-
摘要:
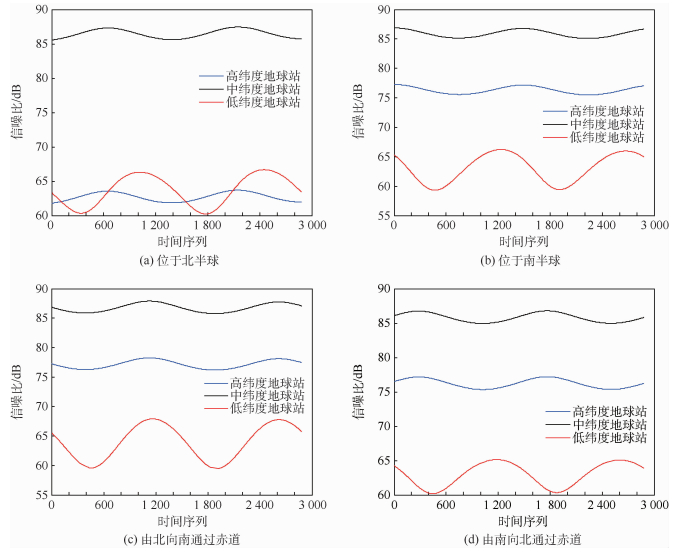
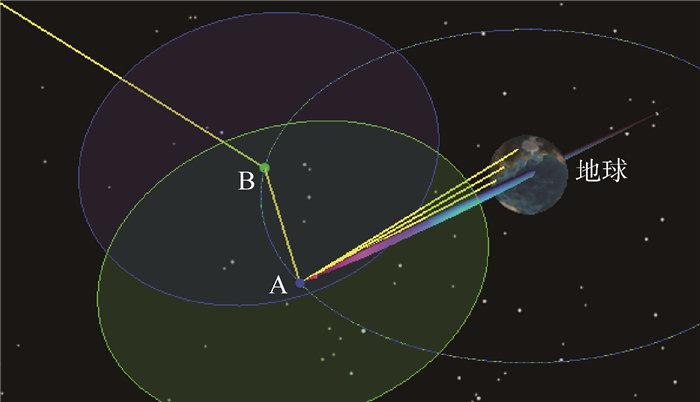
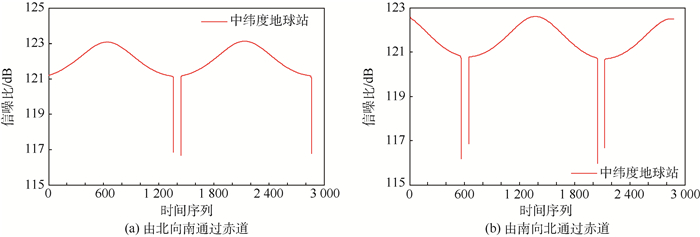
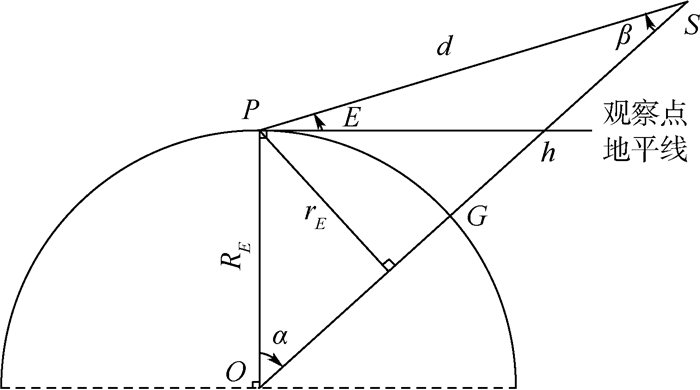
数据传输及处理能力是月基平台构建中的一个重要问题,如何高效准确地传输海量对地观测数据至地球供后续研究是开展月基对地观测的关键环节。通过STK和MATLAB软件联合仿真,模拟月基平台对地观测数据传输链路,首次提出适用于月基平台的下行链路通信方案:通过构建中纬度地球站、最小间隔经度值为40°的2颗中继卫星组的设计方案,可以最大程度地实现全天候、无时断的信号传输,满足下行链路接收端获取足够强度和低误码率的信息,从而保障月基平台的运行。
Abstract:The ability of data transmission and processing is an important factor in the construction of the moon-based platform. How to transmit the observation data to the earth station efficiently and accurately is a critical step to carry out the further researches. Through the joint simulation of STK and MATLAB, we simulate data transmission link from Moon-based platform to Earth and put forward a downlink communication scheme for the platform. It has been proved that the scheme of two relay satellites with 40 degrees apart and of utilizing the middle latitude earth station can receive reliable information all the time. It could make the downlink receiver get information with enough power and low bit error rate, so as to ensure the operation of the moon-based earth observation platform.
-
Key words:
- moon-based platform /
- earth observation /
- deep space communication /
- data transmission /
- link
-
表 1 位置参数
Table 1. Position parameter
类型 名称 位置 地球站 Llat 16°52′N,112°20′E Mlat 39°54′N,116°23′E Hlat 73°15′N,115°05′E 月球站 MBPoint 0°S,0°E 表 2 直传模式地球站可见性概率
Table 2. Visibility probability of earth station in direct transmission mode
% 地球站 月球投影位置 南半球 北半球 由北向南过赤道 由南向北过赤道 Llat 42.94 56.12 46.76 48.11 Mlat 34.03 64.66 46.76 45.58 Hlat 0 100 47.73 34.55 表 3 直传模式地球站有效通信概率
Table 3. Effective communication probability of earth station in direct transmission mode
% 地球站 月球投影位置 南半球 北半球 由北向南过赤道 由南向北过赤道 Llat 29.41 38.96 30.74 39.71 Mlat 29.28 49.11 29.03 41.89 Hlat 0 72.17 5.48 23.81 表 4 单颗中继卫星模式地球站可见性概率
Table 4. Visibility probability of earth station in single relay satellite mode
% 地球站 月球投影位置 南半球 北半球 由北向南过赤道 由南向北过赤道 Llat 100 100 94.76 95.59 Mlat 100 100 94.76 95.59 Hlat 100 100 94.76 95.59 -
[1] NASA. Lunar exploration objectives, version 1[EB/OL]. (2016-12-01)[2017-05-08]. [2] 欧阳自远.我国月球探测的总体科学目标与发展战略[J].地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3):351-358.OUYANG Z Y.China's overall scientific goal and development strategy of lunar exploration[J].Advances about Earth Science, 2004, 19(3):351-358(in Chinese). [3] 郭华东.地球系统空间观测:从科学卫星到月基平台[J].遥感学报, 2016, 20(5):716-723.GUO H D.Spatial observation of earth system:From science satellite to moon platform[J].Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(5):716-723(in Chinese). [4] 丁翼星, 郭华东, 刘广.面向全球变化探测的月基对地观测覆盖性能分析[J].湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 41(10):96-102.DING Y X, GUO H D, LIU G.Coverage performance analysis of earth observation from lunar base for global change detection[J].Journal of Hunan University (Natural Science), 2014, 41(10):96-102(in Chinese). [5] 郭华东, 丁翼星, 刘广, 等.面向全球变化探测的月基成像雷达概念研究[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(11):1760-1769.GUO H D, DING Y X, LIU G, et al.Research on moon's imaging radar concept for global changes detections[J].Chinese Science:Earth Science, 2013, 43(11):1760-1769(in Chinese). [6] 娄岩, 赵义武, 佟首峰, 等.太阳直射对GEO卫星和地面站通信的影响[J].计算机仿真, 2015, 32(3):234-237.LOU Y, ZHAO Y W, TONG S F, et al.Solar radiation impact on GEO satellite to ground laser communication[J].Computer Simulation, 2015, 32(3):234-237(in Chinese). [7] 李博, 叶晖, 张宏伟.基于STK/MATLAB接口的卫星通信链路研究[J].无线电通信技术, 2016, 42(6):37-40.LI B, YE H, ZHANG H W.Dynamical satellite link budget analysis based on STK/MATLAB interface[J].Radio Communications Technology, 2016, 42(6):37-40(in Chinese). [8] 李国军, 霍德聪.利用STK计算卫星通信链路余量[J].空间电子技术, 2012(1):68-72.LI G J, HUO D C.Satellite communication link budget computation using STK[J].Space Electronic Technology, 2012(1):68-72(in Chinese). [9] 韩湘, 郭新哲, 屈会鹏.GEO通信卫星姿态对点波束天线指向影响分析[J].飞行器测控学报, 2015, 34(1):77-82.HAN X, GUO X Z, QU H P.Impact of attitude movement on spot beam pointing for GEO communication satellites[J].Journal of Spacecraft TT & C Technology, 2015, 34(1):77-82(in Chinese). [10] 鲍凯, 徐慨, 项顺祥.基于STK的点波束覆盖分析与仿真[J].通信技术, 2013, 46(1):17-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TXJS201301005.htmBAO K, XU K, XIANG S X.Analysis and simulation of spot beam coverage based on STK[J].Communications Technology, 2013, 46(1):17-19(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TXJS201301005.htm [11] 周帆, 潘成胜, 常小凯.基于STK的卫星通信视景仿真[J].沈阳理工大学学报, 2007, 26(5):25-28.ZHOU F, PAN C S, CHANG X K.Visual simulation for satellite communication based on STK[J].Transactions of Shenyang Ligong University, 2007, 26(5):25-28(in Chinese). [12] 闵士权.卫星通信系统工程设计与应用[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2015:268-280.MIN S Q.Design and application of satellite communication system[M].BeiJing:Electronic Industry Press, 2015:268-280(in Chinese). [13] 丁溯泉, 张波, 刘世勇.STK使用技巧及载人航天工程应用[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2016:54-61.DING S Q, ZHANG B, LIU S Y.STK's using skills and applications on manned space engineering[M].Beijing:National Defense Industry Press, 2016:54-61(in Chinese). [14] 赵业福, 李进华.无线电跟踪测量系统[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2001:56-70.ZHAO Y F, LI J H.Radio's tracking & measurement system[M].Beijing:National Defense Industry Press, 2001:56-70(in Chinese). [15] 方炎申, 顾中舜, 陈英武.中继卫星与用户航天器之间星间链路的研究[J].计算机工程与设计, 2005, 26(8):2064-2066.FANG Y S, GU Z S, CHEN Y W.Research on inter-satellite links between relay satellites and user spacecrafts[J].Computer Engineering and Design, 2005, 26(8):2064-2066(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: