-
摘要:
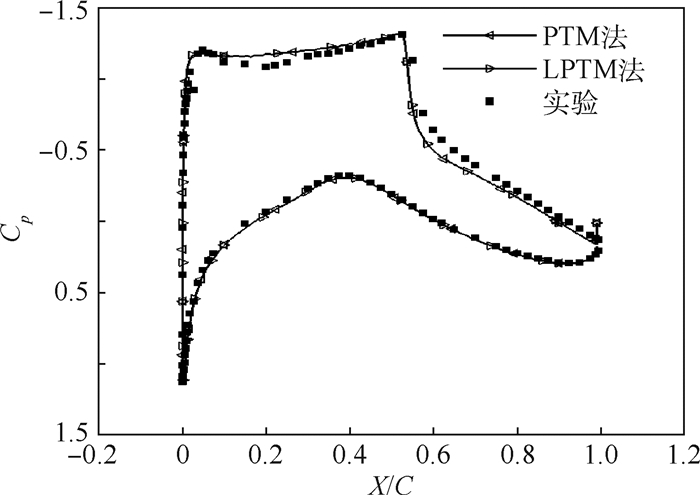
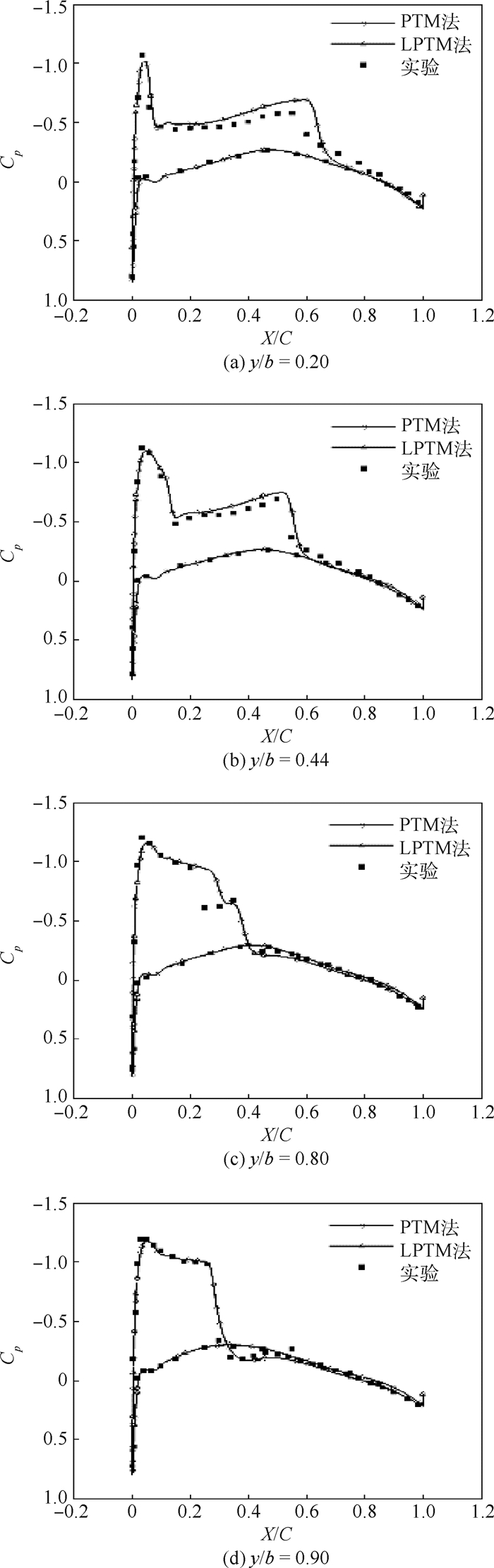
跨声速定常流场的隐式求解相当于使用牛顿迭代法求解一个非线性方程组。为满足牛顿迭代收敛性的要求,通常需要对所求解问题进行全局化处理。在同伦延拓的框架内,提出了一种基于拉普拉斯算子的方程延拓方法,提高了定常流场隐式求解收敛速度。针对定常流场通常初始化为均匀来流的特点,一方面利用拉普拉斯算子的椭圆性加快边界条件信息向流场内部的传播,另一方面利用拉普拉斯算子的线性和正定性改善延拓问题的正则性,综合两者增加拟牛顿算法的稳定性,提高可用CFL数,最终达到提高流场求解效率的目的。由于流场问题的复杂性和非线性,难以通过理论分析得出先验的最优非线性求解策略。因此,通过无黏NACA0012翼型、湍流RAE2822翼型和三维ONERA M6机翼等算例的数值实验,研究了拉普拉斯项参数对收敛效率的影响,给出了效率较优的参数组合,验证了本文方法在跨声速情况下相对于经典伪时间推进法可以节约20%以上的CPU计算时间。
Abstract:The implicit solving approach of steady transonic flow field equals a Newton iteration for a nonlinear equation system. Globalization of Newton iteration is usually necessary in practice in order to fulfill the convergence requirement. In the framework of homogenous continuation, a Laplace operator based function continuation method which accelerates convergence of implicit solving of steady flow field is proposed. Considering that the steady flow field is usually initialized as uniform freestream condition, the Laplace operator is employed to speed up information propagation from wall boundary to internal flow field due to its ellipticity and to improve regularity of the problem due to its linearity and symmetric positive definite property. Thus the stability of Newton's method is improved then larger CFL number could be employed and finally the flow field solving efficiency is improved. Due to the complexity and nonlinearity of the flow field problem, a priori optimal nonlinear solving strategy is impossible to be obtained through theoretical analysis. Thus, the effect of Laplacian coefficient on convergence efficiency is investigated through numerical experiments on inviscid NACA0012 airfoil, turbulent RAE2822 airfoil and ONERA M6 3D wing test cases. Generally pragmatic combination of iteration parameters are also given and the proposed method is proved to gain over 20% saving in CPU computing time compared with the classic pseudo time marching method under transonic condition.
-
Key words:
- nonlinear equations /
- implicit scheme /
- Newton's method /
- aerodynamics /
- transonic /
- steady flow
-
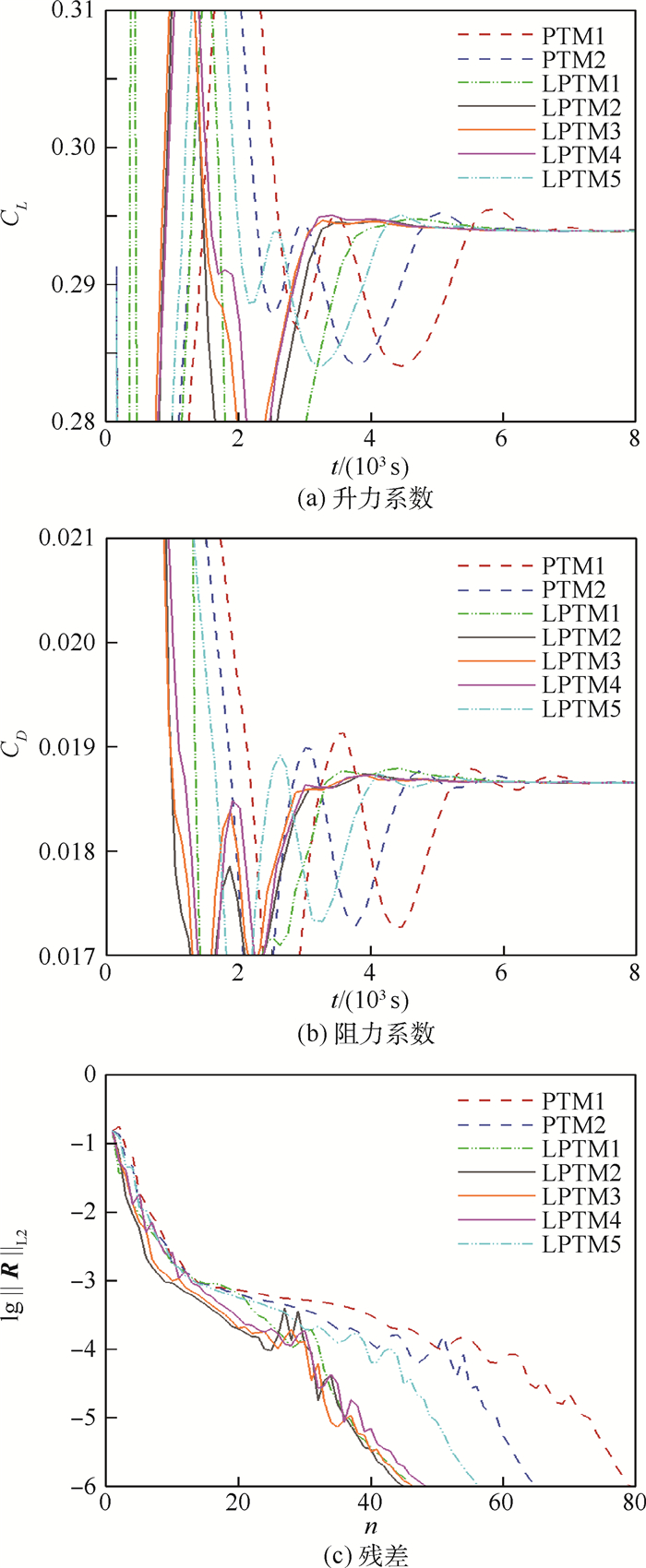
表 1 无黏NACA0012翼型算例的延拓参数和收敛效率
Table 1. Continuation parameters and convergence efficiency of invicid NACA0012 airfoil test case
算例 CFL0 cLP0 n t/s 相对时间节约/% PTM1 6 152 38.79 -28.2 PTM2 8 109 30.25 0 LPTM1 20 5×10-2 67 25.77 14.8 LPTM2 20 5×10-3 66 22.07 27.0 LPTM3 20 1×10-3 64 22.50 25.6 LPTM4 20 5×10-4 62 21.37 29.4 LPTM5 10 5×10-5 92 25.56 15.5 表 2 湍流RAE2822翼型算例的延拓参数和收敛效率
Table 2. Continuation parameters and convergence efficiency for turbulent RAE2822 airfoil test case
算例 CFL0 cLP0 n t/s 相对时间节约/% PTM1 3 94 51.00 -20.4 PTM2 4 78 42.37 0 LPTM1 8 5×10-4 55 36.86 13.0 LPTM2 8 5×10-5 52 31.43 25.8 LPTM3 8 1×10-5 56 33.25 21.5 LPTM4 8 5×10-6 57 32.80 22.6 LPTM5 6 5×10-7 65 36.52 13.8 表 3 ONERA M6机翼算例的延拓参数和收敛效率
Table 3. Continuation parameters and convergence efficiency for 3D ONERA M6 wing test case
算例 CFL0 cLP0 n t/s 相对时间节约/% PTM1 3 80 8 864.73 -12.5 PTM2 4 66 7 877.23 0 LPTM1 10 5×10-4 48 7 167.50 9.0 LPTM2 10 5×10-5 42 6 231.59 20.9 LPTM3 10 1×10-5 43 6 074.64 22.9 LPTM4 10 5×10-6 45 6 154.65 21.9 LPTM5 5 5×10-7 58 7 190.52 8.7 -
[1] GEUZAINE P.Newton-Krylov strategy for compressible turbulent flows on unstructured meshes[J].AIAA Journal, 2001, 39(3):528-531. [2] WONG J S, DARMOFAL D L, PERAIRE J.The solution of the compressible Euler equations at low mach numbers using a stabilized finite element algorithm[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 190(43-44):5719-5737. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(01)00193-1 [3] DENNIS J, SCHNABEL R.Numerical methods for unconstrained optimization and nonlinear equations[M].Philadelphia:Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1996:116-126. [4] MICHALAK C, OLLIVIER-GOOCH C.Globalized matrix-explicit Newton-GMRES for the high-order accurate solution of the euler equations[J].Computers & Fluids, 2010, 39(7):1156-1167. [5] BROWN D A, ZINGG D W. Advances in homotopy continuation methods in computational fluid dynamics: AIAA-2013-2944[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2013. doi: 10.2514/6.2013-2944 [6] LYRA P R M, MORGAN K.A review and comparative study of upwind biased schemes for compressible flow computation.Part Ⅲ:Multidimensional extension on unstructured grids[J].Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2002, 9(3):207-256. doi: 10.1007/BF02818932 [7] KUZMIN D, LOHNER R, TUREK S.Flux-corrected transport:Principles, algorithms, and applications[M].2nd ed.Berlin:Springer, 2012:193-238. [8] KUZMIN D, LOHNER R, TUREK S.Flux-corrected transport:Principles, algorithms, and applications[M].Berlin:Springer, 2005:207-250. [9] COFFEY T S, KELLEY C T, KEYES D E.Pseudotransient continuation and differential-algebraic equations[J].SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2003, 25(2):553-569. doi: 10.1137/S106482750241044X [10] KELLEY C T, LIAO L Z, QI L, et al.Projected pseudotransient continuation[J].SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2008, 46(6):3071-3083. doi: 10.1137/07069866X [11] CEZE M, FIDKOWSKI K J. A robust adaptive solution strategy for high-order implicit CFD solvers: AIAA-2011-3696[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [12] CEZE M, FIDKOWSKI K J.Constrained pseudo-transient continuation[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2015, 102(11):1683-1703. doi: 10.1002/nme.v102.11 [13] YOUNG D P, MELVIN R G, BIETERMAN M B, et al.Global convergence of inexact Newton methods for transonic flow[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1990, 11(8):1075-1095. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0363 [14] HICKEN J, BUCKLEY H, OSUSKY M, et al. Dissipation-based continuation: A globalization for inexact-Newton solvers: AIAA-2011-3237[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [15] HICKEN J, ZINGG D. Globalization strategies for inexact-Newton solvers: AIAA-2009-4139[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-4139 [16] POLLOCK S.A regularized Newton-like method for nonlinear PDE[J].Numerical Functional Analysis and Optimization, 2015, 36(11):1493-1511. doi: 10.1080/01630563.2015.1069328 [17] KNOLL D A, KEYES D E.Jacobian-free Newton-Krylov methods:A survey of approaches and applications[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2004, 193(2):357-397. [18] BLAZEK J.Computational fluid dynamics:Principles and applications[M].2nd ed. Oxford:Elsevier Science, 2005:227-270. [19] SPALART P R, ALLMARAS S R. A one-equatlon turbulence model for aerodynamic flows: AIAA-1992-0439[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1992. [20] POLYANIN A D, NAZAIKINSKII V E.Handbook of linear partial differential equations for engineers and scientists[M].2nd ed.Boca Raton:Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2015:1199-1231. [21] CEZE M, FIDKOWSKI K. Pseudo-transient continuation, solution update methods, and CFL strategies for DG discretizations of the RANS-SA equations: AIAA-2013-2686[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2013. doi: 10.2514/6.2013-2686 [22] MULDER W A, LEER B V.Experiments with implicit upwind methods for the euler equations[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 1985, 59(2):232-246. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(85)90144-5 [23] 张涵信.关于CFD高精度保真的数值模拟研究[J].空气动力学学报, 2016, 34(1):1-4.ZHANG H X.Investigation on fidelity of high order accuate numerical simulation for computational fluid dynamics[J].Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2016, 34(1):1-4(in Chinese). [24] VASSBERG J, JAMESON A. In pursuit of grid convergence, Part Ⅰ: Two-dimensional Euler solutions: AIAA-2009-4114[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2009. doi: 10.2514/6.2009-4114 [25] COOK P H, MCDONALD M A, FIRMIN M C P. Aerofoil RAE2822-Pressure distribution and boundary layer and wake measurements: AGARD-AR-138[R]. Reston: AGARD, 1979. [26] SCHMITT V, CHARPIN F. Pressure distributions on the ONERA-M6-wing at transonic mach numbers: AGARD-AR-138[R]. Reston: AGARD, 1979. -








 下载:
下载: