Off-resonance laser frequency stabilization method for fast and accurate adjustment of frequency lock points
-
摘要:
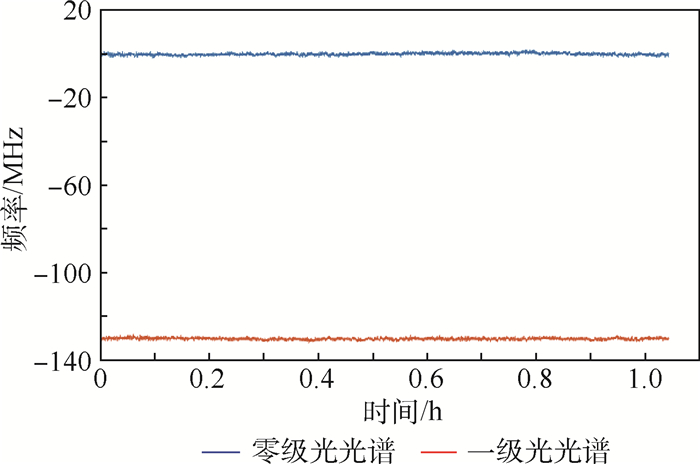
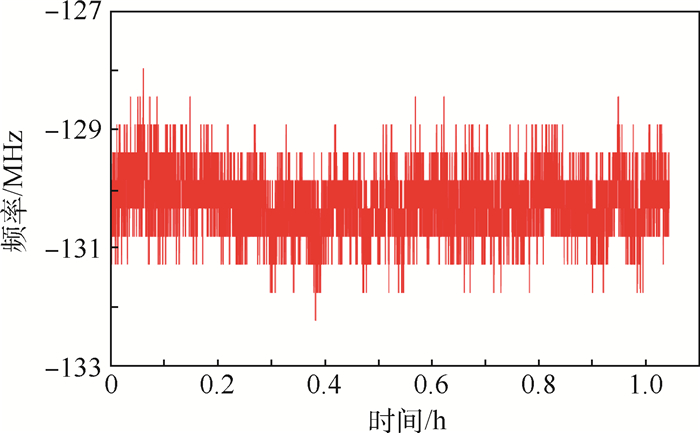
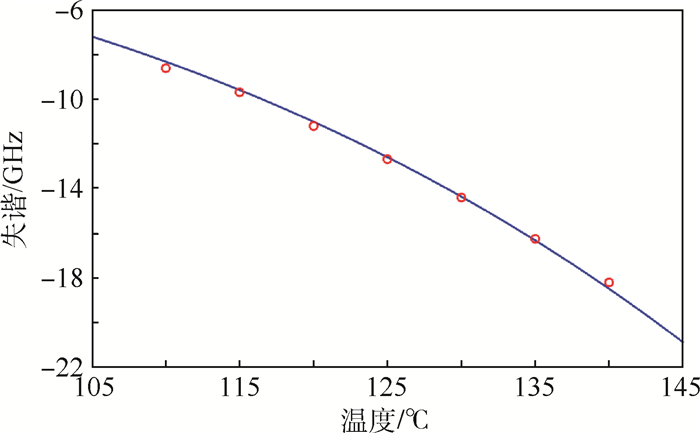
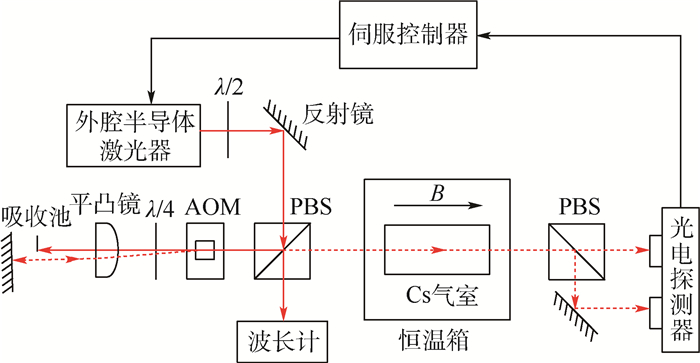
原子磁强计、激光冷却等技术需要将激光频率稳定在远离原子跃迁频率几兆赫兹的大失谐处,法拉第旋光光谱稳频方法能够实现远共振线的大失谐处的稳频,但是存在稳频点调节不便的问题。在法拉第旋光光谱稳频方法的基础上进行改进,提出了一种快速精确调节稳频点的远共振线激光稳频方法,能够在几十至几百兆赫兹范围内对稳频点频率进行快速精确的调节。基于该方法使失谐为-6.2 GHz的稳频点精确频移130 MHz,并实现频率漂移3.3 MHz/h,波动均方根值0.6 MHz/h的激光频率稳定度,满足原子磁强计对失谐及频率稳定性的要求。另外,分析了温度对该稳频方法的影响,推导了预估稳频点频率的物理参数,并将温度调节和声光调制器(AOM)调节相结合,以更好地实现在远共振线大失谐处对激光频率的长期稳定和精确控制。
Abstract:The atomic magnetometer and Raman cooling need to lock the frequency of the laser on the detuning of several gigahertz away from the resonance. The laser frequency stabilization technique in Faraday rotation spectroscopy can stabilize the laser frequency on the large detuning away from the resonance. But, in this method, changing the frequency lock points can be complex and has high latency. We present a far off-resonance laser frequency stabilization method that can fast and accurately adjust the frequency lock points in the range of tens to hundreds of megahertz based on the Faraday rotation spectroscopy. Based on this method, the frequency lock point whose detuning is -6.2 GHz is precisely shifted by 130 MHz, and we obtain a frequency drift of 3.3 MHz/h and a root mean square fluctuation of 0.6 MHz/h. This satisfies the detuning and frequency stability requirements of atomic magnetometer. In this paper, the influence of temperature on the frequency stabilization method is analyzed, the physical constant in the detuning equation is measured to estimate the frequency of the stabilization point, and the temperature regulation and acousto-optic modulator (AOM) regulation are combined to improve the long-term stable and precise control of the laser frequency on the large detuning of off-resonance.
-
-
[1] DEMTRÖDER W.Laser spectroscopy:Basic concepts and instrumentation[M].1st ed.Berlin:Springer, 1996:453-462. [2] SU D Q, MENG T F, JI Z H, et al.Application of sub-Doppler DAVLL to laser frequency stabilization in atomic cesium[J].Applied Optics, 2014, 53(30):7011-7016. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.007011 [3] 江开军, 王谨, 李可, 等.利用原子的塞曼光谱对半导体激光器进行稳频[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2004, 24(6):659-662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2004.06.006JIANG K J, WANG J, LI K, et al.Frequency stabilization of diode laser using Zeeman spectra[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2004, 24(6):659-662(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2004.06.006 [4] GIMA T, KATO H, HONDA T, et al.Modulation-free frequency stabilization based on polarization-split Sagnac loop[J].IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2013, 25(11):1031-1034. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2013.2259475 [5] SUN J F, YIN S Q, XU Z, et al.Optimization of polarization spectroscopy for rubidium D lines[J].Chinese Physics B, 2013, 22(2):271-275. [6] TIWARI V B, SINGH S, MISHRA S R, et al.Laser frequency stabilization using Doppler-free bi-polarization spectroscopy[J].Optics Communications, 2006, 263(2):249-255. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2006.01.028 [7] DANG H B, MALOOF A C, ROMALIS M V.Ultrahigh sensitivity magnetic field and magnetization measurements with an atomic magnetometer[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(15):151110. doi: 10.1063/1.3491215 [8] FANG J, WANG T, ZHANG H, et al.Optimizations of spin-exchange relaxation-free magnetometer based on potassium and rubidium hybrid optical pumping[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85(12):123104. doi: 10.1063/1.4902567 [9] BARBOZA P M T, NASCIMENTO G G, ARAU'JO M O, et al.Stabilization of a laser on a large-detuned atomic-reference frequency by resonant interferometry[J].Journal of Physics B:Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2016, 49(8):085401. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/49/8/085401 [10] MARCHANT A L, HÄNDEL S, WILES T P, et al.Off-resonance laser frequency stabilization using the Faraday effect[J].Optics Letters, 2011, 36(1):64-66. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.000064 [11] QUAN W, LI Y, LI R, et al.Far off-resonance laser frequency stabilization using multipass cells in Faraday rotation spectroscopy[J].Applied Optics, 2016, 55(10):2503-2507. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.002503 [12] KEMP S L, HUGHES I G, CORNISH S L.An analytical model of off-resonant Faraday rotation in hot alkali metal vapours[J].Journal of Physics B:Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2011, 44(23):235004. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/44/23/235004 [13] SIDDONS P, ADAMS C S, HUGHES I G.Off-resonance absorption and dispersion in vapours of hot alkali-metal atoms[J].Journal of Physics B:Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2009, 42(17):175004. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/42/17/175004 [14] SIDDONS P, ADAMS C S, GE C, et al.Absolute absorption on rubidium D lines:Comparison between theory and experiment[J].Journal of Physics B:Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 2008, 41(15):155004. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/41/15/155004 [15] ALCOCK C B, ITKIN V P, HORRIGAN M K.Vapour pressure equations for the metallic elements:298-2500 K[J].Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1984, 23(3):309-313. doi: 10.1179/cmq.1984.23.3.309 [16] DONLEY E A, HEAVNER T P, LEVI F, et al.Double-pass acousto-optic modulator system[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 2005, 76(6):063112. doi: 10.1063/1.1930095 -







 下载:
下载: