-
摘要:
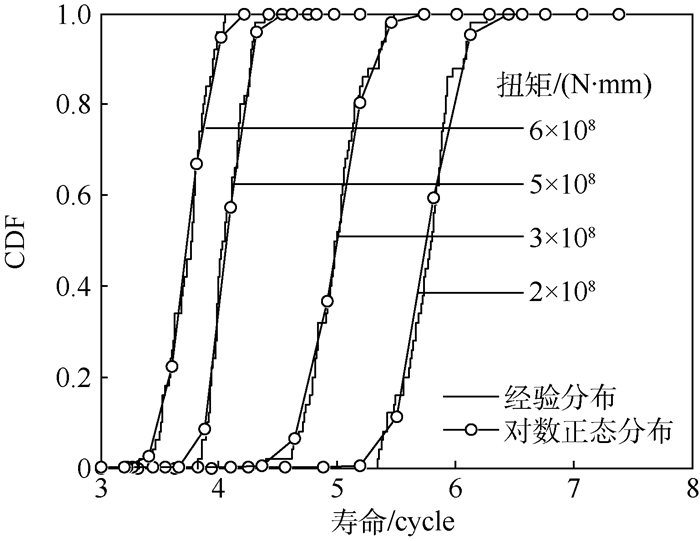
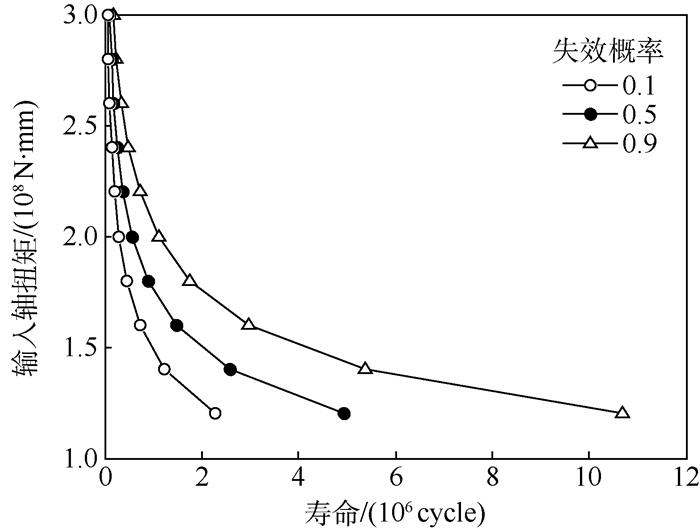
蒙特卡罗方法可以准确评估复杂机械系统疲劳共因失效概率,但效率偏低,因此提出系统PSN曲线的概念和基于此概念的系统可靠度蒙特卡罗评估方法。在给定的恒幅载荷下,基于同一零件的疲劳寿命在不同应力水平下的概率分位点具有一致性的原则,对系统中零件PSN曲线进行随机抽取;根据线性累积损伤法则和相应的系统可靠度模型,得到齿轮传动的恒幅载荷下的疲劳寿命分布,拟合恒幅载荷与寿命分布之间的关系得到系统PSN曲线。将系统视为一个零件,完成"零件"-"系统"-"零件"的寿命分析过程。通过损伤等效原则,将随机载荷下的复杂串联系统可靠度评估问题转化为恒幅载荷下零件的可靠度评估问题。
Abstract:To improve the efficiency of Monte Carlo simulation applied to evaluating the common cause failure probability of complex mechanical system, the concept of system fatigue life PSN curve was set up first, and then a Monte Carlo method for system reliability assessment based on this concept was proposed. With a given constant load, based on the correspondence of probability percentiles between specimen fatigue lives associated with different cyclic stress levels, every single PSN curve of component can be extracted stochastically. According to the linear cumulative damage rule and the corresponding system reliability model, the fatigue life distribution of gear-series-system was acquired. System PSN curve can be obtained by fitting constant load and life distribution. The system can be treated as a component, and the life analysis process of component-system-component has been completed. By means of damage equivalence principle between random load and constant load, the problem of reliability assessment of a complicated series system under random load can be converted to the problem of reliability assessment of component under constant load.
-
Key words:
- fatigue reliability /
- system PSN curve /
- series system /
- common cause failure /
- Monte Carlo
-
表 1 齿轮箱零件参数
Table 1. Gearbox component parameters
参数 太阳轮 行星轮 内齿圈 齿轮4 齿轮5 齿轮6 齿轮7 Z 21 38 99 84 23 92 24 Mn 10 10 10 8 8 5 5 αn/(°) 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 β/(°) 7.5 7.5 7.5 14 14 14 14 αt′/(°) 22.6 22.6 22.6 21.5 21.5 21.5 21.5 表 2 齿面接触应力
Table 2. Gear surface contact stress
啮合齿轮 太阳轮/行星轮 行星轮/内齿圈 齿轮1/齿轮2 齿轮3/齿轮4 σH/MPa 0.052 1 
0.022 5 
0.030 9 
0.031 6 
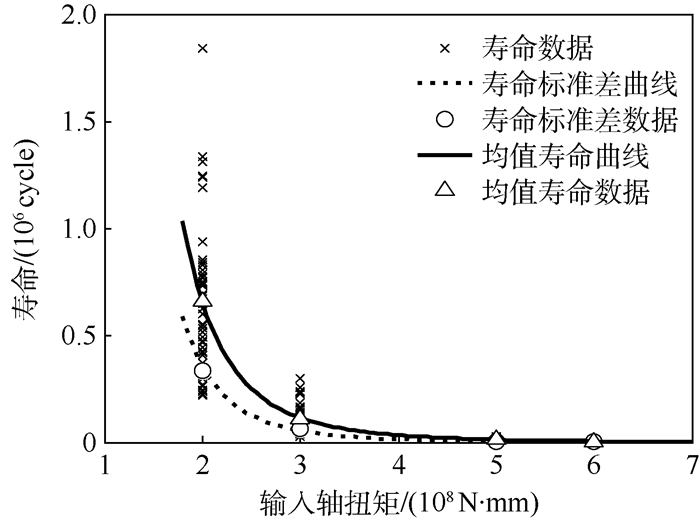
表 3 各级恒幅扭矩下齿轮系统寿命统计及统计矩
Table 3. Gear system life andstatistics moment under various constant torque
输入轴扭矩/(108 N·mm) 寿命标准差/cycle 寿命均值/cycle 2 3.3×105 6.6×105 3 6.2×104 1.1×105 5 4.2×103 1.2×104 6 2.2×103 5.9×103 表 4 3种方法寿命特征值比较
Table 4. Comparison of characteristic life of three methods
方法 系统寿命均值/(104cycle) 系统寿命标准差/(104cycle) 以a为参照的均值相对误差/% 以a为参照的标准差相对误差/% a 9.8 4.0 0 0 b 9.5 3.5 3.1 12.5 c 11 5.3 12.2 32.5 -
[1] ASTRIDGE D G.Helicopter transmissions-design for safety and reliability[J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part G:Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 1989, 203(27):123-138. [2] SHENG S W, Investigation of oil conditioning, real-time monitoring and oil sample analysis for wind turbine gearboxes: NREL/PR-5000-50301[R]. Golden: National Renewable Energy Laboratory, 2011. [3] SHENG S, OYAGUE F, BUTTERFIELD S. Investigation of various wind turbine drive train condition monitoring techniques: NREL/CP-500-46160[R]. Golden: National Renewable Energy Laboratory, 2010. [4] PLACE C S, STRUTT J E, ALLSOPP K, et al.Reliability prediction of helicopter transmission systems using stress-strength interference with underlying damage accumulation[J].Quality & Reliability Engineering International, 1999, 15(2):69-78. [5] DONG W, XING Y, MOAN T, et al.Time domain-based gear contact fatigue analysis of a wind turbine drivetrain under dynamic conditions[J].International Journal of Fatigue, 2013, 48(1):133-146. [6] NEJAD A R, GAO Z, MOAN T.On long-term fatigue damage and reliability analysis of gears under wind loads in offshore wind turbine drivetrains[J].International Journal of Fatigue, 2014, 61(2):116-128. [7] 谢里阳, 周金宇, 李翠玲, 等.系统共因失效分析及其概率预测的离散化建模方法[J].机械工程学报, 2006, 42(1):62-68.XIE L Y, ZHOU J Y, LI C L.Common cause failure analysis and discretely modeling for system probability prediction[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2006, 42(1):62-68(in Chinese). [8] DITLEVSEN O, MADSEN H O.Structural reliability methods[M].New York:John Wiley & Sons, 1996. [9] ZHAO Y G, ONO T.Moment method for structural reliability[J].Structural Safety, 2001, 23(6):47-75. [10] NAESS A, LEIRA B J, BATSEVYCH O.Reliability analysis of large structural systems[J].Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 28(3):164-168. [11] XIE L Y, ZHOU J Y, HAO C Z.System-level load-strength interference based reliability modeling of k-out-of-n system[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2004, 84(3):311-317. [12] 谢里阳, 王正.随机恒幅循环载荷疲劳可靠度异量纲干涉模型[J].机械工程学报, 2008, 44(1):1-6.XIE L Y, WANG Z.Dissimilar-dimension interference model of fatigue reliability under uncertain cyclic load[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 44(1):1-6(in Chinese). [13] 谢里阳, 刘建中, 吴宁祥, 等.风电装备传动系统及零部件疲劳可靠度评估方法[J].机械工程学报, 2014, 50(11):1-8.XIE L Y, LIU J Z, WU N X.Fatigue reliability evaluation method for gear component and system of wind turbine[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(11):1-8(in Chinese). [14] OYAGUE F. Gearbox reliability collaborative (GRC) description and loading: NREL/TP-5000-47773[R]. Golden: Office of Scientific & Technical Information, 2011: 9. [15] 朱孝录.调质钢齿轮接触疲劳强度可靠度试验研究[J].齿轮, 1983, 7(3):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLCS199203003.htmZHU X L.The study of quenched and tempered steel gear contact fatigue strength reliability tests[J].Gear, 1983, 7(3):1-9(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLCS199203003.htm [16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验总局. 金属材料疲劳试验数据统计方案与分析方法: GB/T 24176-2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Metalic materials-fatigue testing-statistical planning and analysis of data: GB/T 24176-2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009(in Chinese). [17] GARDNER E D. Reliability of components subject to cumulative fatigue[D]. Arizona: University of Arizona, 1971: 35-45. [18] CHEN D.New approaches to the estimation of cumulative fatigue reliability[J].Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 1991, 33(2):231-247. doi: 10.1016/0951-8320(91)90061-B -








 下载:
下载: