Effectiveness analysis of pupil diameter detection for air traffic controller's fatigue
-
摘要:
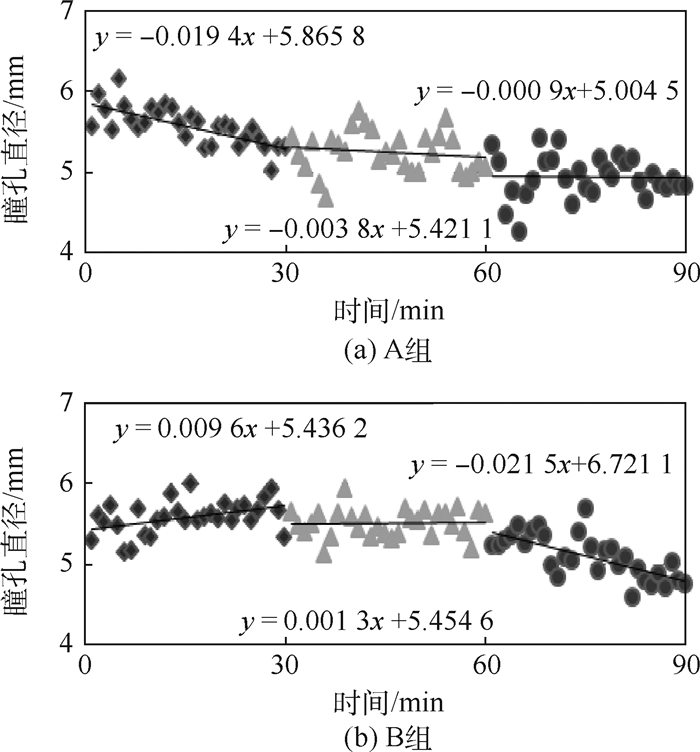
管制疲劳已成为影响民航安全的重大隐患,而准确地检测疲劳是进行疲劳预警、降低疲劳风险的重要手段。为了探讨瞳孔直径是否能有效地检测管制疲劳状态,利用模拟塔台管制软件和眼动仪搭建了实验平台,采集了被试的瞳孔数据和主观疲劳状态,通过分析不同航班流量下疲劳前后瞳孔直径的差异显著性以及变化趋势,探讨了瞳孔直径指标作为检测管制疲劳状态的有效性。研究结果表明:工作时间增大,被动疲劳增加,瞳孔直径减小;航班流量增大,主动疲劳增加,瞳孔直径增大;2种因素共同制约瞳孔直径的变化。通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析可得,瞳孔直径在0.47架次/min与0.9架次/min 2种不同航班流量下的ROC曲线下方面积(AUC值)分别为0.714和0.653,可以作为检测管制疲劳状态的参考指标。
-
关键词:
- 瞳孔 /
- 眼动 /
- 空中交通管制 /
- 疲劳 /
- 受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线
Abstract:Air traffic controllers' fatigue has become a major hazard to affect civil aviation safety, and accurate detection of fatigue is an important means for fatigue warning and fatigue risk reduction. In order to study whether the pupil diameter can detect air traffic controllers' fatigue effectively, an experimental platform was constructed by using tower control simulation software and eye tracker, and the pupil data and subjective fatigue degree were collected. By analyzing the significance test of difference and change tendency of pupil diameter before and after fatigue at different flight flow rates, the effectiveness of pupil diameter index in detecting fatigue state was discussed. The study results show that when working time increases, the passive fatigue increases, and the pupil diameter decreases; when the flight flow increases, the active fatigue increases, and the pupil diameter increases. Both the factors restrict the change of pupil diameter. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis results show that the area under curve (AUC) values of the pupil diameter at 0.47 flight sorties per minute and 0.9 flight sorties per minute were 0.714 and 0.653 respectively, so pupil diameter can be an index for detecting air traffic controllers' fatigue.
-
Key words:
- pupil /
- eye movement /
- air traffic control /
- fatigue /
- receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve
-
表 1 各被试疲劳前后瞳孔直径描述性统计
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of subjects' pupil diameter before and after fatigue
被试编号 A组瞳孔直径/mm B组瞳孔直径/mm 疲劳前 疲劳后 疲劳前 疲劳后 1 5.57(0.39) 4.90 (0.42) 5.58 (0.40) 5.06(0.40) 2 4.71(0.32) 4.00 (0.48) 4.74 (0.34) 4.30(0.37) 4 4.95(0.35) 4.32 (0.41) 4.70 (0.33) 4.46(0.38) 6 6.37(0.35) 5.85 (0.49) 6.00 (0.51) 5.72(0.42) 7 6.06(0.37) 5.94 (0.45) 5.93 (0.51) 5.81(0.43) 8 4.26(0.25) 4.05 (0.35) 4.27 (0.22) 4.17(0.22) 10 4.80(0.32) 4.17 (0.35) 4.69 (0.35) 4.62(0.30) -
[1] MITLER M M, CARSKADON M A, CZEISLER C A, et al.Catastrophes, sleep, and public policy:Consensus report[J].Sleep, 1988, 11(1):100-109. doi: 10.1093/sleep/11.1.100 [2] WILLIAMSON A, LOMBARDI D A, FOLKARD S, et al.The link between fatigue and safety[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2011, 43(2):498-515. [3] 王永刚, 董保健.管制员人为差错影响因素及指标权重分析[J].中国安全生产科学技术, 2011, 7(2):28-33.WANG Y G, DONG B J.Analysis of human error influence factors and evaluation indexes weights determination for air traffic controller[J].Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2011, 7(2):28-33(in Chinese). [4] 孙涛, 陈宇.空中交通管制的疲劳管理和预防[J].空中交通管理, 2005(5):4-10.SUN T, CHEN Y.The management and prevention of ATC fatigue[J].Air Traffic Management, 2005(5):4-10(in Chinese). [5] 孙瑞山, 马广福, 袁乐平.语音反应时特性的管制员疲劳风险分析[J].中国安全科学学报, 2016, 26(12):7-12.SUN R S, MA G F, YUAN L P.Analysis of risk of controller fatigue based on characteristics of speech reaction time[J].China Safety Science Journal, 2016, 26(12):7-12(in Chinese). [6] 汪磊, 孙瑞山.空中交通管制员疲劳状态实时监测方法的实现[J].安全与环境工程, 2013, 20(4):87-91.WANG L, SUN R S.Air traffic controller fatigue state implementation of real time monitoring method[J].Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2013, 20(4):87-91(in Chinese). [7] MOLLARD R, CABON P, BOURGEOIS-BOUGRINE S, et al. Measurement of fatigue and sleepiness in ATC simulation[C]//Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting. London: SAGE Publications, 2000, 44(19): 208-211. [8] DASARI D, CROWE C, LING C, et al. EEG pattern analysis for physiological indicators of mental fatigue in simulated air traffic control tasks[C]//Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting. London: SAGE Publications, 2010, 54(3): 205-209. [9] WIYOR H D, NTUEN C A, STEPHENS J D W, et al.Classifying visual fatigue severity based on neurophysiological signals and psychophysiological ratings[J].International Journal of Human Factors and Ergonomics, 2013, 2(1):11-32. doi: 10.1504/IJHFE.2013.055982 [10] CHARBONNIER S, ROY R N, BONNET S, et al.EEG index for control operators' mental fatigue monitoring using interactions between brain regions[J].Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 52:91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.01.013 [11] IQBAL S T, BAILEY B P. Using eye gaze patterns to identify user tasks[C]//The Grace Hopper Celebration of Women in Computing, 2004: 1-6. [12] HAISONG G, QIANG J. An automated face reader for fatigue detection[C]//FGR'04 Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2004: 111-116. [13] DI S L, MCCAMY M B, CATENA A, et al.Microsaccade and drift dynamics reflect mental fatigue[J].European Journal of Neuroscience, 2013, 38(3):2389-2398. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12248 [14] 马锦飞, 常若松, 高远.瞳孔直径大小检测驾驶员疲劳的实证效度分析[J].辽宁师范大学学报(社会科学版), 2014, 37(1):67-70.MA J F, CHANG R S, GAO Y.An analysis of empirical validity on pupil diameter size in driver fatigue measurement[J].Journal of Liaoning Normal University(Social Science Edition), 2014, 37(1):67-70(in Chinese). [15] 胥川, 王雪松, 陈小鸿.无侵入测量指标的驾驶疲劳检测性能评估[J].西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(4):720-726. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201404025.htmXU C, WANG X S, CHEN X H.Evaluating performance of non-intrusive indicators on drowsy driving detection[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4):720-726(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201404025.htm [16] 丛晓妍, 王增才, 徐俊凯, 等.瞳孔测量法应用于疲劳检测的适应性[J].长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 35(6):135-140.CONG X Y, WANG Z C, XU J K, et al.Pupillary parameters as an objective tool for fatigue assessment[J].Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 35(6):135-140(in Chinese). [17] MORAD Y, LEMBERG H, YOFE N, et al.Pupillography as an objective indicator of fatigue[J].Current Eye Research, 2000, 21(1):535-542. doi: 10.1076/0271-3683(200007)2111-ZFT535 -








 下载:
下载: