-
摘要:
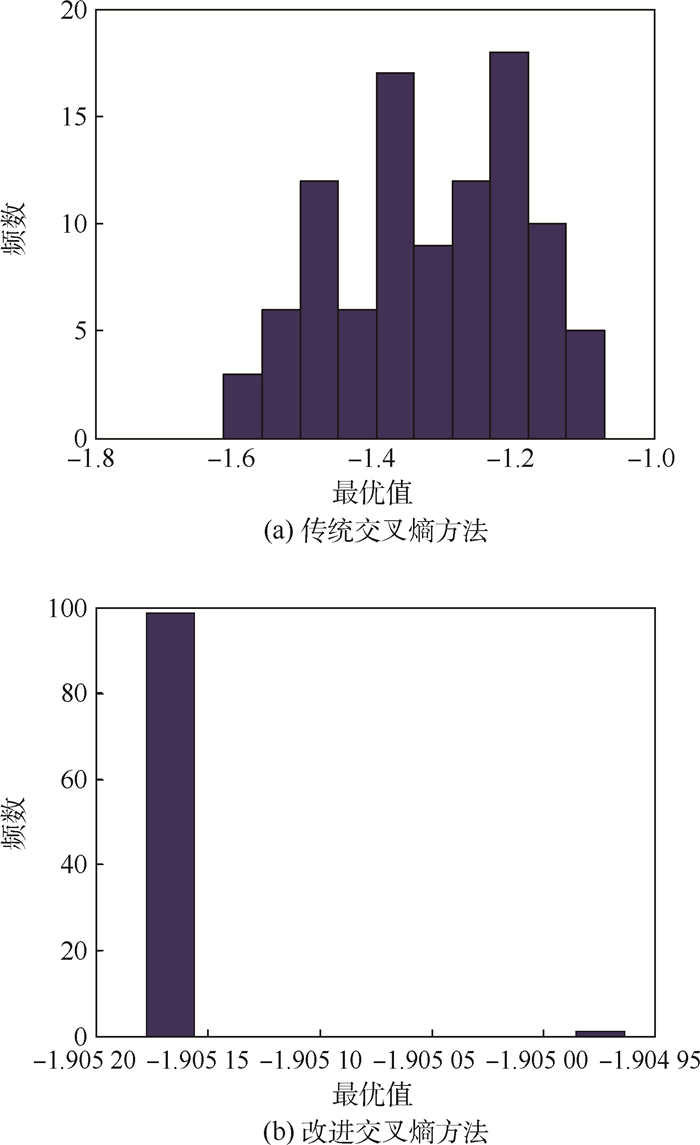
随机优化的交叉熵方法具有高效性和自适应性的特点,在高维和非线性等复杂优化问题中具有巨大的开发潜力。针对传统交叉熵优化方法精度不足的缺点,提出使用“当前精英样本”和“全局精英样本”构建新的参数更新策略,以充分提取迭代历史中的有用信息。采用自适应的平滑策略和变异操作进一步提升计算性能。通过3个计算实例证明,改进后的方法比传统交叉熵方法具有更高的计算精度和更强的全局搜索能力。
Abstract:Cross entropy method is an efficient and adaptive stochastic optimization method and has immense potential in complex optimization problems with high dimension and nonlinear constraints. However, the traditional cross entropy method is lack of accuracy. In this study, both the concepts of current elite samples and global elite samples are introduced to extract more useful information from the whole iterative history. Then, a new parameter updating strategy is established based on these two concepts. New adaptive smoothing strategy and mutation operation are also applied to improve its computing performance. The proposed algorithm is illustrated by three numerical examples. The computational results indicate that the improved cross entropy method has higher calculation accuracy and better global search capability.
-
表 1 不同初值改进前后方法优化结果
Table 1. Optimal solutions of method before and after improvement with different initial values
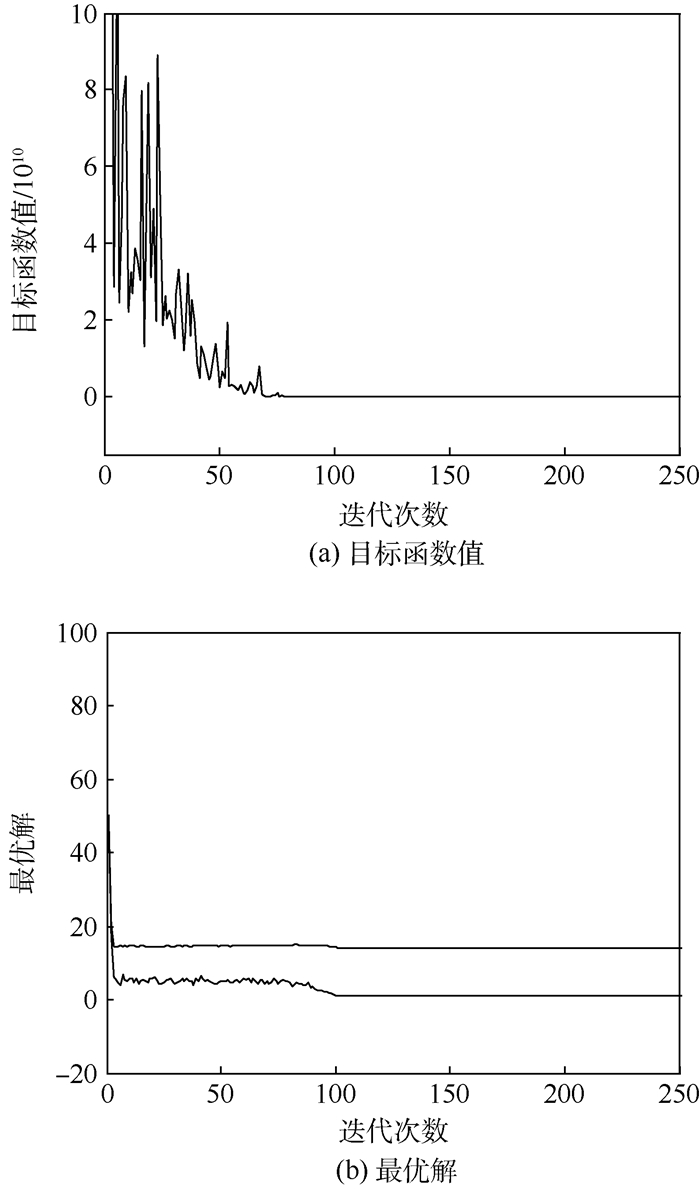
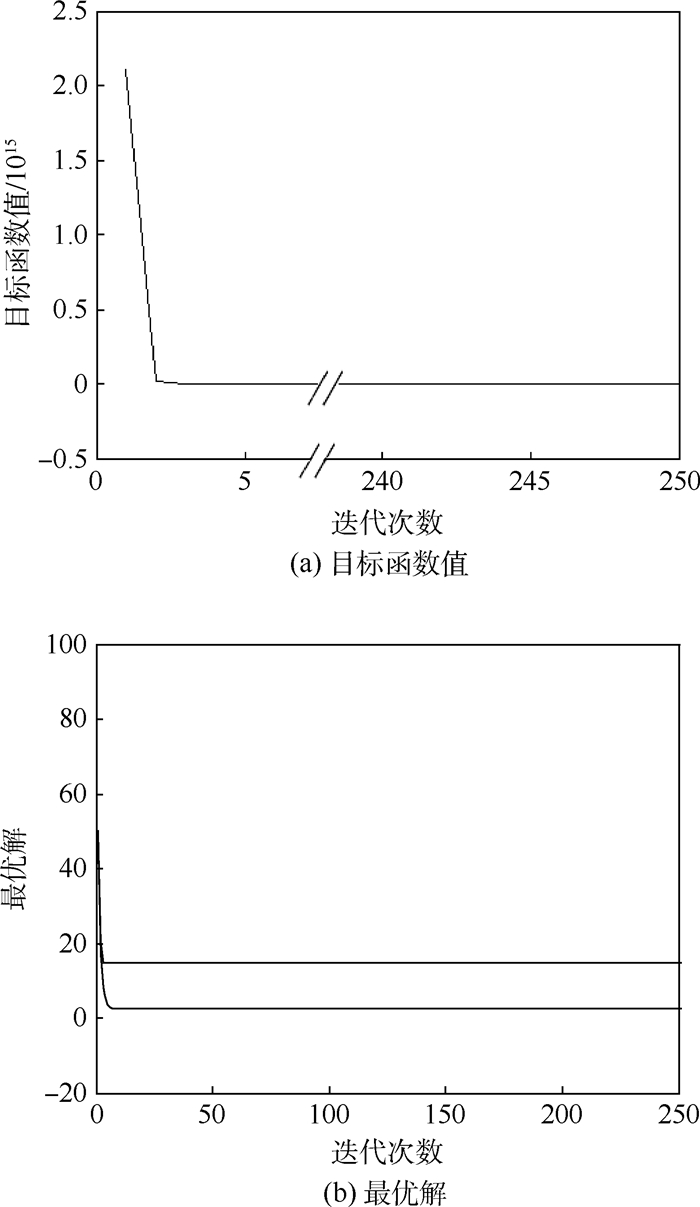
μ0 SCE(x*) SICE(x*) [56.5, 50]T -5 582.658 4 -6968.5867 [100, 100]T 1.9466×1014 -6968.5868 [0, 0]T -6289.1210 -6968.5866 [150, 150]T 1.1289×1016 -6968.5867 [-150, 150]T 1.1618×1014 -6968.5868 表 2 传统交叉熵和改进交叉熵方法目标函数值变化过程
Table 2. Comparison of objective function value in iteration history between traditional CE and ICE methods
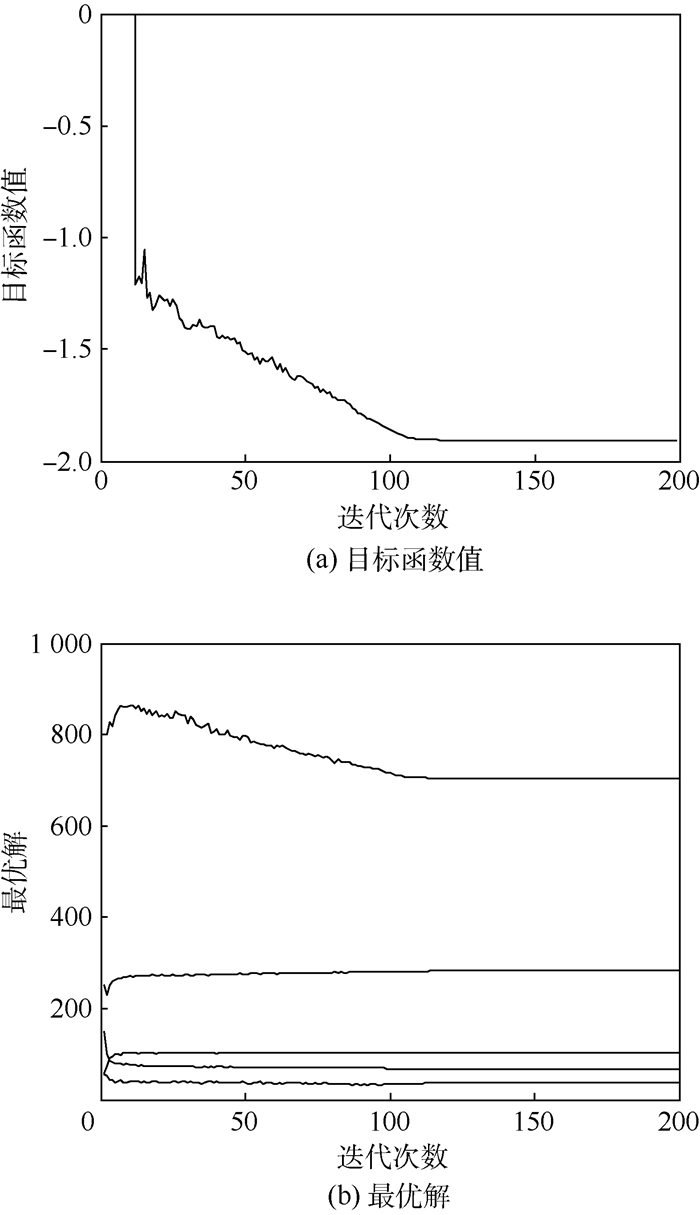
迭代次数 SCE(x*) SICE(x*) 1 3.046 0×1017 1.870 5×1017 2 1.885 2×1016 2.409 6×1016 3 4.116 8×1015 5.599 3×1015 4 8.374 1×1014 3.043 2×1015 5 1.273 0×1014 9.092 1×1014 6 -1.002 9 3.657 2×1014 9 -1.141 5 1.002 9×1013 10 -1.312 0 -0.893 3 50 -1.387 7 -1.508 1 100 -1.387 7 -1.854 4 150 -1.387 7 -1.905 2 200 -1.387 7 -1.905 2 -
[1] HAFTKA R T, GVRDAL Z.Elements of structural optimization[M].Dordrecht:Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1990. [2] RUBINSTEIN R Y.Optimization of computer simulation models with rare events[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 1997, 99(1):89-112. doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(96)00385-2 [3] RUBINSTEIN R Y.The cross-entropy method for combinatorial and continuous optimization[J].Methodology & Computing in Applied Probability, 1999, 1(2):127-190. doi: 10.1023/A:1010091220143.pdf [4] HELVIK B E, WITTNER O.Using the cross-entropy method to guide/govern mobile agent's path finding in networks[M].Berlin:Springer, 2001. [5] ALON G, KROESE D P, RAVIV T, et al.Application of the cross-entropy method to the buffer allocation problem in a simulation-based environment[J].Annals of Operations Research, 2005, 134(1):137-151. doi: 10.1007/s10479-005-5728-8 [6] KUO C, YEARGAIN J R, DOWNEY W J, et al.Solving the vehicle routing problem with stochastic demands using the cross-entropy method[J].Annals of Operations Research, 2005, 134(1):153-181. doi: 10.1007/s10479-005-5729-7 [7] KROESE D P, POROTSKY S, RUBINSTEIN R Y.The cross-entropy method for continuous multi-extremal optimization[J].Methodology & Computing in Applied Probability, 2006, 8(3):383-407. doi: 10.1007/s11009-006-9753-0 [8] HO S L, YANG S.The cross-entropy method and its application to inverse problems[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2010, 46(8):3401-3404. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2010.2044380 [9] 丁卫平, 王建东, 陈森博, 等.基于改进混合蛙跳算法的粗糙属性交叉熵优化约简[J].南京大学学报(自然科学), 2014, 50(2):159-166.DING W P, WANG J D, CHEN S B, et al.Rough attribute reduction with cross-entropy based on improved shuffled frog-leaping algorithm[J].Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 2014, 50(2):159-166(in Chinese). [10] 李国成, 肖庆宪.求解高维函数优化问题的交叉熵蝙蝠算法[J].计算机工程, 2014, 40(10):168-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2014.10.032LI G C, XIAO Q X.Cross-entropy bat algorithm for solving high-dimensional function optimization problem[J].Computer Engineering, 2014, 40(10):168-174(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2014.10.032 [11] GHIDEY H.Reliability-based design optimization with cross-entropy method[D].Trondheim:Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2015. [12] 李洪双, 马远卓.结构可靠性分析与随机优化设计的统一方法[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2015:146-147.LI H S, MA Y Z.Unified methods for structural reliability analysis and stochastic optimization design[M].Beijing:National Defense Industry Press, 2015:146-147(in Chinese). [13] HUI K P, BEAN N, KRAETZL M, et al.The tree cut and merge algorithm for estimation of network reliability[J].Probability in the Engineering & Informational Sciences, 2002, 17(1):23-45. [14] 吴烈. 电磁场逆问题鲁棒优化设计理论和算法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012.WU L.Numerical methodologies for robust optimizations of inverse problems[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2012(in Chinese). [15] LIANG J J, RUNARSSON T P, MEZURA-MONTES E, et al.Problem definitions and evaluation criteria for the CEC 2006 special session on constrained real-parameter optimization[R].Singapore:Nanyang Technological University, 2006. [16] 彭宏, 杨立洪, 郑咸义, 等.计算工程优化问题的进化策略[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 25(12)17-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.1997.12.004PENG H, YANG L H, ZHENG X Y, et al.A new evolutionary strategy for solving engineering optimization problems[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 1997, 25(12):17-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.1997.12.004 -







 下载:
下载: