-
摘要:
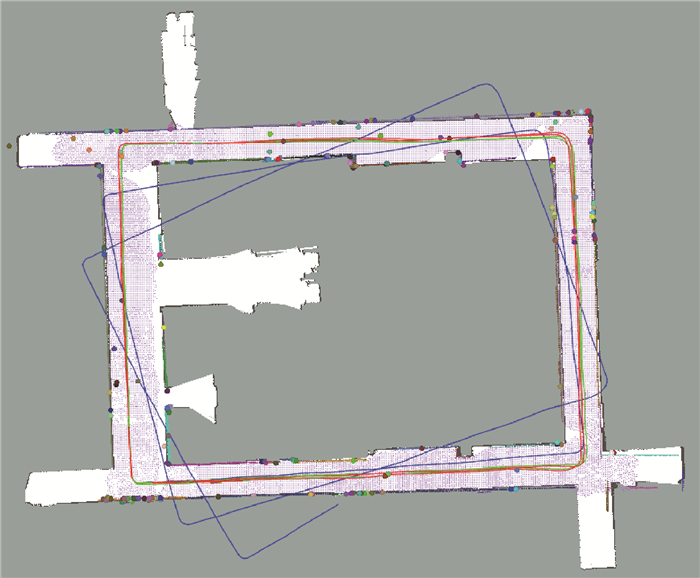
护理机器人在室内三维结构化环境下进行导航时,面临着三维建图计算量大且地图中缺乏语义信息的缺点。提出了基于点和平面特征的混合地图构建方法,结合点和平面在地图构建中的优势,并基于该混合地图搭建室内导航系统。首先,快速地提取特征点和特征平面,使用解释树的方法进行数据关联,并使用平滑建图工具构建因子图,进行机器人位姿和路标的联合优化,改进并更新混合地图。然后,搭建室内导航系统,实现了三维障碍物检测、路径规划与运动控制。最后,在走廊环境下进行了室内导航实验,并以由激光雷达构建的二维栅格地图为参考,分析了地图构建效果和机器人定位精度,证明了基于混合地图的室内导航系统在室内结构化环境下的优势。
Abstract:When the care robot is navigating in the indoor 3D structured environment, it is faced with the disadvantage of the large computational cost for map building and the lack of semantic information in the map. This paper presents a hybrid map building method based on point and plane features, which combines the advantages of point and plane features in the map building. Furthermore, an indoor navigation system is built based on the proposed hybrid map. First, point and plane features are fast extracted, and then data association is achieved using the interpretation tree approach. The smoothing and mapping tool is utilized to construct the factor graph and jointly optimize robot poses and landmarks, and the hybrid map is refined and updated. Second, the indoor navigation system is built, which implements the 3D obstacle detection, path planning and motion control. Finally, the indoor navigation experiments were carried out in a corridor environment. With the 2D occupancy grid map constructed by laser as the reference, the performance of map building and robot localization accuracy were analyzed, which proves that the indoor navigation system based on hybrid map shows its advantages in indoor structured environments.
-
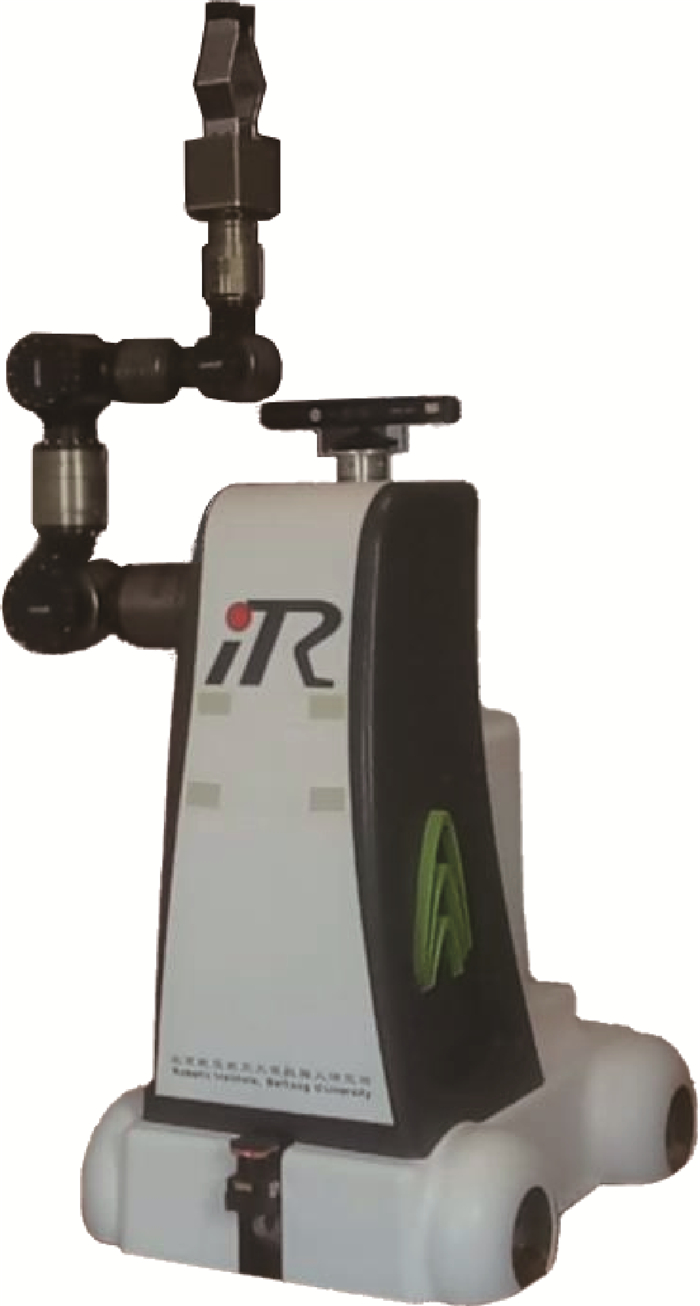
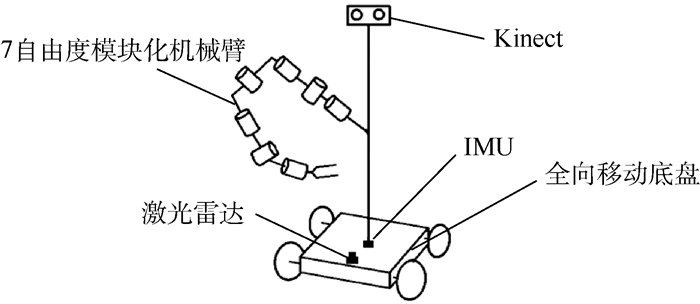
表 1 护理机器人样机指标
Table 1. Care robot prototype index
指标 数值 整机质量/kg 120 外形尺寸/(m×m×m) 0.9×0.65×1.35 机械臂自由度 7 Kinect安装高度/m 1.2 表 2 SLAM实验结果
Table 2. SLAM experimental results
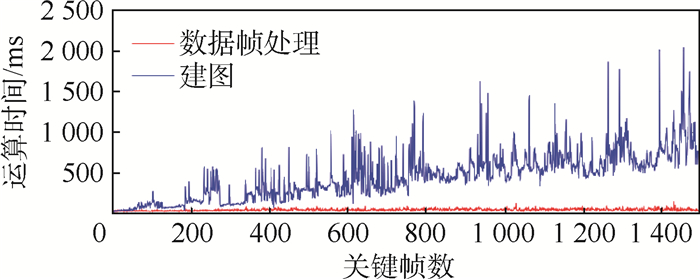
实验结果 数值 轨迹长度/m 179.74 持续时间/s 617.53 数据帧数 6 176 关键帧数 1 495 平移误差均值/m 0.097 0 平移RMSE/m 0.106 3 旋转误差均值/(°) 1.084 0 旋转RMSE/(°) 1.194 1 表 3 SLAM各步骤平均运算时间
Table 3. Each SLAM step average runtime
步骤 运算时间/ms 特征平面提取 17.39 特征点提取 27.11 特征平面数据关联 9.66 特征点数据关联 22.78 因子图优化 116.07 地图改进 100.35 路标更新 193.50 总计 499.36 -
[1] WEINGARTEN J, SIEGWART R. 3D SLAM using planar segments[C]//2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 3062-3067. [2] CASTELLANOS J A, TARDOS J D.Mobile robot localization and map building[M].Berlin:Springer, 1999:9-30. [3] LEE T K, LIM S, LEE S, et al. Indoor mapping using planes extracted from noisy RGB-D sensors[C]//2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 1727-1733. [4] KAESS M. Simultaneous localization and mapping with infinite planes[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 4605-4611. [5] KAESS M, RANGANATHAN A, DELLAERT F.iSAM:Incremental smoothing and mapping[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(6):1365-1378. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2006706 [6] TREVOR A J B, ROGERS J G, CHRISTENSEN H I. Planar surface SLAM with 3D and 2D sensors[C]//2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 3041-3048. [7] TAGUCHI Y, JIAN Y D, RAMALINGAM S, et al. Point-plane SLAM for hand-held 3D sensors[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 5182-5189. [8] ATAER-CANSIZOGLU E, TAGUCHI Y, RAMALINGAM S, et al. Tracking an RGB-D camera using points and planes[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 51-58. [9] SALAS-MORENO R F, GLOCKEN B, KELLY P H J, et al. Dense Planar SLAM[C]//2014 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 157-164. [10] ZHANG L Z, CHEN D S, LIU W H. Point-plane SLAM based on line-based plane segmentation approach[C]//2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 1287-1292. [11] QUIGLEY M, CONLEY K, GERKEY B P, et al. ROS: An open-source robot operating system[C]//ICRA Workshop on Open Source Software. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 1-6. [12] DELLAERT F. Factor graphs and GTSAM: A hands-on introduction: GT-RIM-CP&R-2012-02[R]. Altalanta: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2012: 1-26. [13] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 2564-2571. [14] ZHANG L Z, CHEN D S, LIU W H.Fast plane segmentation with line primitives for RGB-D sensor[J].International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2016, 13(6):1-8. doi: 10.1177/1729881416665846 [15] RUSU R B, COUSINS S. 3D is here: Point cloud library (PCL)[C]//2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 1-4. [16] KLEIN G, MURRAY D. Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces[C]//IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 225-234. [17] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDOS J D.ORB-SLAM2:An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5):1255-1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [18] GAD A, MAJDI F, FAROOQ M. A comparison of data association techniques for target tracking in clutter[C]//2002 IEEE International Conference on Information Fusion. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2002: 1126-1133. [19] POPPINGA J, VASKEVICIUS N, BIRK A, et al. Fast plane detection and polygonalization in noisy 3D range images[C]//2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 3378-3383. [20] KAESS M, JOHANNSSON H, ROBERTS R, et al.iSAM2:Incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree[J].International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(2):216-235. [21] KAMMERL J, BLODOW N, RUSU R B, et al. Real-time compression of point cloud streams[C]//2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 778-785. [22] HART P E, NILSSON N J, RAPHAEL B.A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems Science & Cybernetics, 1968, 4(2):100-107. [23] FOX D, BURGARD W, THRUN S.The dynamic window approach to collision avoidance[J].IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 1997, 4(1):23-33. [24] GRISETTIYZ G, STACHNISS C, BURGARD W. Improving grid-based SLAM with Rao-Blackwellized particle filters by adaptive proposals and selective resampling[C]//2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2005: 2432-2437. [25] STURM J, ENGELHARD N, ENDRES F, et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems[C]//2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 573-580. -







 下载:
下载: