-
摘要:
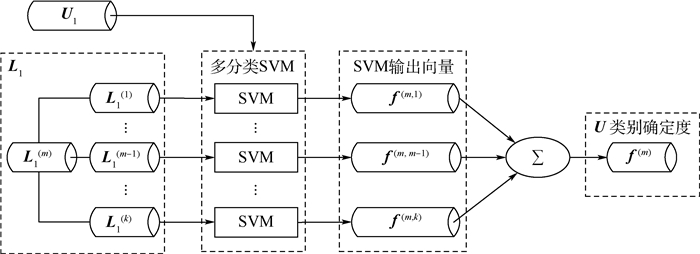
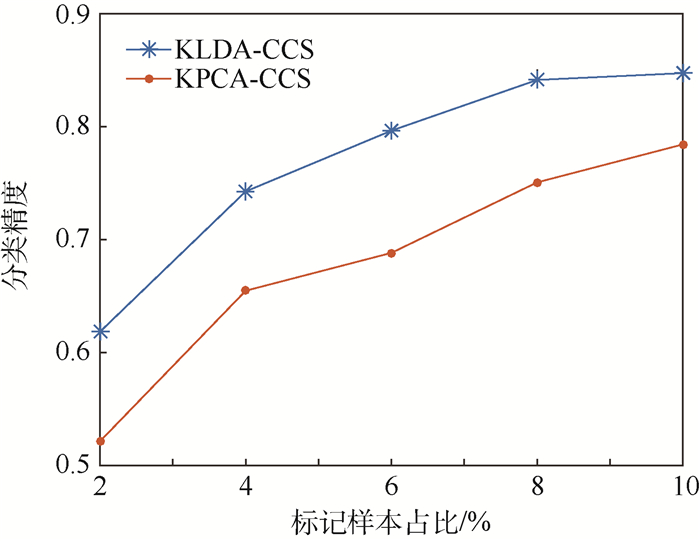
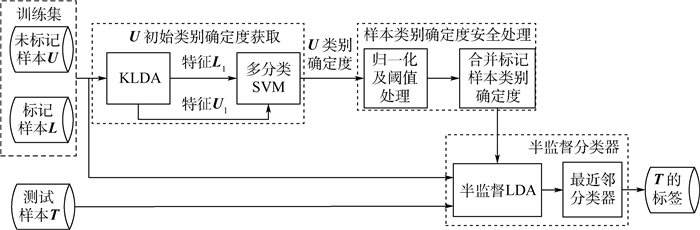
在对遥感图像进行分类时,全监督算法往往需要足够的标记样本进行训练,然而标记的过程是耗时和昂贵的,相反收集大量的无标记样本是很容易的。为了在学习过程中能够有效利用未标记样本的信息,本文提出了基于样本类别确定度(CCS)的半监督分类算法。首先,利用多分类支持向量机(SVM)得到未标记样本属于各类别的确定度,有效地衡量了未标记样本类别可靠性;其次,对样本类别确定度进行预处理,提升利用未标记样本的安全性;最后,基于样本类别确定度设计了半监督线性判别分析(LDA)降维算法并对其进行核化,使得样本在降维后的子空间更具有可分性,并根据降维后的数据特点,采用最近邻分类器对新样本进行分类。利用真实的合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像进行测试,验证了在标记样本较少的情况下,本文算法在性能上优于全监督和其他半监督算法,并能够快速收敛。
Abstract:The performance of supervised learning based algorithms can decrease dramatically in the classification of remote sensing images if labeled samples are insufficient. The collection of labeled samples is generally time-consuming and expensive, though unlabeled samples can be relatively easily obtained. To utilize the information of unlabeled samples in the learning process, this paper proposes a novel semi-supervised classification algorithm based on class certainty of samples (CCS). First, a multi-class support vector machine (SVM) is employed to determine the class certainty of unlabeled samples, which effectively measure the class reliability of unlabeled samples. Then, the pre-processing of sample classification is carried out to enhance the security of unlabeled samples. Finally, a new semi-supervised linear discriminant analysis (LDA) is proposed based on the sample class certainty and results in improved separability of the samples in the projection subspace. Moreover, the semi-supervised LDA can be extended to nonlinear dimensional reduction by combining the class certainty and the kernel based methods. For classification of the testing samples, the nearest neighbor classifier is adopted. In order to assess the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, several experiments are carried out on the actual synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images in comparison with other supervised and semi-supervised algorithms. Using real SAR images, it is proved that the proposed algorithm is superior to all supervised and other semi supervised algorithms in the case of less marked samples. And it can converge quickly.
-
表 1 训练样本与测试样本的种类及样本数量
Table 1. Types and quantities of training samples and testing samples
样本种类 训练样本 测试样本 T72
(sn_132)BMP2
(sn_c21)BTR70
(sn_c71)T72
(sn_s7)BMP2
(sn_c9566)BTR70
(sn_c70)样本数/幅 232 232 232 191 191 191 -
[1] SUN H, LIU S, ZHOU S L, et al. Unsupervised cross-view semantic transfer for remote sensing image classification[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1):13-17. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2491605 [2] CAVALLARO G, MURA M D, BENEDIKTSSON J A, et al.Remote sensing image classification using attribute filters defined over the tree of shapes[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(7):3899-3911. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2530690 [3] BOVOLO F, BRUZZONE L, CARLIN L.A novel technique for subpixel image classification based on support vector machine[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(11):2983-2999. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2051632 [4] BRUZZONE L.An approach to feature selection and classification of remote sensing images based on the Bayes rule for minimum cost[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1):429-438. doi: 10.1109/36.823938 [5] CABEZAS J, GALLEGUILLOS M, PEREZ-QUEZADA J F.Predicting vascular plant richness in a heterogeneous wetland using spectral and textural features and a random forest algorithm[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(5):646-650. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2532743 [6] XIA J S, DU P J, HE X Y, et al.Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification based on rotation forest[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1):239-243. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2254108 [7] SHAHSHAHANI B M, LANDGREBE D A.The effect of unlabeled samples in reducing the small sample size problem and mitigating the Hughes phenomenon[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5):1087-1095. doi: 10.1109/36.312897 [8] COZMAN F G, COHEN I.Unlabeled data can degrade classification performance of generative classifiers[C]//Proceedings of 15th International Florida Artificial Intelligence Society Conference.Reston: AIAA, 2002: 327-331. [9] PASOLLI E, MELGANI F, TUIA D, et al.SVM active learning approach for image classification using spatial information[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(4):2217-2233. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2258676 [10] BLUM A, CHAWLA S.Learning from labeled and unlabeled data using graph mincuts[C]//Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Machine Learning.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2001: 19-26. [11] ROSENBERG C, HEBERT M, SCHNEIDERMAN H.Semi-supervised self-training of object detection models[C]//Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Workshops on Application of Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2005: 29-36. [12] BLUM A.Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training[C]//Proceedings of the 7th Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2000: 92-100. [13] DÓPIDO I, LI J, MARPU P R.Semisupervised self-learning for hyperspectral image classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(7):4032-4044. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2228275 [14] JOACHIMS T.Transductive inference for text classification using support vector machines[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Machine Learning.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1999: 200-209. [15] PERSELLO C, BRUZZONE L.Active and semisupervised learning for the classification of remote sensing images[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(11):6937-6956. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2305805 [16] ZHOU Z H, LI M.Tri-training:Exploiting unlabeled data using three classifiers[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2005, 17(11):1529-1541. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2005.186 [17] TRIGUERO I, GARCIA S, HERRERA F.SEG-SSC:A framework based on synthetic examples generation for self-labeled semi-supervised classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(4):622-634. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2332003 [18] NIGAM K, MCCALLUM A K, THRUN S, et al.Text classification from labeled and unlabeled documents using EM[J].Machine Learning, 2000, 39(2-3):103-134. [19] CHAWLA N, KARAKOULAS G.Learning from labeled and unlabeled data:An empirical study across techniques and domains[J].Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2005, 23(1):331-366. [20] LE T B, KIM S W.A hybrid selection method of helpful unlabeled data applicable for semi-supervised learning algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-2. [21] LI Y F, ZHOU Z H.Towards making unlabeled data never hurt[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(1):175-188. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2299812 [22] LIU X, SONG M L, TAO D C, et al.Random forest construction with robust semisupervised node splitting[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1):471-483. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2378017 [23] CHAPELLEO, ZIEN A.Semi-supervised classification by low density separation[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence & Statistics, 2005: 1-8. [24] LI Y F, KWOK J T, ZHOU Z H.Semi-supervised learning using label mean[C]//Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Machine Learning.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2009: 633-640. [25] ANDREW A M.An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods[J].Kybernetes, 2001, 32(1):1-28. doi: 10.1002-ajpa.21348/ [26] MOSKOWITZ L.The LDA-An integrated diagnostics tool[J].IEEE Aerospace & Electronic Systems Magazine, 1986, 1(7):22-26. [27] KOCSOR A, TOTH L.Kernel-based feature extraction with a speech technology application[J].IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8):2250-2263. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.830995 [28] ZHU X, GHAHRAMANI Z.Learning from labeled and unlabeled data with label propagation[C]//International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2003: 2803-2808. [29] WAGSTAFF K, CARDIE C, ROGERS S, et al.Constrained K-means clustering with background knowledge[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Machine Learning.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2001: 577-584. [30] CAI D, HE X, HAN J.Semi-supervised discriminant analysis[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 9848913. -







 下载:
下载: