-
摘要:
针对信息不一致、不完整下的风险评估不确定性难以刻画与传播问题,提出一种基于变步长离散随机集理论的风险混合不确定性分析方法。将各类不完整、不精确信息转化为随机集刻画框架,在随机集理论框架下建立了统一的混合不确定性传播模型,利用随机扩张原理,计算出风险的不确定性包络曲线。为解决不一致冲突信息的不确定性合成,采用D-S证据合成原则实现多源不确定性的融合。为减小不确定性传播截尾相对误差,提出一种不确定性变量分布的变步长离散随机集刻画策略,并给出了基于变步长离散随机集理论的混合不确定性传播实施步骤。通过一个质量-弹簧-阻尼非线性物理与现象响应模型,验证了方法的有效性和可用性。
Abstract:In view of hybrid uncertainty presentation and propagation considering the dissonance and imprecision of information in risk assessment, a hybrid uncertainty analysis method based on variable step discrete random set theory was proposed. All kinds of incomplete and dissonant knowledge was represented with random set framework, a unified hybrid uncertainty propagation model was built using random extension principle, and uncertainty envelope curvesof risk was calculated at the same time. To solve the uncertainty combination problem of dissonant and conflict informations, D-S evidence combination principle was used to merge multisource uncertainty informations. For reducing the tail relative error, a variable step discrete random set presentation strategy of uncertainty variables was proposed, and the analysis procedure of hybrid uncertainty propagation was put forward based on variable step discrete random set theory. In conclusion, a physics and phenomena response model of a mass-spring-damper system was taken to verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- risk assessment /
- random set theory /
- D-S evidence theory /
- hybrid uncertainty /
- relative error
-
表 1 参数x的证据区间信息
Table 1. Evidence interval information of parameter x
区间信息 焦元1 焦元2 焦元3 区间1 m([0.5, 1.0])=0.3 m([1.0, 1.4])=0.2 m([1.2, 2.0])=0.5 区间2 m([0.6, 1.0])=0.2 m([0.5, 1.4])=0.4 m([1.0, 2.0])=0.4 表 2 参数x的联合证据区间信息
Table 2. Combination of evidence interval information of parameter x
焦元A [0.6, 1.0] [0.5, 1.0] [1.0, 1.4] [1.2, 1.4] [1.2, 2.0] m(A) 0.081 1 0.162 2 0.216 2 0.270 3 0.270 3 表 3 不确定性参数k
Table 3. Uncertainty parameter k
参数 min mod max k1 [100,110] [160,170] [210,220] k2 [90,110] [150,180] [210,220] k3 [80,120] [130,180] [200,230] 表 4 参数m的焦元及其BPA
Table 4. Focal elements and BPA of parameter m
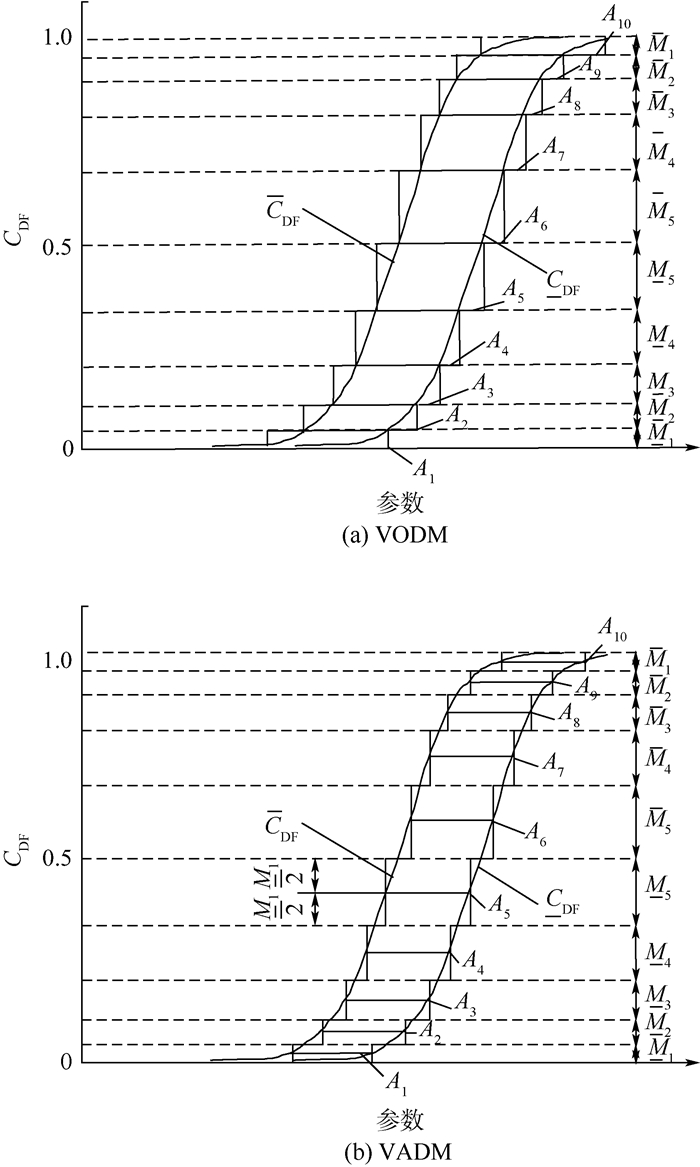
参数 Am, i Mm(Am, i) 1 [10, 10.2] 0.01 2 [10.2, 10.4] 0.05 3 [10.4, 10.6] 0.11 4 [10.6, 10.8] 0.15 5 [10.8, 11] 0.17 6 [11, 11.2] 0.18 7 [11.2, 11.4] 0.16 8 [11.4, 11.6] 0.12 9 [11.6, 11.8] 0.08 10 [11.8.12] 0.02 表 5 不同离散策略下期望μ及其不确定性测度d
Table 5. Expectation μ and uncertainty measure d under different discretization strategies
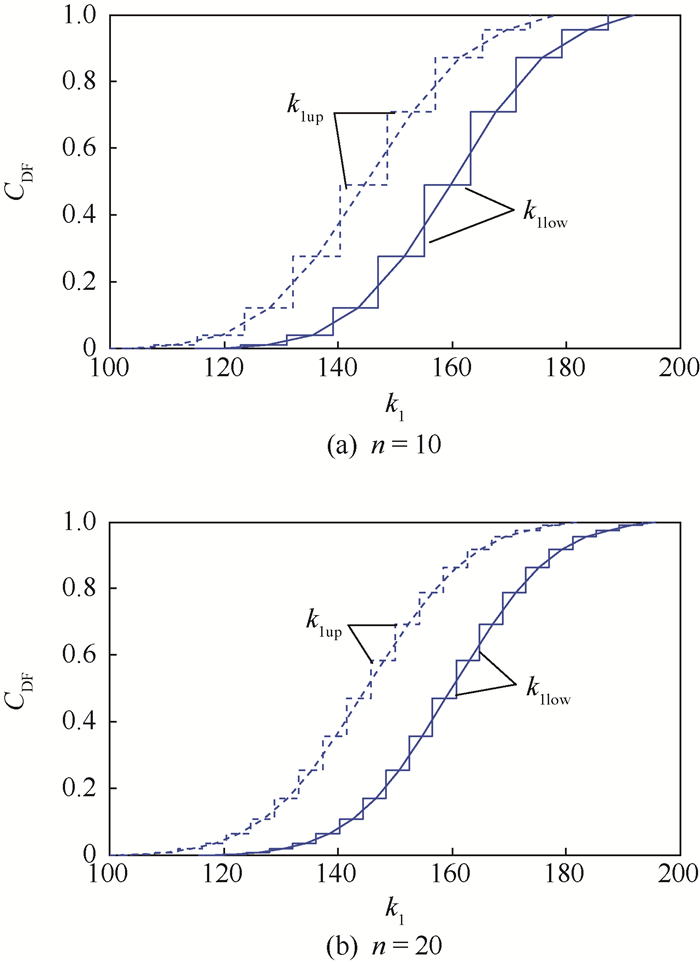
离散策略 μ d ODM(n=10) [1.217 1, 2.716 9] 2.538 VODM(n=10) [1.305 7, 2.693 4] 2.515 ADM(n=10) [1.450 2, 2.399 6] 2.137 VADM(n=10) [1.542 2, 2.373 2] 2.028 ODM(n=20) [1.221 8, 2.708 5] 2.374 VODM(n=20) [1.307 4, 2.682 1] 2.297 ADM(n=20) [1.455 7, 2.396 2] 2.029 VADM(n=20) [1.544 1, 2.366 8] 1.912 表 6 均匀步长离散策略下Ds的下界及其相对误差ΔEA-Binf
Table 6. Lowerbound of Ds and relative errors ΔEA-Binf under uniform step discretization strategy
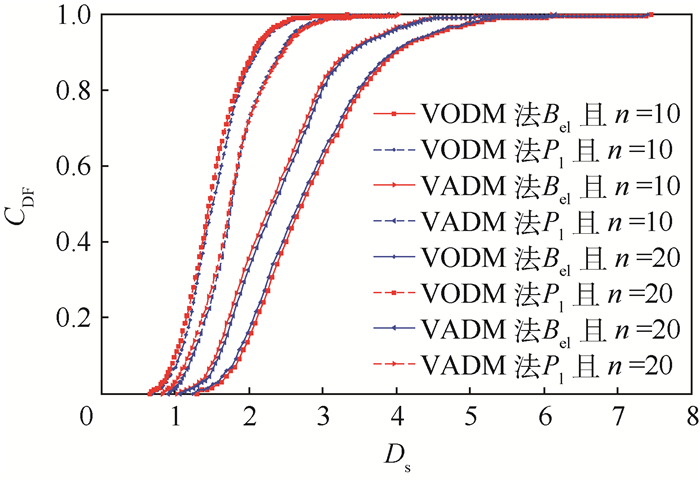
Ds ODM ADM n=10 n=20 ΔEinfA-B/% n=10 n=20 ΔEinfA-B/% 1.3 0.033 6 0.035 2 -4.7 0.110 3 0.114 6 -3.90 1.5 0.095 4 0.097 8 -2.52 0.140 1 0.143 1 -2.14 2 0.312 5 0.316 6 -1.31 0.351 5 0.351 8 -0.09 3 0.665 3 0.669 0 -0.56 0.715 4 0.717 8 -0.34 4 0.962 1 0.961 9 0.08 0.905 0 0.904 5 0.05 5 0.975 5 0.975 2 0.02 0.975 2 0.975 0 0.01 表 7 变步长离散策略下Ds的下界及其相对误差ΔEA-Binf
Table 7. Lowerbound of Ds and relative errors ΔEA-Binf under variable step discretization strategy
Ds VODM VADM n=10 n=20 ΔEinfA-B/% n=10 n=20 ΔEinfA-B/% 1.3 0.043 5 0.044 7 -2.76 0.136 5 0.138 2 -1.26 1.5 0.112 3 0.113 3 -0.89 0.157 1 0.158 4 -0.83 2 0.335 7 0.338 1 -0.71 0.371 5 0.373 5 -0.54 3 0.622 8 0.626 2 -0.55 0.816 3 0.818 7 -0.29 4 0.916 5 0.916 1 0.03 0.951 4 0.951 1 0.03 5 0.979 4 0.979 0 0.02 0.987 2 0.987 0 0.01 -
[1] GIANG P H. Decision making under uncertainty comprising complete ignorance and probability[J].International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2015, 62:27-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2015.05.001 [2] SONG S, LU Z, LI W, et al.The uncertainty importance measures of the structural system in view of mixed uncertain variables[J].Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 2014, 243:25-35. [3] HELTON J C.Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in the presence of stochastic and subjective uncertainty[J].Journal of Statistical Computation & Simulation, 2007, 57(1):3-76. doi: 10.1080/00949659708811803 [4] FERSON S, GINZBURG L R.Different methods are needed to propagate ignorance and variability[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 1996, 54(2):133-144. [5] BAUDRIT C. Comparing methods for joint objective and subjective uncertainty propagation with an example in risk assessment[C]//Proceedings of 4th International Symposium on Imprecise Probabilities and Their Application (ISIPTA'05), 2005: 31-40. [6] GUYONNET D, BAUDRIT C, DUBOIS D.Postprocessing the hybrid method for addressing uncertainty in risk assessments[J].Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2005, 131(12):1750-1754. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2005)131:12(1750) [7] WANG C, QIU Z.Hybrid uncertain analysis for steady-state heat conduction with random and interval parameters[J].International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2015, 80(80):319-328. [8] WALLEY P.Statistical reasoning with imprecise probabilities[M].London:Chapman and Hall, 1991:12-231. [9] DEMPSTER A P.Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multi-valued mapping[J].Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1967, 38(2):325-339. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177698950 [10] SHAFER G.A mathematical theory of evidence[J].Technometrics, 1978, 20(1):1-242. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1978.10489609 [11] SMETS P.The normative representation of quantified beliefs by belief functions[J].Artificial Intelligence, 1997, 92(1-2):229-242. doi: 10.1016/S0004-3702(96)00054-9 [12] ZADEH L A.Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility[J].Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 1978, 1(1):3-28. [13] BAUDRIT C, COUSO I, DUBOIS D, et al.Joint propagation of probability and possibility in risk analysis:Towards a formal framework[J].International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2007, 45(1):82-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2006.07.001 [14] AVEN T.On how to define, understand and describe risk[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2010, 95(6):623-631. [15] YAGER R R.Uncertainty representation using fuzzy measures[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems Man & Cybernetics Part B (Cybernetics), 2002, 32(1):13-20. [16] FLAGE R, BARALDI P, ZIO E, et al.Probability and possibility-based representations of uncertainty in fault tree analysis[J].Risk Analysis, 2013, 33(1):121-133. doi: 10.1111/risk.2013.33.issue-1 [17] HELTON J C, JOHNSON J D, OBERKAMPF W L, et al.Sensitivity analysis in conjunction with evidence theory representations of epistemic uncertainty[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2006, 91(10):1414-1434. [18] GUYONNET D, BOURGINE B, DUBOIS D, et al.Hybrid approach for addressing uncertainty in risk assessments[J].Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2003, 129(1):68-78. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2003)129:1(68) [19] TONON F.Using random set theory to propagate epistemic uncertainty through a mechanical system[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2004, 85(1):169-181. [20] MOLCHANOV I.Theory of random sets[M].Berlin:Springer, 2006:31-210. [21] BERNARDINI A.What are the random and fuzzy sets and how to use them for uncertainty modelling in engineering systems[M].Berlin:Springer, 1999:63-125. [22] DUBOIS D, PRADE H.Random sets and fuzzy interval analysis[J].Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 1991, 42(1):87-101. [23] ALVAREZ D A.On the calculation of the bounds of probability of events using infinite random sets[J].International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2006, 43(3):241-267. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2006.04.005 [24] SADIQ R, NAJJARAN H, KLEINER Y.Investigating evidential reasoning for the interpretation of microbial water quality in a distribution network[J].Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2006, 21(1):63-73. doi: 10.1007/s00477-006-0044-7 [25] GRABISCH M. Dempster-Shafer and possibility theory[M].Berlin:Springer, 2016:377-437. [26] DUBOIS D, FOULLOY L, MAURIS G, et al.Probability-possibility transformations, triangular fuzzy sets, and probabilistic inequalities[J].Reliable Computing, 2004, 10(4):273-297. doi: 10.1023/B:REOM.0000032115.22510.b5 [27] OUSSALAH M.On the probability/possibility transformations:A comparative analysis[J].International Journal of General System, 2000, 29(5):671-718. doi: 10.1080/03081070008960969 [28] 锁斌, 程永生, 曾超, 等.基于证据理论的异类信息统一表示与建模[J].系统仿真学报, 2013, 25(1):6-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ201301004.htmSUO B, CHENG Y S, ZENG C, et al.Unified method of describing and modeling heterogeneous information based on evidence theory[J].Journal of System Simulation, 2013, 25(1):6-11(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ201301004.htm [29] FLOREA M C, JOUSSELME A L, GRENIER D, et al.Approximation techniques for the transformation of fuzzy sets into random sets[J].Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 2008, 159(3):270-288. [30] KOLMOGOROV A N, FOMIN S.Elements of the theory of functions and functional analysis.Vol.1, Metric and normed spaces[M].Rochester:Graylock Press, 1957:372-389. [31] OBERKAMPF W L, HELTON J C, JOSLYN C A, et al.Challenge problems:Uncertainty in system response given uncertain parameters[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2004, 85(1):11-19. -







 下载:
下载: