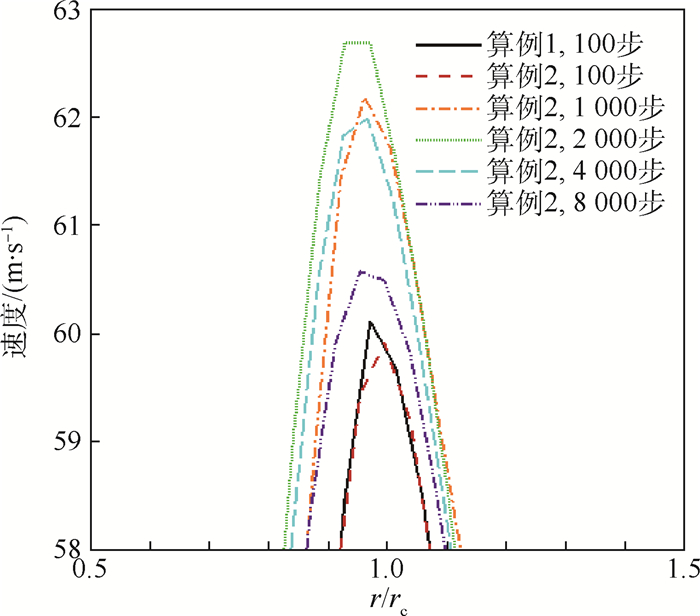
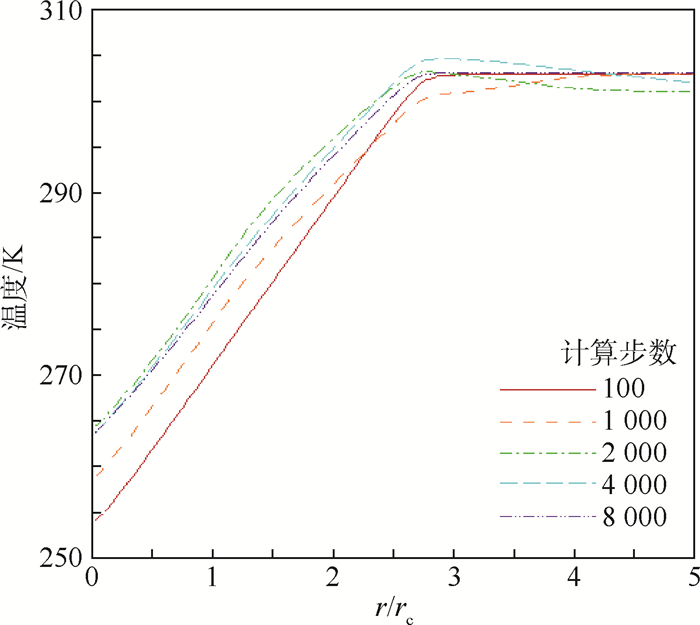
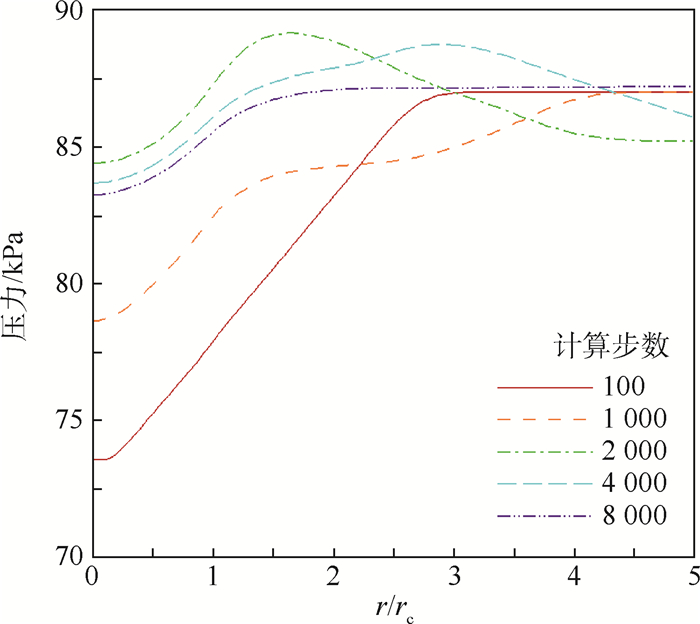
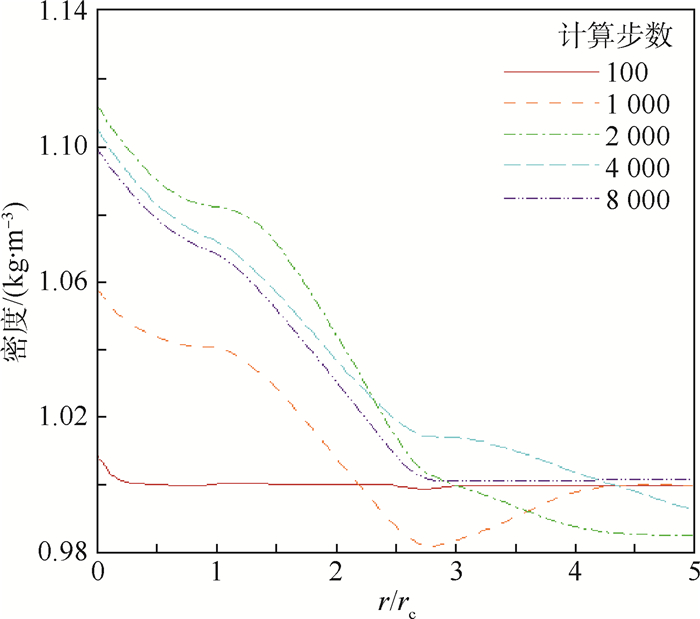
-
摘要:
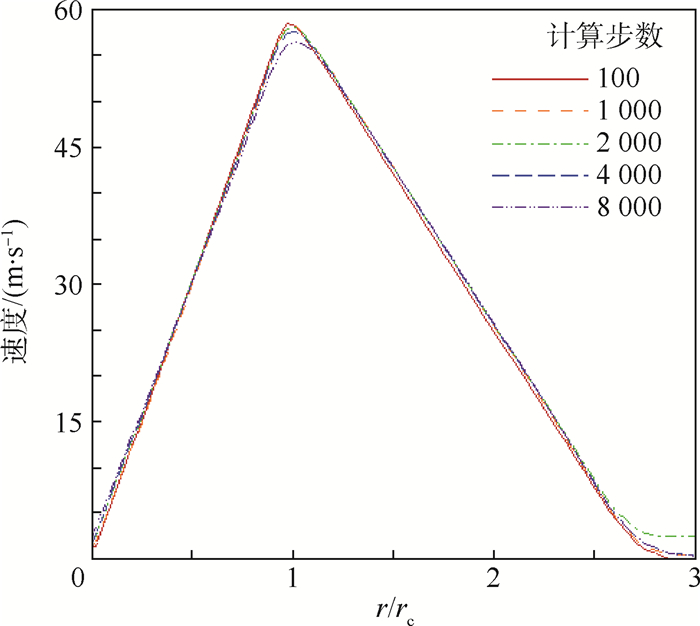
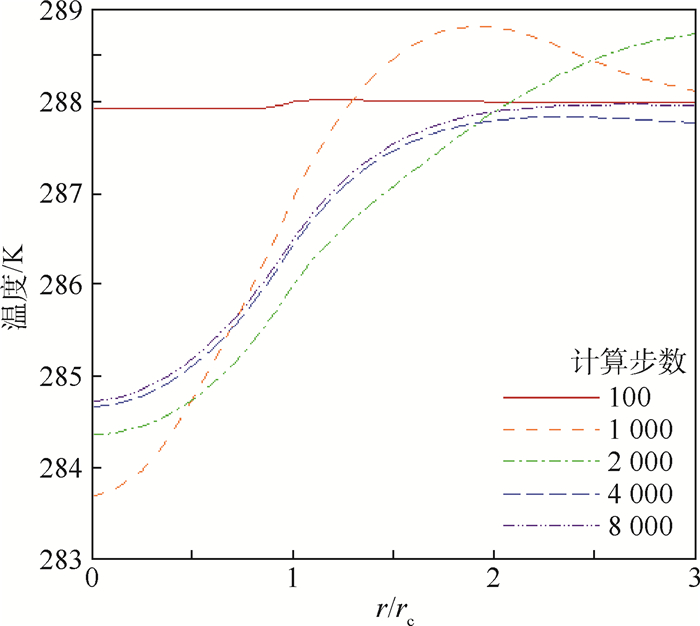
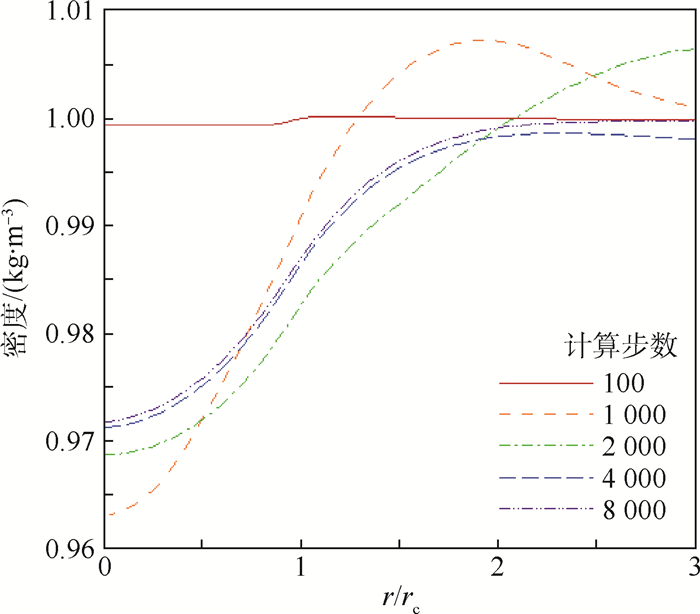
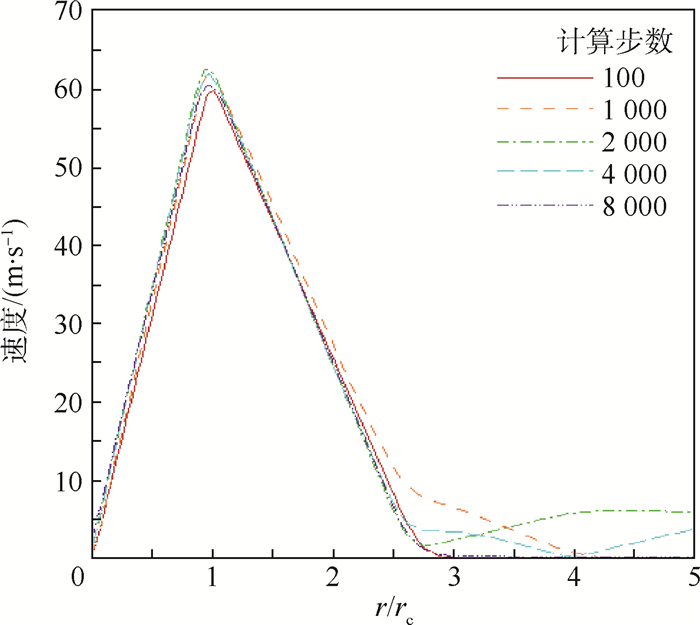
利用计算流体力学(CFD)方法建立了模拟龙卷风的装置模型。基于龙卷风在平面上的速度型,拟合成函数关系式,在三维CFD程序中设置初始速度场以及相关的边界条件,匹配不同的初始温度场进行了关于龙卷风维持和发展的一系列数值模拟。重现并利用漩涡管的Ranque-Hilsch效应以及汇流换热原理分析了本文2种不同的温度型对龙卷风内部流场变量随时间推移所发生的变化,同时揭示了龙卷风产生并维持下去的一种可能性,即冷热气流汇流换热生成温度场可能是产生和维持龙卷风的直接原因,并在此基础上提出使龙卷风削弱甚至消亡的方法,即破坏温度场。
-
关键词:
- 计算流体力学(CFD) /
- 龙卷风 /
- 数值模拟 /
- 汇流换热原理 /
- 温度场
Abstract:A numerical model of the tornado was established by using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method. Based on the speed type of the tornado in the plane, which was fitted to be the function relation, the initial velocity field and the related boundary condition were set in the 3D CFD program. Different initial temperature fields were carried out on a series of numerical simulations of tornado maintenance and development. The Ranque-Hilsch effect of the whirlpool and the convergence heat transfer principle were used to analyze the changes of the internal flow field variables of the two different temperature types in the tornado. It reveals the possibility of how the tornado was produced and continued, that is, the hot and cold air flow mixing and heat transfer which generated a temperature field may be the direct cause for producing and continuing a tornado. And a method to make tornado weak or even disappear was proposed, that is, destroying the temperature field.
-
-
[1] HOECKER W H.Wind speed and air flow patterns in the Dallas tornado of April 2, 1957[J].Monthly Weather Review, 1960, 88(5):167-180. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1960)088<0167:WSAAFP>2.0.CO;2 [2] ALEXANDER C R, WURMAN J.The 30 May 1998 Spencer, South Dakota, storm.Part Ⅰ:The structural evolution and environment of the tornadoes[J].Monthly Weather Review, 2005, 133(1):72-96. doi: 10.1175/MWR-2855.1 [3] WURMAN J, ALEXANDER C R.The 30 May 1998 Spencer, South Dakota, storm.Part Ⅱ:Comparison of observed damage and radar-derived winds in the tornadoes[J].Monthly Weather Review, 2005, 133(1):97-119. doi: 10.1175/MWR-2856.1 [4] CHANG C C. Tornado wind effects on buildings and structures with laboratory simulation[C]//Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Wind Effects on Buildings and Structures, 1971: 231-240. [5] WARD N B.The exploration of certain features of tornado dynamics using a laboratory model[J].Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1972, 29(6):1194-1204. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1972)029<1194:TEOCFO>2.0.CO;2 [6] CHURCH C R, SNOW J T, AGEE E M.Tornado vortex simulation at Purdue University[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1977, 58(9):900-908. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1977)058<0900:TVSAPU>2.0.CO;2 [7] JISCHKE M C, PARANG M.Properties of simulated tornado-like vortices[J].Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1974, 31(2):506-512. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1974)031<0506:POSTLV>2.0.CO;2 [8] SARKAR P P, HAAN F L, GALLUS JR W A, et al. A laboratory tornado simulator: Comparison of laboratory, numerical and full-scale measurements[C]//10th Americas Conference on Wind Engineering. Baton Rouge, LA: American Association for Wind Engineering, 2005. [9] HASSENZAHL H C. Numerical investigations of a tornado vortex using vorticity confinement[D]. Madison: University of Wisconsin Madison, 2007. [10] MARUYAMA T. A numerically generated tornado-like vortex by large eddy simulation[C]//Proceedings of 7th Asia Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering. Taipei: Wind Engineering, 2009. [11] MARUYAMA T.Simulation of flying debris using a numerically generated tornado-like vortex[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2011, 99(4):249-256. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2011.01.016 [12] NATARAJAN D. Numerical simulation of tornado-like vortices[D]. London: The University of Western Ontario, 2011. [13] NATARAJAN D, HANGAN H. Numerical study on the effects of surface roughness on tornado-like flows[C]//11th Americas Conference on Wind Engineering(11ACWE). Baton Rouge, LA: American Association for Wind Engineering, 2009. [14] 徐枫, 肖仪清, 李波, 等.龙卷风风场特性的CFD数值模拟[J].空气动力学学报, 2013, 31(3):350-356.XU F, XIAO Y Q, LI B, et al.Study of the adaptive optimal design method based on design variables space[J].Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2013, 31(3):350-356(in Chinese). [15] KRIST S L, BIEDRON R T, RUMSEY C L. CFL3D user's manual(version5. 0): NASA-TM-1998-208444[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1998. [16] 王锦, 周强, 曹曙阳, 等.龙卷风风场的试验模拟[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(11):1654-1659.WANG J, ZHOU Q, CAO S Y, et al.Physical study on tornado-like flow based on tornado vortex simulator[J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2014, 42(11):1654-1659(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: