Influence of heat treatment and measurement methods on material hardness evaluation by longitudinal wave velocity
-
摘要:
硬度是材料力学性能的重要指标之一,目前采用超声无损检测方法评价材料的硬度指标存在诸多挑战。通过搭建高精度声时测量系统,采用超声纵波脉冲反射回波法测量不同热处理45钢试件沿厚度方向的超声波传播声时,计算超声纵波声速。同时改变门信号的测量方式,研究不同热处理及门信号测量方式对超声纵波声速评价材料硬度的影响。建立材料硬度、微观组织以及超声纵波声速之间的映射关系,得到超声纵波声速评价45钢试件硬度指标的标定模型,并对标定模型进行验证。标定模型预测硬度误差满足工程应用误差10%的要求。
Abstract:Hardness is one of the important indexes of mechanical performance of materials, and employing ultrasonic nondestructive testing method for hardness evaluation faces many challenges now. In this paper, through setting up high-precision ultrasonic wave transmission time measurement system, the longitudinal wave propagation time in the thickness direction of different heat treated 45 steel specimens was measured by pulse reflected echo method, and the longitudinal wave velocity was calculated. Simultaneously, the gate signal measurement methods were changed, and the effects of different heat treatment and gate signal measurement methods on hardness evaluation by the longitudinal wave velocity were studied.On this basis, the mapping relationship among material hardness, microstructure and longitudinal wave velocity was obtained, and the calibration model for evaluating the hardness of 45 steel specimens by longitudinal wave velocity was established and verified. The hardness prediction error by the calibration model meets the error requirement of 10% for engineering application.
-
Key words:
- longitudinal wave velocity /
- hardness /
- microstructure /
- measurement signal /
- mapping relationship
-
材料硬度是材料力学性能的重要指标之一,材料硬度值不仅可以直观反映材料的硬度指标大小,而且可以间接反映材料的强度指标大小,对于在役、在线核心部件,强度指标不能直接测量,可以通过测量部件的硬度指标来估算相应的强度指标。重要构件的耐磨性能、抗腐蚀性能、弹性模量以及抗疲劳性能均与构件的硬度相关,因此,表征材料的硬度指标是材料力学性能测试的重要内容之一[1-3]。
目前构件硬度测量方法主要集中在机械压痕测量,其主要缺点为:①只能表征材料或构件表面硬度;②测量设备较大,只能在测试实验室或特定场所进行;③对材料表面造成一定的损伤,即使纳米压痕法[4]也会对构件表面产生微损伤;④对材料表面粗糙度有一定要求,表面打磨划痕对测量压痕面积大小有一定影响[5-6]。因此采用上述方法很难实现在役、在线、快速硬度的无损评价与表征。
超声检测技术不仅可以对构件的宏观缺陷进行定量评价与表征[7],还可以采用非线性超声检测技术评价材料早期力学性能退化[8],包括疲劳-位错早期损伤、材料热老化损伤、蠕变损伤和辐射损伤;采用超声检测技术还可以评价不锈钢材料的晶间腐蚀[9];基于弱声-弹效应采用超声声速变化评价材料的残余应力[10]及工作应力[11];通过超声纵波声速和横波声速评价材料的弹性模量[12-14]。本文将超声检测技术引入到材料或构件硬度指标的力学性能测量,基于先进高精度超声波声时测量技术、计算机技术、高性能传感器技术以及材料微观组织表征与分析技术,采用超声纵波声速测量实现对材料或构件硬度的无损快速定量评价与表征,误差满足工程应用要求。
1. 检测方法及检测系统
1.1 检测方法
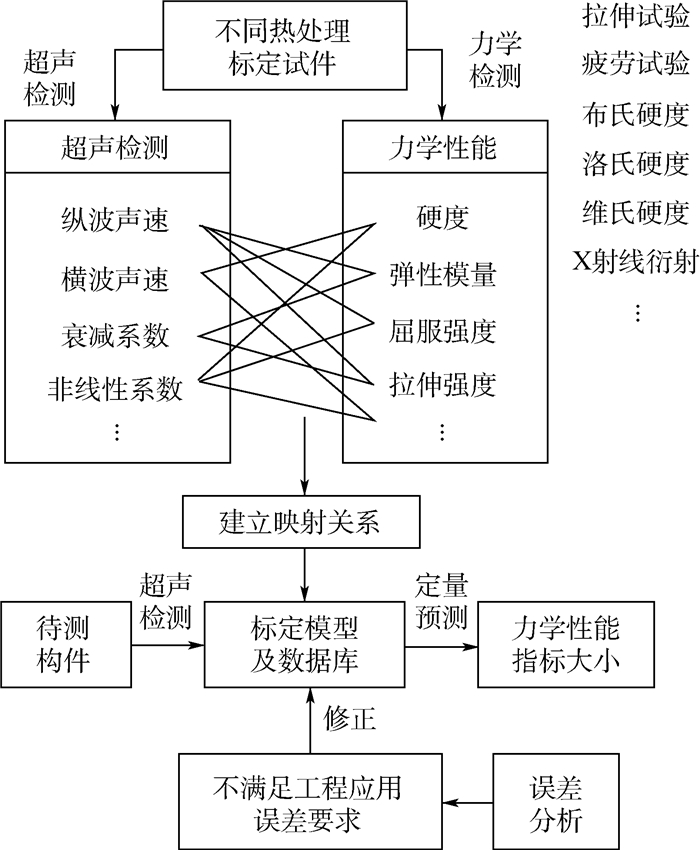
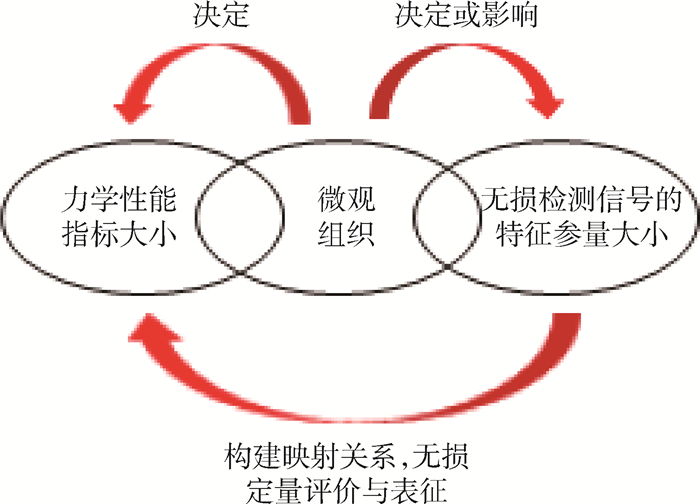
材料的微观组织决定材料的力学性能,同样材料的微观组织决定或影响无损检测信号的特征参量的大小,因此,可以通过无损检测信号特征参量的变化来评价和表征材料的力学性能指标。材料的微观组织可以解释两者之间变化关系,起着桥梁作用,通过上述关系,就可以建立材料力学性能指标-材料微观组织-无损检测信号的特征参量之间非线性或者线性映射关系,如图 1所示。
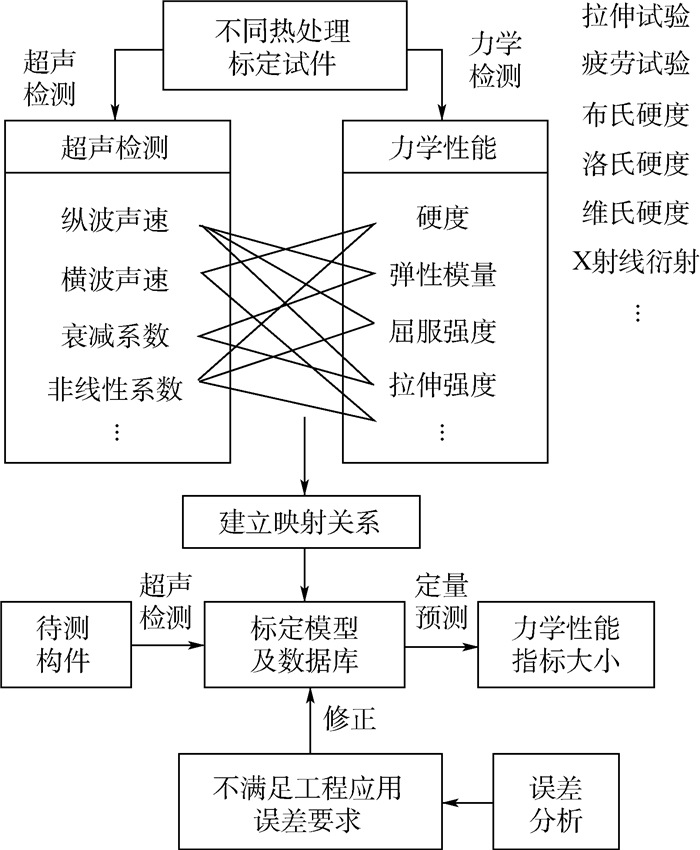
超声纵波声速评价材料硬度指标方法:
1) 将试件进行不同热处理,得到一组具有不同硬度的标定试件。
2) 通过硬度计测量标定试件的硬度,采用超声纵波脉冲反射回波法,通过高精度超声测试系统测量标定试件沿厚度方向超声纵波声时,计算超声纵波声速,对所测硬度值与超声纵波声速进行曲线拟合,得到硬度标定模型。
3) 测试同种材料任意试件的超声纵波声速,代入标定模型,预测出被测试件硬度,并与硬度计所测硬度进行比较,进行误差分析,如果预测硬度误差不满足所提误差指标要求,则对标定模型进行修正,直至误差满足要求,标定实验完成。具体标定过程如图 2所示。
1.2 纵波声速测量方法
1)测量方法1
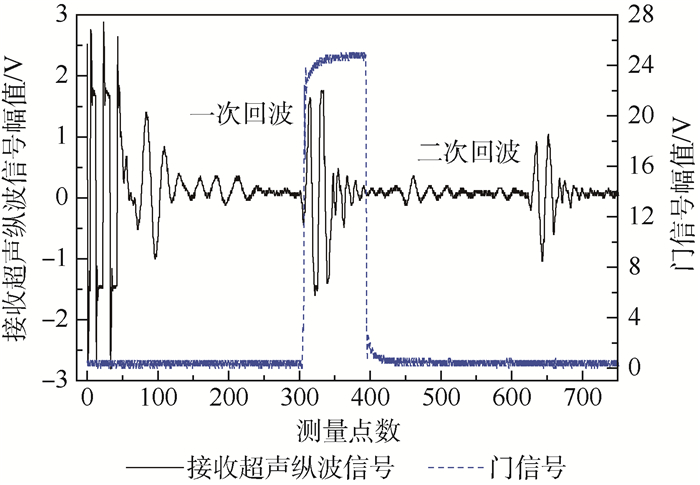
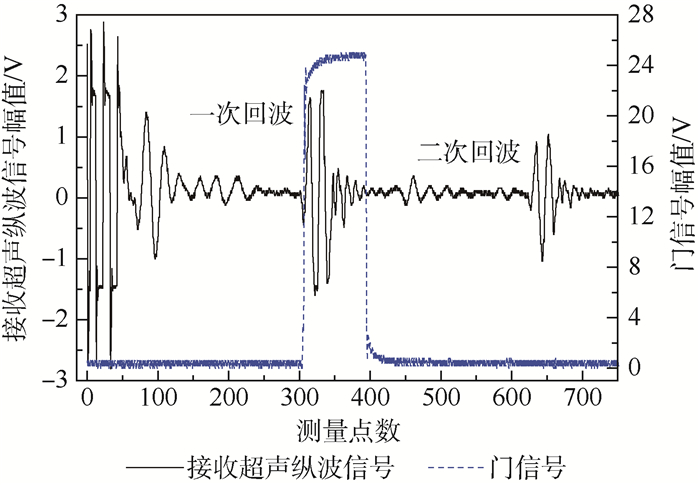
采用单探头脉冲反射回波法测量超声纵波声时,在测量系统中设置门信号的位置,门信号的宽度与接收超声纵波信号持续时间相当,分别测量一次底面反射回波信号声时t1和二次底面反射回波信号声时t2,分别给出2次回波声时测量的均方根误差,2次反射回波信号声时差即为超声纵波在2倍试件厚度声程的传播时间。门信号及接收超声纵波信号位置如图 3所示,超声纵波声速计算式为

(1) 式中:vL为纵波声速;d为试件厚度。
2) 测量方法2
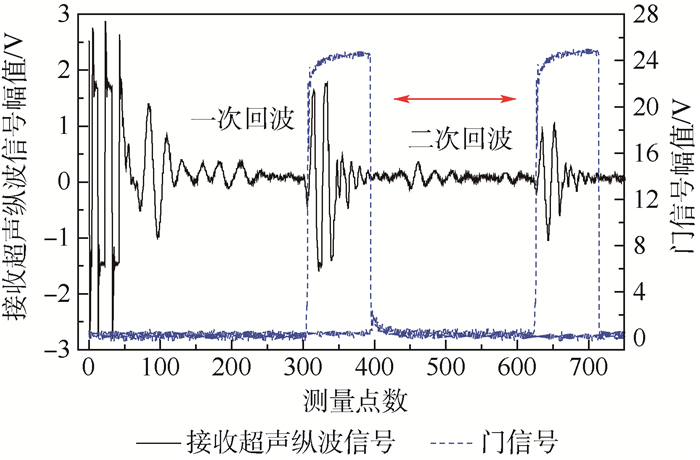
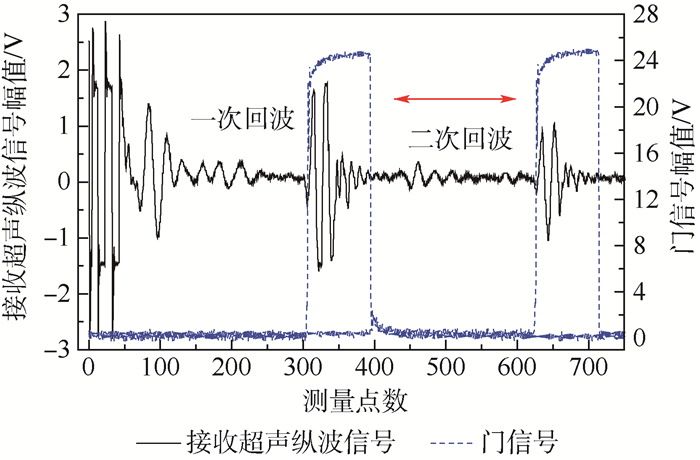
在测量系统中,分别设置门信号位于一次底面反射回波信号和二次底面反射回波信号处,设置门信号的宽度与超声纵波信号持续时间相当。测量开始时,门信号作为测量信号,在一次和二次底面反射回波信号之间来回跳跃,门信号及接收超声纵波信号位置如图 4所示,根据扫频范围和测量步进量确定门信号测量的次数,系统自动计算超声波在试件厚度方向传播的平均声时t,同时给出测量声时均方根误差,超声纵波声速计算式为

(2) 1.3 检测系统
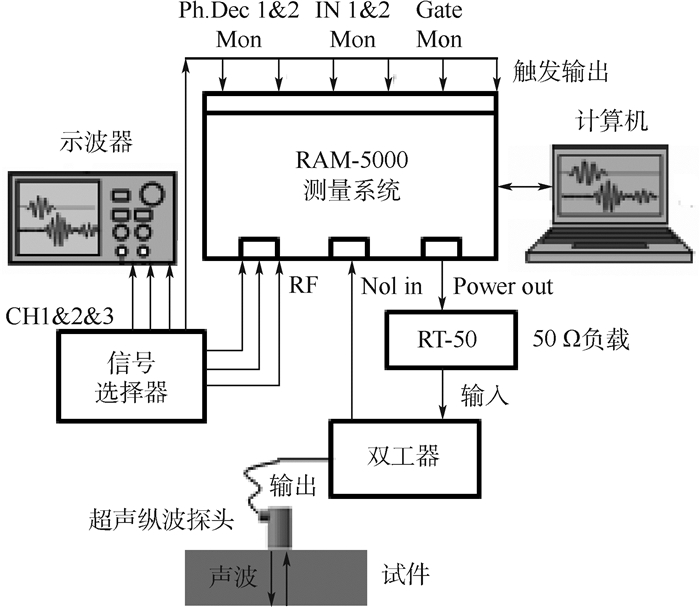
本文采用超声纵波声速评价45钢试件硬度指标,实验系统包括RITEC RAM-5000高精度声时数据采集系统、计算机、示波器(RIGOL DS1054Z)、50 Ω负载(RITEC RT-50)、信号选择器(RITEC RS-5-G2)、双工器(RITEC DIPLEXER)、OLYMPUS 2.25 MHz超声纵波探头(V204-RM)、耦合剂机油,不同热处理45钢标定试件,试件尺寸为150 mm×50 mm×19 mm。实验系统框图如图 5所示。
2. 标定过程及结果分析
2.1 微观组织及硬度
标定试件为45钢,各试件热处理方法及硬度如表 1所示。根据45钢过冷奥氏体连续冷却转变(Continuous Cooling Transition,CCT)曲线确定热处理最高升温为850℃+保温0.5 h,试件分别进行淬火(Water Quenching,WQ)、不同温度的回火(Tempering,T)、正火(Normalizing,N)和退火(Annealing,A),目的是通过热处理得到一组具有不同硬度的标定试件,为后续的标定实验做准备。
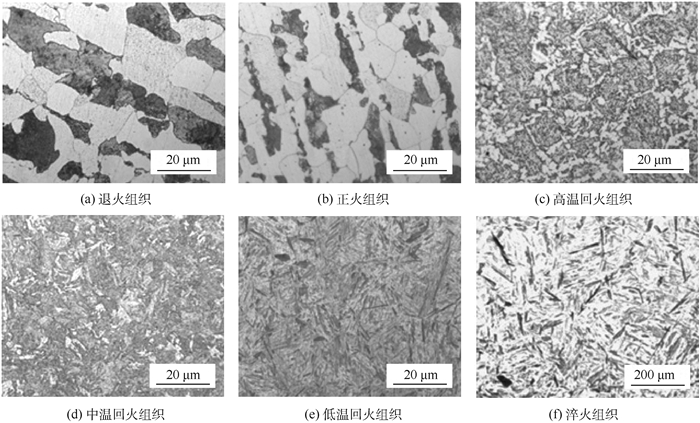
表 1 标定45钢试件热处理方法及硬度Table 1. Heat treatment methods and hardness of calibrated 45 steel specimens热处理方法 冷却方式 回火温度/℃ 保温时间/min 硬度/HBW A 炉冷 129 N 空冷 155 600T 空冷 600 30 192 400T 空冷 400 30 340 200T 空冷 200 30 489 WQ 水冷 522 不同热处理标定试件微观组织如图 6所示,图 6(a)为试件退火后得到铁素体加珠光体组织;图 6(b)为试件正火后得到铁素体加珠光体组织;图 6(c)为试件淬火+600℃回火得到索氏体组织;图 6(d)为试件淬火+400℃回火得到回火屈氏体组织;图 6(e)为试件淬火+200℃回火得到回火马氏体组织;图 6(f)为试件淬火得到马氏体加残余奥氏体组织。
2.2 纵波声速测量
2.2.1 探头幅频特性测定
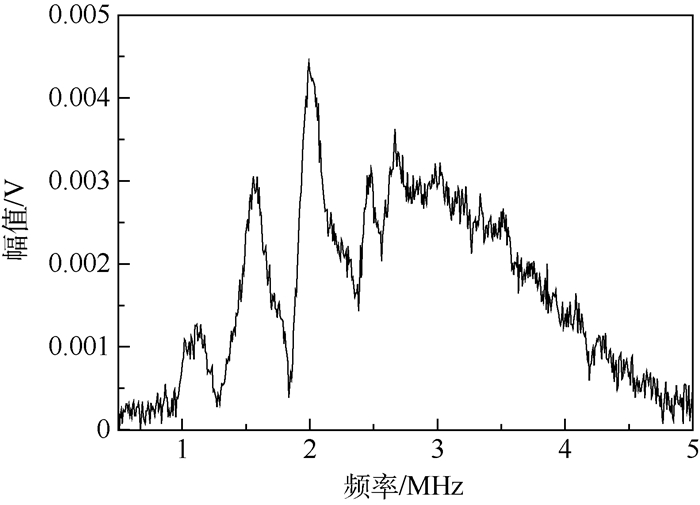
探头技术说明书已经给出超声纵波的中心频率,但是为确定探头的检测能力及选择探头激发信号的频率,需要对超声纵波探头的频谱特性进行测定,绘制相应的幅频特性曲线。图 7为中心频率为2.25 MHz超声纵波探头幅频特性。
由超声纵波的幅频特性可以看出,探头的中心频率并非在探头标注的2.25 MHz,而是1.992 5 MHz,幅值为0.004 426 V,这样就为探头激发信号的中心频率选择提供实验依据。从探头的幅频特性还可以看出,探头的频带较宽,说明其检测能力较强;同时探头在高频段幅值衰减较慢,对中心频率的检测波存在干扰,因此检测超声纵波信号需要进行适当的滤波处理。
2.2.2 纵波声时测量及声速计算
不同热处理45钢试件微观组织各异,宏观表现就是试件硬度的差异性,最终反映在超声纵波声速的变化。实验采用2种门信号检测方法对超声纵波传播声时进行精确测量,根据式(1)、式(2)计算相应的纵波声速,建立超声纵波声速、试件硬度以及微观组织之间的映射关系,构建超声纵波声速与试件硬度之间的标定模型,并对标定模型进行验证;同时比较2种测量方法所得声速构建的标定模型的预测精度,为后续门信号检测方式的选择提供实验依据。
检测系统参数设置为:激发信号频率设置为2.25 MHz,信号周期为1cycle,依据实测探头频谱特性,扫频范围设置为2.05~2.45 MHz,步进为0.001 MHz,采样点数为401,信号增益为60 dB,滤波器设置高通截止频率为1 MHz,低通截止频率为20 MHz,门信号一次反射回波延时9.1 μs,二次反射回波延时15.5 μs,门宽1.7 μs。
表 2和表 3分别为采用2种门信号测量方法所得纵波传播声时以及计算纵波声速。其中:Et1、Et2为对应t1、t2的均方根误差,t为门信号自动测量计算超声纵波在厚度方向声程的声时,Et为对应t的均方根误差。上述测量值均为测量6次求其平均值,采用游标卡尺测量3次求其平均值所得。
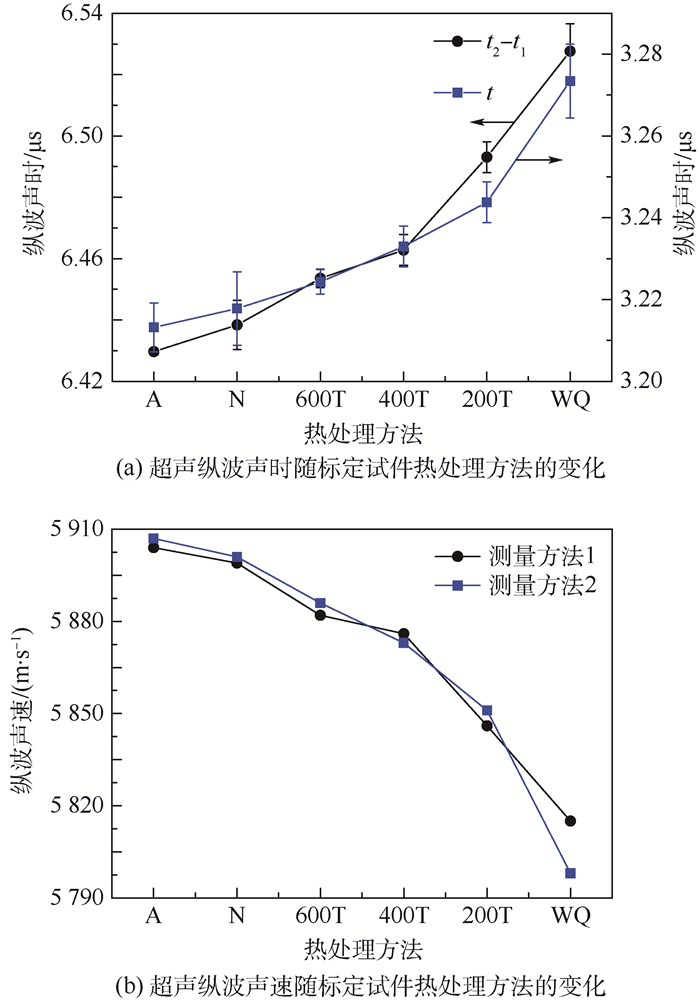
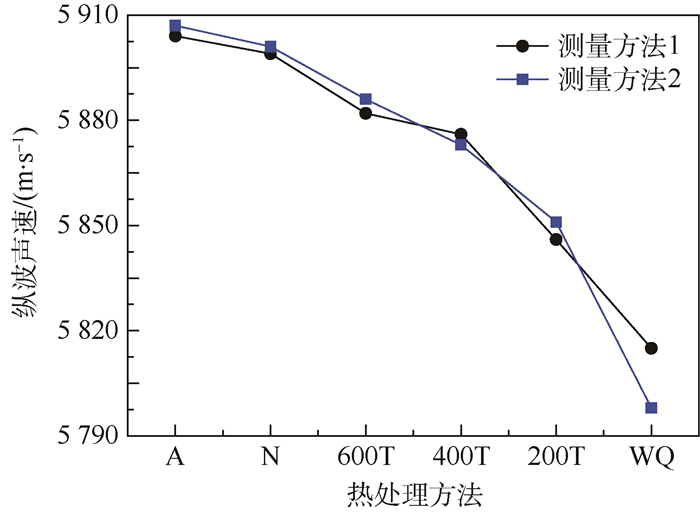
表 2 标定试件超声纵波声速(测量方法1)Table 2. Calibrated specimen ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity (Measuring method 1)热处理方法 d/mm 一次回波 二次回波 vL/(m·s-1) t1/μs Et1/μs t2/μs Et2/μs A 18.98 9.397 9 0.001 15.827 6 0.001 5 904 N 18.99 9.391 7 0.001 15.830 1 0.008 5 899 600T 18.98 9.373 4 0.002 15.827 0 0.003 5 882 400T 18.99 9.351 3 0.004 15.814 1 0.005 5 876 200T 18.98 9.335 4 0.003 15.828 5 0.005 5 846 WQ 18.98 9.315 4 0.008 15.843 0 0.009 5 815 表 3 标定试件超声纵波声速(测量方法2)Table 3. Calibrated specimen ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity (Measuring method 2)热处理方法 d/mm t/μs Et/μs vL/(m·s-1) A 18.98 3.213 2 0.006 5 907 N 18.99 3.217 8 0.009 5 901 600T 18.98 3.224 3 0.003 5 886 400T 18.99 3.233 0 0.005 5 873 200T 18.98 3.243 8 0.005 5 851 WQ 18.98 3.273 4 0.009 5 798 图 8(a)为采用2种测量方法超声纵波声时随标定试件不同热处理方法的变化曲线。可以看出,2种测量方法测得声时变化趋势一致,超声纵波声时测量均方根误差控制在纳秒量级,声时测量误差均满足纵波声速精确测量要求。图 8(b)为采用2种测量方法测量纵波声速随标定试件不同热处理方法变化曲线。可以看出,2种测量方法测得超声纵波声速随热处理方法的变化趋势一致;不同之处在于,采用测量方法1测得的纵波声速大小整体上小于测量方法2测得的纵波声速,只有在400℃回火和淬火时略大于测量方法2所测纵波声速大小,哪种测量方法能够更准确地评价材料的硬度,通过建立超声纵波声速与材料布氏硬度标定模型,预测验证试件硬度,得出标定模型预测误差,为选择测量方法提供实验依据。
2.3 建立标定模型
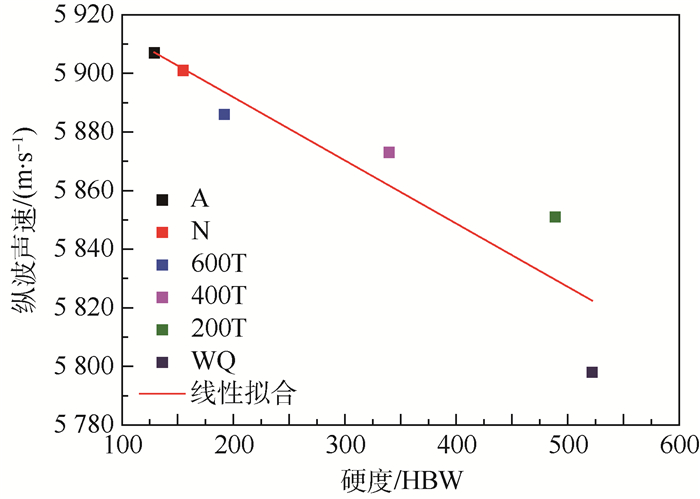
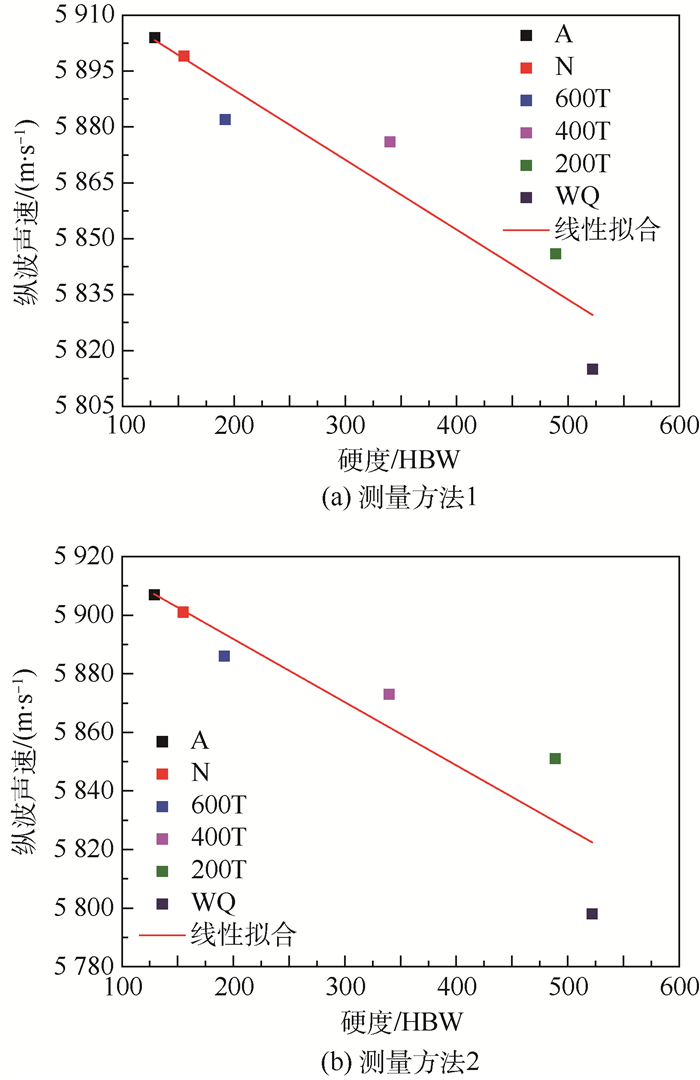
图 9(a)为采用线性函数对测量方法1所得超声纵波声速随标定试件布氏硬度的变化进行拟合,拟合度R2=0.879 11,拟合度较高,拟合函数为

(3) 式中:x为材料的布氏硬度;y为超声纵波声速。
为验证标定模型的准确性,对760℃淬火45钢试件纵波声时进行测量,计算声速为5 879 m/s,代入式(3),预测硬度为258 HBW,布氏硬度计测试硬度为254 HBW,误差为1.57%。
图 9(b)为采用线性函数对测量方法2所得超声纵波声速随标定试件布氏硬度的变化进行拟合,拟合度R2=0.809 01,拟合度较高,拟合函数为

(4) 为验证标定模型的准确性,对760℃淬火45钢试件纵波声时进行测量,计算声速为5 882 m/s,代入式(4),预测硬度为246 HBW,布氏硬度计测试硬度为254 HBW,误差为3.15%。
由式(3)、式(4)标定模型预测精度可以得出:2种测量方法所得超声纵波声速建立的45钢硬度标定模型,预测精度均较高,均满足工程应用10%的误差要求;采用测量方法1计算超声纵波声速建立的标定模型预测精度比测量方法2高。主要原因在于:方法1拟合曲线的拟合度较高,拟合参数之间相关性较高;采用测量方法1测量时超声纵波的声程为试件厚度的2倍,与测量方法2比较,声程测量引入的相对误差较小;测量声时时,测量方法1每个回波信号测量401次求其平均值,测量方法2是将一次回波信号及二次回波信号的声时差进行测量401次求其平均值,测量均方根误差比测量方法1大。
2.4 相关性分析
从2.3节标定试件超声纵波声速变化来看,退火试件超声纵波声速最快,正火试件声速略小于退火试件,之后依次是高温回火、中温回火和低温回火试件,淬火试件纵波声速最慢。从不同热处理45钢标定试件微观组织角度分析,退火试件微观组织铁素体相含量最高且铁素体声阻抗最低,超声纵波声速最快;正火试件微观组织珠光体层间距要比退火件小,更密集的层片结构使得超声波传播变慢,同时珠光体组织含量比退火试件高,珠光体纵波声速比铁素体要慢;淬火试件纵波声速最慢,原因在于45钢中马氏体是经过过冷奥氏体经无扩散相变转变而来,组织内部由于晶格体积发生变化导致大量位错,产生大量的内部张力及残余应力,最终造成超声波声速大幅度下降,马氏体的低弹性模量也是造成声速降低的主要原因之一,超声纵波在马氏体组织传播声速比在珠光体和铁素体中慢;回火45钢试件中超声波声速相比淬火态有不同程度的增加,这是由于回火过程释放了马氏体相变造成的组织应力,缓解了晶格畸变程度,提高了组织的弹性模量,使超声波传播速度更快;同时随着回火温度的提高,200℃低温回火试件马氏体组织含量减小,400℃中温回火试件组织转变为屈氏体,马氏体针状形态逐渐消失,600℃高温回火试件组织转变为回火索氏体,超声纵波声速较正火组织慢。
实验采用的标定试件及验证试件热处理时奥氏体化温度和保温时间一致,从而保证初始奥氏体晶粒尺寸一致,因此只考虑微观应力对X射线衍射峰半高宽的影响,即只考虑晶格畸变程度,如式(5)所示[15]:

(5) 式中:Strain表示微观应变,晶格畸变程度,即应变量相对于面间距的比值,用百分数表示;Δl为晶格应变量;L为晶格面间距;FW(S)为试件衍射峰宽化,rad;θ为衍射角度。
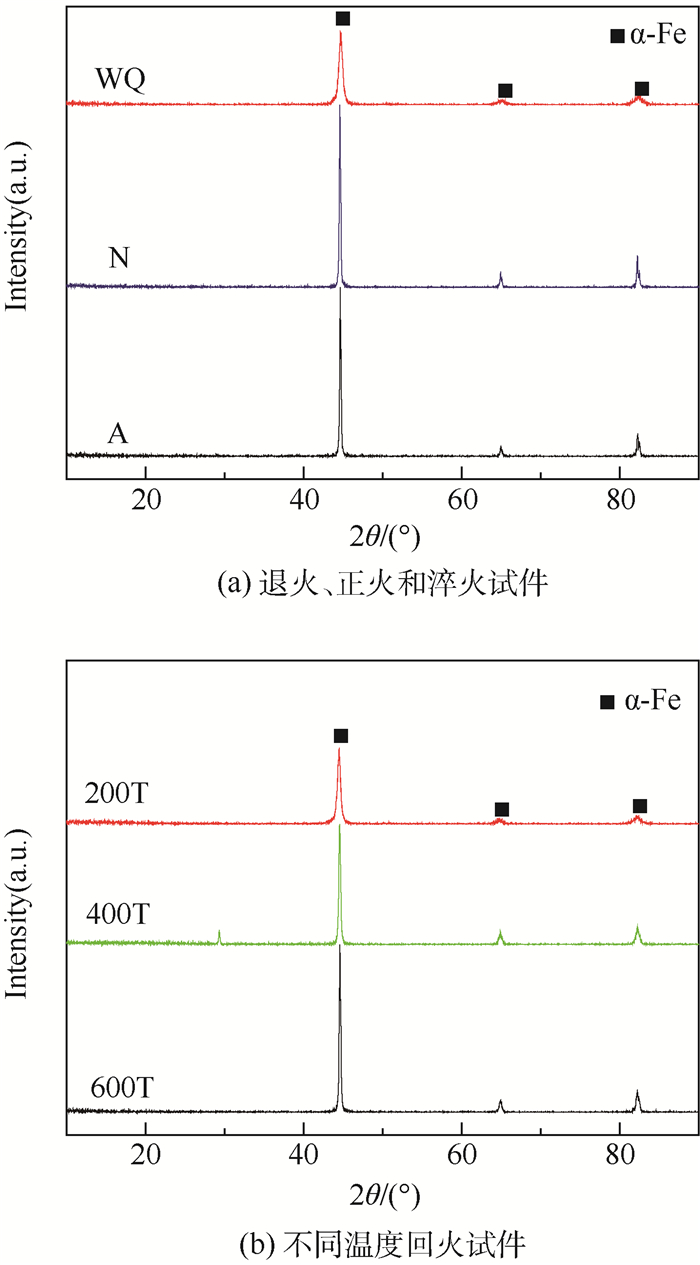
图 10为不同热处理45钢标定试件X射线衍射图。从图中可以看出, 热处理后试件的衍射峰θ角度几乎没有变化,但FW(S)变化明显,说明不同热处理试件晶格畸变程度各异。
采用Jade软件分析得不同热处理试件微观组织晶格畸变程度,结果如表 4所示。正火45钢试件晶格畸变程度略大于退火试件,正火45钢和退火45钢组织差别不明显,前者仅珠光体含量高于后者,并且铁素体较珠光体比体积更小;淬火45钢试件的晶格畸变程度要明显大于其他热处理45钢试件,由于在高冷却速度下,, 面心立方(Face-Centered Cube,FCC)结构的奥氏体组织突然进行非扩散型相变,转变为体心正方(Body-Centered Tetragonal,BCT)结构的马氏体组织,晶粒体积的变化产生大量的位错和内部应力;回火处理会在不同程度上释放材料快冷所产生的晶格畸变引起的应力,回火45钢试件晶格畸变程度随回火温度的升高而降低。图 11为不同热处理45钢试件硬度随晶格畸变程度的变化关系,基本呈线性变化。
表 4 不同热处理45钢试件晶格畸变程度Table 4. Degree of lattice distortion of different heat treated 45 steel specimens热处理方法 晶格畸变程度/% A 0 N 0.033 600T 0.094 400T 0.168 200T 0.369 WQ 0.509 不同热处理45钢试件由于晶格应力等因素引起晶格畸变程度的差异性,宏观表现就是材料硬度的差异性,导致超声纵波声速的变化,在受到压力P作用下,介质中纵波声速与应力之间的关系为[16]

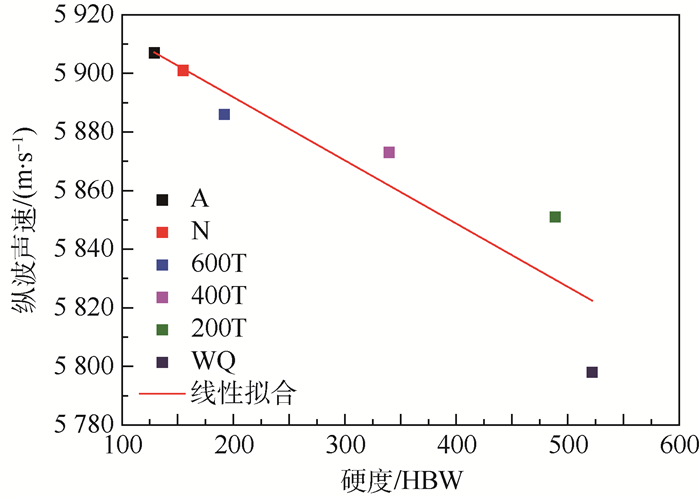
(6) 式中:ρ0为介质发生形变前的密度;P为材料所受压力,压应力为正,拉应力为负;λ和μ为材料二阶弹性常数,K0=λ+2μ/3;l和m为材料三阶弹性系数;v11P2为介质中任意方向的纵波声速。图 12为不同热处理45钢试件超声纵波声速随晶格畸变程度的变化关系,其变化趋势基本呈线性关系。
综上所述,不同热处理45钢试件微观组织各异,宏观表现就是材料硬度指标的差异性,直接反映在超声纵波声速的变化。通过建立材料硬度指标、超声纵波声速与不同热处理45钢试件晶格畸变程度的映射关系,将材料力学性能硬度指标、材料微观组织与无损检测参量关联起来,最终建立它们之间的定量映射关系,得到材料硬度与超声纵波声速之间的标定模型,通过精确测量被测试件超声纵波声速,实现对45钢硬度指标的定量表征与预测。
3. 结论
1) 通过对不同热处理标定试件超声纵波声时的测量,计算相应超声纵波声速,结合材料微观组织,建立了超声纵波声速评价材料力学性能硬度指标的标定方法和标定模型,预测硬度误差指标达到工程应用误差10%的要求。
2) 同时采用2种门信号测量方法对试件底面反射回波声时进行精确测量,声时均方根误差均达到纳秒量级,满足超声纵波声速测量精度;采用门信号分别测量2次反射回波信号声时,计算超声纵波声速,建立的45钢超声纵波声速-硬度标定模型预测精度更高,预测硬度误差更小,为测量信号测量方式的选择提供实验基础。
3) 建立了45钢试件力学性能硬度指标-材料微观组织-超声纵波声速之间对应定量映射关系,从不同热处理45钢试件微观组织和晶格畸变程度2方面解释了不同热处理45钢试件超声纵波声速随试件硬度的变化趋势,为采用超声纵波声速无损、快速、定量评价材料力学性能硬度指标提供了理论基础和实验支撑。
-
表 1 标定45钢试件热处理方法及硬度
Table 1. Heat treatment methods and hardness of calibrated 45 steel specimens
热处理方法 冷却方式 回火温度/℃ 保温时间/min 硬度/HBW A 炉冷 129 N 空冷 155 600T 空冷 600 30 192 400T 空冷 400 30 340 200T 空冷 200 30 489 WQ 水冷 522 表 2 标定试件超声纵波声速(测量方法1)
Table 2. Calibrated specimen ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity (Measuring method 1)
热处理方法 d/mm 一次回波 二次回波 vL/(m·s-1) t1/μs Et1/μs t2/μs Et2/μs A 18.98 9.397 9 0.001 15.827 6 0.001 5 904 N 18.99 9.391 7 0.001 15.830 1 0.008 5 899 600T 18.98 9.373 4 0.002 15.827 0 0.003 5 882 400T 18.99 9.351 3 0.004 15.814 1 0.005 5 876 200T 18.98 9.335 4 0.003 15.828 5 0.005 5 846 WQ 18.98 9.315 4 0.008 15.843 0 0.009 5 815 表 3 标定试件超声纵波声速(测量方法2)
Table 3. Calibrated specimen ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity (Measuring method 2)
热处理方法 d/mm t/μs Et/μs vL/(m·s-1) A 18.98 3.213 2 0.006 5 907 N 18.99 3.217 8 0.009 5 901 600T 18.98 3.224 3 0.003 5 886 400T 18.99 3.233 0 0.005 5 873 200T 18.98 3.243 8 0.005 5 851 WQ 18.98 3.273 4 0.009 5 798 表 4 不同热处理45钢试件晶格畸变程度
Table 4. Degree of lattice distortion of different heat treated 45 steel specimens
热处理方法 晶格畸变程度/% A 0 N 0.033 600T 0.094 400T 0.168 200T 0.369 WQ 0.509 -
[1] 蔡鹏, 程玉华, 谢驰, 等.超声波技术用于零件表面硬度无损检测的研究[J].工具技术, 2007, 41(2):85-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2007.02.024CAI P, CHENG Y H, XIE C, et al.Research on non-destructive detection of part surface hardness with ultrasonic technology[J].Tool Engineering, 2007, 41(2):85-89(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2007.02.024 [2] 刘志军.金属基复合材料高温界面特性及耐磨性能研究[J].热加工工艺, 2016, 45(12):110-112.LIU Z J.High temperature interface properties and wear resistance of metal matrix composite[J].Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45(12):110-112(in Chinese). [3] BAO Y W, WANG W, ZHOU Y C.Investigation of the relationship between elastic modulus and hardness based on depth-sensing indentation measurements[J].Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(18):5397-5404. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.08.002 [4] ZHU L N, XU B S, WANG H D, et al.Determination of hardness of plasma-sprayed FeCrBSi coating on steel substrate by nanoindentation[J].Materials Science & Engineering A, 2010, 528(1):425-428. [5] 萨殊利, 肖春燕, 朱衡君, 等.电涡流无损检测淬火钢轨踏面硬度定量分析[J].铁道学报, 2001, 23(3):33-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2001.03.007SA S L, XIAO C Y, ZHU H J, et al.Quantitative analysis of quenched rail surface hardness by eddy current nondestructive testing[J].Journal of the China Railway Society, 2001, 23(3):33-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2001.03.007 [6] 付强, 李世波.金属材料几种常见硬度的区别与联系[J].山东化工, 2016, 45(6):70-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.06.026FU Q, LI S B.Difference and contact of metal materials several common hardness[J].Shandong Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(6):70-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.06.026 [7] ZENG W, WANG H, TIAN G, et al.Detection of surface defects for longitudinal acoustic waves by a laser ultrasonic imaging technique[J].Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(1):415-419. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.09.175 [8] 门平, 董世运, 康学良, 等.材料早期损伤的非线性超声诊断[J].仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(5):1101-1118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.05.008MEN P, DONG S Y, KANG X L, et al.Material early damage diagnosis with nonlinear ultrasound[J].Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(5):1101-1118(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.05.008 [9] JIAO J, FAN Z, ZHONG F, et al.Application of ultrasonic methods for early detection of intergranular corrosion in austenitic stainless steel[J].Research in Nondestructive Evaluation, 2016, 27(4):193-203. doi: 10.1080/09349847.2015.1103922 [10] CHEREPETSKAYA E B, KARABUTOV A A, MIRONOVA E A, et al.Contact laser-ultrasonic evaluation of residual stress[J].Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2016, 843(7):118-124. [11] LIU B, DONG S.Stress evaluation of laser cladding coating with critically refracted longitudinal wave based on cross correlation function[J].Applied Acoustics, 2016, 101(8):98-103. [12] FREITAS V L D A, ALBUQUERQUE V H C D, SILVA E D M, et al.Nondestructive characterization of microstructures and determination of elastic properties in plain carbon steel using ultrasonic measurements[J].Materials Science & Engineering A, 2010, 527(16):4431-4437. [13] YU Z, LIU C, ZHANG F, et al.Experimental study and finite element analysis based on equivalent load method for laser ultrasonic measurement of elastic constants[J].Ultrasonics, 2016, 69(3):243-247. [14] 邓雯, 杨建华, 张扬.基于孤立波的杨氏模量无损检测换能器研究[J].仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(11):2762-2768. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.11.018DENG W, YANG J H, ZHANG Y.HNSWs based transducers in measuring Young's modulus nondestructively[J].Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(11):2762-2768(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.11.018 [15] 周玉.材料分析方法[M].北京:机械工业出版社, 2011:40-54.ZHOU Y.Material analysis method[M].Beijing:Machinery Industry Press, 2011:40-54(in Chinese). [16] ROSE J L.固体中的超声波[M].何存富, 吴斌, 王秀彦, 译.北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 242-247.ROSE J L.Ultrasonic waves in solid media[M].HE C F, WU B, WANG X Y, translated.Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 242-247(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载:












 下载:
下载: