-
摘要:
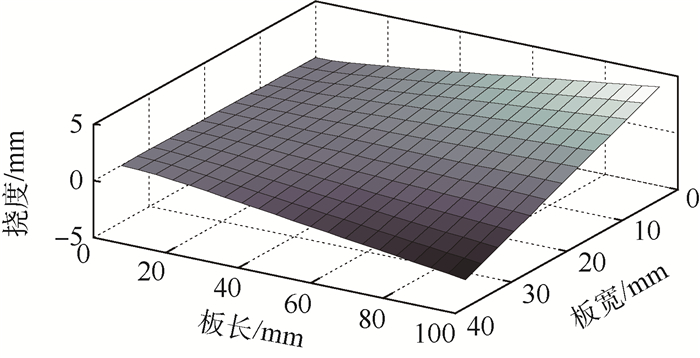
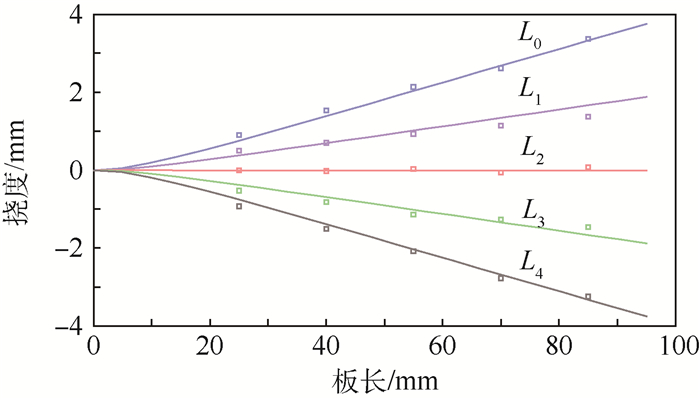
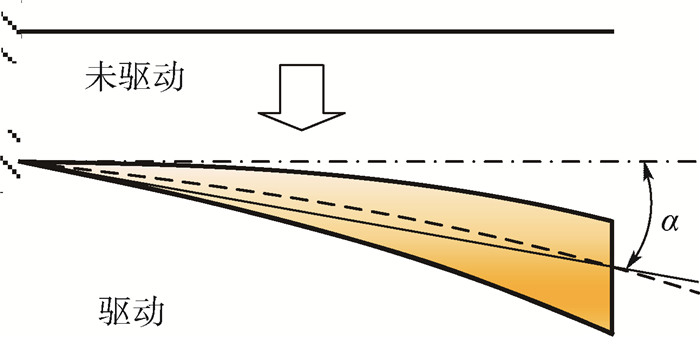
含有主动材料的复合结构越来越多地应用于自适应结构中。主动纤维材料的应用为复合结构带来了新的特性也使其设计更为复杂。针对受压电纤维材料(MFC)驱动的主动材料复合板的变形进行研究,目的在于获得MFC驱动复合板扭曲变形与MFC纤维铺设及驱动模式的关系。基于弹性力学理论建立了受电压作用主动纤维产生的应变与由此导致的复合板的内力、变形之间的关系,并利用Ritz法,通过假设双向梁函数组合级数的位移场建立了该问题的求解方法,经推导得到了MFC驱动下位移场的求解方程,实验结果验证了其有效性。为了评估MFC驱动复合板在不同条件下的驱动效果,针对复合板变形所具有的弯扭耦合特点,在定义复合板截面等效扭转角和等效弯曲角的基础上提出了主动复合板驱动扭曲变形效率的概念和计算方法,利用该方法分析了MFC的铺设角度以及电压驱动模式对复合板扭曲变形效率的影响。依据分析所得到的结果给出了对应不同约束条件的MFC驱动复合板主动纤维布置及驱动模式的选择方案。
Abstract:More and more composite structures containing active materials are applied to adaptive structures. The integration of active materials in structures has brought new characteristics but made the design more complicated. In this paper, the deformation of the active composite plate actuated by the macro fiber material (MFC) is studied. The purpose is to obtain the relationship between the twist deformation of the actuated composite plate and the MFC fiber laying and the actuation mode. Based on the elastic mechanics theory, the relationship between the strain of active fiber actuated by voltage and induced internal force and deformation of the composite plate is established. The solution of the problem is conducted using Ritz's method and taking the displacement function as a linear combination of the two-dimension beam-modes. The solving equation of the displacement field actuated by MFC is derived, and the analytical result is verified by the experiment. In order to evaluate the actuation effect of MFC composite plate under different conditions and to consider the bending-torsion coupling characteristics of composite plate deformation, the concept and the calculation of actuation efficiency of an active composite plate are proposed, which is based on the definition of equivalent bending and twist angle of section. Then the evolution of the actuation efficiency with the laying angle of MFC and the mode of input voltage is analyzed. Corresponding to different constraint conditions, the laying of piezoelectric fiber-direction and the selection of actuation-mode are given based on the obtained analysis results.
-
Key words:
- macro fiber composite /
- active composite plate /
- twist deformation /
- fiber direction /
- actuation mode
-
表 1 MFC和基板的材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of MFC and substrate
材料 E/GPa υ G/GPa t/mm Λ/10-6 E1 E2 υ12 υ21 M-8528-F1 30.336 15.857 0.31 0.16 5.515 0.3 [1 350, 0, 0]T 基底 44 0.27 3.1 0.3 — 表 2 试件的几何参数
Table 2. Geometric parameters of specimen
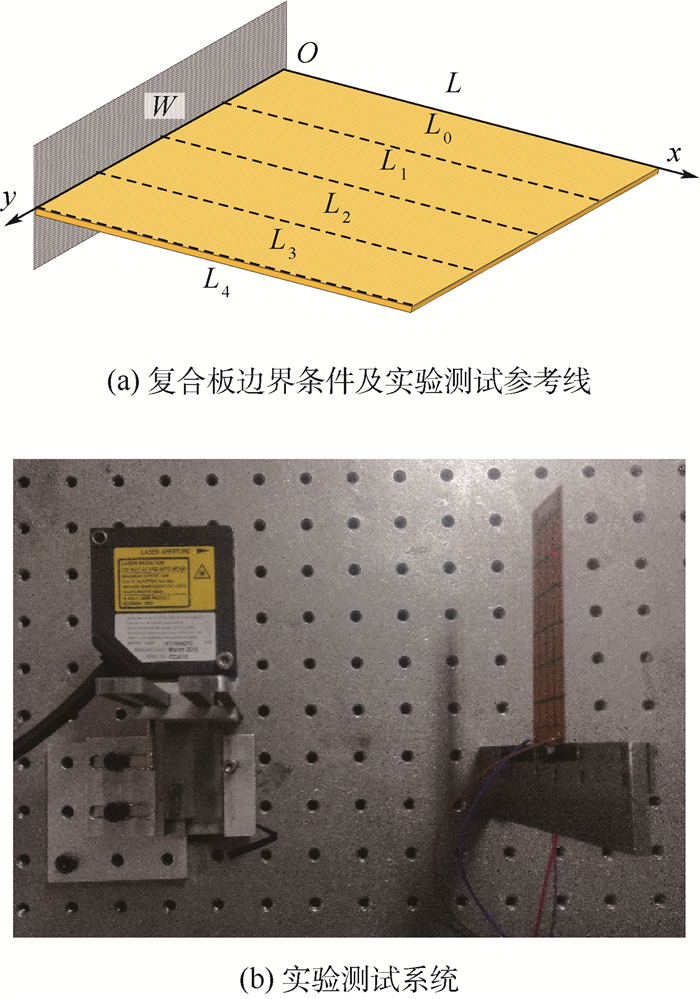
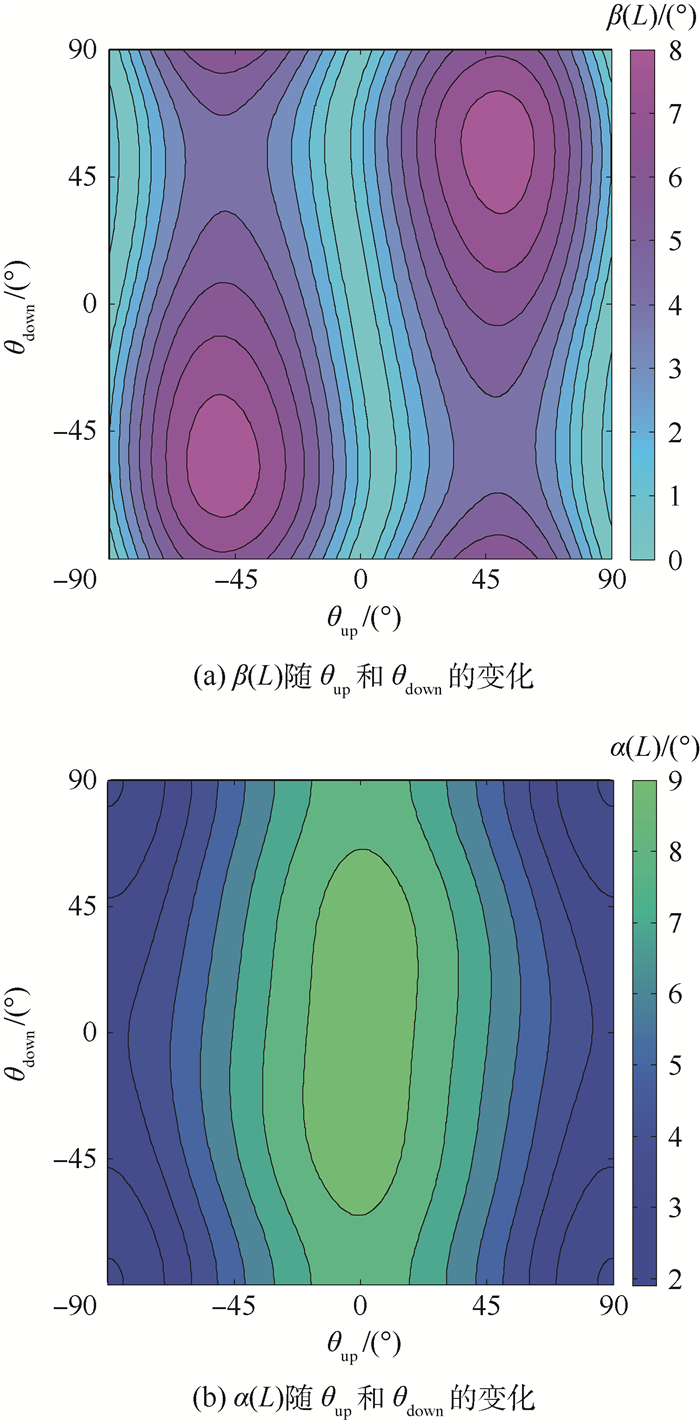
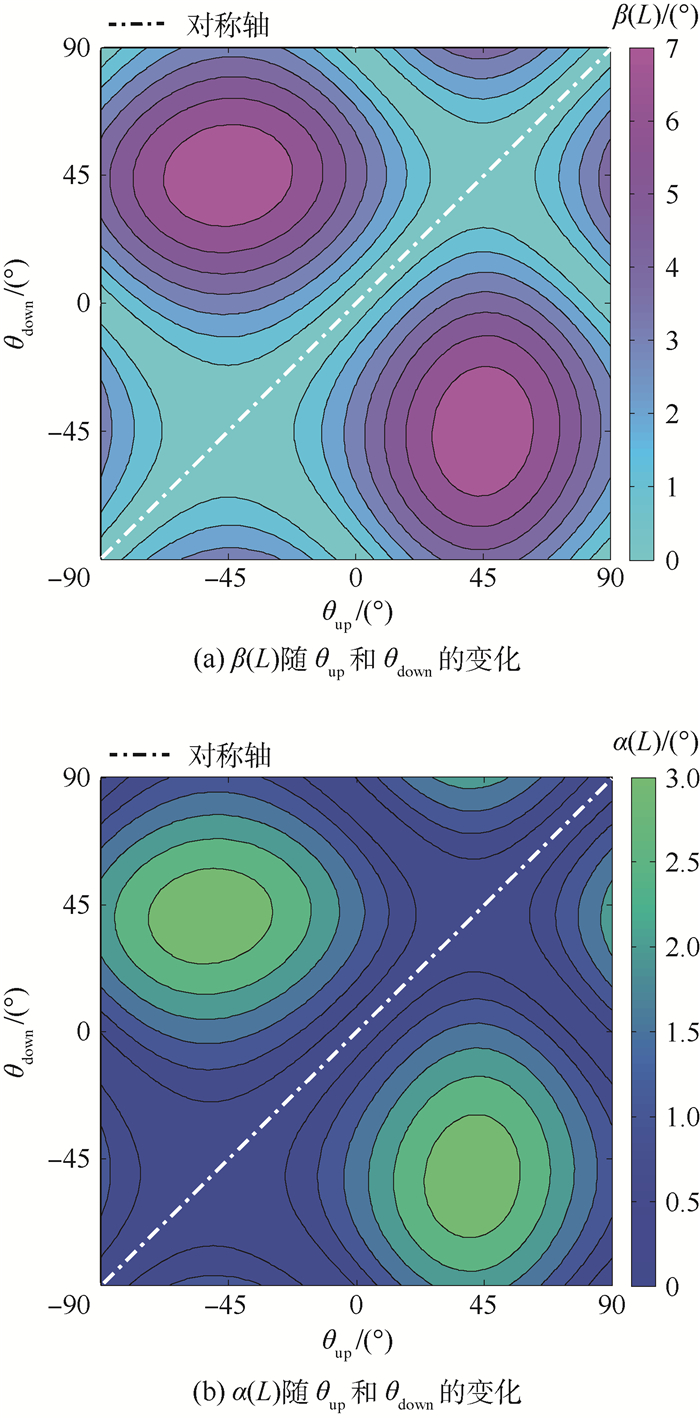
试件 布置形式 x方向边界条件 y方向边界条件 W/mm L/mm θup/(°) θdown/(°) 1# bimorph C-F F-F 35 95 45 -45 表 3 CFFF约束的MFC复合板在2种驱动模式下的自由边截面等效扭转角极值
Table 3. Maximum equivalent torsional angles of free edge section of MFC composite plate under two actuation modes with constraint condition of CFFF
L/W 驱动模式 βmax/(°) θup/(°) θdown/(°) 2 +/+ 15.75 -46.8 46.8 +/- 9.50 46.8 54 1 +/+ 13.90 -47.7 47.7 +/- 8.59 50.4 55.8 0.25 +/+ 5.82 -50.4 50.4 +/- 3.93 55.8 57.6 表 4 CFCF约束的MFC复合板在2种驱动模式下的自由边截面等效扭转角极值
Table 4. Maximum equivalent torsional angles of free edge section of MFC composite plate under two actuation modes with constraint condition of CFCF
L/W 驱动模式 βmax/(°) θup/(°) θdown/(°) 4 +/+ 3.05 -34.2 50.4 +/- 3.98 41.4 -34.2 1 +/+ 7.84 -45 45 +/- 8.93 45 45 0.25 +/+ 3.05 -55.8 39.6 +/- 3.98 48.6 55.8 -
[1] BARBARINO S, BILGEN O, AJAJ R M, et al.A review of morphing aircraft[J].Journal of Intelligent Material Systems & Structures, 2011, 22(9):823-877. [2] SOFLA A Y N, MEGUID S A, TAN K T, et al.Shape morphing of aircraft wing:Status and challenges[J].Materials & Design, 2010, 31(3):1284-1292. [3] 冷劲松, 孙健, 刘彦菊.智能材料和结构在变体飞行器上的应用现状与前景展望[J].航空学报, 2014, 35(1): 29-45.LENG J S, SUN J, LIU Y J.Application status and future prospect of smart materials and structures in morphing aircraft[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 29-45 (in Chinese). [4] MANZO J, GARCIA E, WICKENHEISER A, et al.Design of a shape-memory alloy actuated macro-scale morphing aircraft mechanism[J].Proceedings of SPIE-the International Society for Optical Engineering, 2005, 5764:232-240. doi: 10.1117/12.601372.full [5] MANZO J, GARCIA E.Demonstration of an in situ morphing hyperelliptical cambered span wing mechanism[J].Smart Materials & Structures, 2010, 19(19):328-335. [6] SHELTON A, TOMAR A, PRASAD J, et al.Active multiple winglets for improved unmanned-aerial-vehicle performance[J].Journal of Aircraft, 2015, 43(43):110-116. [7] BARTLEY-CHO J D, WANG D P, MARTIN C A, et al.Development of high-rate, adaptive trailing edge control surface for the smart wing phase 2 wind tunnel model[J].Journal of Intelligent Material Systems & Structures, 2004, 15(4):279-291. doi: 10.1177/1045389X04042798 [8] BARRETT R M.Design, fabrication, and testing of a new twist-active wing design[J].Proceedings of SPIE-the International Society for Optical Engineering, 1998, 3329. doi: 10.1117/12.316919.full [9] 柴双双, 张卫平, 柯希俊, 等.仿昆扑翼微飞行器中压电驱动器的性能参数分析[J].上海交通大学学报, 2015, 49(5):663-668.CHAI S S, ZHANG W P, KE X J, et al.Piezoelectric actuators for insect-like flapping-wing micro aerial vehicle[J].Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(5):663-668(in Chinese). [10] 程春晓, 李道春, 向锦武, 等.柔性后缘可变形机翼气动特性分析[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(2):360-367.CHENG C X, LI D C, XIANG J W, et al.Analysis on aerodynamic characteristics of morphing wing with flexible trailing edge[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(2):360-367(in Chinese). [11] LIN X J, ZHOU K C, ZHANG X Y.Development, modeling and application of piezoelectric fiber composites[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1):98-107. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62435-8 [12] COBB R, BROWNING J, CANFIELD R, et al. F-16 ventral fin buffet alleviation using piezoelectric actuators[C]//AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2009. [13] OHANIAN O, HICKLING C, STILTNER B, et al. Piezoelectric morphing versus servo-actuated MAV control surfaces[C]//AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Resson: AIAA, 2012: 23-26. [14] LIU S, TONG L, LIN Z.Simultaneous optimization of control parameters and configurations of PZT actuators for morphing structural shapes[J].Finite Elements in Analysis & Design, 2008, 44(6-7):417-424. [15] LUO Q, TONG L.Design and testing for shape control of piezoelectric structures using topology optimization[J].Engineering Structures, 2015, 97:90-104. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.04.006 [16] QUAN N, TONG L.Shape control of smart composite plate with non-rectangular piezoelectric actuators[J].Composite Structures, 2004, 66(1-4):207-214. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.04.039 [17] MUKHERJEE A, JOSHI S.Piezoelectric sensor and actuator spatial design for shape control of piezolaminated plates[J].AIAA Journal, 2015, 40(6):1204-1210. [18] BÜTER A, BREITBACH E.Adaptive blade twist-calculations and experimental results[J].Aerospace Science & Technology, 1999, 4(5):309-319. [19] 曹志远.板壳振动理论[M].北京:中国铁道出版社, 1989:32-51.CAO Z Y.Vibration theory of plates and shells[M].Beijing:China Railway Publishing House, 1989:32-51(in Chinese). [20] 毛柳伟, 王安稳, 胡明勇.粘-弹层合悬臂板瞬态响应的近似解析解[J].固体力学学报, 2010, 31(4):379-384.MAO L W, WANG A W, HU M Y.Approximate analytical solution for transient response of a visco-elastic laminated cantilever plate[J].Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2010, 31(4):379-384(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: