-
摘要:
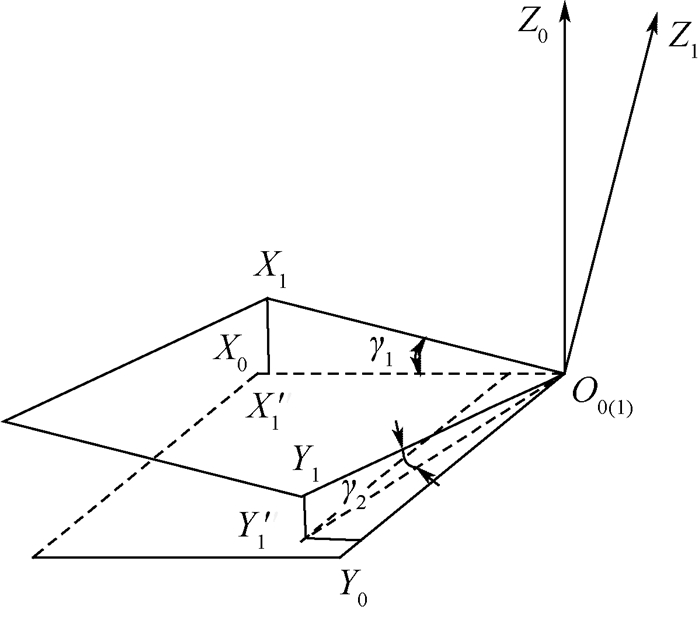
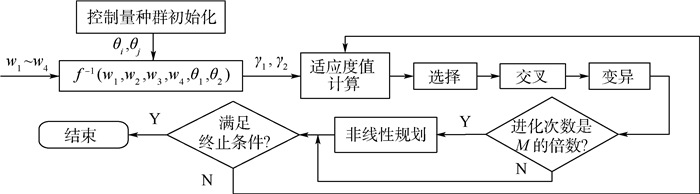
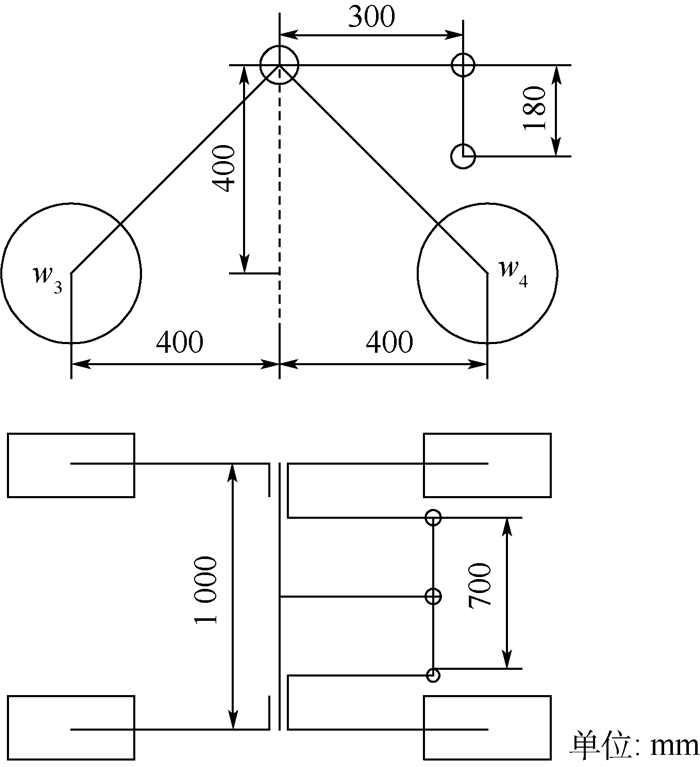
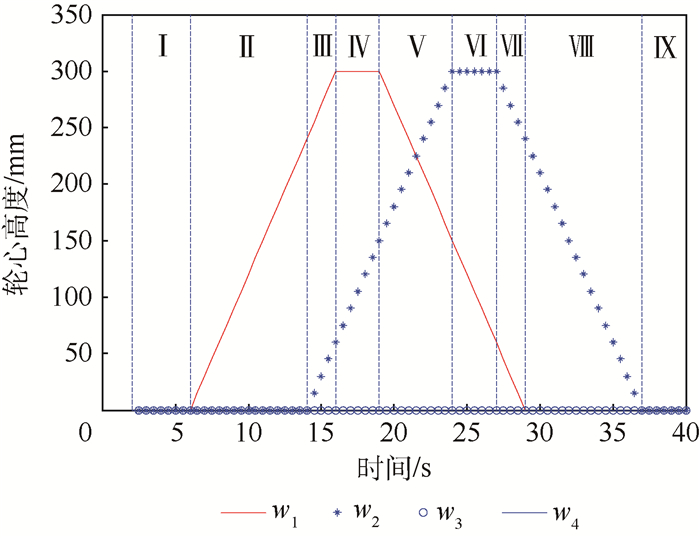
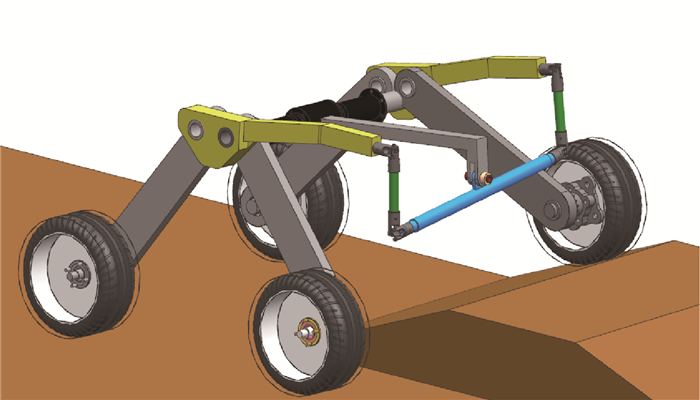
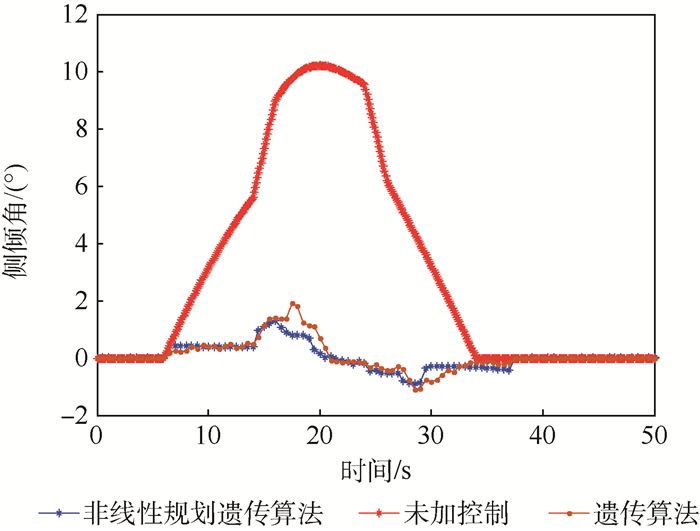
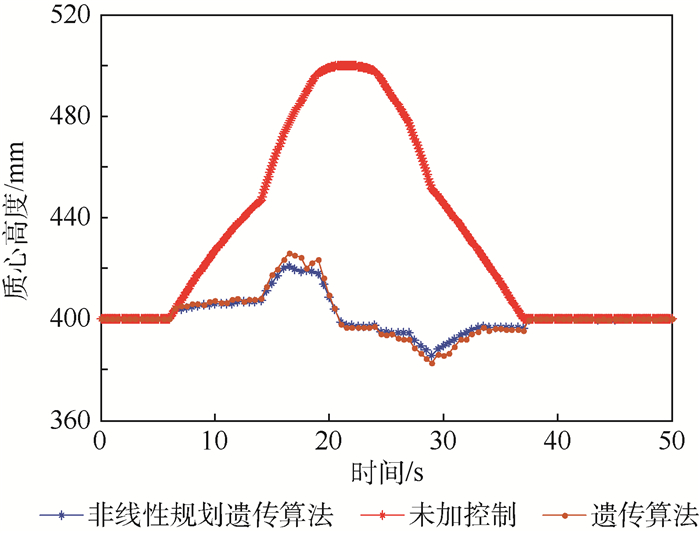
以具有平衡摇臂机构的移动机器人为研究对象,设计一种基于非线性规划遗传算法的姿态控制算法,提高越障过程中工作平台的平稳性。首先简化平衡摇臂机构并定义表征移动机器人空间状态的姿态参数。利用空间机构学位姿变换方程推导出所定义的空间姿态参数与轮心相对位置之间的数学关系。然后设计非线性规划遗传算法,以移动机器人稳定性条件为约束设计遗传算法适应度函数并求解目标姿态控制参数。为验证所设计的姿态控制算法,在ADAMS软件中搭建移动机器人三维模型和障碍路面模型,并联合MATLAB/Simulink对移动机器人进行了运动学仿真。仿真结果表明在该姿态算法的控制下,与不施加主动姿态控制相比较,移动机器人通过搭建的障碍路面时最大侧倾角由10.8°降低到了1.8°,质心高度变化幅值度由96.4 mm降低到了34.9 mm,证明了姿态控制算法的有效性。
Abstract:In order to improve the stability of working platform in the process of obstacle negotiation, with balancing-arm mobile robot as research object, an attitude control algorithm was designed based on nonlinear programming genetic algorithm. First, the simplified model of balancing-arm mechanism was built and spatial posture parameters were defined to character the space state of robot. Mathematical relationship between spatial posture parameters and wheel center positions was deduced by coordinate transformation equation based on spatial mechanism. Then, a nonlinear programming genetic algorithm was designed. The genetic algorithm fitness function used to solve objective control parameters was established under the constraint of stability. To verify the performance of the proposed attitude control algorithm, 3D model of the mobile robot and road were built in the ADAMS software, and then kinematics simulation studies were carried out by ADAMS and MATLAB/Simulink. The results of simulation show that when balance-arm mobile robot passes through the designed obstacles with the designed controller, the roll angle falls from 10.8° to 1.8° compared with no controller and the amplitude of wheel center position falls from 96.4 mm to 34.9 mm as also. The simulation results demonstrate the validity of the proposed attitude control algorithm.
-
Key words:
- balancing-arm /
- kinematical modeling /
- spatial attitude /
- genetic algorithm /
- nonlinear programming
-
-
[1] 马金猛, 李小凡, 姚辰, 等.地面移动机器人越障动力学建模与分析[J].机器人, 2008, 30(3):273-278.MA J M, LI X F, YAO C, et al.Dynamic modeling and analysis for obstacle negotiation of ground mobile robot[J].Robot, 2008, 30(3):273-278(in Chinese). [2] 叶锦华. 不确定非完整轮式移动机器人的运动控制研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2013: 6-13.YE J H. Research on motion control of uncertain nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2013: 6-13(in Chinese). [3] 王佐伟, 梁斌, 吴宏鑫.六轮月球探测车运动学建模与分析[J].宇航学报, 2003, 24(5):1-10.WANG Z W, LIANG B, WU H X.Kinematical modeling and analysis of six-wheel lunar rover[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2003, 24(5):1-10(in Chinese). [4] 徐坤, 郑羿, 丁希仑, 等.六轮腿式机器人结构设计与运动模式分析[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(1):59-71.XU K, ZHENG Y, DING X L, et al.Structure designe and motion mode analysis of a six wheel-legged robot[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(1):59-71(in Chinese). [5] 周开波, 王旭永, 罗小桃, 等.摇臂式六轮探测车空间姿态建模与求解[J].上海交通大学学报, 2013, 47(7):1093-1098.ZHOU K B, WANG X Y, LUO X T, et al.Spatital attitude model of six-wheeled rocker rover and its mathematical solution[J].Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2013, 47(7):1093-1098(in Chinese). [6] 崔莹, 高峰.可变直径轮月球探测车运动学建模与分析[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2008, 34(3):348-352.CUI Y, GAO F.Kinematic modeling and analysis of variable diameter wheeled lunar rover[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008, 34(3):348-352(in Chinese). [7] PANSINI V, MONNET A, SALLERON J, et al.Development of a genetic algorithm for multi-objective assembly line balancing using multiple assignment approach[J].The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 77(5):1419-1432. [8] 陶建国, 邓宗全, 高海波, 等.月球车连杆式差速平衡机构的运动学分析[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2009, 41(9):21-26.TAO J G, DENG Z Q, GAO H B, et al.Kinematics analysis of differential bar linkage on lunar rover[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009, 41(9):21-26(in Chinese). [9] MICHALEWICZ Z, JANIKOW C Z, KRAWCZYK J B.A modified genetic algorithm for optimal control problems[J].Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 1992, 23(12):83-94. [10] 朱会霞, 王福林, 张勇, 等.改进遗传算法优化非线性规划问题[J].数学的实践与认识, 2013, 43(7):117-125.ZHU H X, WANG F L, ZHANG Y, et al.Improved genetic algorithm to optimize the nonlinear programming problem[J].Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2013, 43(7):117-125(in Chinese). [11] KWOK D P, SHENG F. Genetic algorithm and simulated annealing for optimal robot arm PID control[C]//IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1994, 2: 707-713. [12] FU Y Y, KO C N, LEE T L, et al.A nonlinear programming method for time-optimal control of an omni-directional mobile robot[J].Journal of Vibration & Control, 2008, 14(14):1729-1747. doi: 10.1177/1077546307086442 [13] CHEN J L, CHANG W D.Feedback linearization control of a two-link robot using a multi-crossover genetic algorithm[J].Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36(2):4154-4159. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.01.048 [14] 史峰, 王辉, 郁磊, 等.MATLAB智能算法[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 2011:17-24.SHI F, WANG H, YU L, et al.MATLAB intelligent algorithm[M].Beijing:Beihang University Press, 2011:17-24(in Chinese). [15] 李金良, 包继华, 于岩, 等.基于遗传算法的腿轮式机器人运动姿态优化[J].机床与液压, 2010, 38(21):23-25.LI J L, BAO J H, YU Y, et al.Kinetic optimization for a leg-wheeled robot based on genetic algorithm[J].Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2010, 38(21):23-25(in Chinese). [16] ZHOU L F, HONG B R.A knowledge based genetic algorithm for path planning of a mobile robot[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(5):911-914. 期刊类型引用(8)
1. 姜惠,唐小虎,张旭烽,徐国艳,高峰. 丘陵山地姿态调整轮式拖拉机运动控制研究. 农业机械学报. 2024(06): 392-403 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 刘辉,刘宝帅,廖登廷,韩立金,崔山. 基于前馈补偿的轮腿式机动平台姿态自适应控制. 兵工学报. 2023(09): 2756-2767 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 尚哲,王挺,徐瑶,吴英彪,邵沛瑶,邵士亮. 六轮摇臂移动机器人结构设计与越障动力学研究. 兵工学报. 2023(11): 3478-3488 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 付苗苗,沈红伟. 基于激光与视觉感知的机器人姿态自动控制研究. 激光杂志. 2021(05): 138-142 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 王志龙,党新安. 无速度平衡自行车的积分分离PID控制算法仿真. 计算机仿真. 2019(04): 99-102 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 张丹,郝尚清,宋胜伟. 运动状态检测的采煤机捷联惯导系统误差组合算法. 黑龙江科技大学学报. 2019(03): 299-303 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 于燕,李宁. 基于北斗和激光雷达的机器人导航控制方法研究. 中国农机化学报. 2019(08): 165-170 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 马芳武,倪利伟,吴量,聂家弘,徐广健. 轮腿式全地形移动机器人位姿闭环控制. 吉林大学学报(工学版). 2019(06): 1745-1755 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(8)
-








 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术

