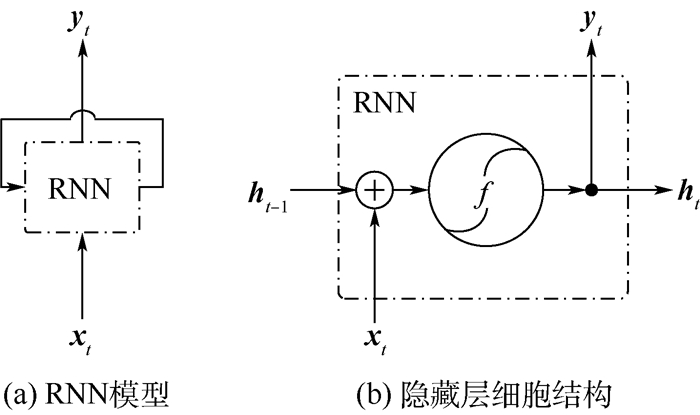
-
摘要:
有效地预测使用阶段的故障数据对于合理制定可靠性计划以及开展可靠性维护活动等具有重要的指导意义。从复杂系统的历史故障数据出发,提出了一种基于长短期记忆(LSTM)循环神经网络的故障时间序列预测方法,包括网络结构设计、网络训练和预测过程实现算法等,进一步以预测误差最小为目标,提出了一种基于多层网格搜索的LSTM预测模型参数优选算法,通过与多种典型时间序列预测模型的实验对比,验证了所提出的LSTM预测模型及其参数优选算法在故障时间序列分析中具有很强的适用性和更高的准确性。
-
关键词:
- 长短期记忆(LSTM)模型 /
- 循环神经网络 /
- 故障时间序列预测 /
- 多层网格搜索 /
- 深度学习
Abstract:Effectively forecasting the failure data in the usage stage is essential to reasonably make reliability plans and carry out reliability maintaining activities. Beginning with the historical failure data of complex system, a long short-term memory (LSTM) based recurrent neural network for failure time series prediction is presented, in which the design of network structure, the procedures and algorithms of network training and forecasting are involved. Furthermore, a multilayer grid search algorithm is proposed to optimize the parameters of LSTM prediction model. The experimental results are compared with various typical time series prediction models, and validate that the proposed LSTM prediction model and the corresponding parameter optimization algorithm have strong adaptiveness and higher accuracy in failure time series prediction.
-
表 1 不同预测模型实验结果对比(A飞机)
Table 1. Experimental results for different prediction models (Aircraft A)
模型 模型参数 训练集
拟合
RMSE值测试集预测RMSE值 耗时/s 1个测试点 2个测试点 3个测试点 6个测试点 12个测试点 Holt-Wintersa α=0.044,β=0.073,γ=0.223 2.617 0.088 0.069 2.278 2.882 2.595 0.02 Holt-Wintersm α=0,β=0,γ=0.6 3.199 1.704 1.205 2.837 3.179 3.066 0.02 ARIMA p=2,d=1,q=2 2.329 1.475 1.224 2.712 2.832 2.509 1.53 SSAr Lssa=96,Gssa=list(1:50) 0.770 2.487 1.781 1.871 2.437 2.622 0.02 SSAv Lssa=96,Gssa=list(1:50) 0.770 2.509 1.843 2.175 2.500 2.295 0.02 MLR Lmlr=24 2.221 2.490 1.773 2.602 2.617 2.381 0.02 SVR Lsvr=24, C=3,ε=0.259,σsvr=0.023 1.167 1.740 1.526 1.967 2.139 2.321 0.03 RNN L=2, Sstate=6,seed=1, steps=500,η=0.1 2.183 1.716 1.225 1.995 2.528 2.595 0.61 GRU L=2, Sstate=6,seed=1, steps=500,η=0.1 1.982 1.921 1.651 2.920 2.691 2.248 0.78 LSTM L=2, Sstate=6,seed=1, steps=500,η=0.1 1.962 1.919 1.577 2.745 2.109 2.196 0.81 注:最小RMSE值和最小耗时由下划线标记。 表 2 不同预测模型实验结果对比(B飞机)
Table 2. Experimental results for different prediction models (Aircraft B)
模型 模型参数 训练集
拟合
RMSE值测试集预测RMSE值 耗时/s 1个测试点 2个测试点 3个测试点 6个测试点 12个测试点 Holt-Wintersa α=0.011, β=0.210, γ=0.191 2.907 1.749 3.605 3.353 2.609 2.474 0.02 Holt-Wintersm α=0, β=0, γ=0.438 3.231 1.837 4.252 3.807 2.950 2.816 0.02 ARIMA p=4,d=1,q=1 2.565 1.719 2.079 2.566 2.091 2.021 1.77 SSAr Lssa=96,Gssa=list(1:50) 0.853 0.178 2.142 1.768 4.289 5.023 0.02 SSAv Lssa=96,Gssa=list(1:50) 0.853 0.730 1.686 1.987 2.904 3.161 0.02 MLR Lmlr=24 2.547 1.729 2.026 2.912 2.418 2.360 0.02 SVR Lsvr=24, C=3,ε=0.252,σsvr=0.023 1.353 0.241 1.374 2.893 2.278 2.121 0.03 RNN L=12, Sstate=6,seed=100, steps=1 000,η=0.03 2.058 0.828 2.630 2.556 2.484 2.671 3.13 GRU L=12, Sstate=6,seed=100, steps=1 000,η=0.03 1.559 1.696 1.257 3.525 2.815 2.690 5.36 LSTM L=12, Sstate=6,seed=100, steps=1 000,η=0.03 1.276 0.956 1.691 1.703 1.237 1.580 5.64 注:最小RMSE值和最小耗时由下划线标记。 表 3 LSTM模型前5组最优参数组合以及对应的模型精度(A飞机)
Table 3. The first five groups of optimal parameters andcorresponding model accuracy for LSTM model (Aircraft A)
排名 模型参数 训练集
拟合RMSE值测试集预测RMSE值 耗时/s L Sstate η 1个测试点 2个测试点 3个测试点 6个测试点 12个测试点 1 3 21 0.005 1.261 0.694 0.921 1.261 1.154 1.676 1.56 2 14 10 0.03 0.321 2.539 1.834 2.506 2.390 1.909 3.63 3 17 8 0.005 1.311 1.923 1.824 2.137 2.004 2.041 3.94 4 19 11 0.03 0.289 0.054 0.762 1.290 2.058 2.061 4.84 5 4 16 0.03 0.584 3.860 2.759 2.395 1.991 2.081 1.66 表 4 LSTM模型前5组最优参数组合以及对应的模型精度(B飞机)
Table 4. The first five groups of optimal parameters and corresponding model accuracy for LSTM model (Aircraft B)
排名 模型参数 训练集
拟合RMSE值测试集预测RMSE值 耗时/s L Sstate η 1个测试点 2个测试点 3个测试点 6个测试点 12个测试点 1 10 7 0.005 1.794 1.703 1.209 1.005 0.942 0.864 2.55 2 3 18 0.003 2.288 0.833 1.398 1.162 1.227 1.571 1.44 3 19 18 0.005 0.945 0.495 1.804 2.206 2.093 1.636 5.95 4 3 13 0.003 1.978 0.306 1.400 1.517 1.300 1.647 1.31 5 3 6 0.01 2.056 0.563 1.436 1.440 1.182 1.647 0.97 -
[1] VICHARE N M, PECHT M G.Prognostics and health management of electronics[J].IEEE Transactions on Components & Packaging Technologies, 2006, 29(1):222-229. doi: 10.1002/9780470061626.shm118/pdf [2] SAPANKEVYCH N I, SANKAR R.Time series prediction using support vector machines:A survey[J].IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2009, 4(2):24-38. doi: 10.1109/MCI.2009.932254 [3] 王鑫, 吴际, 刘超, 等.奇异谱分析在故障时间序列分析中的应用[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(11):2321-2331. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjhkhtdxxb201611006WANG X, WU J, LIU C, et al.Application of singular spectrum analysis for failure time series[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(11):2321-2331(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjhkhtdxxb201611006 [4] 李瑞莹, 康锐.基于ARMA模型的故障率预测方法研究[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(8):1588-1591. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95985X/200808/28187729.htmlLI R Y, KANG R.Research on failure rate forecasting method based on ARMA model[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(8):1588-1591(in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95985X/200808/28187729.html [5] ROCCO S C M.Singular spectrum analysis and forecasting of failure time series[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2013, 114(6):126-136. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0951832013000185 [6] MOURA M D C, ZIO E, LINS I D, et al.Failure and reliability prediction by support vector machines regression of time series data[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2011, 96(11):1527-1534. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0951832011001256 [7] XU K, XIE M, TANG L C, et al.Application of neural networks in forecasting engine systems reliability[J].Applied Soft Computing, 2003, 2(4):255-268. doi: 10.1016/S1568-4946(02)00059-5 [8] WANG X, WU J, LIU C, et al.A hybrid model based on singular spectrum analysis and support vector machines regression for failure time series prediction[J].Quality & Reliability Engineering International, 2016, 32(8):2717-2738. doi: 10.1002/qre.2098 [9] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G.Deep learning[J].Nature, 2015, 521(7553):436-444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [10] GRAVES A.Long short-term memory[M].Berlin:Springer, 2012:1735-1780. [11] SRIVASTAVA N, MANSIMOV E, SALAKHUTDINOV R. Unsupervised learning of video representations using LSTMs[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: JMLR W & CP, 2015: 843-852. [12] DONAHUE J, HENDRICKS L A, ROHRBACH M, et al.Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2015, 39(4):677-691. https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2015/html/Donahue_Long-Term_Recurrent_Convolutional_2015_CVPR_paper.html [13] VINYALS O, TOSHEV A, BENGIO S, et al. Show and tell: A neural image caption generator[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 3156-3164. [14] MA X, TAO Z, WANG Y, et al.Long short-term memory neural network for traffic speed prediction using remote microwave sensor data[J].Transportation Research Part C Emerging Technologies, 2015, 54:187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.03.014 [15] HANSON J, YANG Y, PALIWAL K, et al.Improving protein disorder prediction by deep bidirectional long short-term memory recurrent neural networks[J].Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(5):685. https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/33/5/685/2725549 [16] GREFF K, SRIVASTAVA R K, KOUTNIK J, et al.LSTM:A search space odyssey[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2016, PP(99):1-11. http://www.doc88.com/p-9032396768064.html [17] GRAVES A, SCHMIDHUBER J.Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures[J].Neural Networks, 2005, 18(5-6):602. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.06.042 [18] AMARI S I.Backpropagation and stochastic gradient descent method[J].Neurocomputing, 1993, 5(4-5):185-196. doi: 10.1016/0925-2312(93)90006-O [19] DUCHI J, HAZAN E, SINGER Y.Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12(7):257-269. https://web.stanford.edu/~jduchi/projects/DuchiHaSi12_ismp.pdf [20] YEUNG S, RUSSAKOVSKY O, NING J, et al.Every moment counts:Dense detailed labeling of actions in complex videos[J].International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017(8):1-15. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1507.05738 [21] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]//ICLR 2015, 2015: 1-15. https://dare.uva.nl/search?identifier=a20791d3-1aff-464a-8544-268383c33a75 [22] CHUNG J, GULCEHRE C, CHO K H, et al. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling[C]//NIPS 2014 Deep Learning and Representation Learning Workshop, 2014: 1-9. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67220-5_10 [23] CHEN P W, WANG J Y, LEE H M. Model selection of SVMs using GA approach[C]//IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2004: 2035-2040. [24] BRATTON D, KENNEDY J. Defining a standard for particle swarm optimization[C]//IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 120-127. [25] SNOEK J, LAROCHELLE H, ADAMS R P. Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe: Curran Associates Inc., 2012: 2951-2959. [26] HSU C W,CHANG C C,LIN C J.A practical guide to support vector classification[EB/OL].(2016-05-19)[2017-03-20]. https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/guide/guide.pdf. [27] SU C, JIN Q, FU Y.Correlation analysis for wind speed and failure rate of wind turbines using time series approach[J].Journal of Renewable & Sustainable Energy, 2012, 4(3):687-700. doi: 10.1002/we.1887 [28] CHATFIELD C.The Holt-Winters forecasting procedure[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1978, 27(3):264-279. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2347162?seq=6 [29] BARTHOLOMEW D J.Time series analysis forecasting and control[J].Journal of the Operational Research Society, 1971, 22(2):199-201. doi: 10.1057/jors.1971.52 [30] HYNDMAN R J, KHANDAKAR Y.Automatic time series forecasting:The forecast package for R[J].Journal of Statistical Software, 2008, 27(3):1-22. https://cloud.r-project.org/web/packages/forecast/vignettes/JSS2008.pdf [31] VAUTARD R, YIOU P, GHIL M.Singular-spectrum analysis:A toolkit for short, noisy chaotic signals[J].Physica D-Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 58(1-4):95-126. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90103-T [32] GOLYANDINA N, KOROBEYNIKOV A.Basic singular spectrum analysis and forecasting with R[J].Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2014, 71(1):934-954. http://www.doc88.com/p-1704502615665.html [33] NIKOLOPOULOS K, GOODWIN P, PATELIS A, et al.Forecasting with cue information:A comparison of multiple regression with alternative forecasting approaches[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 180(1):354-368. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.03.047 [34] BIANCO V, MANCA O, NARDINI S.Electricity consumption forecasting in Italy using linear regression models[J].Energy, 2009, 34(9):1413-1421. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2009.06.034 [35] BRERETON R G, LLOYD G R.Support vector machines for classification and regression[J].Analyst, 2010, 135(2):230-267. doi: 10.1039/B918972F [36] CHERKASSKY V, MA Y.Practical selection of SVM parameters and noise estimation for SVM regression[J].Neural Networks, 2004, 17(1):113-126. doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(03)00169-2 [37] Google. tensorflow rminer 1. 4. 2[EB/OL]. [2017-03-20]. https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r0.12. [38] R Core Team. The R project for statistical computing[EB/OL]. [2017-03-20]. https://www.r-project.org. [39] HYNDMAN R. robjhyndman/forecast[EB/OL]. [2017-03-20]. https://github.com/robjhyndman/forecast. [40] KOROBEYNIKOV A. asl/rssa[EB/OL]. [2017-03-20]. https://github.com/asl/rssa. [41] PAULO C. rminer: Data mining classification and regression methods[EB/OL]. [2017-03-20]. https://cran.r-project.org/package=rminer. -







 下载:
下载: