-
摘要:
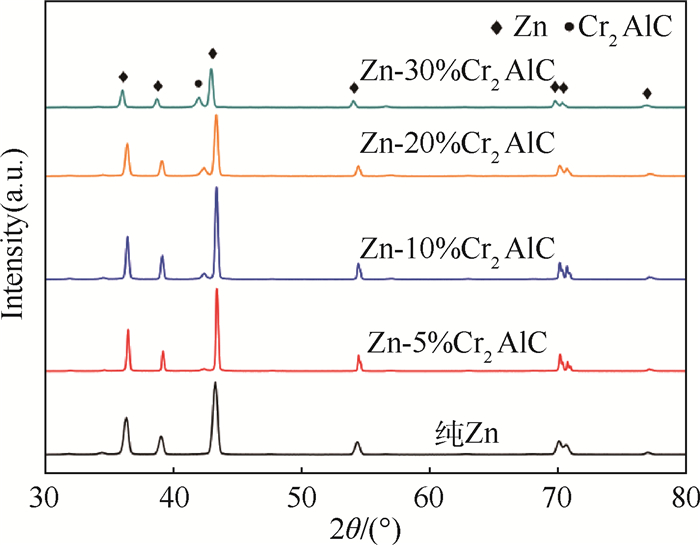
为改善金属Zn的摩擦磨损性能,采用热压法制备Cr2AlC陶瓷颗粒增强Zn基复合材料,并研究了Cr2AlC质量分数对复合材料的金相组织、维氏硬度、相对密度及摩擦磨损性能的影响。结果表明,复合材料的硬度随着Cr2AlC质量分数的适量增加而明显升高。当Cr2AlC的质量分数达到20%时,复合材料的硬度是纯Zn的1.52倍。摩擦磨损实验表明,Cr2AlC颗粒的引入,可显著改善复合材料的摩擦磨损性能,摩擦系数由纯Zn的0.75降到Zn-20%Cr2AlC的0.65,Zn-30%Cr2AlC的磨损率相比纯Zn下降了80.54%。分析磨损表面形貌,得出其磨损类型为磨粒磨损和剥层磨损。
Abstract:In order to improve the friction and wear properties of Zn, Cr2AlC ceramic particle reinforced Zn matrix composites were prepared by hot pressing method. The effects of Cr2AlC content on the metallographic structure, Vickers-hardness, relative density and tribological properties of the Zn-based composites were investigated. The results show that the hardness of the composites is improved obviously with the proper increase of Cr2AlC content. When the mass fraction of Cr2AlC reaches 20%, the hardness of the composite is 1.52 times higher than that of pure Zn. The introduced Cr2AlC particles can significantly improve the tribological properties of the composites. The friction coefficient decreases from 0.75 in pure Zn to 0.65 in Zn-20%Cr2AlC, and the wear rate of Zn-30%Cr2AlC is reduced by 80.54% compared to pure Zn. Analysis on the worn surface morphology indicates that the wear mechanism is abrasive wear and delamination wear.
-
[1] EL-KHAIR M T A, LOTFY A, DAOUD A, et al.Microstructure, thermal behavior and mechanical properties of squeeze cast SiC, ZrO2 or C reinforced ZA27 composites[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2011, 528(6):2353-2362. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.060 [2] BABIC M, SLOBODAN M, DZUNIC D, et al.Tribological beh-avior of composites based on ZA-27 alloy reinforced with g-raphite particles[J].Tribology Letters, 2009, 37(2):401-410. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=381d9821530edfeb4fb245adf9af409c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] RANGANATH G, SHARMA S C, KRISHNA M.Dry sliding wear of garnet reinforced zinc/aluminium metal matrix comp-osites[J].Wear, 2001, 250(1-12):1408-1413. [4] LI Z G.Fabrication of in situ TiB2 particulates reinforced zinc alloy matrix composite[J].Materials Letters, 2014, 121:1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.01.050 [5] MIROSLAV B, MITROVIC S, ZIVIC F, et al.Wear behavior of composites based on ZA-27 alloy reinforced by Al2O3 particles under dry sliding condition[J].Tribology Letters, 2010, 38(3):337-346. doi: 10.1007/s11249-010-9613-5 [6] DEHSORKHI R N, QODS F, TAJALLY M.Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn composite during accumulative roll bonding (ARB) process[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2011, 530(1):63-72. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509311010008 [7] PRASAD B K.Sliding wear response of a zinc-based alloy and its composite and comparison with a gray cast iron:Influence of external lubrication and microstructural features[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2005, 392(1-2):427-439. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.10.031 [8] TAVOOSI M, KARIMZADEH F, ENAYATI M H, et al.Bulk Al-Zn/Al2O3 nanocomposite prepared by reactive milling and hot pressing methods[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 475(1-2):198-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.049 [9] BARSOUM M W, RADOVIC M.Elastic and mechanical prop-erties of the MAX phases[J].Annual Review of Materials Re-search, 2011, 41(1):195-227. doi: 10.1146/annurev-matsci-062910-100448 [10] SUN Z M.Progress in research and development on MAX phases:A family of layered ternary compounds[J].International Materials Reviews, 2013, 56(3):143-166. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7651ccc4b31467b6aba7e51a0ca5268e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] BARSOUM M W.The Mn+1AXn phases:A new class of soli-ds:Thermodynamically stable nanolaminates[J].Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2000, 28(1):201-281. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261035741_Formation_Routes_of_Nanocomposite_Coatings_in_Detonation_Spraying_of_Ti3SiC2-Cu_Powders [12] GUPTA S, HABIB M A, DUNNIGAN R, et al.Synthesis and characterization of Ti3SiC2 particulate-reinforced novel Zn matrix composites[J].Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2015, 24(10):4071-4076. doi: 10.1007/s11665-015-1691-y [13] LI H Y, ZHOU Y, CHEN C, et al.Microstructure and mechanic-al properties of Zn based composites reinforced by Ti3AlC2[J].Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2015, 114(6):315-320. doi: 10.1179/1743676115Y.0000000007 [14] LIN Z, ZHUO M, ZHOU Y, et al.Atomic scale characterization of layered ternary Cr2AlC ceramic[J].Journal of Applied Phy-sics, 2006, 99(7):076109. doi: 10.1063/1.2188074 [15] TIAN W, WANG P, ZHANG G, et al.Synthesis and thermal and electrical properties of bulk Cr2AlC[J].Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54(5):841-846. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.11.009 [16] 雷宇, 刘锦云, 王敏, 等.Cr2AlC颗粒增强Cu基复合材料的制备及力学性能研究[J].粉末冶金技术, 2013, 31(5):340-343. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fmyjjs201305004LEI Y, LIU J Y, WANG M, et al.Preparation and mechanical properties of Cr2AlC particulate reinforced Cu matrix composi-tes[J].Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2013, 31(5):340-343(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fmyjjs201305004 [17] GUPTA S, HAMMANN T, JOHNSON R, et al.Synthesis and characterization of novel Al-matrix composites reinforced with Ti3SiC2 particulates[J].Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2015, 24(2):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s11665-014-1330-z.pdf [18] GUPTA S, BARSOUM M W.On the tribology of the MAX phases and their composites during dry sliding:A review[J].Wear, 2011, 271(9-10):1878-1894. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.043 -







 下载:
下载: