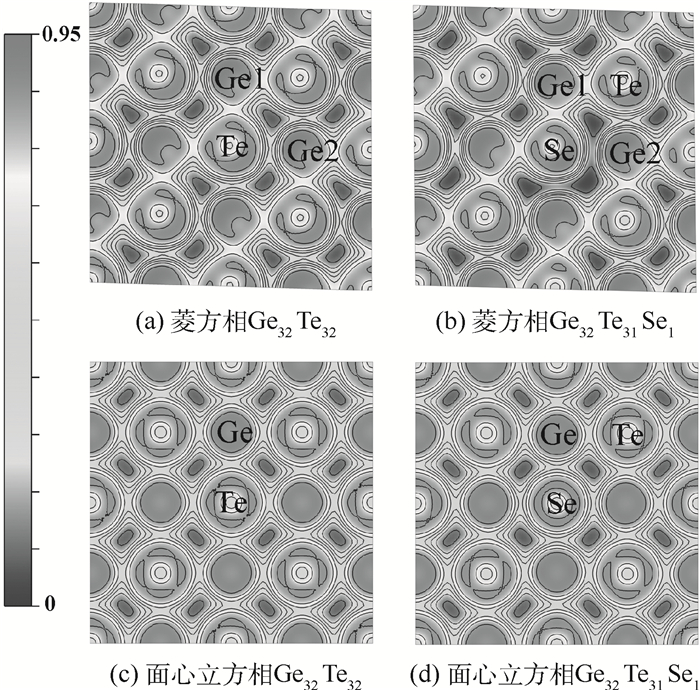
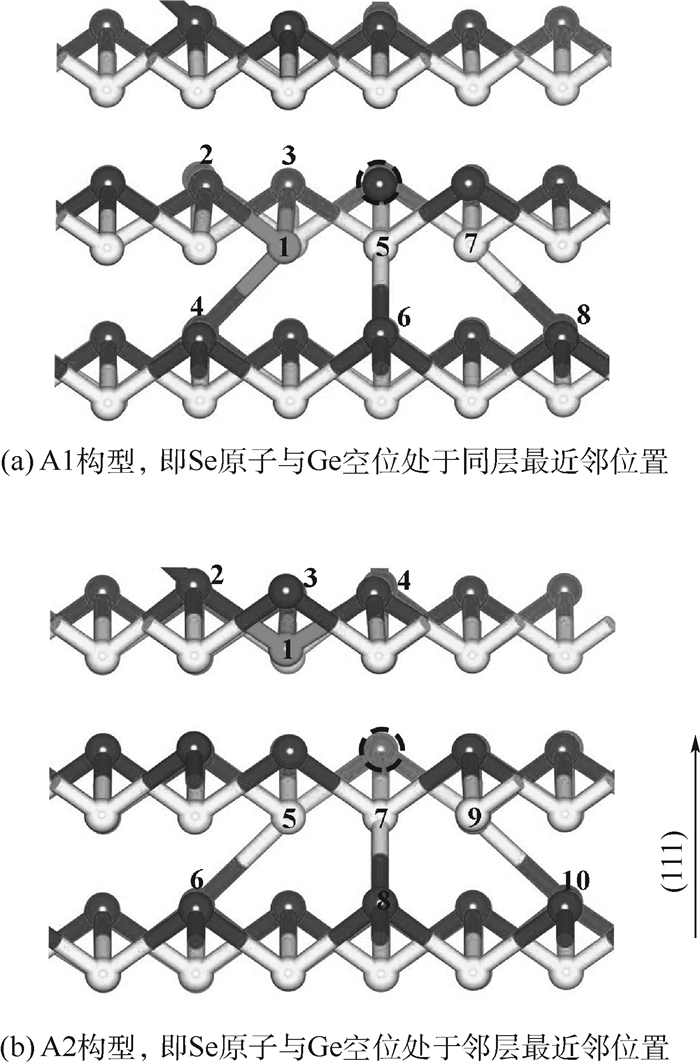
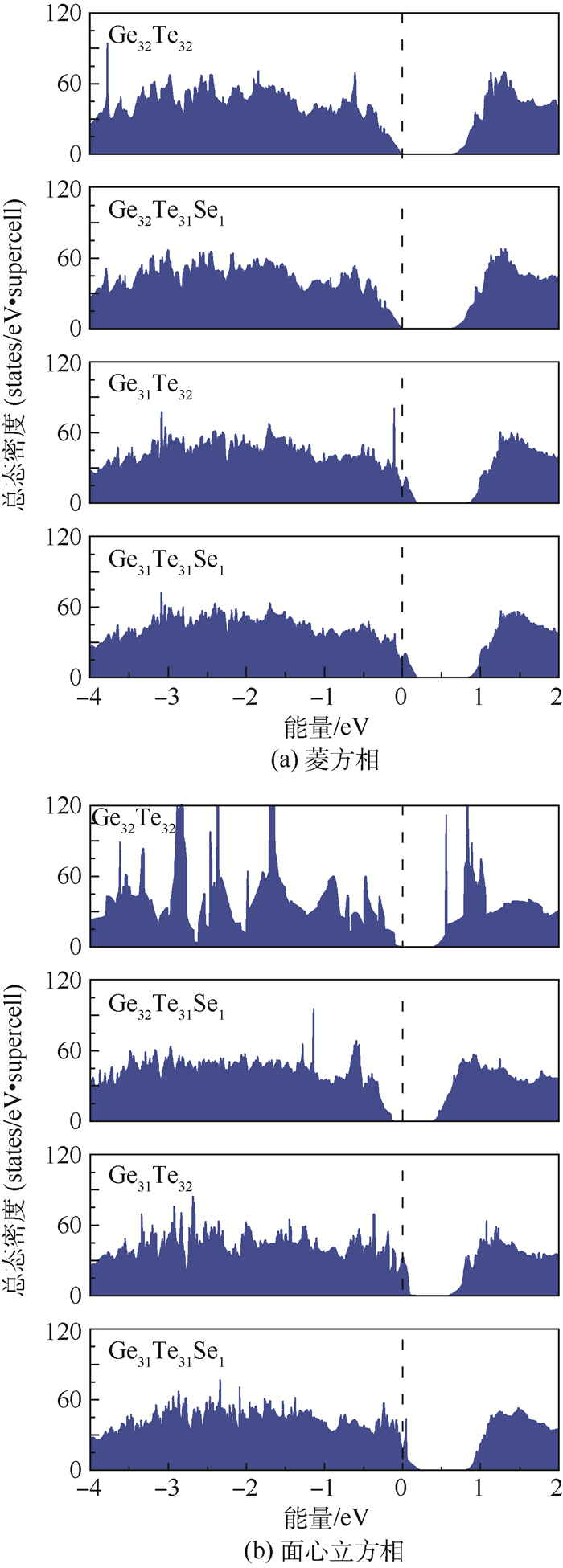
-
摘要:
硒(Se)掺杂可以大幅提高锗碲(GeTe)相变存储材料的再结晶温度,使其具有更高的服役温度和更好的数据保持力,然而Se掺杂对GeTe微观结构和电学性质的影响机制尚不清楚。采用第一性原理计算方法,对Se掺杂GeTe相变存储材料的几何构型、成键性质和电子性质进行了理论研究。结果表明,对于GeTe完美晶体,掺杂的Se原子优先取代Te原子。而对含本征Ge空位的GeTe体系,Se倾向于取代与Ge空位最近邻的Te原子。Se原子与Ge空位具有吸引作用,抑制了Ge空位的移动,从而提高其再结晶温度。Se掺杂导致含Ge空位的菱方相体积收缩,带隙减小,而使含Ge空位的面心立方相体积膨胀,带隙增大。Se掺杂减小了GeTe两晶相的体积差异。计算结果为解释实验中Se掺杂导致的奇特相变性质提供了重要线索。
Abstract:Doping Se can significantly improve the recrystallization temperature of GeTe phase-change material according to recent experiments, endowing GeTe with a higher working temperature and better data retention. However, the impact of Se on the structure and electrical properties of GeTe is not clear. In this paper, we investigated the effect of Se on the microstructure, bonding characters and electrical properties of crystalline GeTe using first-principles calculation. The results show that the doping Se atom prefers to replace Te in ideal GeTe, while for GeTe systems with intrinsic Ge vacancies, Se tends to replace the Te atoms which are the nearest neighbors of Ge vacancy. The attraction between Se atom and Ge vacancies hinders the movement of Ge vacancies, and thus increases the recrystallization temperature. Furthermore, a shrink of lattice volume and a small reduction of band gap are found in rhombohedral GeTe with Ge vacancies through doping Se, while in face-centered cubic GeTe with Ge vacancies, Se doping causes an expansion in lattice volume and an increase in band gap. Doping Se reduces the volume discrepancy between the two crystalline phases. The calculation results provide clues for explaining the unique phase transformation phenomena of Se doped phase-change materials.
-
Key words:
- Se doped GeTe /
- Ge vacancy /
- phase-change materials /
- first-principles calculation /
- elemental doping
-
表 1 计算得到的单胞晶格数据
Table 1. Calculated crystal lattice datas of single cell
结构 a0/nm α/(°) V/nm3 Eg/eV 菱方相GeTe 0.608 6 88.14 0.225 05 0.62 菱方相Ge32Te31Se1 0.608 3 87.94 0.224 62 0.58 菱方相Ge31Te31Se1 0.605 8 87.77 0.221 88 0.58 菱方相Ge31Te32 0.606 2 87.82 0.222 34 0.59 菱方相Ge31Se1Te32 0.608 4 88.12 0.224 86 — 面心立方相GeTe 0.601 9 90 0.218 08 0.38 面心立方相Ge32Te31Se1 0.600 3 90 0.216 34 0.40 面心立方相Ge31Te31Se1 0.602 4 90 0.218 52 0.52 面心立方相Ge31Te32 0.599 4 90 0.215 37 0.31 面心立方相Ge31Se1Te32 0.601 0 90 0.217 04 — 注:晶格常数a0、晶胞角度α、惯用胞体积V以及带隙Eg。 表 2 Se掺杂完美GeTe不同取代位置的形成能
Table 2. Formation energy of Se doping at different substitution positions in ideal GeTe eV
eV Se掺杂 菱方相 面心立方相 富Ge 富Te 富Ge 富Te 取代Ge 1.05 0.88 0.67 0.50 取代Te -0.41 -0.24 -0.54 -0.37 -
[1] OVSHINSKY S R.Reversible electrical switching phenomena in disordered structures[J].Physical Review Letters, 1968, 21(20):1450-1453. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.21.1450 [2] RAOUX S, WELNIC W, IELMINI D.Phase change materials and their application to nonvolatile memories[J].Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(1):240-267. doi: 10.1021/cr900040x [3] WONG H S P, SALAHUDDIN S.Memory leads the way to better computing[J].Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(3):191-194. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.29 [4] LENCER D, SALINGA M, GRABOWSKI B, et al.A map for phase-change materials[J].Nature Materials, 2008, 7(12):972-977. doi: 10.1038/nmat2330 [5] LENCER D, SALINGA M, WUTTIG M.Design rules for phase-change materials in data storage applications[J].Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(18):2030-2058. doi: 10.1002/adma.v23.18 [6] RAOUX S.Phase change materials[J].Annual Review of Materials Research, 2009, 39(1):25-48. doi: 10.1146/annurev-matsci-082908-145405 [7] PERNIOLA L, SOUSA V, FANTINI A, et al.Electrical behavior of phase-change memory cells based on GeTe[J].IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2010, 31(5):488-490. doi: 10.1109/LED.2010.2044136 [8] BRUNS G, MERKELBACH P, SCHLOCKERMANN C, et al.Nanosecond switching in GeTe phase change memory cells[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 95(4):043108. doi: 10.1063/1.3191670 [9] CHONG T, SHI L, ZHAO R, et al.Phase change random access memory cell with superlattice-like structure[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(12):122114. doi: 10.1063/1.2181191 [10] VINOD E M, SINGH A K, GANESAN R, et al.Effect of selenium addition on the GeTe phase change memory alloys[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 537(19):127-132. [11] VINOD E M, SANGUNNI K S.The effect of Se doping on spectroscopic and electrical properties of GeTe[J].Thin Solid Films, 2014, 550(1):569-574. [12] KOLOBOV A V, TOMINAGA J, FONS P, et al.Local structure of crystallized GeTe films[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 82(3):382-384. doi: 10.1063/1.1539926 [13] TONG F, MIAO X S, WU Y, et al.Effective method to identify the vacancies in crystalline GeTe[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(26):261904. doi: 10.1063/1.3531664 [14] VINOD E M, RAMESH K, SANGUNNI K S.Structural transition and enhanced phase transition properties of Se doped Ge2Sb2Te5 alloys[J].Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:8050. doi: 10.1038/srep08050 [15] WANG M, LU Y, SHEN X, et al.Effect of Sb2Se on phase change characteristics of Ge2Sb2Te5[J].CrystEngComm, 2015, 17(26):4871-4876. doi: 10.1039/C5CE00656B [16] HAFNER J.Ab-initio simulations of materials using VASP:Density-functional theory and beyond[J].Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2008, 29(13):2044-2078. doi: 10.1002/jcc.v29:13 [17] BLÖCHL P E.Projector augmented-wave method[J].Physical Review B, 1994, 50(24):17953-17979. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.17953 [18] PERDEW J P, WANG Y.Pair-distribution function and its coupling-constant average for the spin-polarized electron gas[J].Physical Review B, 1992, 46(20):12947-12954. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.46.12947 [19] MIAO N, SA B, ZHOU J, et al.Investigation on Ge5-xSbxTe5 phase-change materials by first-principles method[J].Applied Physics A, 2010, 99(4):961-964. doi: 10.1007/s00339-010-5709-x [20] GOLDAK J, BARRETT C S, INNES D, et al.Structure of alpha GeTe[J].The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1966, 44(9):3323-3325. doi: 10.1063/1.1727231 [21] LEVIN E M, BESSER M F, HANUS R.Electronic and thermal transport in GeTe:A versatile base for thermoelectric materials[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(8):083713. doi: 10.1063/1.4819222 [22] CHATTOPADHYAY T, BOUCHERLE J.Neutron diffraction study on the structural phase transition in GeTe[J].Journal of Physics C:Solid State Physics, 1987, 20(10):1431. doi: 10.1088/0022-3719/20/10/012 [23] PEIERLS R E.Quantum theory of solids[M].Oxford:Oxford University Press, 1955. [24] SUN Z, TIAN S, SA B.Investigation of the structure and properties of rhombohedral Cu-Ge-Te alloys by ab initio calculations[J].Intermetallics, 2013, 32(2):292-296. [25] ZHANG S, WEI S H, ZUNGER A, et al.Defect physics of the CuInSe2 chalcopyrite semiconductor[J].Physical Review B, 1998, 57(16):9642. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.57.9642 [26] WEI S H.Overcoming the doping bottleneck in semiconductors[J].Computational Materials Science, 2004, 30(3):337-348. [27] NAM S W, CHUNG H S, LO Y C, et al.Electrical wind force-driven and dislocation-templated amorphization in phase-change nanowires[J].Science, 2012, 336(6088):1561-1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1220119 [28] NUKALA P, AGARWAL R, QIAN X, et al.Direct observation of metal-insulator transition in single-crystalline germanium telluride nanowire memory devices prior to amorphization[J].Nano Letters, 2014, 14(4):2201-2209. doi: 10.1021/nl5007036 [29] SUN Z, ZHOU J, BLOMQVIST A, et al.Formation of large voids in the amorphous phase-change memory Ge2Sb2Te5 alloy[J].Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102:075504. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.075504 [30] UPADHYAY M, ABHAYA S, MURUGAVEL S, et al.Experimental evidence for presence of voids in phase change memory material[J].RSC Advances, 2014, 4(8):3659-3668. doi: 10.1039/C3RA44246B -







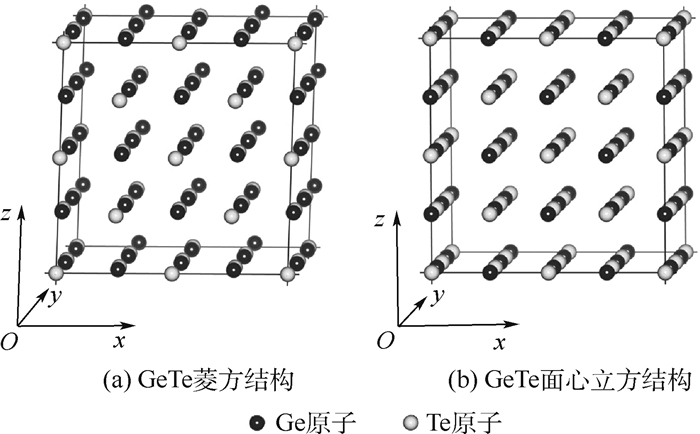
 下载:
下载: