Adjustable-parameter dynamical decoupling protocol for 13C nuclear addressing in diamond
-
摘要:
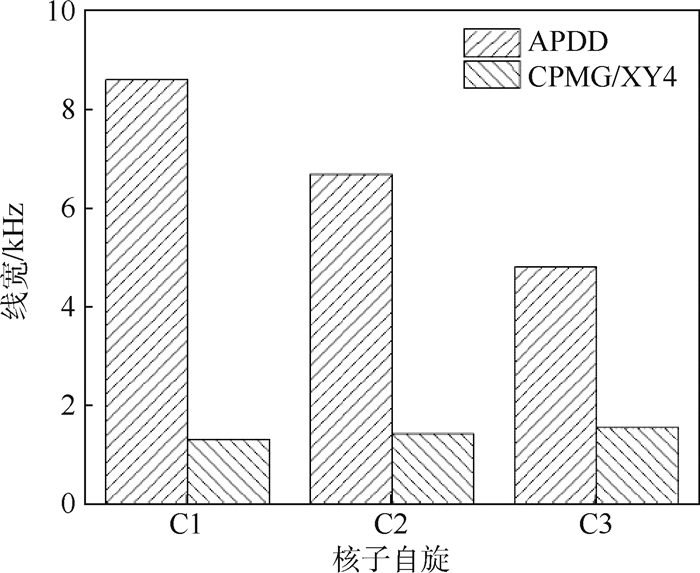
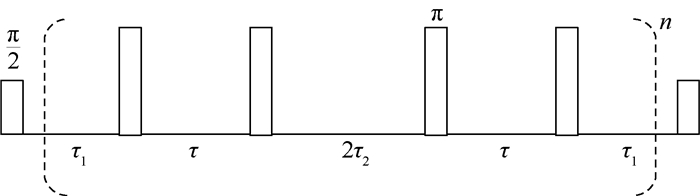
针对金刚石内13C核自旋的逐个定位,提出了一种非均匀分布周期内对称的动态解耦序列--可调动态解耦(APDD)序列。针对该序列,进行了理论推导和仿真分析;并就13C核自旋定位精度指标,与目前金刚石内原子量子态操控使用最为广泛的CPMG(Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill)脉冲序列和XY4序列进行了比较。结果表明,相比于CPMG序列与XY4序列,APDD序列可将单个13C核自旋的定位精度提高6.27倍。进一步研究表明,在单个周期内比值
τ 1/τ 介于0.51~0.58范围为APDD序列核子定位最优工作条件。因此,APDD序列能被用于控制毗邻金刚石中NV-色心的核自旋,并且在量子信息和量子探测器领域有着重要的应用。Abstract:A symmetric non-equally spaced protocol named adjustable-parameter dynamical decoupling (APDD) was proposed to individually map 13C nuclear spin in diamond. The principles of the APDD sequence are in detail numerically calculated and simulation analyzed. The 13C nuclear spin addressing accuracy of APDD protocol was compared with Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) and XY4 protocol, which are most widely used in diamond atom quantum manipulation. Results show that the 13C nuclear spin addressing accuracy of APDD protocol was 6.27 times higher than CPMG and XY4 sequences. Furthermore,
τ 1/τ ratio ranging from 0.51 to 0.58 is the best operating condition for APDD protocol. The APDD protocol will pave the way towards manipulation of the nuclear spins surrounding the NV-color center in diamond, which has significant applications in quantum information and quantum detector.-
Key words:
- diamond /
- NV- color center /
- dynamical decoupling /
- nuclear spin /
- addressing
-
-
[1] ZHANG C, YUAN H, TANG Z, et al.Inertial rotation measurement with atomic spins:From angular momentum conservation to quantum phase theory[J].Applied Physics Reviews, 2016, 3(4):041305. doi: 10.1063/1.4972187 [2] BIGNEY E.Flawed to perfection:Ultra-pure synthetic diamonds offer advances in fields from quantum computing to cancer diagnostics[J].Nature News, 2014, 505:472-474. doi: 10.1038/505472a [3] ALEGRE T P M, SANTORI C, MEDEIROS-RIBEIRO G, et al.Polarization-selective excitation of nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond[J].Physical Review B, 2007, 76(16):165205. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.165205 [4] NEUMANN P, BECK J, STEINER M, et al.Single-shot readout of a single nuclear spin[J].Science, 2010, 329(5991):542-544. doi: 10.1126/science.1189075 [5] ALBRECHT A, PLENIO M B.Filter design for hybrid spin gates[J].Physical Review A, 2015, 92(2):02340. [6] LONDON P, SCHEUER J, CAI J M, et al.Detecting and polarizing nuclear spins with double resonance on a single electron spin[J].Physical Review Letters, 2013, 111(6):467-473. [7] CYWINSKI L, LUTCHYN R M, NAVE C P, et al.How to enhance dephasing time in superconducting qubits[J].Physical Review B, 2008, 77(17):998-1002. [8] YUGE T, SASAKI S, HIRAYAMA Y.Measurement of the noise spectrum using a multiple-pulse sequence[J].Physical Review Letters, 2011, 107(17):170504. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.170504 [9] MEIBOOM S, GILL D.Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times[J].The Review of Scientific Instruments, 1958, 29(8):688-691. doi: 10.1063/1.1716296 [10] MIZUOCHI N, ISOYA J, NⅡTSUMA J, et al.Isotope effects between hydrogen and deuterium microwave plasmas on chemical vapor deposition homoepitaxial diamond growth[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101(10):103501. doi: 10.1063/1.2727380 [11] ZHAO N, HONERT J, SCHMID B, et al.Sensing single remote nuclear spins[J].Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7:657-662. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.152 [12] ZHAO N, WRACHTRUP J, LIU R B.Dynamical decoupling design for identifying weakly coupled nuclear spins in a bath[J].Physical Review A, 2014, 90(3):032319. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.90.032319 [13] VAN DER SAR T, WANG Z H, BLOK M S, et al.Decoherence-protected quantum gates for a hybrid solid-state spin register[J].Nature, 2012, 484(7392):82-86. doi: 10.1038/nature10900 [14] TAMINIAU T H, WAGENAAR J J, VAN DER SAR T, et al.Detection and control of individual nuclear spins using a weakly coupled electron spin[J].Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(13):137602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.137602 [15] KOLKOWITZ S, UNTERREITHMEIER Q P, BENNETT S D, et al.Sensing distant nuclear spins with a single electron spin[J].Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(13):137601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.137601 [16] ZHANG N, ZHANG C, XU L X, et al.Microwave magnetic field coupling with nitrogen-vacancy center ensembles in diamond with high homogeneity[J].Applied Magnetic Resonance, 2016, 47(6):589-599. doi: 10.1007/s00723-016-0777-5 [17] WANG Z Y, HAASE J F, CASANOVA J, et al.Positioning nuclear spins in interacting clusters for quantum technologies and bio-imaging[J].Physical Review B, 2016, 93(17):174104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.174104 [18] ZHAO N, HO S W, LIU R B.Decoherence and dynamical decoupling control of nitrogen vacancy center electron spins in nuclear spin baths[J].Physical Review B, 2012, 85(11):115303. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.115303 [19] ÁLVAREZ G A, AJOY A, PENG X, et al.Performance comparison of dynamical decoupling sequences for a qubit in a rapidly fluctuating spin-bath[J].Physical Review A, 2010, 82(4):042306. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.82.042306 [20] WANG Z H, LANGE G, RISTÈD, et al.Comparison of dynamical decoupling protocols for a nitrogen-vacancy center in diamond[J].Physical Review B, 2012, 85(15):155204. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.155204 -







 下载:
下载: