A global network flight flow assignment algorithm based on civil-military integration
-
摘要:
随着飞行活动需求的持续快速增长和空域资源使用矛盾的日益凸显,全局飞行流量协同优化已成为减少飞行延误、降低飞行危险、确保空域运行安全的一个重要手段。空中交通管理作为军民融合发展的重点领域,迫切需要对军民航飞行流量实施统一、高效、兼顾各自特点的协同优化。在实际研究中,全局飞行流量协同优化问题具有大规模、多目标、难分解等特点,是一类复杂的工程优化问题。本文贯彻军民融合发展思想,设计了一种基于军民航异质化飞行活动管制要求、考虑差异化调配方法与代价、兼顾军民航管制员各自工作特点、有效解决扇区网络运行安全性和经济性问题的全局飞行流量多目标协同优化模型——CMI模型;为解决种群在进化过程中“不平衡不充分”的问题,提出了一种动态自适应多目标遗传算法(DA-MOGA),并针对性设计了基于聚集距离和种群多样性的交叉变异概率动态调整机制。利用中国扇区网络实际数据,对本文提出的模型和算法进行了验证,算法结果优于2种经典的多目标进化算法。
Abstract:With the rapidly continuing growth in demand for flight activities and the increasing airspace usage conflicts, the global optimization of air traffic flow management has become an essential approach to reduce flight delays, decrease flight risk and ensure airspace operation safety. As a typical area of civil-military integration development, air traffic management needs the uniform and efficient integration optimization of the civil and military aviation flight plans. The global optimization of air traffic flow management problem is a complex real-world optimization problem due to its large-scale and multi-objective, and nonseparable characteristics. This paper presents a civil-military integration flight flow multi-objective optimization——CMI model, which considers the difference in civil and military flight plans, the efficiency and safty of sector network, and the civil and military controllers operating features. In order to resolve the unbalance and inadequacy problem lying in population evolution process, a dynamic adaptive multi-objective genetic algorithm (DA-MOGA), which designs the dynamic adjustment mechanism of crossover and variation based on the crowding distance and diversity, is proposed in this paper. The validation results based on the actual data from the sector networks in China show that the DA-MOGA outperforms the two well-known multi-objective evolutionary algorithms.
-
表 1 算法主要参数取值
Table 1. Main parameter setting of algorithms
算法 种群个数 进化代数 交叉概率 变异概率 MOGA 100 100 0.5 0.09 NSGA-Ⅱ 100 100 0.7 0.07 DA-MOGA 100 100 表 2 主要性能评价指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of main performance evaluation indexes
算法 Ih(方差) Id(方差) Δ(方差) MOGA 0.559 9
(0.274 8)0.395 8
(0.362 6)0.999 5
(0.001 1)NSGA-Ⅱ 0.546 4
(0.207 0)0.294 0
(0.215 3)0.998 5
(0.001 4)DA-MOGA 0.605 9
(0.228 3)0.241 2
(0.307 1)0.999 4
(0.000 8)表 3 3种算法目标函数值对比
Table 3. Comparison of objective function value among three algorithms
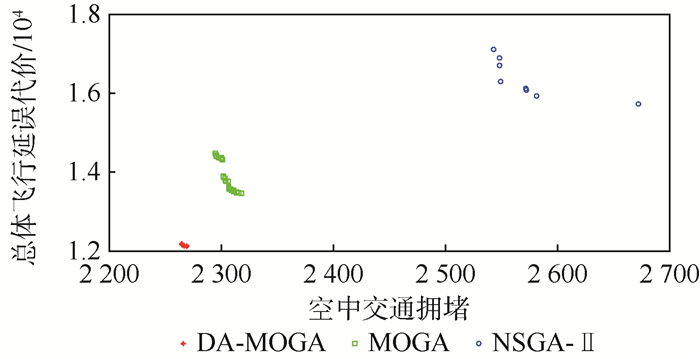
优先考虑 目标函数值 MOGA NSGA-Ⅱ DA-MOGA DA-MOGA比MOGA减少比例/% DA-MOGA比NSGA-Ⅱ减少比例/% 效率 空中交通拥堵 2 318.44 2 672.48 2 276.39 1.81 14.82 总体飞行延误代价 13 457.6 15 728 11 736 12.79 25.38 安全 空中交通拥堵 2 294.87 2 543.53 2 266.92 1.22 10.88 总体飞行延误代价 14 480.3 17 108 11 906 17.78 30.41 表 4 DA-MOGA时间复杂度s
Table 4. Time complexity of DA-MOGA
伪代码步骤 时间复杂度 选择 O(N|F|) 遗传操作 O(N|F|) 约束处理 O(N|F|) 动态自适应算子计算 O(N) 目标函数计算 O(MN|T|) 重组和保留 O(N2) -
[1] DE MATOS P A L, POWELL P L.Decision support for flight rerouting in Europe[J].Decision Support Systems, 2002, 34(4):397-412. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ029893188 [2] BERTSIMAS D, LULLI G, ODONI A.The air traffic flow management problem: An integer optimization approach[C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Integer Programming and Combinatorial Optimization.Berlin: Springer, 2008: 36-46. [3] SHERALI H, STAATS R, TRANI A.An airspace planning and collaborative decision-making model:Part Ⅰ-Probabilistic conflicts, workload, and equity considerations[J].Transportation Science, 2003, 37(4):434-456. doi: 10.1287/trsc.37.4.434.23272 [4] SHERALI H, STAATS R, TRANI A.An airspace-planning and collaborative decision-making model:Part Ⅱ-Cost model, data considerations, and computations[J].Transportation Science, 2006, 40(2):147-164. doi: 10.1287/trsc.1050.0141 [5] DELL'OLMO P, LULLI G.A new hierarchical architecture for air traffic management:Optimization of airway capacity in a free flight scenario[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 2002, 144(1):179-193. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d90a5a264823d257831d1144aae275ec&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [6] DANIEL D, OUSSEDIK S, STEPHANE P.Airspace congestion smoothing by multi-objective genetic algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 ACM Symposiumon on Applied Computing.New York: ACM, 2005: 907-912. [7] YAOWIWAT S, LOHATEPANONT M, PUNYABUKKANA P.Multi objective micro genetic algorithm for combine and reroute problem[J].International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Technologies, 2007, 2(4):245-255. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/242405340_Multi_Objective_Micro_Genetic_Algorithm_for_Combine_and_Reroute_Problem [8] MA Z P, CUI D G, CHENG P.Dynamic network flow model for short-term air traffic flow management[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and Humans, 2004, 34(3):351-358. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2003.822969 [9] CAI K Q, ZHANG J, ZHOU C, et al.Using computational intelligence for large scale air route networks design[J].Applied Soft Computing, 2012, 12(9):2790-2800. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2012.03.063 [10] GUAN X M, ZHANG X J, ZHU Y B, et al.An airway network flow assignment approach based on an efficient multiobjective optimization framework[J].The Scientific World Journal, 2015, 2015:302615. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000004268376 [11] XIAO M M, CAI K Q, LINKE F.An evolutionary multi-objective approach for stochastic air traffic network flow optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 2059-2065. [12] MEI Y, TANG K, YAO X.Decomposition-based memetic algorithm for multi-objective capacitated arc routing problem[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 15(2):151-165. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2010.2051446 [13] ZITZLER E, LAUMANNS M, THIELE L.SPEA2: Improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm[C]//Proceedings of Evolutionary Methods for Design Optimization and Control with Applications to Industrial Problems, 2002: 95-100. [14] CZYZZAK P, JASZKIEWICZ A.Pareto simulated annealing-A metaheuristic technique for multiple-objective combinatorial optimization[J].Journal of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis, 1998, 7(1):34-47. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1360(199801)7:1<34::AID-MCDA161>3.0.CO;2-6 [15] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S.A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ[J].IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computing, 2002, 6(2):182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 -







 下载:
下载: