-
摘要:
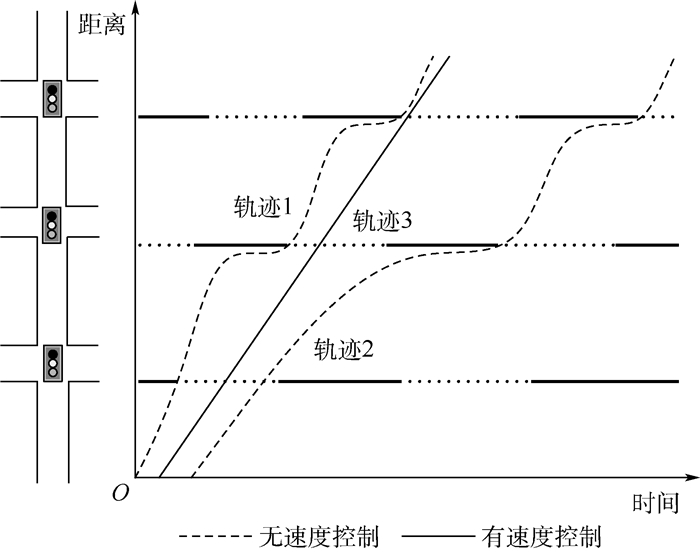
为了提高车辆在城市道路上行驶时的燃油经济性,同时减少污染物的排放,针对车联网环境下自动驾驶车辆可以与路侧设施及区域中心控制系统实时信息交互的特征,提出了连续信号交叉口车速控制方法。当车辆距下游各信号交叉口的距离和下游交叉口信号相位及时长可以提前获取时,通过提出的自动驾驶车速控制模型计算出一个使车辆能够连续通过下游多个信号交叉口的恒定速度,同时为了保证驾驶舒适性,采用平滑的三角函数曲线表征加/减速过程中的速度变化,避免了车辆在交叉口处急刹车或急加速的情况。为验证车速控制方法的有效性,基于多智能体技术建立了车联网环境下连续信号交叉口车速控制仿真系统,模拟对比分析了有速度控制和无速度控制下车辆连续通过3个信号交叉口的燃油消耗量、CO2排放量以及行程时间。结果表明:在低密度车流下,运用该车速控制方法,车辆连续通过3个信号交叉口的平均燃油消耗量与CO2排放量均减少了30%以上,行程时间减少了约5%;在中、高密度车流下,车辆的平均燃油消耗量与CO2排放量减少了约20%,并能够节省约15%的行程时间。另外,通过与目前已有的针对单点信号交叉口的车速控制模型的比较,本文提出的连续信号交叉口车速控制模型在节能减排方面更具优势。
Abstract:In order to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions on the urban road, a speed control method in successive signalized intersections was proposed for autonomous vehicles to interact with the roadside facilities and the regional center control system under the connected vehicles environment. The proposed automatic driving speed control model computes a constant speed that a vehicle can pass multiple downstream signalized intersections based on the information obtained in advance such as the distance between the vehicle and downstream signal intersections and the signal phasing and timing information. Meanwhile, in order to guarantee driving comfort and avoid sharp acceleration/deceleration at the intersection, we use the smooth curve of trigonometric function to represent the change of speed during the acceleration or deceleration process. To verify the efficiency of the speed control algorithm, the speed control simulation system embodying the cha-racteristics of the connected vehicles environment in successive signalized intersections is developed using the multi-agent technology, in which the fuel consumption, CO2 emissions and travel time under the speed control algorithm are compared with those without speed control algorithm when vehicles pass three signalized intersections. The results show that when vehicles go through the three successive intersections under low traffic density, the average fuel consumption and CO2 emissions are reduced by more than 30% by the aid of the speed control algorithm, and the travel time is reduced by about 5%; the fuel consumption and CO2 emissions can be reduced by approximately 20%, and the travel time is reduced by about 15% under the medium and high traffic density. In addition, compared with the current speed control model for the isolated signalized intersection, the proposed speed control model in successive signalized intersections has some advantages in energy saving and emission reduction.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameter setting
参数 数值 vmax/(km·h-1) 60 vmin/(km· h-1) 10 L1/m 400 L2/m 900 L3/m 1 400 amax/(m· s-2) 2.5 amin/(m· s-2) -2.5 jmax/(m· s-3) 10 g11/s 10 r11/s 60 g21/s 80 r21/s 20 g31/s 30 r31/s 80 仿真时间/min 120 表 2 低密度车流下有速度控制和无速度控制车辆的平均燃油消耗量、CO2排放量、行程时间比较
Table 2. Comparison of vehicle average fuel consumption, CO2 emissions and travel time with and without speed control under low traffic density
指标 有速度控制 无速度控制 平均值 标准差 平均值 标准差 燃油消耗量/(L·s-1) 1.96 1.14 2.85 1.88 CO2排放量/(mg·s-1) 4.68 2.71 7.05 4.50 行程时间/s 192.31 19.37 201.75 63.13 表 3 中、高密度车流下有速度控制和无速度控制车辆的平均燃油消耗量、CO2排放量、行程时间比较
Table 3. Comparison of vehicle average fuel consumption, CO2 emissions and travel time with and without speed control under medium and high traffic density
指标 有速度控制 无速度控制 平均值 标准差 平均值 标准差 燃油消耗量/(L·s-1) 7.25 3.47 9.36 2.94 CO2排放量/(mg·s-1) 18.49 4.81 23.05 4.74 行程时间/s 287.12 10.28 340.77 20.56 表 4 不同车速控制方法下车辆的平均燃油消耗量、CO2排放量、行程时间比较
Table 4. Comparison of vehicle average fuel consumption, CO2 emissions and travel time among different speed control methods
方法 燃油消耗量/(L·s-1) CO2排放量/(mg·s-1) 行程时间/s 低密度 中、高密度 低密度 中、高密度 低密度 中、高密度 单点信号交叉口 2.68 9.62 6.41 23.27 164.76 283.49 连续信号交叉口 1.96 7.25 4.68 18.49 192.31 287.12 -
[1] 安实, 姚焓东, 姜慧夫, 等.信号交叉口绿色驾驶车速控制方法[J].交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(5):53-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2015.05.008AN S, YAO H D, JIANG H F, et al.A green driving speed control method at signal intersection[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(5):53-59(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6744.2015.05.008 [2] 姚焓东.面向绿色驾驶的信号交叉口车速动态控制方法研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1015981827.htmYAO H D.Vehicle speed dynamic control method research at signal intersection for green driving[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015(in Chinese). http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1015981827.htm [3] MYHRBERG S.Saving fuel and environment with intelligent speed adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the 15th World Congress on Intelligent Transport Systems and ITS America's 2008 Annual Meeting.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008. [4] PIERRE G S, EHRLICH J.Impact of intelligent speed adaptation systems on fuel consumption and driver behavior[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(49):34345-34351. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806352200 [5] LI M, BORIBOONSOMSIN K, WU G, et al.Traffic energy and emission reductions at signalized intersections:A study of the benefits of advanced driver information[J].International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, 2009, 7(1):49-58. [6] BARTH M, BORIBOONSOMSIN K.Energy and emissions impacts of a freeway-based dynamic eco-driving system[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment, 2009, 14(6):400-410. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2009.01.004 [7] 陈晓博.发展自动驾驶汽车的挑战和前景展望[J].综合运输, 2016, 38(11):9-13. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93306X/201611/670681428.htmlCHEN X B.The study on the challenge and development prospect of automated vehicles[J].Comprehensive Transportation, 2016, 38(11):9-13(in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93306X/201611/670681428.html [8] SERVIN O, BORIBOONSOMSIN K, BARTH M.An energy and emissions impact evaluation of intelligent speed adaptation[C]//IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 1257-1262. [9] ZHENG S J, XU J M.Research on red wave and green wave coordinated control model in arterial road for different traffic demands[C]//Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 1661-1664. [10] YANG Z Y, DING Z J.Actuated green wave control for grid-like network traffic signal coordination[C]//2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 953-958. [11] LI X H, TAN G Z, CHEN C.Urban arterial road green-wave control based on genetic algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 3087-3092. [12] YE B L, WU W M, ZHOU X H, et al.A green wave band based method for urban arterial signal control[C]//Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 126-131. [13] CHEN S Y, SUN J, YAO J.Development and simulation application of a dynamic speed dynamic signal strategy for arterial traffic management[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International IEEE Annual Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 1349-1354. [14] 林培群, 卓福庆, 姚凯斌, 等.车联网环境下交叉口交通流微观控制模型及其求解与仿真[J].中国公路学报, 2015, 28(8):82-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.08.011LIN P Q, ZHUO F Q, YAO K B, et al.Solving and simulation of microcosmic control model of intersection traffic flow in connected-vehicle network environment[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(8):82-90(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.08.011 [15] 李鹏凯, 杨晓光, 吴伟, 等.车路协同环境下信号交叉口车速引导建模与仿真[J].交通信息与安全, 2012, 30(3):136-140. doi: 10.3963/j.ISSN1674-4861.2012.03.031LI P K, YANG X G, WU W, et al.Modeling vehicle speed guidance at signal intersection under IntelliDriverSM[J].Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2012, 30(3):136-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.ISSN1674-4861.2012.03.031 [16] KUNDU S, KUNDU S.Flexible vehicle speed control algorithms for eco-driving[C]//IEEE 82nd Vehicular Technology Conference.Picsataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-5. [17] CHANG C C.Cooperative traffic control with driving efficiency optimization for multiple intersections based on vehicular networks[D].Hsinchu: National Chiao-Tung University, 2014. [18] ASADI B, VAHIDI A.Predictive cruise control:Utilizing upcoming traffic signal information for improving fuel economy and reducing trip time[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2011, 19(3):707-714. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2010.2047860 [19] RAKHA H, IEEE M, KAMALANATHAHARMA R K.Eco-driving at signalized intersections using V2I communication[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International IEEE Annual Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 341-346. [20] XIA H, BORIBOONSOMSIN K, BARTH M.Dynamic eco-driving for signalized arterial corridors and its indirect network-wide energy/emissions benefits[J].Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 17(1):31-41. doi: 10.1080/15472450.2012.712494 [21] AHN K, RAKHA H, ASCE M, et al.Estimating vehicle fuel consumption and emissions based on instantaneous speed and acceleration levels[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2002, 128(2):182-190. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2002)128:2(182) [22] YANG H, RAKHA H, IEEE M, et al.Eco-cooperative adaptive cruise control at signalized intersections considering queue effects[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(6):1575-1585. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2c459d87415d6a57d2654e98f4fc5196 [23] YI K S, CHUNG J T.Nonlinear brake control for vehicle CW/CA systems[J].IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2001, 6(1):17-25. doi: 10.1109/3516.914387 [24] RAKHA H, AHN K, TRANI A.Development of VT-micro model for estimating hot stabilized light duty vehicle and truck emi-ssions[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment, 2004, 9(1):49-74. doi: 10.1016/S1361-9209(03)00054-3 [25] AHN K.Microscopic fuel consumption and emission modeling[D].Blacksburg: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, 1998. -







 下载:
下载: