Emergency strategy operation optimization for atmosphere environment control system in space station
-
摘要:
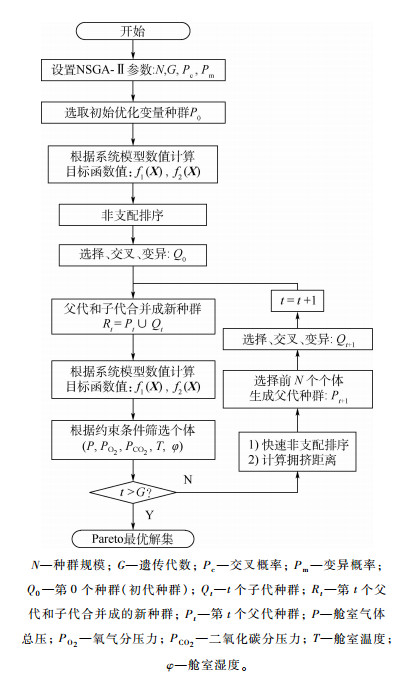
空间站大气环控系统(ECS)由多个相互耦合的子系统组成,主要控制舱室气体成分和环境参数,对保障航天员生命安全具有重要意义。该系统正常运行严重依赖于供电系统的工作稳定性,因此长期在轨运行要求ECS应具有适应供电不足的应急运行能力。针对可能面临的供电不足情况,开展了大气ECS应急运行策略优化研究。为了研究出多约束多目标优化问题,首先建立了大气ECS物质、能量和功耗模型,并提出了非再生物资使用时长评估函数。其次以非再生物资使用时长最大和电能需求最小为目标函数,以子系统可调的运行参数为优化参数,在舱室五大环境参数的约束下,采用快速非支配排序遗传算法-Ⅱ(NSGA-Ⅱ)获得了ECS Pareto最优解集,进而获得了Pareto最优前沿(POF)。由于多目标函数具有相同重要性,最终可从POF上获得了大气ECS应急运行策略。优化研究结果表明:该方法能够确定不足电能情况下各子系统的应急电能最优分配方案,从而确定出应急时的子系统最优重构运行方案,以保证最大系统使用时长和最小电能需求的要求。
-
关键词:
- 大气环控系统(ECS) /
- 应急运行策略 /
- 多目标优化 /
- Pareto最优解集 /
- 非支配排序遗传算法-Ⅱ(NSGA-Ⅱ)
Abstract:Environment control system (ECS) in a space station is an essential system for the astronaut life safety. Composed of a number of coupling subsystems, the ECS functions as the controller of the cabin air condition and the environmental parameters, which are essential parts to the astronauts' life safety. As its subsystems are power-consuming, the system's regular operation highly relies on the stability of the power supply system and the ECS should have the ability to reconfigure operation strategy in some emergency conditions. In this paper, the emergency strategy optimization method of ECS is studied under potential insufficient power supply condition. To study this issue, we establish basic ECS mathematical models involving its substances, energy as well as consumption, and the non-regenerative substance lifetime conception, which represents the remaining amount of non-regenerative life support substance. A multi-objective optimization method is developed to search the ECS emergency strategy. The maximum non-regenerative substance lifetime and the minimum power consumption are chosen as the optimization objective functions. Some adjustable key variables are chosen as the optimal variables, which represent the way to reconfigure the operation strategy. With the constraints of 5 main environmental parameters, the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-Ⅱ (NSGA-Ⅱ) is adopted to obtain the Pareto optimal solution set and the Pareto optimal frontier (POF). The results of optimization research show that the presented optimal method can obtain the optimal emergency electric energy allocation strategy for subsystems under different insufficient power supply conditions, and the optimal reconfigured operation strategy can meet the maximum system lifetime and minimum system supply energy requirement.
-
表 1 优化变量及可调范围
Table 1. Optimization variables and adjustable range
变量 最小值 最大值 wTHCS/(kg·min-1) 5 14 ISPES/A 0 16 wCDRA/(kg·h-1) 5 22 表 2 相关参数
Table 2. Related parameters
参数 数值 舱室体积/m3 100 氧气存储质量/kg 9.762 氧气罐个数 2 LiOH质量/kg 12 LiOH罐个数 2 供氧速率/(L·min-1) 40 供氮速率/(L·min-1) 40 表 3 人体热湿实验数据
Table 3. Experimental data of human body heat and humidity
热湿参数 睡眠 静息 轻度 中度 耗氧消耗量/(kg·d-1) 0.468 0.571 2 0.823 2 1.545 6 CO2消耗量/(kg·d-1) 0.528 0.648 0.936 1.752 产热/W 83 93 150 280 排湿/(kg·d-1) 1.2 1.44 1.92 3.72 表 4 4种给定电能情况下系统运行策略最优重构方案
Table 4. Optimal reconfiguration scheme of system operation strategy under given electric energy
应急工况 Lsys/
dWsys/
WwCDRA/
(kg·h-1)ISPES/
AwTHCS/
(kg·min-1)A 199 1 164 8.60 12.95 7.80 B 79 1 123 8.34 12.05 7.92 C 26 950 6.07 8.89 7.41 D 9 774 5.16 0.32 6.68 -
[1] LARSON W J, PRANKE L K.Human spaceflight:Mission analysis and design[M].Columbus:McGraw-Hill, 2007:539-574. [2] WIELAND P O.Living together in space:The design and operation of the life support systems on the international space station[M].Huntsville, AL:National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Marshall Space Flight Center, 1998:120-156. [3] ROMANI R, GOES L C S.Cabin temperature control model for commercial aircraft[C]//Proceedings of AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference.Reston:AIAA, 2012:1-15. [4] 靳健, 侯永青.载人航天器空气环境参数控制非定常仿真分析[J].航空学报, 2014, 35(11):2970-2978. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201411008.htmJIN J, HOU Y Q.Unsteady simulation analysis on air environment parameters control of manned spacecraft[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(11):2970-2978(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201411008.htm [5] ANDERSON G, MARTIN C E.Evaluation and application of Apollo ECLS/ATCS systems to future manned missions[C]//43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit.Reston:AIAA, 2005:1-13. [6] HAJELA G, COHEN F, DALTON P.International space station power reinitialization[J].IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2003, 18(4):19-24. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2003.1194085 [7] MAK T.A study of on-orbit spacecraft failures[J].Acta Astronautica, 2009, 64(2):195-205. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0094576508003019 [8] KIM S Y, CASTET J F, SALAH J H.Spacecraft electrical power subsystem:Failure behavior, reliability, and multi-state failure analyses[J].Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2012, 98:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2011.10.005 [9] 孙晨, 徐向华, 梁新刚.空间站主动热控回路的热负荷分配优化[J].工程热物理学报, 2014, 35(10):2049-2052. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB201410035.htmSUN C, XU X H, LIANG X G.Heat load distribution optimization of active thermal control system for space station[J].Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2014, 35(10):2049-2052(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB201410035.htm [10] LIN K P, LUO Y Z, TANG G J.Optimization of logistics strategies for long-duration space-station operation[J].Journal of Spacecraft And Rockets, 2014, 51(5):1709-1720. doi: 10.2514/1.A32773 [11] 任建勋, 张信荣, 尚传勋, 等.载人航天器SPE制氧系统性能分析[J].清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 42(8):1102-1105. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXB200208028.htmREN J X, ZHANG X R, SHANG C X, et al.Performance analysis of SPE oxygen generation system in manned spacecraft[J].Journal of Tsinghua University(Natural Science Edition), 2002, 42(8):1102-1105(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXB200208028.htm [12] LIU M, YANG D, PANG L, et al.Experimental and computational investigation of adsorption performance of TC-5A and PSA-5A for manned spacecraft[J].Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(6):1583-1592. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.08.003 [13] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al.A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2):182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [14] ARIAS-MONTA A, COELLO C A C, MEZURA-MONTES E.Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms in aeronautical and aerospace engineering[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 16(5):662-694. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2011.2169968 [15] DEB K.An efficient constraint-handling method for genetic algorithms[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics & Engineering, 2000, 186(2-4):311-338. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045782599003898 -







 下载:
下载: