-
摘要:
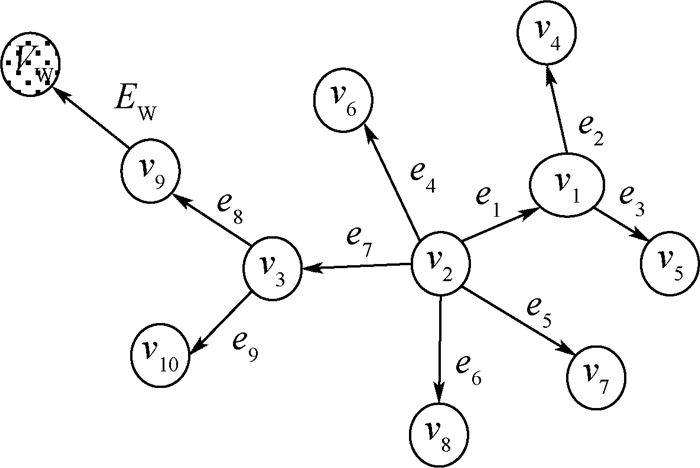
图结构异常检测可以发现金融欺诈行为、网络入侵和可疑的社交行为。针对当前检测图异常算法的计算复杂度高、不能处理大规模动态图的缺点,研究并提出了一种增量并行式的算法以便更有效地发现和检测大规模动态图中的异常。该算法使用时间滑动窗口对图进行划分,在初始化阶段选取
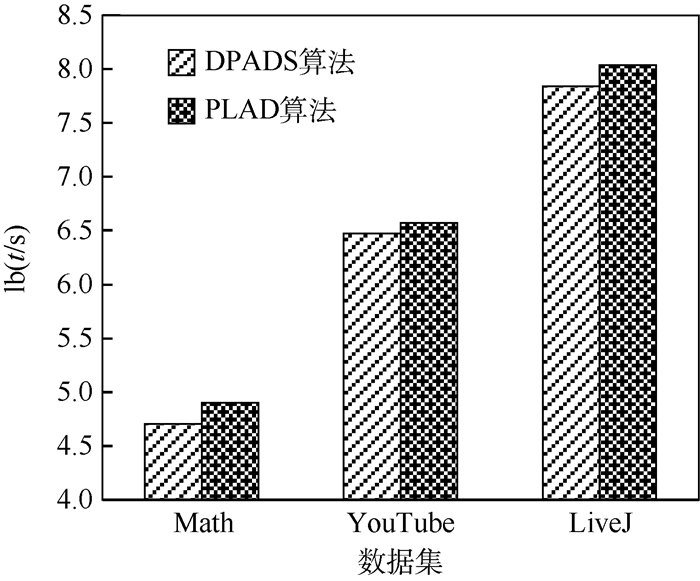
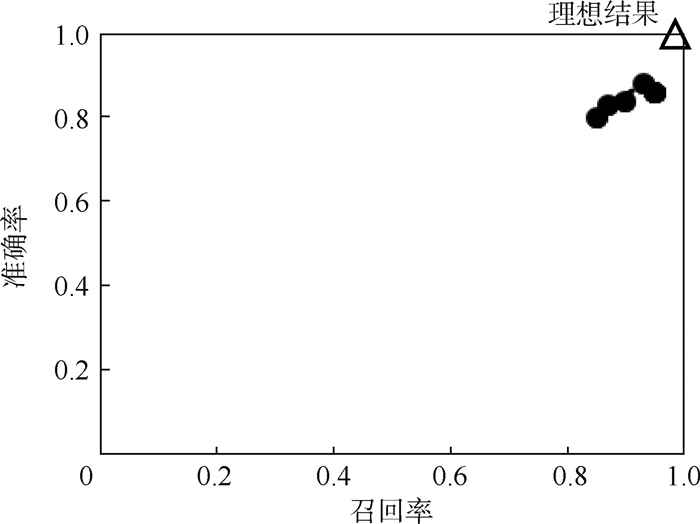
N 个子图,使用最小描述长度(MDL)原理并行检测正常模式和异常模式,并行迭代地检测其他子图中的正常结构和异常结构。在多个大规模图数据集上的实验结果表明,检测动态图结构异常准确率达到96%,召回率达到85%,运行时间减少了一个数量级。同时还讨论了滑动窗口大小和并行数量对算法运行时间的影响。-
关键词:
- 异常检测 /
- 增量 /
- 并行 /
- 滑动窗口 /
- 最小描述长度(MDL)原理
Abstract:Financial fraud behavior, network intrusion and suspicious social actions can be detected by structural anomaly detection in graphs. The existing anomaly detection algorithms require high computational complexity and cannot process large-scale dynamic graphs. So an incremental and parallel algorithm is proposed to discover and detect abnormal patterns in dynamic graphs effectively and efficiently. The whole graph was partitioned into subgraphs by time sliding windows.
N subgraphs in time sliding windows were processed in parallel by minimum description length (MDL) principle to discover both normal and abnormal patterns. Structural outliers can be detected gradually in parallel based on normal patterns. The results of experiments conducted in multiple large-scale graphs show that the precision rate for detecting the abnormal patterns of dynamic graph reaches 96%, recall rate reaches 85%, and running time reduces by an order of magnitude. The impact of the size of sliding windows and the number of parallel on running time of the algorithm is also discussed.-
Key words:
- anomaly detection /
- incremental /
- parallel /
- sliding window /
- minimum description length (MDL) principle
-
表 1 实验数据集
Table 1. Experimental data sets
数据名称 类型 结点个数 边个数 YouTube 无向图 1 134 890 2 987 624 LiveJ 有向图 484 751 68 993 773 Math 有向时序图 24 818 50 650 -
[1] AHMED N K, NEVILLE J, KOMPELLA R.Network sampling:From static to streaming graphs[J].ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data(TKDD), 2014, 8(2):7:1-7:56. [2] EBERLE W, HOLDER L.Anomaly detection in data represented as graphs[J].Intelligent Data Analysis, 2007, 11(6):663-689. [3] EBERLE W, HOLDER L, GRAVES J.Insider threat detection using a graph-based approach[J].Journal of Applied Security Research, 2011, 6(1):32-81. [4] NOBLE C C, COOK D J. Graph-based anomaly detection[C]//Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM Press, 2003: 631-636. [5] AKOGLU L, MCGLHON M, FALOUSTSOS C. OddBall: Spotting anomalies in weighted graphs[C]//Proceedings of the 14th Pacific-Asia conference on Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2010, 3: 410-421. [6] FEIGENBAUM J, KANNAN S, MCGREGOR A, et al.On graph problems in a semi-streaming model[J].Theoretical Computer Science, 2005, 348(2-3):207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2005.09.013 [7] DEMETRESCU C, FINOCCHI I, RIBICHINI A.Trading off space for passes in graph streaming problems[J].ACM Transactions on Algorithms(TALG), 2009, 6(1):6:1-6:17. [8] AGGARWAL G, DATAR M, RAJAGOPALAN S, et al. On the streaming model augmented with a sorting primitive[C]//Proceedings of the 45th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science(FOCS). Washington, D. C. : IEEE Computer Society, 2004: 540-549. [9] SARMA A, GOLLAPUDI S, PANIGRAHY R. Estimating PageRank on graph streams[C]//Proceedings of the 27th ACM Sigmod-Sigact-Sigart Symposium on Principles of Database Systems. New York: ACM Press, 2008: 69-78. [10] SHIN K, ELIASSI-RAD T, FALOUTSOS C. CoreScope: Graph mining using k-core analysis-Patterns, anomalies and algorithms[C]//2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). Washington, D. C. : IEEE Computer Society, 2017: 469-478. [11] BRIDGES R A, COLLINS J P, FERRAGUT E M, et al. Multi-level anomaly detection on time-varying graph data[C]//2015 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM). New York: ACM Press, 2016: 579-583. [12] EBERLE W, HOLDER L. A partitioning approach to scaling anomaly detection in graph streams[C]//2014 IEEE International Conference on Big Data. Washington, D. C. : IEEE Computer Society, 2014: 17-24. [13] AKOGLU L, TONG H, KOUTRA D.Graph based anomaly detection and description:A survey[J].Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2015, 29(3):626-688. doi: 10.1007/s10618-014-0365-y [14] 吴烨, 钟志农, 熊伟, 等.一种高效的属性图聚类算法[J].计算机学报, 2013, 36(8):1704-1713.WU Y, ZHONG Z N, XIONG W, et al.An efficient method for attributed graph clustering[J].Chinese Journal of Computers, 2013, 36(8):1704-1713(in Chinese). [15] EBERLE W, HOLDER L. Incremental anomaly detection in graphs[C]//2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops. Washington, D. C. : IEEE Computer Society, 2013: 521-528. [16] EPASTO A, LATTANZI S, SOZIO M. Efficient densest subgraph computation in evolving graphs[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web. Geneva: International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, 2015: 300-310. [17] YANG J, LESKOVEC J. Defining and evaluating network communities based on ground-truth[C]//Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD Workshop on Mining Data Semantics. New York: ACM Press, 2012, 3: 1-3: 8. -








 下载:
下载: