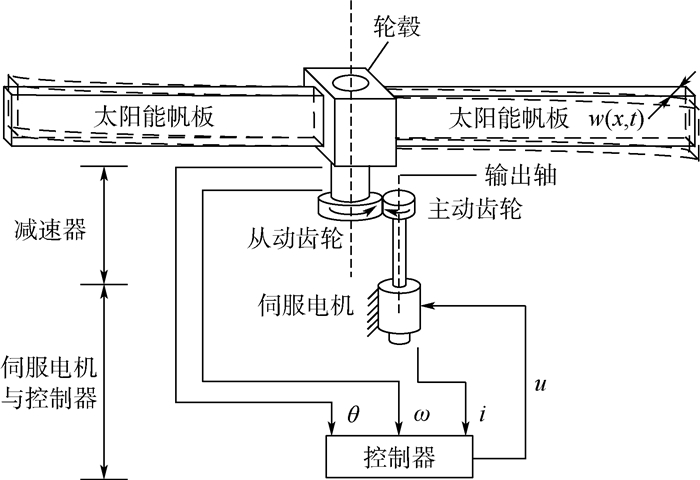
-
摘要:
为提高太阳能帆板驱动系统(SADS)的角位置控制性能和抑制太阳能帆板的柔性振动,提出了一种自适应滑模控制(ASMC)与输入成形技术相结合的控制策略。该控制策略通过自适应滑模控制保证了系统在不确定性影响下的一致有界性和渐进一致有界性,从而提高了太阳能帆板驱动系统的角位置控制性能。同时,通过基于参考模型的输入成形器(IS)规划了指令轨迹,进而抑制了太阳能帆板的柔性振动。仿真结果表明了控制策略的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 输入成形 /
- 自适应滑模控制(ASMC) /
- 太阳能帆板 /
- 驱动系统 /
- 柔性振动
Abstract:This paper proposes a control strategy which combines adaptive sliding mode control (ASMC) with input shaping technology for the solar array drive system (SADS) to improve the angular position control performance and suppress the flexible vibration. To improve the angular position control performance, ASMC is introduced, which is able to guarantee the uniform boundedness and uniform ultimate boundedness, regardless of the uncertainty. The command trajectory is planned by the input shaper (IS) based on the reference model, which suppresses the flexible vibration of solar array. The simulation results verify the validity of the proposed control strategy.
-
Key words:
- input shaping /
- adaptive sliding mode control (ASMC) /
- solar array /
- drive system /
- flexible vibration
-
参数 数值 定子电阻/Ω 28 定子电感/H 0.134 极对数 12 转矩常数/(N·m·A-1) 9.22 额定电流/A 1.4 额定功率/W 22 传动比 325 最大静摩擦力矩/(N·m) 404.54 第一阶模态耦合系数 188.7 第二阶模态耦合系数 30.1 第一阶模态阻尼比 0.01 第二阶模态阻尼比 0.01 第一阶模态角频率/(rad·s-1) 1.789 第二阶模态角频率/(rad·s-1) 11.21 转动惯量/(kg·m2) 1.7×106 滑动摩擦力矩/(N·m) 324.31 表 2 3种控制器的仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters of three controllers
控制器 参数 数值 PID控制 比例系数(位置环) 0.075 积分系数(位置环) 0.000 8 微分系数(位置环) 2 比例系数(速度环) 33.3 积分系数(速度环) 0.1 微分系数(速度环) 0 比例系数(电流环) 500 积分系数(电流环) 6 000 微分系数(电流环) 0 ASMC KP 1 530 KD 89 760 k 3 κ 150 χ 3 IS A1 0.26 A2 0.25 A3 0.25 A4 0.24 t1/s 0 t2/s 0.28 t3/s 1.76 t4/s 2.03 -
[1] JOSE S, GOPALAKRISHNAN E, TANGIRALA A K, et al.Stiffness control of cylindrical shells under axial compression using piezocomposite actuators-An experimental investigation[J].Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2017, 24(1):16-26. doi: 10.1080/15376494.2015.1091531 [2] SHIN C, HONG C, JEONG W B, et al.Active vibration control of plates using positive position feedback control with PZT actuators[J].Noise Control Engineering Journal, 2016, 64(2):279-289. doi: 10.3397/1/376378 [3] OMIDI E, MAHMOODI S N. Novel hybrid positive feedback control for active vibration suppression in flexible structure[C]//2014 American Control Conference. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 2723-2728. [4] GASBARRI P, SABATINI M, LEONANGELI N, et al.Flexibility issues in discrete on-off actuated spacecraft:Numerical and experimental tests[J].Acta Astronautica, 2014, 101:81-97. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.04.012 [5] GASBARRI P, MONTI R, SABATINI M.Very large space structures:Non-linear control and robustness to structural uncertainties[J].Acta Astronautica, 2014, 93:252-265. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2013.07.022 [6] NA S, TANG G, CHEN L.Vibration reduction of flexible solar array during orbital maneuver[J].Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, 2014, 86(2):155-164. doi: 10.1108/AEAT-05-2012-0072 [7] PAI M.Closed-loop input shaping control of vibration in flexible structures via adaptive sliding mode control[J].Shock and Vibration, 2012, 19(2):221-233. doi: 10.1155/2012/803479 [8] SINGHOSE W, PORTER L, KENISON M, et al.Effects of hoisting on the input shaping control of gantry cranes[J].Control Engineering Practice, 2000, 8(10):1159-1165. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(00)00054-X [9] SINGER N, SEERING W.Preshaping command inputs to reduce system vibration[M].Cambridge:MIT Press, 1988:76-82. [10] LU D, LIU Y.Singular formalism and admissible control of spacecraft with rotating flexible solar array[J].Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2014, 27(1):136-144. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2013.12.010 [11] LEE K W, SINGH S N.L1 adaptive control of flexible spacecraft despite disturbances[J].Acta Astronautica, 2012, 80:24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2012.05.007 [12] HU Q.Robust adaptive attitude tracking control with L2-gain performance and vibration reduction of an orbiting flexible spacecraft[J].Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, Transactions of the ASME, 2011, 133(1):011009. doi: 10.1115/1.4001703 [13] PUKDEBOON C.Adaptive-gain second-order sliding mode control of attitude tracking of flexible spacecraft[J].Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, 2014(5):693-697. [14] CHU M, CHEN G, JIA Q, et al.Simultaneous positioning and non-minimum phase vibration suppression of slewing flexible-link manipulator using only joint actuator[J].Journal of Vibration and Control, 2014, 20(10):1488-1497. doi: 10.1177/1077546312470477 [15] ALIPOUR K, ZARAFSHAN P, EBRAHIMI A.Dynamics modeling and attitude control of a flexible space system with active stabilizers[J].Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 84(4):2535-2545. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2663-y [16] PAI M.Discrete-time dynamic output feedback input shaping control of vibration in uncertain time-delay flexible structures[J].Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 250:675-688. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2014.11.038 [17] PAI M.Robust input shaping control for multi-mode flexible structures using neuro-sliding mode output feedback control[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2012, 349(3):1283-1303. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2012.01.012 [18] HU Q.Robust adaptive sliding mode attitude control and vibration damping of flexible spacecraft subject to unknown disturbance and uncertainty[J].Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2012, 34(4):436-447. doi: 10.1177/0142331210394033 [19] XU W, MENG D, CHEN Y, et al.Dynamics modeling and analysis of a flexible-base space robot for capturing large flexible spacecraft[J].Multibody System Dynamics, 2014, 32(3):357-401. doi: 10.1007/s11044-013-9389-0 [20] 白圣建, 黄新生.快速机动大型挠性航天器的动力学建模[J].航空学报, 2009, 30(10):1985-1992. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.10.032BAI S J, HUANG X S.Dynamic modeling of large flexible spacecraft undergoing fast maneuvering[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2009, 30(10):1985-1992(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.10.032 [21] LI J, LI S, CHEN X.Adaptive speed control of a PMSM servo system using an RBFN disturbance observer[J].Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2012, 34(5):615-626. doi: 10.1177/0142331211410920 [22] LIU H, LI S.Speed control for PMSM servo system using predictive functional control and extended state observer[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(2):1171-1183. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2162217 [23] LIANG H, SUN Z, WANG J.Robust decentralized attitude control of spacecraft formations under time-varying topologies, model uncertainties and disturbances[J].Acta Astronautica, 2012, 81(2):445-455. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2012.08.017 [24] WU S, RADICE G, GAO Y, et al.Quaternion-based finite time control for spacecraft attitude tracking[J].Acta Astronautica, 2011, 69(1-2):48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2011.03.001 [25] HU Q.Input shaping and variable structure control for simultaneous precision positioning and vibration reduction of flexible spacecraft with saturation compensation[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 318(1-2):18-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2008.03.068 [26] SUNG Y G, SINGHOSE W E.Robustness analysis of input shaping commands for two-mode flexible systems[J].IET Control Theory and Applications, 2009, 3(6):722-730. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2007.0328 [27] CORLESS M J, LEITMANN G.Continuous state feedback guaranteeing uniform ultimate boundedness for uncertain dynamic systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1981, 26(5):1139-1144. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1981.1102785 [28] IOANNO P A, KOKOTOVIC P V.Robust redesign of adaptive control[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1984, 29(3):202-211. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1984.1103490 [29] LIM T W, COOPER P A, AYERS J K. Structural dynamic interaction with solar tracking control for evolutionary space station concepts[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1992: 2108-2117. [30] BOUCHER R L. Mechanically induced g-jitter from space station rotary joints: JSC-CN-6110[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 2000. [31] BOUCHER R L. Identification and mitigation of low frequency vibration sources on space station[C]//Dynamics Specialists Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1996: 451-462. -







 下载:
下载: