-
摘要:
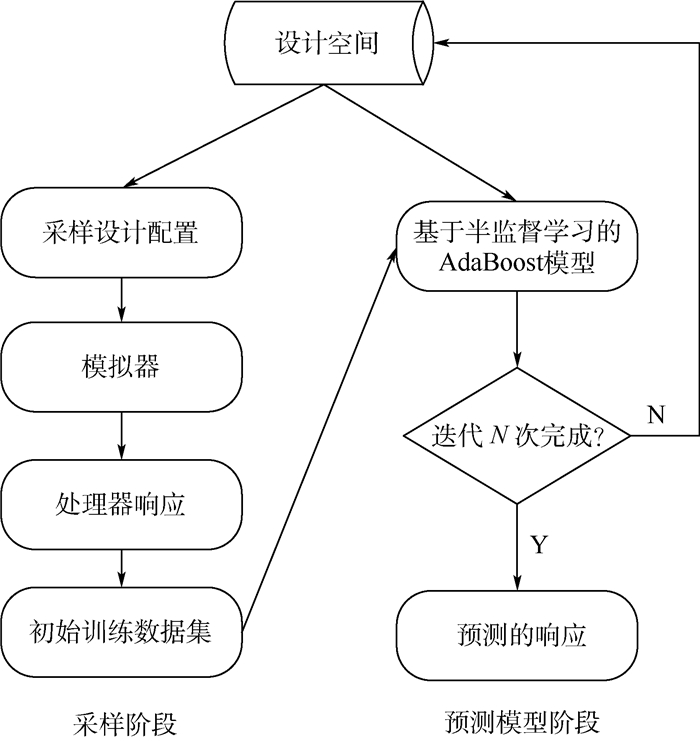
随着处理器的系统结构日趋复杂,设计空间呈指数式增长,并且软件模拟技术极为费时,成为处理器设计的重要挑战。提出了一种结合集成学习和半监督学习技术的高效设计空间探索方法。具体而言,该方法包括2个阶段:使用均匀随机采样方法从处理器设计空间中选择一小组具有代表性的设计点,通过模拟获得性能响应,从而组成训练数据集;提出基于半监督学习的AdaBoost(SSLBoost)模型预测未模拟的样本配置的响应,从而搜索最优的处理器设计配置。实验结果表明,与现有的基于人工神经网络和支持向量机(SVM)的有监督预测模型相比,SSLBoost模型能够使用更少的模拟样本构建出不差于现有方法性能的预测模型;而当模拟样本数量相同时,SSLBoost模型的预测精度更高。
Abstract:With the increasing complexity of microprocessor architecture, the design space is growing exponentially and the software simulation technology is extremely time-consuming. Design space exploration becomes one major challenge when processors are designed. The paper proposed an efficient design space exploration method combining semi-supervised learning and ensemble learning techniques. Specifically, it includes two phases:uniform random sampling method is firstly employed to select a small set of representative design points, and then simulation is conducted with the points to constitute the training set; semi-supervised learning based AdaBoost (SSLBoost) model is further proposed to predict the responses of the configurations that have not been simulated. Then the optimal processor design configuration is found. The experimental results demonstrate that compared with the prediction models based on the existing artificial neural network and support vector machine (SVM), the proposed SSLBoost model can build a comparable accurate model using fewer simulations. When the number of simulation examples is fixed, the prediction accuracy of SSLBoost model is higher.
-
Key words:
- design space exploration /
- semi-supervised learning /
- ensemble learning /
- AdaBoost /
- microprocessor /
- predictive model
-
表 1 多核设计空间
Table 1. Multicore design space
设计参数 设计参数取值 数量 Band Width/(GB·s-1) 8~64:8+ 8 Frequency/GHz 1~4.5: 0.5+ 8 Issue Width 1, 2, 4, 8 4 Number of Cores 1, 2, 4, 8 4 L2 Cache Size/MB 2, 4, 8, 16 4 L2 Cache Block Size/B 16, 32, 64, 128 4 L2 Cache Associativity 2, 4, 8, 16 4 L2 Cache MSHR 32~256:2* 4 L1 Dcache/KB 16, 32, 64, 128 4 L1 ICache/KB 16, 32, 64, 128 4 表 2 为达到SSLBoost模型相同的预测精度,ANN和SVM所需要的模拟配置(训练样本)数量
Table 2. Numbers of simulated configurations (training examples) required by ANN and SVM to achieve the same level of prediction accuracy as SSLBoost model
基准程序 配置数量 ANN SVM blackscholes 360 500+ bodytrack 350 300 canneal 320 500+ dedup 370 270 facesim 440 500+ ferret 310 480 fluidanimate 430 500+ freqmine 470 500+ streamcluster 400 500+ vips 370 500+ 平均 382 455+ 表 3 各种模型预测的最优配置对比(vips)
Table 3. Predicted optimal configurations of different models(vips)
设计参数及性能 SSLBoost模型 ANN SVM Band Width/(GB·s-1) 64 8 40 Frequency/GHz 4.5 4.5 4 Issue/Fetch/Commit Width 4 2 4 Number of Cores 1 1 2 L2 Cache Size/MB 4 2 2 L2 Cache Block Size/B 64 128 64 L2 Cache Associativity 8 2 2 L2 Cache MSHR 128 64 128 L1 Dcache/KB 128 128 64 L1 ICache/KB 64 16 16 真实模拟性能/ms 11.52 11.78 13.68 预测性能/ms 11.12 10.27 10.42 预测误差/% 3.5 12.9 23.8 -
[1] NOONBURG D B, SHEN J P. Theoretical modeling of superscalar processor performance[C]//Proceeding of International Symposium on Microarchitecture. New York: ACM, 1994: 52-62. [2] KARKHANIS T S, SMITH J E. Automated design of application specific superscalar processors: An analytical approach[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Symposium on Computer Architecture. New York: ACM, 2007: 402-411. [3] HAMERLY G, PERELMAN E, CALDER B.How to use SimPoint to pick simulation points[J].ACM Sigmetrics Performance Evaluation Review, 2004, 31(4):25-30. doi: 10.1145/1054907 [4] WUNDERLICH R E, WENISCH T F, FALSAFI B, et al. SMARTS: Accelerating microarchitecture simulation via rigorous statistical sampling[C]//Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture. New York: ACM, 2003: 84-97. [5] WANG S, HU X, YU P S, et al. MMRate: Inferring multi-aspect diffusion networks with multi-pattern cascades[C]//ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2014: 1246-1255. [6] WANG S, LI Z, CHAO W, et al. Applying adaptive over-sampling technique based on data density and cost-sensitive SVM to imbalanced learning[C]//International Symposium on Neural Networks. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 1-8. [7] JOSEPH P J, VASWANI K, THAZHUTHAVEETIL M J. Construction and use of linear regression models for processor performance analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 99-108. [8] JOSEPH P J, VASWANI K, THAZHUTHAVEETIL M J. A predictive performance model for superscalar processors[C]//Proceedings of the 39th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 161-170. [9] LEE B C, BROOKS D M. Accurate and efficient regression modeling for microarchitectural performance and power prediction[C]//Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Language and Operating Systems. New York: ACM, 2006: 185-194. [10] LEE B C, COLLINS J, WANG H, et al. CPR: Composable performance regression for scalable multiprocessor models[C]//Proceedings of the 41 st Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 270-281. [11] ÏPEK E, MCKEE S A, CARUANA R, et al. Efficiently exploring architectural design spaces via predictive modeling[C]//Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Language and Operating Systems. New York: ACM, 2006: 195-206. [12] 郭崎, 陈天石, 陈云霁.基于模型树的多核设计空间探索技术[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2012, 24(6):710-720. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201206001.htmGUO Q, CHEN T S, CHEN Y J.Model tree based multi-core design space exploration[J].Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2012, 24(6):710-720(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJF201206001.htm [13] PANG J F, LI X F, XIE J S, et al.Microarchitectural design space exploration via support vector machine[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2010, 46(1):55-63. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290771725_Microarchitectural_design_space_exploration_via_support_vector_machine [14] PALERMO G, SILVANO C, ZACCARIA V.ReSPIR:A response surface-based Pareto iterative refinement for application-specific design space exploration[J].IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2009, 28(12):1816-1829. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2009.2028681 [15] XYDIS S, PALERMO G, ZACCARIA V, et al.SPIRIT:Spectral-aware Pareto iterative refinement optimization for supervised high-level synthesis[J].IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2015, 34(1):155-159. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2014.2363392 [16] GUO Q, CHEN T, ZHOU Z H, et al.Robust design space modeling[J].ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, 2015:20(2):18. http://pages.saclay.inria.fr/olivier.temam/files/eval/todaes.pdf [17] LI D, YAO S, LIU Y H, et al. Efficient design space exploration via statistical sampling and AdaBoost learning[C]//Design Automation Conference. New York: ACM, 2016: 1-6. [18] KHAN S, XEKALAKIS P, CAVAZOS J, et al. Using predictivemodeling for cross-program design space exploration in multicore systems[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 327-338. [19] DUBACH C, JONES T, OBOYLE M. Microarchitectural design space exploration using an architecture-centric approach[C]//Proceedings of the 40th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 262-271. [20] LI D, WANG S, YAO S, et al. Efficient design space exploration by knowledge transfer[C]//Eleventh IEEE/ACM/IFIP International Conference on Hardware/software Codesign and System Synthesis. New York: ACM, 2016: 1-10. [21] SHRESTHA D L, SOLOMATINE D P.Experiments with AdaBoost.RT, an improved boosting scheme for regression[J].Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7):1678-1710. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1678 [22] ZHOU Z H, LI M.Semi-supervised learning by disagreement[J].Knowledge and Information Systems, 2010, 24(3):415-439. doi: 10.1007/s10115-009-0209-z [23] BINKERT N, BECKMANN B, BLACK G, et al.The gem5 simulator[J].ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2011, 39(2):1-7. doi: 10.1145/2024716 [24] BIENIA C, KUMAR S, SINGH J P, et al. The PARSEC benchmark suite: Characterization and architectural implications[C]//Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Parallel Architecture and Compilation Techniques. New York: ACM, 2008: 72-81. [25] HAMED V, RONG J, ANIL K. Semi-supervised boosting for multi-class classification[C]//European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2008: 522-537. [26] ZHOU Z H, LI M. Semi-supervised regression with co-training[C]//Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2005: 908-913. [27] CHANG C C, LIN C J.LIBSVM:A library for support vector machines[J].ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2011, 2(3):27-1-27-27. https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm -







 下载:
下载: