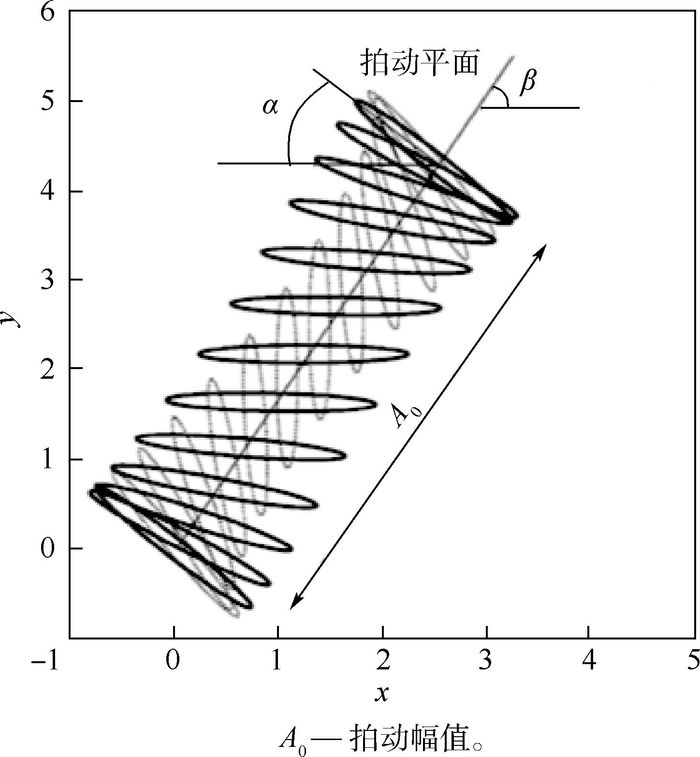
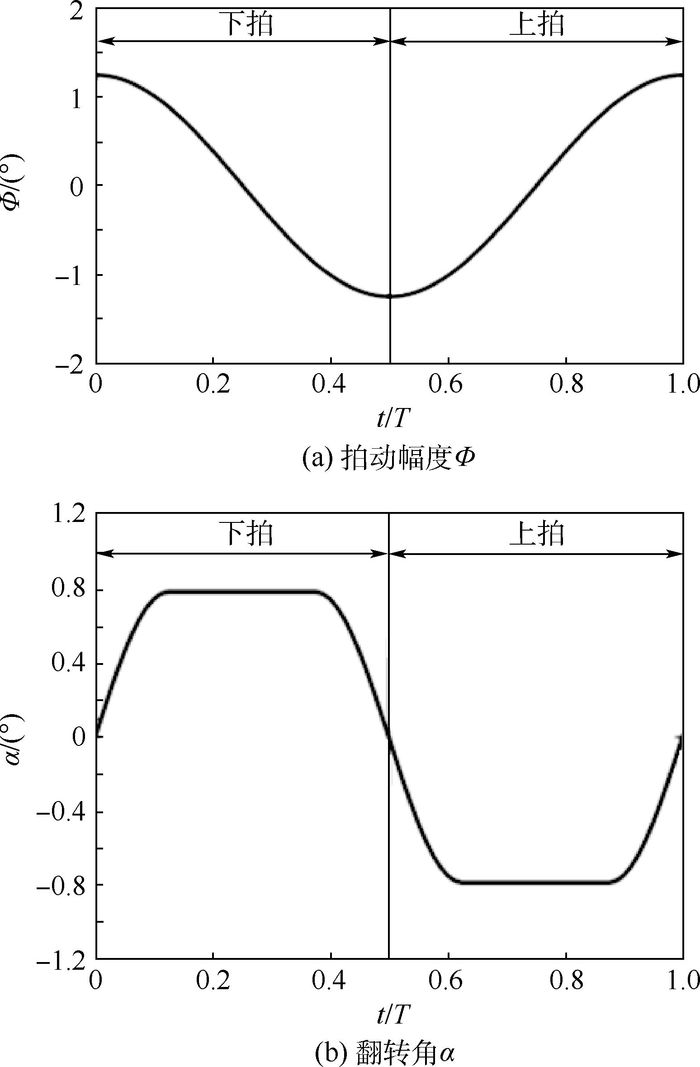
Numerical study on intermittent flapping flight performance of dragonfly during climbing
-
摘要:
采用数值模拟方法研究了蜻蜓双翼做间歇性拍动运动时的气动特征。计算结果表明,在所研究的雷诺数工况下(
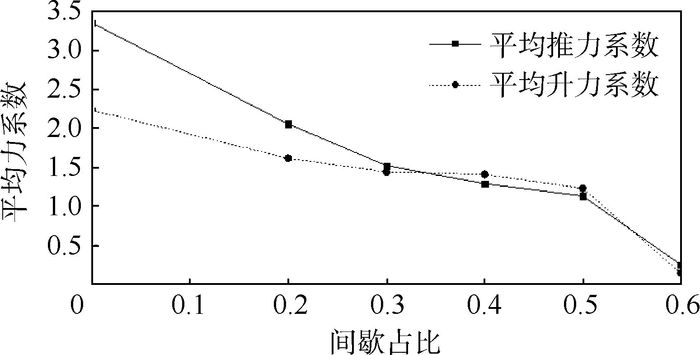
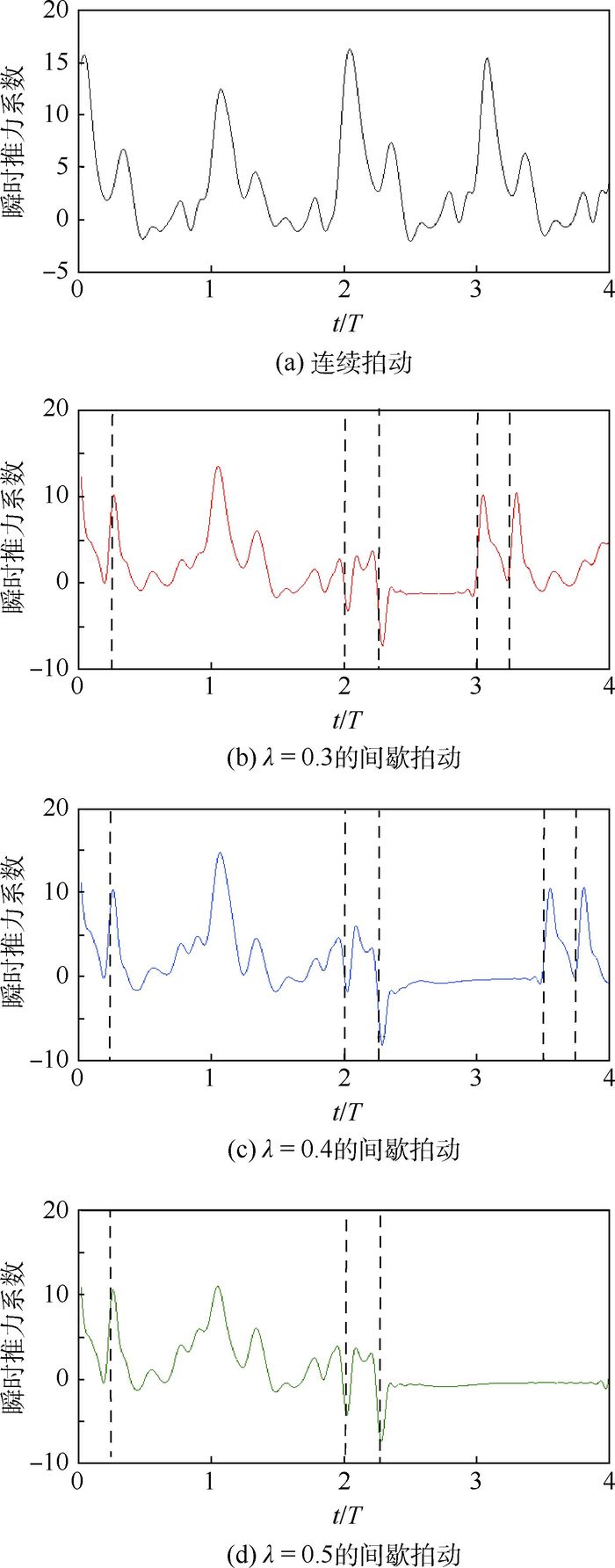
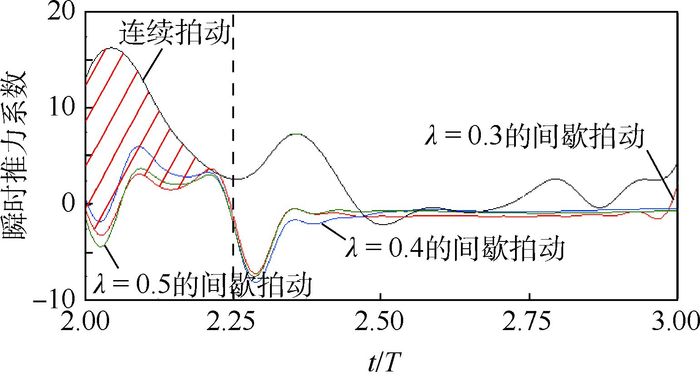
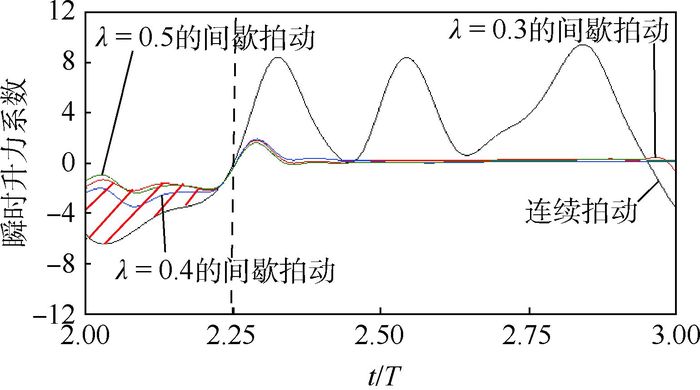
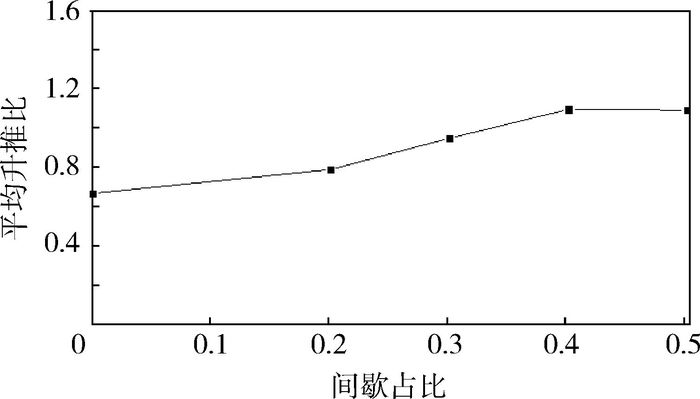
Re =157),模型翼的平均升力系数和平均推力系数随着间歇占比的增大而减小,前段下降较快,中段下降平缓,后段下降至零。其中平均推力系数受到的影响相对平均升力系数更大,当连续飞行转变为间歇性飞行时,短暂滑翔初期和短暂滑翔稳定阶段均大幅削弱推力系数,共占42.7%;而对于升力系数,短暂滑翔稳定期对升力系数的削弱作用很大,占41.4%,但短暂滑翔初期却对平均升力系数的提高贡献8%。间歇拍动飞行能够提高蜻蜓飞行的升推比,当滑翔时长占间歇飞行周期之比为0.3时,平均升推比接近为1。Abstract:Aerodynamic force generation in a dragonfly intermittent flapping flight with modeled wings was studied using the method of numerical simulation. The computational results show that the average lift coefficient and average thrust coefficient of the modeled wing decrease with the increase of the intermittent proportion at the Reynolds number of 157. They descend faster in the frontal part, while gently in the middle part, and decrease to zero in the latter part. The average thrust coefficient is affected greater than the average lift coefficient. When the continuous flight turns into intermittent flight, the thrust coefficient during the early phase and stable phase of short gliding is significantly weakened with totally 42.7%; For the lift coefficient, it is mainly weakened during the stable phase of short gliding, accounting for 41.4%, but the early phase of short gliding has a contribution of 8% to the increase of average lift coefficient. Intermittent flapping flight is possible to improve the lift-thrust ratio in dragonfly flight. When the the proportion of gliding time to intermittent flight cycle is 0.3, the average lift-thrust ratio is close to 1.
-
Key words:
- dragonfly /
- intermittent flapping /
- asynchronous flapping /
- thrust coefficient /
- lift coefficient
-
-
[1] SUN M.Insect flight dynamics:Stability and control[J].Reviews of Modern Physics, 2014, 86(2):615-646. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.86.615 [2] WEIS-FOGH T.Quick estimates of flight fitness in hovering an-imals, including novelmechanism for lift production[J].Journal of Experimental Biology, 1973, 59(1):169-230. [3] ELLINGTON C P, VAN DEN BERG C, WILLMOTT A P.Leading edge vortices in insect flight[J].Nature, 1996, 384(6610):626-630. doi: 10.1038/384626a0 [4] DICKINSON M H, LEHMANN F O, SANE S P.Wing rotation and the aerodynamic basis of insect flight[J].Science, 1999, 284(5422):1954-1960. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5422.1954 [5] SUN M, TANG J.Unsteady aerodynamic force generation by a model fruit flywing in flappingmotion[J].Journal of Experimental Biology, 2002, 205(1):55-70. [6] AZUMA A, WATANABE T.Flight performance of a dragonfly[J].Journal of Experimental Biology, 1988, 137(1):221-252. [7] WAKELING J M, ELLINGTON C P.Dragonfly flight.Ⅱ.Velocities, accelerations and kinematics of flapping flight[J].Journal of Experimental Biology, 1997, 200(3):557-582. [8] WAKELING J M, ELLINGTON C P.Dragonfly flight.I.Gliding flight and steady-state aerodynamic forces[J].Journal of Experimental Biology, 1997, 200(3):543-556. [9] WAKELING J, ELLINGTON C.Dragonfly flight.Ⅲ.Lift and power requirements[J].Journal of Experimental Biology, 1997, 200(3):583-600. [10] WANG Z J, RUSSELL D.Effect of forewing and hindwing interactions on aerodynamic forces and power in hovering dragonfly flight[J].Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(14):12243-12254. [11] DONG H, KOEHLER C, LIANG Z, et al.An integrated analysis of a dragonfly in free flight:AIAA-2010-4390[R].Reston:AIAA, 2010. [12] 高倩, 郑孟宗, 李志平, 等.蜻蜓爬升过程飞行特征实验研究[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(6):1271-1278.GAO Q, ZHENG M Z, LI Z P, et al.Experimental study on flight performance of dragonfly during climbing[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2016, 42(6):1271-1278(in Chinese). [13] FADLUN E A, VERZICCO R, ORLANDI P, et al.Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three-dimensional complex flow simulations[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 161(1):35-60. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6484 [14] MOHD-YUSOF J.Combined immersed-boundary/B-spline methods for simulations of flow in complex geometries[C]//Annual Research Briefs, 1997:317-327. [15] GRESHO P M, CHAN S T, LEE R L, et al.A modified finite element method for solving the time-dependent, incompressible Navier-Stokes equations.Part 2:Applications[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1984, 4(7):619-640. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0363 [16] SAIKI E M, BIRINGEN S.Numerical simulation of a cylinder in uniform flow:Application of a virtual boundary method[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 1996, 123(2):450-465. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1996.0036 [17] COUTANCEAU M, BOUARD R.Experimental determination of the main features of the viscous flow in the wake of a circular cylinder in uniform translation.Part 2.Unsteady flow[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1977, 79(2):257-272. doi: 10.1017/S0022112077000147 [18] SILVA L E, SILVEIRA-NETO A, DAMASCENO J J R.Numerical simulation of two-dimensional flows over a circular cylinder using the immersed boundary method[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 189(2):351-370. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00214-6 [19] PARK J, KWON K, CHOI H.Numerical solutions of flow past a circular cylinder at Reynolds numbers up to 160[J].KSME International Journal, 1998, 12(6):1200-1205. doi: 10.1007/BF02942594 [20] WIESELSBERGER C.New data on the laws of fluid resistance[J].Physikalische Zeitschrift, 1921, 22:321-328. [21] RELF E F.An electrical method for tracing stream lines in the two-dimensional motion of a perfect fluid[J].Philosophical Magazine, 1924, 29(285):535-539. [22] JANE W Z.Two dimensional mechanism for insect hovering[J].Physical Review Letters, 2000, 85(10):2216-2219. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.2216 -








 下载:
下载: