Judgement criterion for terrain false matching based on joint probability of multiple reference points
-
摘要:
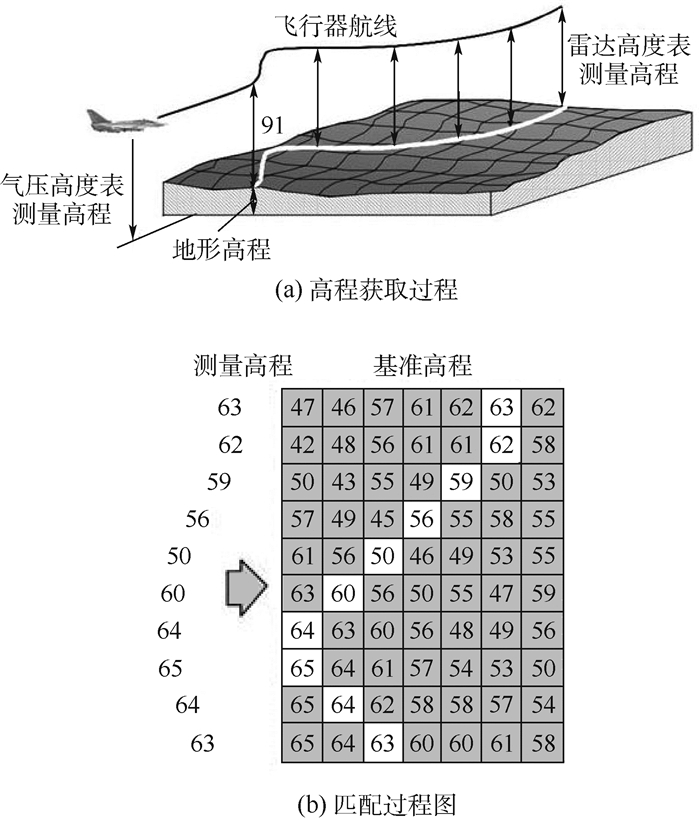
针对地形轮廓匹配(TERCOM)算法容易受高程测量误差和地形相似性等影响而出现误匹配的问题,以平均平方差(MSD)匹配准则为例,提出了一种相关面内多参照点联合概率误匹配在线判断准则。首先,对测量高程数据和基准高程数据做相关运算,获得待匹配区域内各点的MSD值,即相关面;其次,通过分析高程量测噪声的统计分布,建立待匹配点的MSD概率分布密度函数;最后,计算选取待匹配点为正确匹配点的多点联合概率,并通过阈值判定此待匹配点是否为正确匹配点。仿真结果表明,选取不同的匹配序列长度和测量噪声的情况下,当判定阈值设为0.9时,对正确匹配的判断正确率达到97%以上,且90%以上的正确匹配点都能被保留下来,可以极大程度地避免误匹配。
-
关键词:
- 地形匹配 /
- 地形轮廓匹配(TERCOM)算法 /
- 误匹配 /
- 匹配概率 /
- 虚定位
Abstract:Since the terrain contour matching (TERCOM) algorithm is easy to mismatch due to measurement error and terrain self-similarity, an on-line false matching judgement criterion based on the joint probability of multiple reference points in a correlation plane was proposed by taking mean square difference (MSD) as an example. Firstly, the MSD correlation plane was calculated by the correlation of the measured elevation data with the reference elevation data. Then, the MSD probability distribution density function of the candidate matching points was derived by analyzing the statistical distribution of elevation measurement error. Finally, the multi-point joint probabilities were calculated for all the candidate points in the correlation plane so that they are compared with a threshold to judge the matching of the point with the minimum MSD value false or not. The simulation results show that 97% false matching points can be detected and 90% correct matching points can be preserved when the threshold is set to 0.9, implying that false matching can be avoided to a great extent.
-
表 1 图 4相关面对应极值点区域联合概率
Table 1. Regional joint probability of extreme points corresponding to correlation plane of Fig. 4
编号 极小值点坐标 MSD值 区域联合概率 1 (90, 90) 347.6 0.31 2 (111, 112) 351.4 0.69 3 (69, 9) 526.8 0 4 (127, 161) 546.9 0 5 (37, 142) 595.5 0 6 (147, 153) 685.3 0 7 (62, 181) 723.6 0 8 (103, 119) 767 0 9 (114, 63) 809.5 0 10 (135, 52) 947.2 0 表 2 图 5相关面对应极值点区域联合概率
Table 2. Regional joint probability of extreme points corresponding to correlation plane of Fig. 5
编号 极小值点坐标 MSD值 区域联合概率 1 (33, 49) 67.6 0.97 2 (108, 14) 93.5 0 3 (102,107) 130.7 0 4 (93, 1) 209.2 0 5 (48,169) 289.2 0 6 (63, 109) 303.5 0 7 (113, 144) 315.9 0 8 (38, 56) 358.7 0.03 9 (199, 200) 407.5 0 10 (129, 134) 458.9 0 表 3 遍历仿真试验结果
Table 3. Traversal simulation test results
序列长度 σn/m 
正确点保留率/% 匹配准确率/% 无阈值 阈值为0.6 阈值为0.9 无阈值 阈值为0.6 阈值为0.9 100 10 4.6 100 97.9 97.9 94.5 98.9 99.4 17 2.7 100 95.9 94.1 86 97 98.8 24 1.9 100 90.9 90.4 83.5 96.2 97.4 150 10 4.6 100 99 99 98 100 100 17 2.7 100 98.5 98.5 97.5 99.5 99.5 24 1.9 100 96.8 96.2 92.5 98.4 98.9 200 10 4.6 100 99.5 98.9 98.5 100 100 17 2.7 100 99 99 97.5 99.5 100 24 1.9 100 98.9 98.4 95.5 99.5 100 -
[1] WIENER T F. Terrain contour matching(TERCOM): A cruise missile guidance aid[C]//Proceedings of 24th Annual Technical Symposium. Bellingham: SPIE, 1980: 10-18. doi: 10.1117/12.959127 [2] 徐克虎, 沈春林.地形特征匹配辅助导航方法研究[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 30(3):113-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2000.03.025XU K H, SHEN C L.Study of terrain feature matching aided navigation method[J].Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2000, 30(3):113-117(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0505.2000.03.025 [3] 李雄伟, 刘建业, 康国华.TERCOM地形高程辅助导航系统发展及应用研究[J].中国惯性技术学报, 2006, 14(1):34-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zggxjsxb200601008LI X W, LIU J Y, KANG G H.Development and application of TERCOM elevation-aided navigation system[J].Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2006, 14(1):34-40(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zggxjsxb200601008 [4] FENG Q, SHEN L, CHANG W. Terrain aided navigation using PDAF[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Intelligent Systems and Signal Processing. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2003: 1063-1068. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1285737/ [5] 张凯, 赵建虎, 施闯, 等.BP神经网络用于水下地形适配区划分的方法研究[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2013, 38(1):56-59. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92848A/201301/44772511.htmlZHANG K, ZHAO J H, SHI C, et al.Study on classification of matching area of underwater topography based on BP neural network[J].Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2013, 38(1):56-59(in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92848A/201301/44772511.html [6] 徐晓苏, 汤郡郡, 张涛, 等.基于熵值法赋权灰色关联决策的地形辅助导航适配区选择[J].中国惯性技术学报, 2015, 23(2):201-206. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/word/9967beef65ce050876321373-1.docXU X S, TANG J J, ZHANG T, et al.Selection for matching area in terrain aided navigation based on entropy-weighted grey correlation decision-making[J].Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(2):201-206(in Chinese). https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/word/9967beef65ce050876321373-1.doc [7] 王立辉, 乔楠, 余乐.水下地形导航匹配区选取的模糊推理方法[J].西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(1):140-145. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZXGH201511006074.htmWANG L H, QIAO N, YU L.Fuzzy deduction methods of selecting the underwater terrain navigation matching area[J].Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science), 2017, 44(1):140-145(in Chinese). http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZXGH201511006074.htm [8] ZHANG X, HE Z, LIANG Y, et al. Selection method for scene matching area based on information entropy[C]//International Symposium on Computational Intelligence & Design. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 364-368. [9] 冯庆堂. 地形匹配新方法及其环境适应性研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2004: 42-44. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-90002-2005144392.htmFENG Q T. The research on new terrain elevation matching approaches and their applicability[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2004: 42-44(in Chinese). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-90002-2005144392.htm [10] 刘徐德.地形辅助导航技术[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 1994:27-59.LIU X D.Terrain-aided navigation technology[M].Beijing:Electronic Industry Press, 1994:27-59(in Chinese). [11] 杨勇, 王可东.ICCP中单纯形优化的误匹配检测[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2009, 35(3):334-337. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8972.shtmlYANG Y, WANG K D.Mismatching judgement in simplex optimization for ICCP algorithm[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009, 35(3):334-337(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8972.shtml [12] 朱华勇, 沈林成.地形相关算法度量值的统计特性[J].国防科技大学学报, 1999, 21(4):91-95. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gfkjdxxb200004023ZHU H Y, SHEN L C.Research on statistical properties of measures of terrain correlation algorithms[J].Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 1999, 21(4):91-95(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gfkjdxxb200004023 [13] JOHNSON M W. Analytical development and test results of acquisition devices used in navigation systems[C]//10th Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 1972: 1-9. doi: 10.2514/6.1972-122 [14] JOHNSON L, KORTZ S, BALAKRISHNAN N.Continuous univariate distributions-Ⅱ[M].Boston:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 1970:130-146. [15] 茆诗松, 程依明, 濮晓龙.概率论与数理统计[M].2版.北京:高等教育出版社, 2011:252-349.MAO S S, CHENG Y M, PU X L.Probability and mathematical statistics tutorial[M].2nd ed.Beijing:Higher Education Press, 2011:252-349(in Chinese). [16] 中国科学院计算机网络信息中心地理空间数据云平台. DDEMV2数字高程数据[DB/OL]. NASA, METI, 2015[2017-03-07]. http://www.gscloud.cn.Geospatial Data Cloud Platform of Computer Network Information Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Digital elevation data of DDEMV2[DB/OL]. NASA, METI, 2015[2017-03-07]. http://www.gscloud.cn(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: