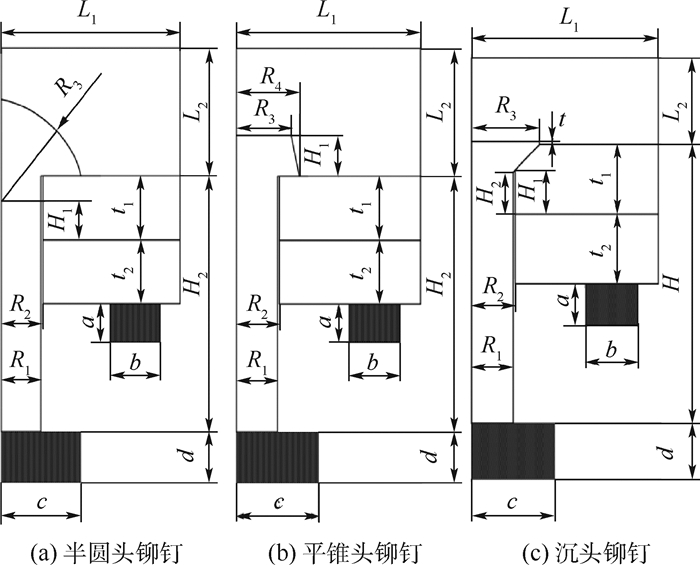
-
摘要:
针对目前对多钉铆接连接件进行疲劳寿命分析时的可行性不高、计算量较大等问题,提出一种更加有效可靠的预测多钉铆接连接件的疲劳寿命的方法。对多钉铆接连接件进行疲劳寿命分析时,先对压铆铆接过程进行了显示动力学分析,获得铆接后的钉、孔变形形式和干涉量,并编写了APDL子程序用于各种形式试件的铆接过程分析。用紧固件的载荷-位移曲线进行细节应力分析。基于三维弹塑性有限元法建立铆接连接件的载荷-位移计算方法,并通过与试验结果对比,说明用本文方法获取载荷-位移曲线的可靠性。在ANSYS中建立钉单元,并实现参数化建模进行钉载计算。使用应力严重系数法估算连接件疲劳寿命。开展典型航空铆接连接件疲劳试验,计算结果与试验结果一致性较好,说明计算方法的可行性。
Abstract:In the analysis of fatigue life of multiple riveted joints, the explicit dynamic analysis of the pressing and riveting process was carried out, and the deformation form and interference after riveting process were obtained. An APDL subroutine was developed to analyze the riveting process of various forms of specimens. Detailed stress was analyzed by using load-displacement curves of fastener. The load-displacement calculation method of riveted joint was proposed based on the three-dimensional elastoplastic finite element method, and compared with the experimental results, the reliability of using this method to obtain load-displacement curves was validated. Riveting units were established in ANSYS by using parametric modeling to carry out the calculation of riveting load. The fatigue life of the joint is estimated by the stress severity coefficient method. The fatigue test of typical aviation riveted joint was carried out. The calculation results are in good agreement with the test results, which indicates the feasibility of this method.
-
表 1 TB2-1钛合金基本力学性能参数
Table 1. Basic mechanical property parameters of TB2-1 titanium alloy
力学性能参数 数值 弹性模量/MPa 85 000 泊松比 0.33 密度/(kg·m-3) 4.83 屈服强度/MPa 880 表 2 疲劳试验结果与计算结果
Table 2. Fatigue test results and computing results
组别 中值疲劳寿命/cycles 计算与试验结果相对误差/% 试验结果 计算结果 1 192 909 169 489 12.14 2 72 598 64 937 10.55 3 41 271 35 886 13.05 4 277 469 312 001 12.45 5 121 505 140 670 15.77 6 52 113 59 389 13.96 -
[1] 飞机结构强度研究所.航空结构连接件疲劳分析手册[M].西安:飞机结构强度研究所, 1985:21-23.Aircraft Structure Strength Research Institute. Fatigue analysis manual of aircraftjoints[M]. Xi'an:Aircraft Structure Strength Research Institute, 1985:21-23(in Chinese). [2] BOFF A.飞机制造工艺学[M].佘公藩, 张钧, 等译.西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 1989: 205-221.BOFF A. Aircraft manufacturing technology[M].SHE G F, ZHANG J, et al., translated. Xi'an: Northwest Industrial University Press, 1989: 205-221(in Chinese). [3] ROSENFELDS J.Analytical and experimental investigation of bolted joints: NACA TN-1458[R].Washington, D.C.: NACA, 1458. [4] JARFALL L E. Optimun design of joints:The stress severity factor concept[J].Aircraft Fatigue, 1967, 56(2):49-63. [5] TATE M B, ROSENFELD S J. Preliminary investigation of theloads carried by individual bolts in bolted joints: NACA TN-10511[R].Washington, D.C.: NACA, 1946. [6] NELSON W D, BUNIN B L, HART-SMITHL J. Critical joints in large composite aircraft structure: NASA CR-3710[R].Washington, D.C.: NASA, 1983. [7] SWIFT T.Fracture analysis of stiffened structure: ASTM STP842[R].New York: ASTM, 1984. [8] HUTH H.Influence of the fastener flexibility on the prediction of load transfer and fatigue life for multi-row joints: ASTM STP927[R].New York: ASTM, 1986. [9] 梁沛权.紧固件载荷-变形曲线的计算方法研究[D].西安: 西北工业大学, 1987.LIANG P Q.Study on the numerical calculations of P-δ curves of fasteners[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 1987(in Chinese). [10] 陈涛, 何宇廷, 韩宏文, 等.螺栓连接件的紧固件P-δ曲线计算方法研究[J].科学技术与工程2014, 14(28):140-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.28.027CHEN T, HE Y T, HAN H W, et al.Study on the numerical calculations of P-δ curves of fasteners for bolted joints[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(28):140-147(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.28.027 [11] 师访.ANSYS二次开发及应用实例详解[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社, 2012:121-126.SHI F.Secondary development of ANSYS and detailed application example[M].Beijing:China Water Power Press, 2012:121-126(in Chinese). [12] 王勖成.有限单元法[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2009:576-579.WANG X C.Finite element method[M]. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2009:576-579(in Chinese). [13] 袁立.航空制造工程手册:飞机装配[M].北京:航空工业出版社, 2010:390-401.YUAN L.Handbook of aeronautical manufacturing engineering:Aircraft assembly[M].Beijing:Aviation Industry Press, 2010:390-401(in Chinese). [14] 熊竣江.飞行器结构疲劳与寿命设计[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 2004:85-111.XIONG J J. Structure fatigue and life design of aircraft[M].Beijing:Beihang University Press, 2004:85-111(in Chinese). [15] 李艳, 于克杰, 李小雷.铆钉材料对铆接变形影响的有限元分析[J].机床与液压, 2013, 41(4):50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.04.015LI Y, YU K J, LI X L.Finite element analysis for the influence of rivet materials on rivet deformation[J]. Machine Tool and Hydraulics, 2013, 41(4):50-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.04.015 [16] BARROIS W. Stresses and displacements due to load-transfer by fasteners instructural assemblies[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1978, 10(1):115-176. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(78)90055-3 [17] MCCARTHY M A, MCCARTHY C T, PADHI G S. A simple method for determining theeffects of bolt-hole clearance on load distribution in single-column, multi-bolt composite joints[J]. Composite Structures, 2006, 73(1):78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.01.028 [18] MCCARTHY C T, GRAY P J. An analytical model for the prediction of loaddistribution in highly torqued multi-bolt composite joints[J].Composite Structures, 2011, 92(2):287-298. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=60d4f2b3df32647e090c2287893d4555&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [19] 郑晓玲.民机结构耐久性与损伤容限设计手册[M].北京:航空工业出版社, 2003:38-44.ZHENG X L.Handbook of civil aircraft structures durability and damage tolerance design[M]. Beijing:Aviation Industry Press, 2003:38-44(in Chinese). [20] 薛景川, 杨玉功.紧固件载荷变形曲线的试验方法[M].西安:飞机结构强度研究所, 1982:22-26.XUE J C, YANG Y G.Test method for buckling deformation curve of fastener[M]. Xi'an:Aircraft Structure Strength Research Institute, 1982:22-26(in Chinese). [21] 薛景川, 杨玉功.紧固件载荷变形曲线的工程确定方法[M].西安:飞机结构强度研究所, 1984:23-29.XUE J C, YANG Y G.Engineering determination method for buckling deformation curve of fastener[M].Xi'an:Aircraft Structure Strength Research Institute, 1984:23-29(in Chinese). [22] 刘仁宇.某型飞机外翼下壁板连接件细节应力分析和疲劳性能研究[D].西安: 空军工程大学, 2008: 43-48.LIU R Y.Failure analysis for lap joint panel of an outer wing in fatigue test[D].Xi'an: Air Force Engineering University, 2008: 43-48(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: