Computation method of collision probability of space object based on Laplace transformation
-
摘要:
碰撞概率是空间碎片碰撞预警中评判碰撞发生可能性大小的重要依据,对航天器机动规避具有重要意义。基于拉普拉斯变换的碰撞概率计算方法利用拉普拉斯变换以及幂级数的定义,推导了在短时间接近情况下碰撞概率的幂级数表达式,分析了碰撞概率的截断误差并确定了在不同精度要求下的幂级数项数。针对2009年美俄卫星的碰撞事件,将基于拉普拉斯变换的碰撞概率计算结果与Chan方法、Monte Carlo方法的计算结果进行比较,验证了基于拉普拉斯变换方法在计算精度上的优势。
Abstract:The collision probability of space object is an important information for judging whether a collision occurs in the space debris collision warning, and is important for the maneuvering avoidance of the spacecraft. Based on the Laplace transformation and the definition of the power series, the collision probability calculation method and the collision probability expression expressed by the power series in the short-term encounter were discussed. The truncation error in the form of power series was determined and the number of terms of power series was analyzed under different precision requirements. The results of collision probability calculation based on Laplace transformation are compared with those of Chan method and Monte Carlo method for 2009 US-Russian satellite collision event. The validity of Laplace transformation method and the advantage of computing accuracy are verified.
-
Key words:
- space debris /
- collision warning /
- collision probability /
- Laplace transformation /
- power series
-
表 1 主、从目标的位置参数
Table 1. Position parameters of primary and secondary object
km/s 目标 x y z 主目标 -1 457.353 760 1 589.546 912 6 814.195 621 从目标 -1 457.572 590 1 589.024 470 6 814.313 123 表 2 主、从目标的速度参数
Table 2. Velocity parameters of primary and secondary objectkm/s
km/s 目标 vx vy vz 主目标 -7.001 700 -2.439 510 -0.926 295 从目标 3.578 697 -6.172 823 2.200 328 表 3 主、从目标在RSW坐标系下的位置误差标准差
Table 3. Standard deviation of position error of primary and secondary object in RSW coordinate system
目标 σR/km σS/km σW/km 主目标 0.231 207 0.206 188 5 0.071 975 从目标 0.036 323 4 0.410 206 9 0.034 114 表 4 Chan方法下Pk的计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of Pk by Chan method
k Pk/10-4 1 1.817 439 461 411 834 2 1.828 466 082 330 511 3 1.828 488 389 607 843 4 1.828 488 412 175 072 5 1.828 488 412 188 786 6 1.828 488 412 188 801 7 1.828 488 412 188 806 8 1.828 488 412 188 808 9 1.828 488 412 188 809 10 1.828 488 412 188 809 表 5 基于拉普拉斯变换方法下Pk和Sk的计算结果
Table 5. Calculation results of Pk and Sk based on Laplace transformation method
k Pk/10-4 Sk 1 1.772 573 705 611 427 8.291 431 627 403 867×10-7 2 1.815 996 175 328 694 2.031 139 453 405 921×10-8 3 1.817 048 378 909 693 3.317 101 046 456 115×10-10 4 1.817 052 720 190 974 4.062 926 108 033 688×10-12 5 1.817 053 331 566 511 3.981 155 431 361 421×10-14 6 1.817 053 372 236 674 3.250 858 729 893 972×10-16 7 1.817 053 375 065 217 2.275 308 404 578 399×10-18 8 1.817 053 375 264 924 1.393 447 138 227 291×10-20 9 1.817 053 375 279 203 7.585 569 687 077 649×10-23 10 1.817 053 375 280 234 3.716 451 044 970 535×10-25 表 6 Monte Carlo方法、Chan方法、基于拉普拉斯变换方法的碰撞概率计算结果
Table 6. Collision probability calculation results of Monte Carlo, Chan and based on Laplace transformation methods
方法 碰撞概率 Monte Carlo 0.000 181 848 841 218 880 Chan 0.000 182 848 841 218 880 9 拉普拉斯变换 0.000 181 705 337 528 023 4 表 7 Chan方法、基于拉普拉斯变换方法与Monte Carlo方法的碰撞概率相对误差
Table 7. Relative error of collision probability between Monte Carlo method and Chan, based on Laplace transformation method
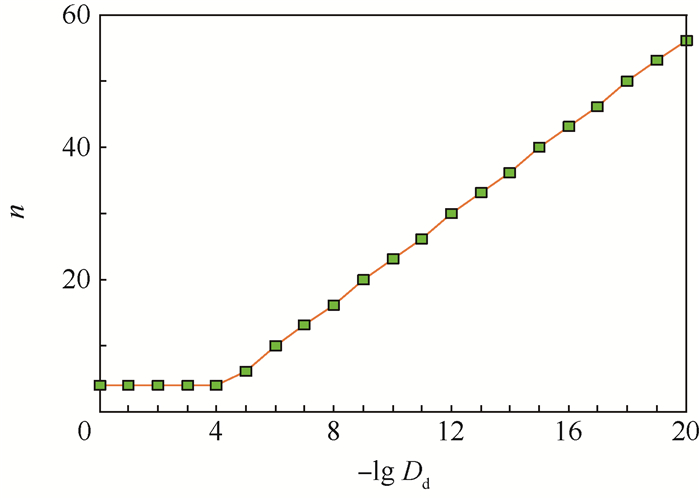
方法 相对误差/% Chan 0.549 9 拉普拉斯变换 0.078 9 表 8 精确位数-lg Dd不同时所需的幂级数项数、碰撞概率和截断误差
Table 8. Number of terms of power series, collision probability and truncation error with different exact digits -lg Dd
-lg Dd n Pc Sn 4 3 0.000 181 704 837 890 969 3 9.122 027 877 754 318×10-10 5 6 0.000 181 705 337 223 667 4 5.108 492 289 833 384×10-16 6 9 0.000 181 705 337 527 920 3 8.344 126 655 785 414×10-23 -
[1] ALFANO S.Satellite conjunction Monte Carlo analysis[J].Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 2009, 134:2007-2024. [2] FOSTER J L, ESTES H S. A parametric analysis of orbital debris collision probability and maneuver rate for space vehicles: NASA/JSC-25898[R]. Houston: NASA Johnson Space Flight Center, 1992. [3] PATERA R P.General method for calculating satellite collision probability[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2001, 24(4):716-722. doi: 10.2514/2.4771 [4] ALFANO S.Satellite collision probability enhancements[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2006, 29(3):588-592. doi: 10.2514/1.15523 [5] CHAN F K.Collision probability analysis for earth orbiting satellites[J].Advances in the Astronautically Sciences, 1997(96):1033-1048. doi: 10.2514/6.2010-2298 [6] CHAN F K.Spacecraft collision probability[M].El Segundo, CA:Aerospace Press, 2008. [7] 陈磊, 韩蕾, 白显宗, 等.空间目标轨道力学与误差分析[M].长沙:国防科技大学出版社, 2010:178-180.CHEN L, HAN L, BAI X Z, et al.Orbit target orbit mechanics and error analysis[J].Changsha:National University of Defense Technology Press, 2010:178-180(in Chinese). [8] SERRA R, ARZELIER D, JOLDES M, et al.Fast and accurate computation of orbital collision probability for short-term encounters[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(5):1-13. [9] ALFRIEND K T.AKELLAM R, FRISBEE J, et al.Probability of collision error analysis[J].Space Debris, 1999, 1(1):21-35. doi: 10.1023/A:1010056509803 [10] AKELLA M R, ALFRIEND K T.Probability of collision between space objects[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2000, 23(5):769-772. doi: 10.2514/2.4611 [11] ALFANO S.A numerical implementation of spherical object collision probability[J].Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2005, 53(1):103-109. [12] CHEVILLARD S, MEZZAROBBA M. Multiple-precision evaluation of the Airy Ai function with reduced cancellation[C]//21st IEEE Symposium on Computer Arithmetic (ARITH). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 175-182. [13] GAWRONSKI W, MVLLER J, REINHARD M.Reduced cancellation in the evaluation of entire functions and applications to the error function[J].SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2007, 45(6):2564-2576. doi: 10.1137/060669589 [14] HACKBUSCH W, SCHWARZ H R.Teubner-taschenbuch der mathematik[M].Berlin:Springer, 2013:595. [15] 李甲龙, 熊建宁, 许晓丽, 等.碰撞风险评估标准适用性分析[J].天文学报, 2014, 55(5):404-414.LI J L, XIONG J N, XU X L, et al.A research on adaptability of collision criteria[J].Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2014, 55(5):404-414(in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: