不足,基于振动声调制理论,提出了一套板类结构中裂纹损伤定位方法。通过分析仅有高频(HF)激励和高低频(HF和LF)同时激励时,声波在含裂纹结构中的传播路径及其信号成分组成,提出了一种含损伤信息信号的提取技术,继而结合延时叠加算法,参考有基准的线性Lamb波损伤定位方法,对板类结构中的疲劳裂纹进行了定位成像。试验证明,该方法可在无需原始健康基准信号的前提下,有效定位出平板结构中的疲劳裂纹,为结构中接触类损伤的定位成像提供了思路。
Abstract:To overcome the shortcomings of linear Lamb waves in closed crack and micro crack monitoring, a imaging method of crack damage localization in plate-like structure based on vibro-acoustic modulation theory and delay and sum algorithm is proposed. The signal components of acoustic wave are analyzed in the crack structure when there is only high-frequency (HF) excitation and there are low-frequency (LF) and HF excitation at the same time. And then, a signal extraction technology is put forward to extract the signal containing damage information. Fatigue crack is located and imaged in plate-like structure based on delay and sum algorithm referring to linear Lamb wave damage localization method. Experiments prove that the proposed method can locate the crack position effectively without the original health reference signal, which provides a way for contact-like damage localization and imaging.
-
-
[1] 张行.断裂与损伤力学[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 2006:1-38.ZHANG X.Fracture and damage mechanics[M].Beijing:Beihang University Press, 2006:1-38(in Chinese). [2] 袁慎芳.结构健康监控[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2007:206-212.YUAN S F.Structural health monitoring and damage control[M].Beijing:National Defence Industry Press, 2007:206-212(in Chinese). [3] STASZEWSKI W J, BOLLER C, TOMLINSON G R.Health monitoring of aerospace structures:Smart sensor technologies and signal processing[M].Chichester:Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2004:102-137. [4] GRABOWSKI K, GAWRONSKI M, BARAN I, et al.Time-distance domain transformation for acoustic emission source localization in thin metallic plates[J].Ultrasonics, 2016, 68:142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2016.02.015 [5] ZHAO X, ROYER R L, OWENS S E, et al.Ultrasonic Lamb wave tomography in structural health monitoring[J].Smart Materials & Structures, 2011, 20(10):105002-105011. [6] NOVAK A, BENTAHAR M, TOURNAT V, et al.Nonlinear acoustic characterization of micro-damaged materials through higher harmonic resonance analysis[J].NDT & E International, 2011, 45(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007%2Fs12541-009-0019-y.pdf [7] PIECZONKA L, KLEPKA A, STASZEWSKI W J.Nonlinear vibroacoustic wave modulation for structural damage detection:An overview[J].Optical Engineering, 2016, 55(1):011005. [8] ROSE J L.Ultrasonic guided waves in solid media[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2014:61-89. [9] BRODA D, STASZEWSKI W J, MARTOWICZ A, et al.Modelling of nonlinear crack-wave interactions for damage detection based on ultrasound-A review[J].Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2014, 333(4):1097-1118. [10] 吴斌, 颜丙生, 何存富, 等.AZ31镁合金早期力学性能退化非线性超声检测[J].航空材料学报, 2011, 31(1):87-92. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKCB201101017.htmWU B, YAN B S, HE C F, et al.AZ31 magnesium early mechanical performance degradation nondestructive testing using nonlinear ultrasonic[J].Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2011, 31(1):87-92(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKCB201101017.htm [11] 焦敬品, 孙俊俊, 吴斌, 等.结构微裂纹混频非线性超声检测方法研究[J].声学学报, 2013, 38(6):648-656. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBA201306002.htmJIAO J P, SUN J J, WU B, et al.A frequency-mixing nonlinear ultrasonic technique for micro-crack detection[J].Acta Acusitca, 2013, 38(6):648-656(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBA201306002.htm [12] DUTTA D, SOHN H, HARRIES K, et al.A nonlinear acoustic technique for crack detection in metallic structures[C]//Proceedings of Health Monitoring of Structural and Biological Systems.Orlando:SPIE, 2009:251-262. [13] SOLODOV I, PFLEIDERER K, BUSSE G.Nonlinear acoustic NDE:Inherent potential of complete nonclassical spectra[M].New York:Springer, 2006:467-486. [14] DZIEDZIECH K, PIECZONKA L, KIJANKA P, et al.Enhanced nonlinear crack-wave interactions for structural damage detection based on guided ultrasonic waves[J].Structural Control & Health Monitoring, 2016, 23(8):1108-1120. [15] PIECZONKA L, KLEPKA A, UHL T, et al.Damage imaging in nonlinear vibro-acoustic modulation tests[C]//Proceedings of Health Monitoring of Structural and Biological Systems.Orlando:SPIE, 2015:9438E. [16] SOHN H, LIM H J, DESIMIO M P, et al.Nonlinear ultrasonic wave modulation for online fatigue crack detection[J].Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2014, 333(5):1473-1484. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/25/12/125034/pdf [17] 胡海峰. 板状金属结构健康监测的非线性超声理论与关键技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2011: 45-50.HU H F.Research on theory and key technologies of nonlinear ultrasonics for health monitoring of plate-like metallic structures[D].Changsha:National University of Defense Technology, 2011:45-50(in Chinese). [18] 焦敬品, 何存富, 吴斌.接触缺陷的振动调制超声导波检测技术研究[J].声学学报, 2009, 34(3):242-248. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBA200903010.htmJIAO J P, HE C F, WU B.Vibro-modulation and guided wave techniques for contact defect detection in plate[J].Acta Acustica, 2009, 34(3):242-248(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XIBA200903010.htm [19] KIM S, ADAMS D E, SOHN H, et al.Crack detection tech-nique for operating wind turbine blades using vibro-acoustic modulation[J].Structural Health Monitoring, 2014, 13(6):660-670. doi: 10.1177/1475921714553732 [20] ZHANG C, QIU J, JI H, et al.Damage localization using warped frequency transform in active structural health monitoring[J].International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics & Mechanics, 2015, 47(4):897-909. [21] GIURGIUTIU V.Tuned Lamb wave excitation and detection with piezoelectric wafer active sensors for structural health monitoring[J].Journal of Intelligent Material System and Structures, 2005, 16(4):291-305. doi: 10.1177/1045389X05050106 -







 下载:
下载: