Path following of underactuated USV based on modified integral line-of-sight guidance strategies
-
摘要:
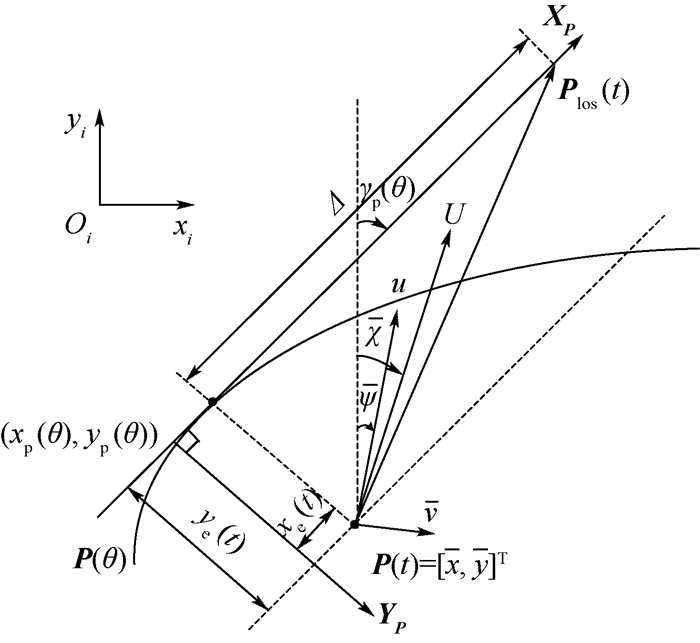
路径跟踪控制是无人水面艇(USV)自主完成各项任务使命的关键技术之一,受到国内外运动控制领域的普遍关注。为提高风浪流等外界环境干扰下,无人水面艇(USV)路径跟踪控制的准确性和鲁棒性,研究海流等外界扰动环境下一类非对称欠驱动无人水面艇的路径跟踪问题,提出了2种改进积分视线(ILOS)导引策略,并基于改进导引策略和反馈控制思想实现了无人水面艇水平面的路径跟踪。与传统ILOS导引策略相比,第1种改进策略具有变积分增益能够避免积分饱和及超调现象;第2种改进策略在前者的基础上将前视距离设计为时变量,使得无人水面艇操纵更加灵活,其中积分增益和前视距离均为垂直距离误差的不同函数,引导无人水面艇灵活快速地跟踪期望路径。基于级联系统理论证明了当所有控制目标实现时,控制系统为全局
k -指数稳定(GKES)的,理论分析和仿真实验证明了算法的有效性和先进性。-
关键词:
- 欠驱动控制 /
- 无人水面艇(USV) /
- 积分视线(ILOS)导引 /
- 路径跟踪 /
- 级联系统 /
- 稳定性证明
Abstract:Path following control is one of the key technologies for unmanned surface vehicle (USV) to complete its mission, which is widely concerned by the field of motion control at home and abroad. In order to improve the accuracy and robustness of USV's path following control under the disturbance of the external environment such as wind, wave and flow, path following control problem of the asymmetry underactuated USV under external disturbances such as current is discussed, and two modified integral line-of-sight(ILOS) guidance strategies are proposed. Based on the modified guidance strategies and feedback control theory, path following of the USV at horizontal level is realized. Compared to the conventional ILOS guidance strategy, the first modified strategy with time-varying integral gain can avoid integral windup and overshoot phenomenon; on the basis of the first modified strategy, the lookahead distance is designed as a time-varying element in the second modified strategy, making the USV control more flexible. In the modified strategies, integral gain and lookahead distance are all computed as different functions of cross-track error, which can conduce the USV to converge to desired path in an elegant and fast manner. Based on the cascaded system theory, the control system proposed is proved to be global
k -exponential stable (GKES) when the target tasks are all achieved. The theoretical analysis and simulations show effectiveness and advancement of the proposed method. -
表 1 USV模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of USV
参数 数值 m11 25.8 m22 33.8 m23 -11.748 m32 -11.748 m33 6.813 b11 1 b22 0 b32 1 d11 2.0 d22 7.0 d23 -2.542 5 d32 -2.542 5 d33 1.422 -
[1] 张树凯, 刘正江, 张显库, 等.无人船艇的发展及展望[J].世界海运, 2015, 38(9):29-36. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_sjhy201509008.aspxZHANG S K, LIU Z J, ZHANG X K, et al.The development and outlook of unmanned vessel[J]. World Shipping, 2015, 38(9):29-36(in Chinese). http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_sjhy201509008.aspx [2] 薛春祥, 黄孝鹏, 朱咸军, 等.外军无人系统现状与发展趋势[J].雷达与对抗, 2016(36):1-5. http://www.doc88.com/p-0886924547542.htmlXUE C X, HUANG X P, ZHU X J, et al.Status quo and development trends of foreign military's unmanned systems[J]. Radar & ECM, 2016(36):1-5(in Chinese). http://www.doc88.com/p-0886924547542.html [3] FOSSEN T I.Handbook of marine craft hydrodynamics and motion control[M]. Hudson County:John Wiley & Sons, 2011:60-89. [4] CAHARIJA W, PETTERSEN K Y, SØRENSEN A J, et al.Relative velocity control and integral LOS for path following of autonomous surface vessels:Merging intuition with theory[J]. Engineering for the Marine Environment, 2014, 228(2):180-191. doi: 10.1177/1475090213512293 [5] 田勇, 王丹, 彭周华, 等.无人水面艇直线航迹跟踪控制器的设计与验证[J].大连海事大学学报, 2015, 41(4):14-18. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97801A/201603/668294658.htmlTIAN Y, WANG D, PENG Z H, et al.Design and validation of path tracking controller for USV along straight-lines[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2015, 41(4):14-18(in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97801A/201603/668294658.html [6] FOSSEN T I, LEKKAS A M.Direct and indirect adaptive integral line-of-sight path-following controllers for marine craft exposed to ocean currents[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2015, 28(3):20-35. doi: 10.1002/acs.2550/citedby [7] BØRHAUG E, PAVLOV A, PETTERSEN K Y. Integral LOS control for path following of underactuated marine surface vessels in the presence of constant ocean currents[C]//Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 4984-4991. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4739352 [8] WANG H, WANG D, PENG Z H.Adaptive neural control for cooperative path following of marine surface vehicles:State and output feedback[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2016, 47(2):343-359. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2015.1056274 [9] FREDRIKSEN E, PETTERSEN K Y.Global-exponential waypoint maneuvering of ships:Theory and experiments[J]. Automatica, 2006, 42(4):677-687. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2005.12.020 [10] FOSSEN T I, PETTERSEN K Y, GALEAZZI R.Line-of-sight path following for Dubins paths with adaptive sideslip compensation of drift forces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23(2):820-827. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2338354 [11] LEKKAS A M, FOSSEN T I.Integral LOS path following for curved paths based on a monotone cubic Hermite spline parametrization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2014, 22(6):2287-2301. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2306774 [12] ZHENG Z W, HUO W, WU Z.Direct-adaptive fuzzy path following control for an autonomous airship[J]. Control and Decision, 2014, 29(3):1418-1424. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285989220_Direct-adaptive_fuzzy_path_following_control_for_an_autonomous_airship [13] WⅡG M S, PETTERSEN K Y, KROGSTAD T R.Uniform semiglobal exponential stability of integral line-of-sight guidance laws[J]. IFAC Papers Online, 2015, 48(16):61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.10.259 [14] FOSSEN T I, PETTERSEN K Y.On uniform semiglobal exponential stability (USGES) of proportional line-of-sight guidance laws[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(11):2912-2917. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.018 [15] BREIVIK M. Nonlinear maneuvering control of underactuated ships[D]. Trondheim: Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2003: 10-30. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215523100_Nonlinear_Maneuvering_Control_of_Underactuated_Ships -







 下载:
下载: