Impact factor weight analysis of atmospheric corrosion rate of carbon steel based on MIV
-
摘要:
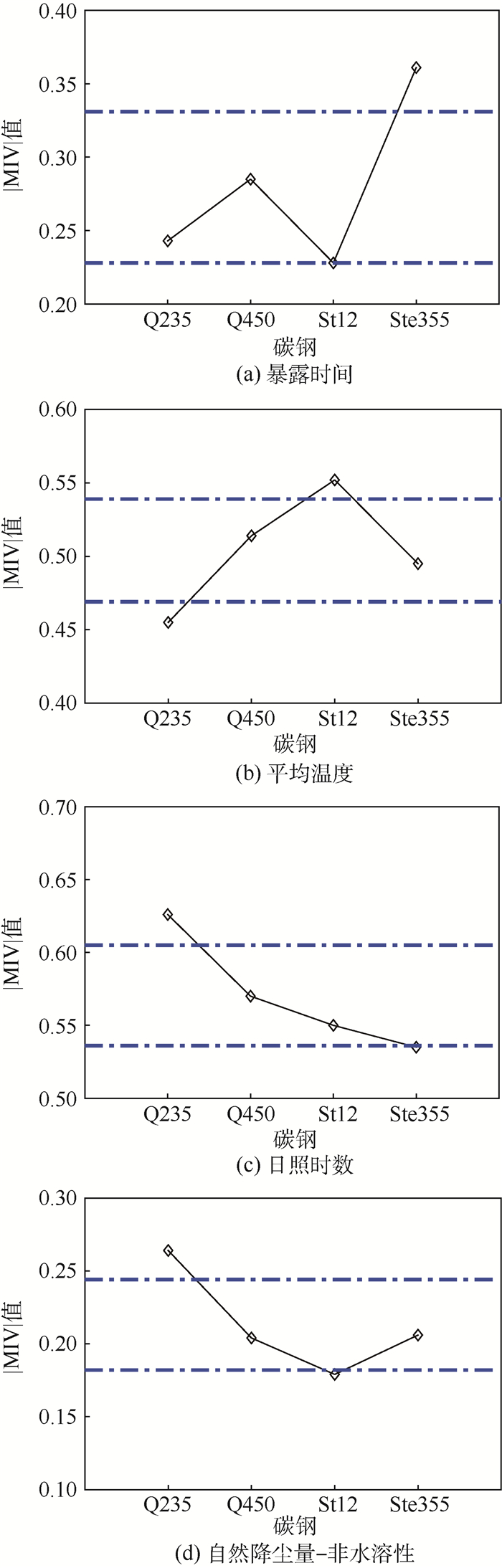
通过平均影响值(MIV)影响因子权重分析算法,以碳钢Q235、Ste355、St12和Q450腐蚀速率的暴露时间、气候因素和环境因素数据为依据,以|MIV|值为评价依据,定量分析15种影响因子(暴露时间、平均温度、平均相对湿度、日照时数、降水量、平均风速、海盐粒子浓度、SO2、HCl、NO2、H2S、硫酸盐化速率、NH3、降尘量-非水溶性、降尘量-水溶性)对碳钢腐蚀速率影响的权重大小。结果表明: 当MIV调节率从5%逐步递增至25%时,同种影响因子对腐蚀速率的影响权重变化不大,但4种碳钢对各影响因子的敏感度略有不同;气候因素对腐蚀速率影响最大,其次为暴露时间,环境因素中SO2和降尘量对腐蚀速率影响较大;平均相对湿度、日照时数、平均温度是影响腐蚀速率最主要的3个因子。
-
关键词:
- 碳钢 /
- 腐蚀速率 /
- 平均影响值(MIV) /
- 影响因子 /
- 大气腐蚀
Abstract:Based on the mean impact value (MIV) which is an impact factor weight analysis method, the weights of fifteen impact factors on corrosion rate of four types of carbon steels (Q235, Ste355, St12, and Q450) were evaluated. The impact factors were corrosion duration, temperature, humidity, sunshine hours, precipitation, wind speed, sea salt ion concentration, SO2, HCl, NO2, H2S, sulfation rate, NH3, water soluble dust fall, and non-water soluble dust fall. These fifteen factors cover three important categories: corrosion duration, climatic factor, and environmental factor. The results show that when the regulation rate of MIV increases from 5% to 25% gradually, for different carbon steels, the weights of impact factors were similar, while the degrees of sensitivity were a little different; in the three categories, the climatic factor is of the largest impact on corrosion rate, followed by corrosion duration. The weights of SO2 and dust fall are larger among the environmental factors. The most important three factors influencing the corrosion rate are mean relative humidity, sunshine hours, and mean temperature.
-
Key words:
- carbon steel /
- corrosion rate /
- mean impact value (MIV) /
- impact factor /
- atmospheric corrosion
-
表 1 腐蚀速率影响及评价因子数据
Table 1. Impact and evaluation factor data of corrosion rate
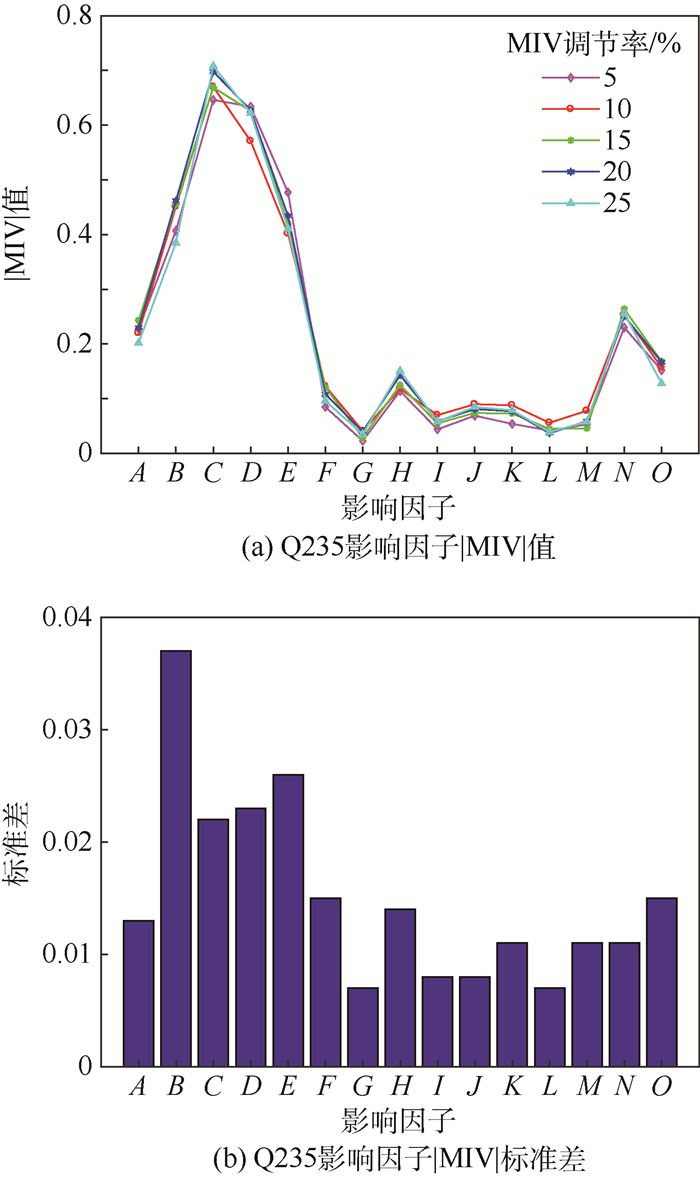
评价因子 数值 实验时间/a 1 平均温度/℃ 12.750 平均相对湿度/% 50.151 日照时数/h 85.642 降水量/mm 50.879 平均风速/(m·s-1) 2.025 瞬时法SO2/(mg·cm-3) 0.001 瞬时法HCl/(mg·cm-3) 0.052 连续法NO2/(mg·(100 m2·d)-1) 0.106 连续法H2S/(mg·(100 m2·d)-1) 0.056 连续法硫酸盐化速率/(mg·(100 m2·d)-1) 0.320 连续法NH3 /(mg·(100 m2·d)-1) 0.054 连续法海盐粒子浓度/(mg·(100 m2·d)-1) 0.010 自然降尘量-非水溶性/(g·(cm2·mol·L-1)-1) 4.371 自然降尘量-水溶性/(g·(cm2·mol·L-1)-1) 1.496 表 2 不同调节率下Q235的各影响因子|MIV|值
Table 2. |MIV| values of impact factors of Q235 with different regulation rates
MIV调节率/% A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O 5 0.228 0.407 0.646 0.634 0.477 0.085 0.023 0.114 0.044 0.069 0.054 0.042 0.053 0.230 0.152 10 0.220 0.451 0.670 0.571 0.402 0.123 0.041 0.118 0.070 0.090 0.088 0.056 0.078 0.253 0.157 15 0.243 0.455 0.669 0.626 0.419 0.121 0.029 0.125 0.055 0.074 0.073 0.045 0.046 0.264 0.168 20 0.230 0.462 0.698 0.627 0.434 0.108 0.040 0.143 0.059 0.081 0.077 0.037 0.059 0.251 0.167 25 0.202 0.385 0.708 0.622 0.411 0.096 0.035 0.151 0.058 0.085 0.079 0.039 0.058 0.256 0.128 注: A为暴露时间; B为平均温度; C为平均相对湿度; D为日照时数; E为降水量; F为平均风速; G为连续法海盐粒子浓度; H为瞬时法SO2; I为瞬时法HCl; J为连续法NO2; K为连续法H2S; L为连续法硫酸盐化速率; M为连续法NH3; N为自然降尘量-非水溶性; O为自然降尘量-水溶性。 表 3 不同调节率下Q450的各影响因子|MIV|值
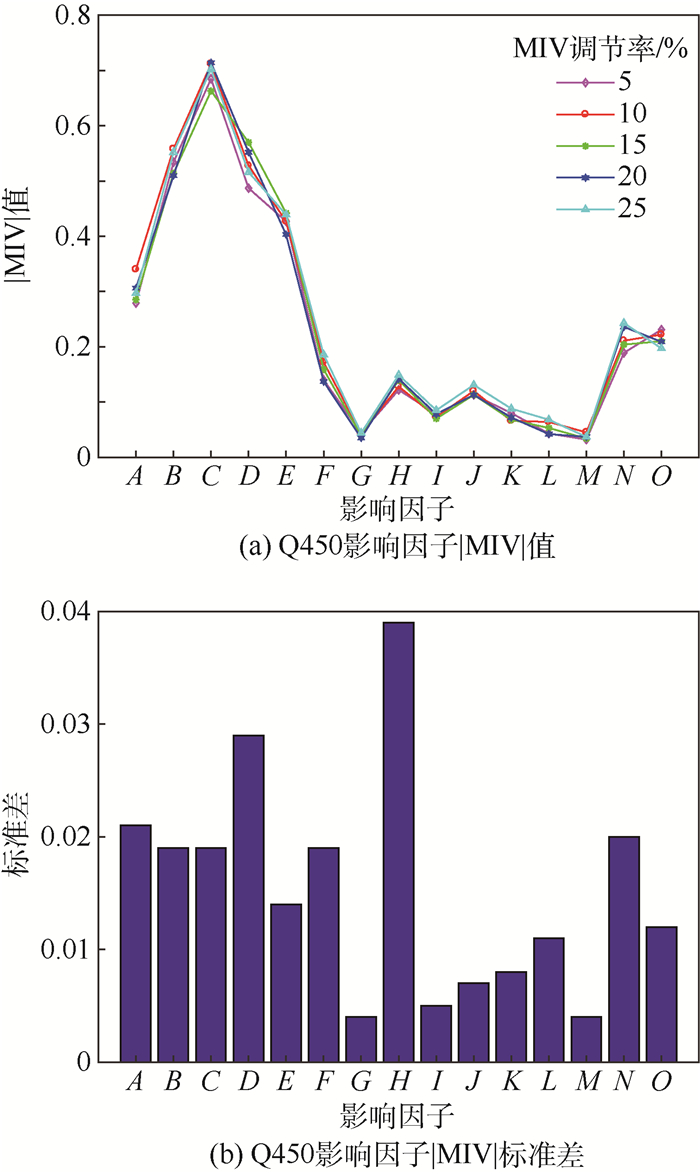
Table 3. |MIV| values of impact factors of Q450 with different regulation rates
MIV调节率/% A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O 5 0.279 0.534 0.685 0.487 0.427 0.140 0.044 0.122 0.078 0.113 0.080 0.043 0.032 0.189 0.231 10 0.340 0.558 0.712 0.528 0.427 0.172 0.043 0.128 0.073 0.120 0.066 0.064 0.045 0.211 0.222 15 0.285 0.514 0.663 0.570 0.442 0.159 0.039 0.130 0.070 0.113 0.068 0.053 0.034 0.204 0.210 20 0.306 0.510 0.714 0.552 0.403 0.137 0.035 0.142 0.078 0.113 0.072 0.042 0.037 0.236 0.209 25 0.297 0.552 0.702 0.516 0.439 0.186 0.044 0.149 0.085 0.131 0.088 0.068 0.037 0.243 0.197 表 4 不同调节率下St12的各影响因子|MIV|值
Table 4. |MIV| values of impact factors of St12 with different regulation rates
MIV调节率/% A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O 5 0.228 0.448 0.755 0.560 0.427 0.124 0.050 0.112 0.057 0.102 0.065 0.031 0.026 0.162 0.174 10 0.244 0.477 0.749 0.540 0.441 0.128 0.058 0.118 0.061 0.107 0.091 0.034 0.029 0.170 0.188 15 0.228 0.552 0.719 0.550 0.397 0.134 0.047 0.120 0.068 0.113 0.085 0.030 0.024 0.179 0.184 20 0.216 0.457 0.758 0.546 0.336 0.126 0.045 0.124 0.064 0.108 0.076 0.017 0.039 0.180 0.153 25 0.224 0.474 0.731 0.538 0.437 0.120 0.029 0.130 0.045 0.096 0.070 0.042 0.029 0.183 0.191 表 5 不同调节率下Ste355各影响因子|MIV|值
Table 5. |MIV| values of impact factors of Ste355 with different regulation rates
MIV调节率/% A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O 5 0.286 0.476 0.681 0.523 0.497 0.153 0.032 0.121 0.058 0.100 0.062 0.040 0.030 0.157 0.148 10 0.304 0.473 0.692 0.551 0.425 0.139 0.031 0.128 0.063 0.121 0.073 0.049 0.028 0.190 0.181 15 0.361 0.495 0.720 0.535 0.460 0.183 0.045 0.135 0.091 0.120 0.076 0.059 0.036 0.206 0.186 20 0.304 0.549 0.732 0.562 0.417 0.152 0.042 0.131 0.082 0.121 0.080 0.038 0.030 0.191 0.199 25 0.334 0.598 0.760 0.530 0.421 0.177 0.047 0.150 0.104 0.105 0.083 0.070 0.039 0.193 0.234 -
[1] 王振尧, 于国才, 韩薇.我国自然环境大气腐蚀性调查[J].腐蚀与防护, 2003, 24(8):323-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-748X.2003.08.001WANG Z Y, YU G C, HAN W.A survey of the atmospheric corrosiveness of nature environments in China[J].Corrosion & Protection, 2003, 24(8):323-326(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-748X.2003.08.001 [2] 柯伟.中国腐蚀调查报告[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2003:13.KE W.Chinese corrosion survey report[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2003:13(in Chinese). [3] 柯伟, 王振尧, 韩薇.大气腐蚀与装备环境工程[J].装备环境工程, 2004, 1(4):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2004.04.001KE W, WANG Z Y, HAN W.Atmospheric corrosion and materiel environmental engineering[J].Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2004, 1(4):1-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2004.04.001 [4] 梁彩凤.钢在中国大陆的大气腐蚀研究[J].电化学, 2001, 7(2):215-219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3471.2001.02.012LIANG C F.Atmospheric corrosion of steels in China[J].Electrochemistry, 2001, 7(2):215-219(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3471.2001.02.012 [5] COLE I S, GANTHER W D, SINCLAIR J D, et al.A study of the wetting of metal surfaces in order to understand the processes controlling atmospheric corrosion[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2004, 151(12):B627-B635. doi: 10.1149/1.1809596 [6] 林翠, 刘月娥.高湿度无污染大气中温度对碳钢腐蚀的影响[J].腐蚀与防护, 2009, 30(12):874-878.LIN C, LIU Y E.Effect of temperature on corrosion behavior of carbon steel in pollution-free atmosphere with high relative humidity[J].Corrosion & Protection, 2009, 30(12):874-878(in Chinese). [7] SONG L, CHEN Z.The role of UV illumination on the NaCl-induced atmospheric corrosion of Q235 carbon steel[J].Corrosion Science, 2014, 86(9):318-325. [8] MA Y, LI Y, WANG F.Corrosion of low carbon steel in atmospheric environments of different chloride content[J].Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(5):997-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2009.02.009 [9] WANG C, WANG Z, KE W.Initial corrosion behavior of carbon steel Q235 in the atmosphere with SO2[J].Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 44(6):729-734. [10] 闫松涛, 文磊, 金莹. 大气沉积颗粒物对碳钢腐蚀行为的影响[J/OL]. 中国科技论文在线(2016-06-20)[2017-08-01].YAN S T, WEN L, JIN Y. The influence of the deposited atmospheric particulates on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel[J/OL]. Sciencepaper Online(2016-06-20)[2017-08-01]. (in Chinese). [11] SINGH D D N, YADAV S, SAHA J K.Role of climatic conditions on corrosion characteristics of structural steels[J].Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(1):93-110. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.06.026 [12] 汪川, 曹公旺, 潘辰, 等.碳钢、耐候钢在3种典型大气环境中的腐蚀规律研究[J].中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2016, 36(1):39-46.WANG C, CAO G W, PAN C, et al.Atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel and weathering steel in three environments[J].Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2016, 36(1):39-46(in Chinese). [13] 朱世东, 尹志福, 白真权, 等.温度对P110钢腐蚀行为的影响[J].中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2009, 29(6):493-498.ZHU S D, YANG Z F, BAI Z Q, et al.Influences of temperature on corrosion behaviour of P110 steel[J].Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2009, 29(6):493-498(in Chinese). [14] 李牧铮, 张军, 祁凤玉.环境因子与大气腐蚀关系的数学模型和大气腐蚀预测[J].中国腐蚀与防护学报, 1993, 13(1):10-18.LI M Z, ZHANG J, QI F Y.Mathematical models for dependence of atmospheric corrosion on environment factors and prediction of atmospheric corrosion[J].Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 1993, 13(1):10-18(in Chinese). [15] 崔梦晨, 穆志纯, 付冬梅, 等.大气环境中碳钢腐蚀速率推测方法[J].腐蚀与防护, 2016, 37(6):503-507.CUI M C, MU Z C, FU D M, et al.Speculation of carbon steel corrosion rate in atmospheric environment[J].Corrosion & Protection, 2016, 37(6):503-507(in Chinese). [16] 冯志兰, 刘桂芬, 刘力生, 等.缺失数据的多重估算[J].中国卫生统计, 2005, 22(5):274-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2005.05.001FENG Z L, LIU G F, LIU L S, et al.Multiple estimates of missing data[J].Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 2005, 22(5):274-277(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3674.2005.05.001 [17] 孙文彬, 刘希亮, 王洪斌, 等.基于MIV的抛掷爆破影响因子权重分析[J].中国矿业大学学报, 2012, 41(6):993-998.SUN W B, LIU X L, WANG H B, et al.Weight analysis of cast blasting effective factors based on MIV method[J].Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2012, 41(6):993-998(in Chinese). [18] 武田艳, 占建军, 严韦.基于MIV-BP型网络实验的房地产价格影响因素研究[J].数学的实践与认识, 2015, 45(18):43-50.WU T Y, ZHAN J J, YAN W.Research on influence factors of real estate price based on MIV-BP neural network test[J].Journal of Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2015, 45(18):43-50(in Chinese). [19] 周莹. 基于MIV特征筛选和BP神经网络的滚动轴承故障诊断技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2011: 25.ZHOU Y. Research on ball fault diagnosis technology based on MIV algorithm selection and BP neural network[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011: 25(in Chinese). [20] 聂铭, 周冀衡, 杨荣生, 等.基于MIV-SVM的烤烟评吸质量预测模型[J].中国烟草学报, 2014, 20(6):56-62.NIE M, ZHOU J H, YANG R S, et al.MIV-SVM-based prediction model for smoking quality of flue-cured tobacco[J].Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2014, 20(6):56-62(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: