-
摘要:
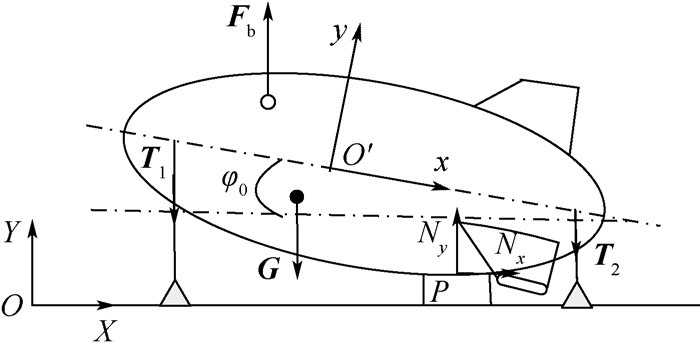
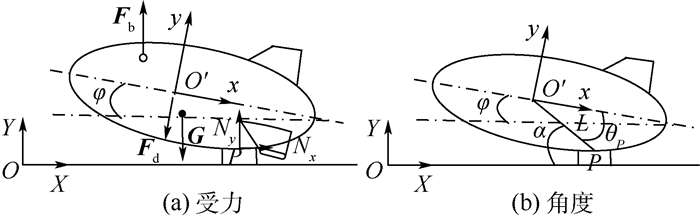
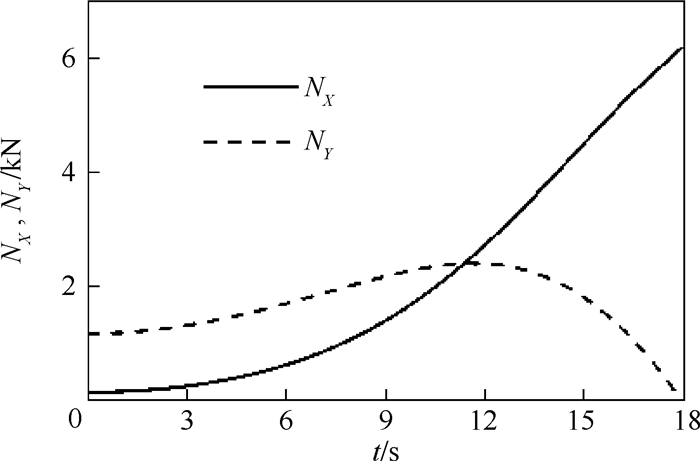
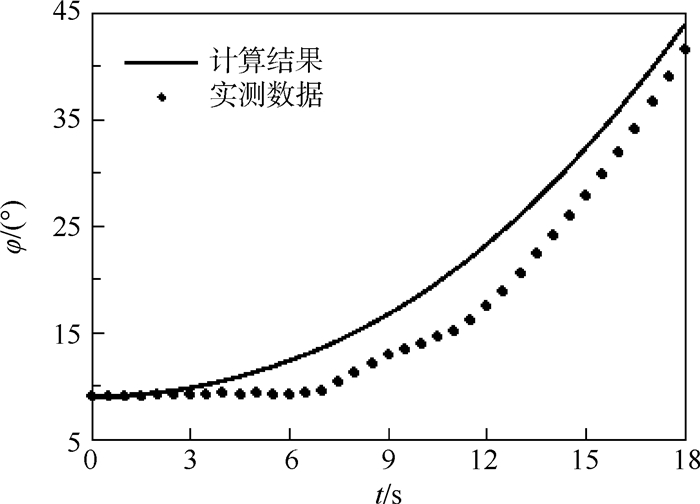
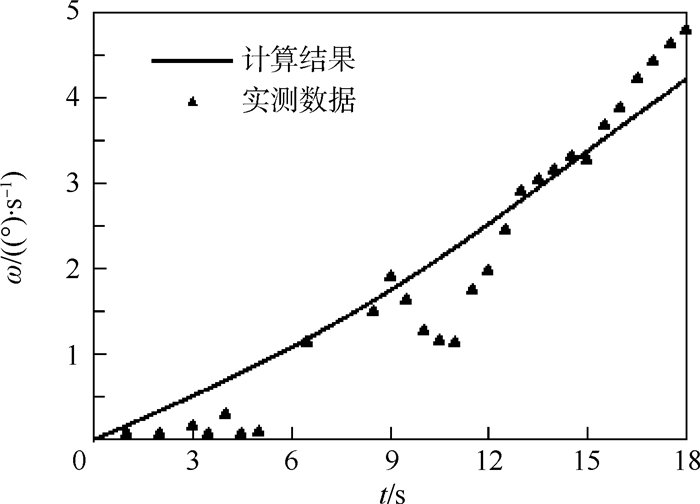
平流层飞艇放飞方式是其安全起飞的先决条件。本文对平流层飞艇放飞过程动力学响应建立了力学模型,提出了解析求解方法,开展了定量分析研究。依据影响平流层飞艇放飞过程的关键因素,对单氦气囊结构以及多氦气囊结构的平流层飞艇放飞过程进行了动力学分析,将单氦气囊结构飞艇动力学响应的定量分析结果与飞行试验过程中获得的数据进行对比,验证了分析方法的准确性,为进一步优化放飞过程的操作提供了依据。
Abstract:Launch mode of the stratospheric airship is the prerequisite factor to safely reach the target altitude. In this paper, a dynamics model for the launch process of stratospheric airship is firstly established, and the analytical solution method is put forward, and the quantitative analysis is carried out. Secondly, according to the typical issues that influence the launch process, the dynamic analysis of both the single-helium and multi-helium envelope structure are carried out, including dynamics response and force status. Furthermore, the numerical results of a single helium envelope structure are obtained and then compared with experimental data. The result verified the accuracy of the analytical method, which can also provide the basis for launch process of the airship and the design of the launch equipment.
-
表 1 不同浮重比飞艇稳定仰角和升速
Table 1. Stable pitch angle and rising velocity of airship for different buoyancy-weight ratios
浮重比 仰角/(°) 升速/(m·s-1) 1.1 11.13 1.56 1.2 11.41 2.20 1.3 11.56 2.69 1.4 11.66 3.11 1.5 11.72 3.47 1.6 11.77 3.81 1.7 11.81 4.11 1.8 11.84 4.39 1.9 11.86 4.66 2.0 11.88 4.91 表 2 两种氦气囊结构对比
Table 2. Comparison between two kinds of helium envelope structure
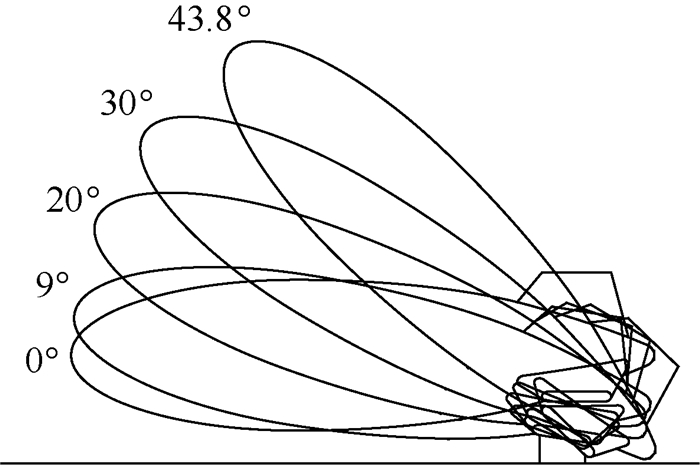
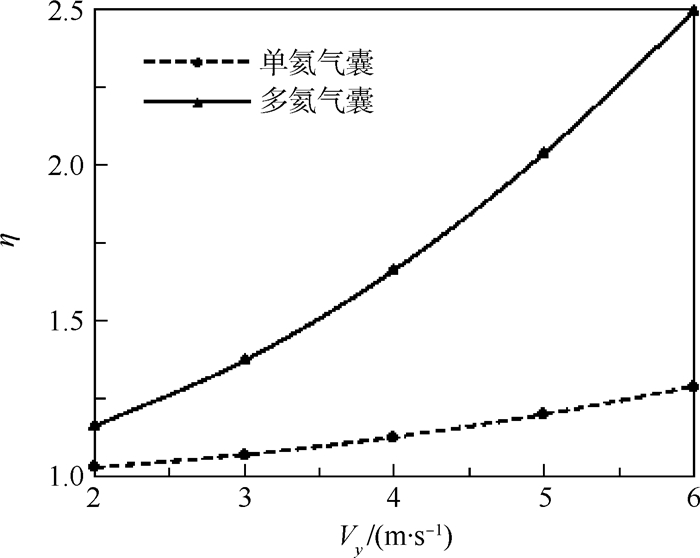
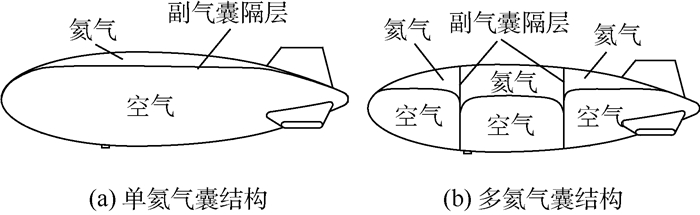
比较项目 单氦气囊结构 多氦气囊结构 氦气分布 同一容腔 多个容腔 飞艇浮心变化 很大,不可控 很小,受控 升空姿态 大仰角 小仰角,可选择 放飞时飞艇姿态 加速抬头,尾部下顿 仰角不变 排气方式 尾部集中排气 分段排气 升速/(m·s-1) 5~10 2~5 浮重比 小 大 副气囊结构 简单 复杂 加工工艺 简单 复杂 压控 简单 复杂 放飞形式 复杂 简单 典型案例 日本SPF-1 美国HALE-D -
[1] LIAO L, PASTERNAK I.A review of airship structural research and development[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2009, 45(4-5):83-96. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2009.03.001 [2] STOCKBRIDGE C, CERUTI A, MARZOCCA P.Airship research and development in the areas of design, structures, dynamics and energy systems[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical & Space Sciences, 2012, 13(2):170-187. [3] WILSON J R.A new era for airships[J]. Aerospace America, 2004, 42(5):27-31. [4] STEVE S. The HiSentinel airship[C]//7th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration and Operations Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2007. [5] SMITH I, LEE M, FORTNEBERRY M, et al. HiSentinel80: Flight of a high altitude airship[C]//11th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [6] Lockheed Martin Space System Company High altitude airship[EB/OL]. (2014-11-10)[2017-04-13]. [7] GAO. Future aerostat and airship investment decisions drive oversight and coordination needs: GAO-13-81[R]. Washington, D. C. : GAO, 2012. [8] JAXA. Ground-to-stratosphere flight test and evaluation of materials and structure for stratospheric airship test vehicle: JAXA-RM-04-012[R]. Tokyo: JAXA, 2004: 7-35. [9] SHUNICHI O, NOBORU S. R&D status of RFC technology for SPF airship in Japan[C]//9th Annual International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [10] SELBY C. High altitude airship station keeping and launch model development using output from numerical weather prediction models[D]. West Lafayette: Purdue University, 2008. [11] 赵攀峰, 王永林, 刘传超.平流层飞艇放飞、回收过程初步分析[J].航空科学技术, 2007(4):24-29.ZHAO P F, WANG Y L, LIU C C.Preparatory analyse on the release and recovery course of stratosphere airship[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology, 2007(4):24-29(in Chinese). [12] 郭虓, 祝明, 武哲.综合热力学模型的平流层飞艇上升轨迹优化[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2012, 38(10):1346-1351.GUO X, ZHU M, WU Z.Ascent trajectory optimization for stratospheric airships with thermal effects[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012, 38(10):1346-1351(in Chinese). [13] 吴雷, 李勇, 梁栋. 平流层飞艇放飞段动力学建模[C]//第25届中国控制会议, 2006: 546-550.WU L, LI Y, LIANG D. Dynamics modeling on the launch process for a stratospheric airship[C]//Proceeding of the 25th Chinese Control Conference, 2006: 546-550(in Chinese). [14] BLACKINGTON E. United States air force, schriever air force base: AIAA-2003-6005[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2003. [15] 周江华. 平流层飞艇运动控制律与定点控制律设计[D]. 北京: 中国科学院空间科学与应用中心, 2009: 22-26.ZHOU J H. Control law design for motion control and station-keeping control of stratospheric platform airship[D]. Beijing: Center for Space Science and Applied Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009: 22-26(in Chinese). [16] CUI Y X, YANG Y C, ZHOU J H, et al. Numerical aerodynamic investigations on stratospheric airships of different tail configurations[C]//IEEE Aerospace Conference. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 3-4. [17] KHOURY G, GILLELT J.Airship technology[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 1999:20-23. [18] LI Y W, NATHON M.Modeling and simulation of airship dynamics[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2007, 30(6):1691-1700. doi: 10.2514/1.29061 [19] 张泰华, 姜鲁华, 张冬辉, 等.临近空间飞艇艇库外约束及稳定性分析[J].中国空间科学技术, 2016, 36(5):72-80.ZHANG T H, JIANG L H, ZHANG D H, et al.Constraint and stability analysis of near space airship outside hangar[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2016, 36(5):72-80(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: