Control design and experimental verification of three-bed onboard oxygen generation system
-
摘要:
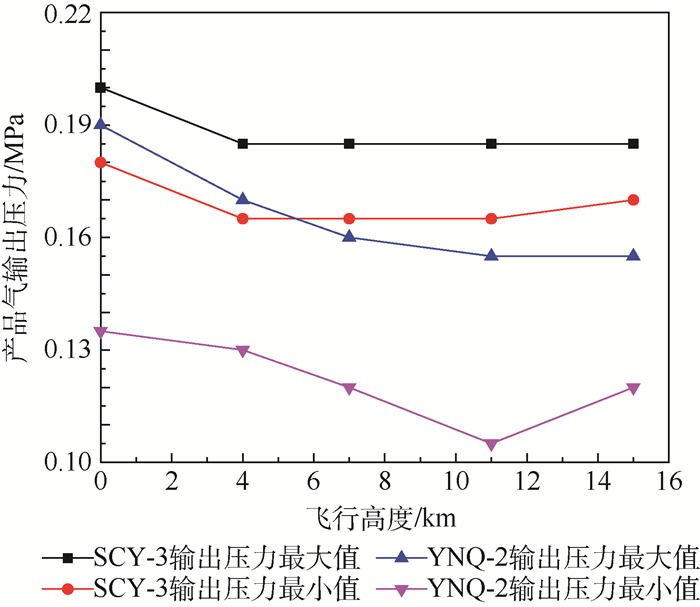
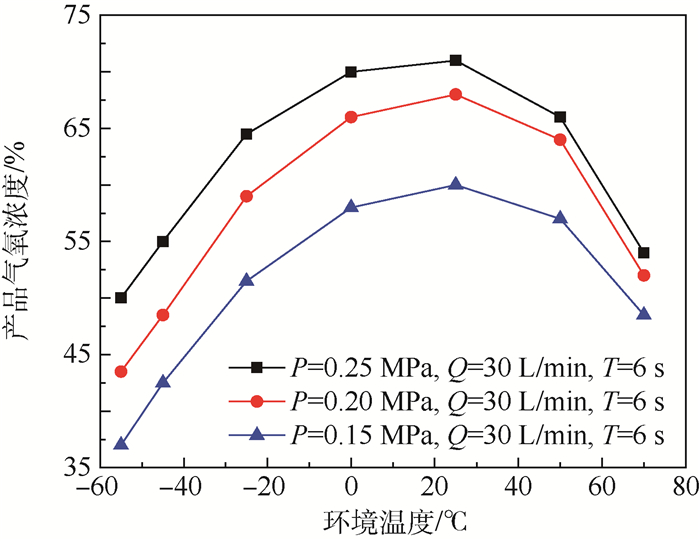
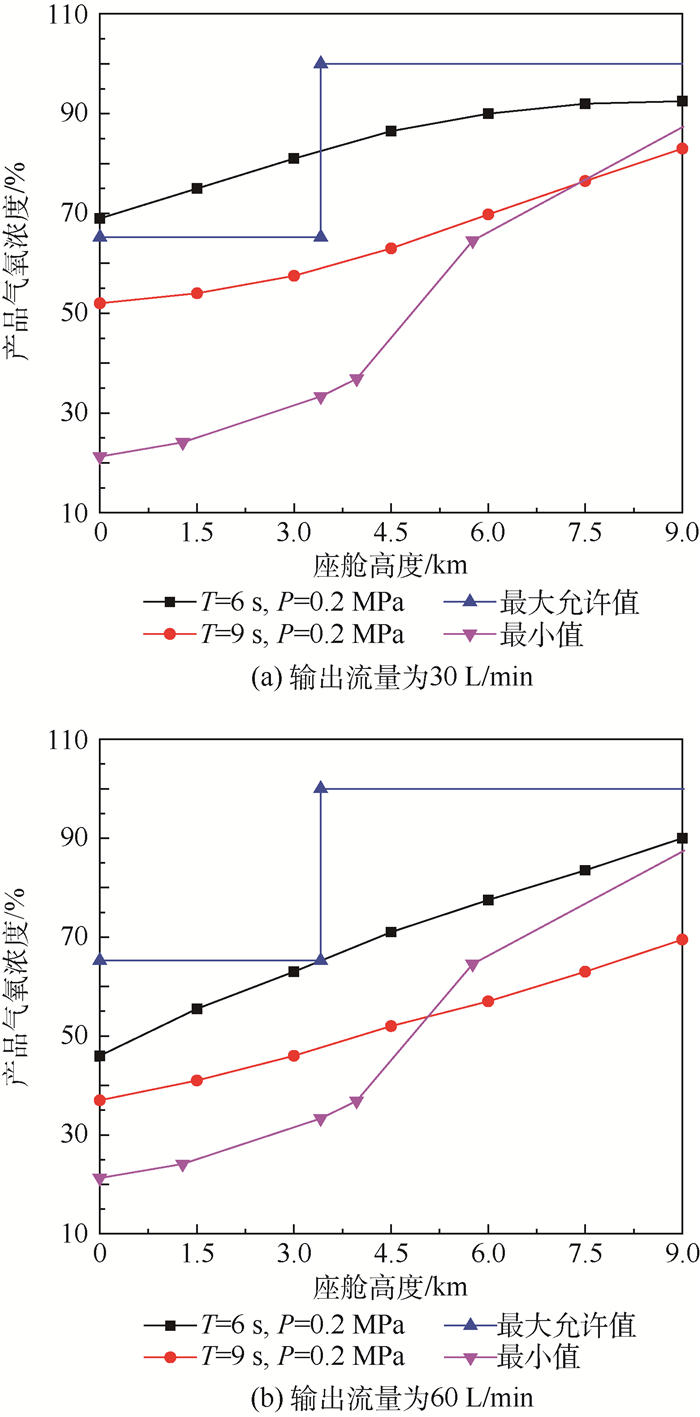
为解决两床型机载制氧系统在实际应用过程中出现的输出压力波动大及低空氧浓度偏高等问题,需研制与开发三床型机载制氧系统。为此,依据系统控制逻辑,采用电磁阀驱动电控气动阀循环工作的控制模式,开展了三床型机载制氧系统的控制设计,提出了高低空分段调节循环周期的控制方法,并在不同输入压力、流量条件下,对三床型机载制氧系统进行了循环周期实验,探索了产品气氧浓度随循环周期时间的变化规律。研究结果表明:当采用高空循环周期为6 s,低空循环周期为9 s,高低空分段高度为3.5 km等控制参数时,系统控制设计可适用于三床型机载制氧系统,并满足三床型机载制氧系统控制设计的需求。
Abstract:Two-bed onboard oxygen generation system is facing the problem of large pressure fluctuation of output gas and high oxygen concentration at low altitude during the practical application process. In order to solve these problems, three-bed onboard oxygen generation system needs to be developed. According to the system control logic, the control mode that the electronic controlled pneumatic servo valve worked circularly was adopted. The control design of three-bed onboard oxygen generation system has been proposed. The control method of segmented regulation was proposed, in which different cycle time was applied depending on the altitude. Under different input pressure and flow conditions, the experiments of the three-bed onboard oxygen generation system were performed to investigate the influence of the cycle time on the oxygen concentration of product gas. The study results show that when the cycle time for low altitude and high altitude is determined to be 9 s and 6 s, respectively, and the segmented altitude is determined to be 3.5 km, the system control design is suitable for the three-bed onboard oxygen generation system, and meets the requirements for the control design of three-bed oxygen generation system.
-
Key words:
- three-bed /
- onboard oxygen generation system /
- system control /
- cycle period /
- experiment
-
表 1 主要实验仪器
Table 1. Main experimental instruments
仪器名称 量程 精度等级 备注 测氧仪 0~100% ±2% 压力表1 0~1 MPa 1.6级 压力表2 0~1 MPa 0.6级 浮子流量计 0~100 L/min 2.5级 高度表 0~20 km 直流稳压电源 0~32 V/0~10 A 高度监控仪 0~20 km 高温箱 室温~80℃ ±2℃ 低温箱 -60~0℃ ±2℃ 真空泵 101.3 kPa~1.3 Pa 空压机 0.975 MPa 高空舱 0~20 km -
[1] REGE S U, YANG R T.Limits for air separation by adsorption with LiX zeolite[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1997, 36(12):5358-5365. [2] 戴先知, 刘应书.变压吸附过程数学模型及其应用[J].低温与特气, 2006, 24(1):36-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7804.2006.01.010DAI X Z, LIU Y S.Mathematical model and application of PSA process[J].Low Temperature and Special Gas, 2006, 24(1):36-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7804.2006.01.010 [3] 刘峰.航空个体防护技术与装备[M].北京:科学出版社, 2008.LIU F.Aviation personal protection technology and equipment[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2008(in Chinese). [4] 肖华军.航空供氧装备应用生理学[M].北京:军事医学科学出版社, 2015.XIAO H J.Applied physiology of aviation oxygen supply equipment[M].Beijing:Military Medical Science Press, 2015(in Chinese). [5] 顾飞龙. 碳分子筛变压吸附(PSA)法制取高纯度氮气的工艺研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2010.GU F L. Study on manufacturing high-purity nitrogen by carbon molecular sieve pressure swing adsorption process[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2010(in Chinese). [6] 王刚.碳分子筛制氮机新型高效吸附塔充填技术[J].煤矿安全, 2014, 45(7):56-58.WANG G.New and high efficient adsorption tower filling technique for carbon molecular sieve nitrogen machine[J].Laboratory of Coal Safety Technology, 2014, 45(7):56-58(in Chinese). [7] 耿正波. 医用分子筛吸附制氧机的设计与开发[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010.GENG Z B. The design and development of medical molecularsieve adsorption oxygen plant[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010(in Chinese). [8] 龙春霞.制纯氧分子筛[J].广州化工, 2010, 38(11):67-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2010.11.024LONG C X.Zeolite for producing high-purity oxygen[J].Guang-zhou Chemical Industry, 2010, 38(11):67-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2010.11.024 [9] TEAGUE K G, EDGAR T F.Predictive dynamic model of a small pressure swing adsorption air separation unit[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(10):3761-3775. doi: 10.1021/ie990181h [10] 杨锋, 林贵平, 赵竞全.分子筛浓缩器非等温吸附模型[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2002, 28(1):8-11.YANG F, LIN G P, ZHAO J Q.Nonisothermal adsorption model for molecular sieve oxygen concentrator(MSOC)[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2002, 28(1):8-11(in Chinese). [11] WU Y, LIN G P.Modeling and numerical simulation of onboard molecular sieve oxygen generation system[J].Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2004, 21(1):47-52. [12] 王慧丹. 机载分子筛制氧系统的实验与仿真研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2011.WANG H D. Experimental and simulation study of onboard molecular sieve oxygen generation system[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2011(in Chinese). [13] 肖华军.英国机载三层同心圆型分子筛制氧系统[J].国际航空, 1994(1):60-61.XIAO H J.British onboard three layers concentric circular molecular sieve oxygen generation system[J].National Defense Aviation, 1994(1):60-61(in Chinese). [14] LOVETT N P J, ASHDOWN R. Development of the OBOGS and BRAG valve for the F-22 life support system[R]. Phoenix: SAFE Association, 1998: 62-71. [15] SANTOS J C G F. Study of new adsorbents and operation cycles for medical PSA units[D]. Oporto City: Universidade do Porto, 2005. -








 下载:
下载: