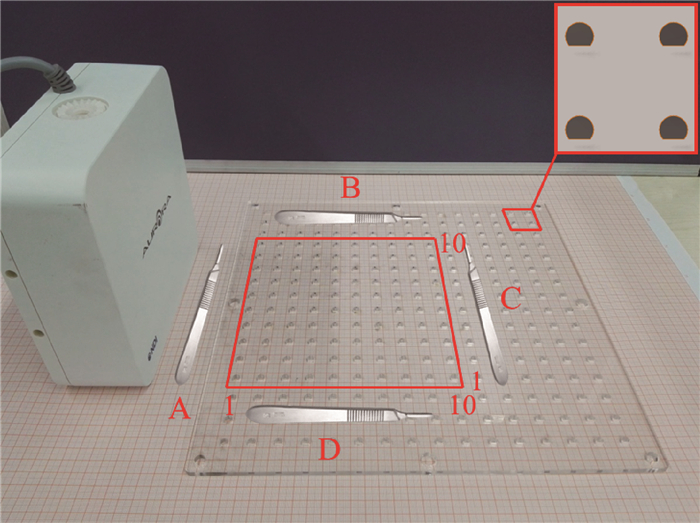
A thin plate spline based method for correction of position and posture of electromagnetic tracking system
-
摘要:
电磁定位系统(EM)凭借其精度高、反应灵活、操作简便、价格便宜以及无遮挡效应等优点,被广泛应用于各种需要进行跟踪定位的领域。在介入手术中,EM可以很好地解决因人体组织对介入器械的遮挡而无法进行精确光学定位的问题,能够对介入器械的位姿进行精确定位。但EM是通过电磁感应原理对介入器械进行跟踪定位,因此手术环境中存在的铁磁性物质产生的干扰磁场会导致EM的磁场产生畸变,从而影响其定位精度。对EM的定位原理进行了分析,通过分析EM受干扰前后传感器在相同位置的位姿变化,提出一种基于薄板样条函数的电磁定位系统校正方法,对EM受干扰后的位姿进行校正,并通过实验验证该方法的有效性。
Abstract:Electromagnetic tracking system (EM) is widely used in various environments needing tracking or positioning, due to its high accuracy, flexible reaction, simple operation, cheap price and insensitivity to blocks. In vascular interventional surgery, EM performs well in clinical environment with inaccurate optical positioning due to tissue occlusion. However, EM suffers a lot from the principle of electromagnetic induction which makes it sensitive to ferromagnetic material, like steel. The magnetic field generated by ferromagnetic materials in the operation environment will cause the distortion of the magnetic field of EM, which affects the positioning accuracy seriously. In this paper, the positioning principle of EM is analyzed. By analyzing the position and orientation changes of sensors at the same position before and after the EM interference, a correction method of the electromagnetic tracking system based on the thin plate spline function is proposed to correct the position and posture of the EM after interference.The effectiveness of our method is verified by experiments.
-
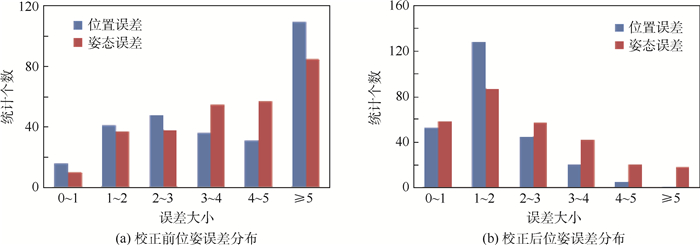
表 1 同一平面不同干扰源校正结果
Table 1. Correction results of different interferences on the same plane
干扰位置 Δx/mm Δy/mm Δz/mm Δα/(°) Δβ/(°) Δγ/(°) RMSt/mm RMSr/(°) A(校正前) 2.210 1.906 6.414 5.977 1.739 4.752 7.533 8.147 A(校正后) 0.715 0.841 0.604 0.872 0.862 0.838 1.447 1.642 B(校正前) 7.730 4.542 3.215 3.826 3.158 2.154 9.913 5.873 B(校正后) 0.697 0.995 0.909 0.845 1.615 0.889 1.665 2.136 C(校正前) 0.697 1.824 1.560 2.191 2.538 1.690 2.661 4.010 C(校正后) 0.383 1.209 0.765 1.722 1.019 0.755 1.708 2.356 D(校正前) 1.607 0.534 1.204 0.897 1.081 1.723 2.157 2.383 D(校正后) 0.317 0.177 0.420 0.368 0.564 0.445 0.604 0.901 表 2 同一干扰源空间校正结果
Table 2. Correction results of the same interference in space
校正前后 Δx/mm Δy/mm Δz/mm Δα/(°) Δβ/(°) Δγ/(°) RMSt/mm RMSr/(°) 校正前 7.910 3.046 3.328 3.074 2.932 2.398 9.602 5.577 校正后 1.024 0.772 1.331 1.889 1.182 1.782 2.184 3.042 -
[1] FRANZ A M, HAIDEGGER T, BIRKFELLNER W, et al.Electromagnetic tracking in medicine:A review of technology, validation, and applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2014, 33(8):1702-1725. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2321777 [2] BIRKFELLNER W, WATZINGER F, WANSCHITZ F, et al.Calibration of tracking systems in a surgical environment[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1998, 17(5):737-742. doi: 10.1109/42.736028 [3] PÉRIÉ D, TATE A J, CHENG P L, et al.Evaluation and calibration of an electromagnetic tracking device for biomechanical analysis of lifting tasks[J].Journal of Biomechanics, 2002, 35(2):293-297. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9290(01)00188-9 [4] FEUERSTEIN M, REICHL T, VOGEL J, et al.Magneto-optical tracking of flexible laparoscopic ultrasound:Model-based online detection and correction of magnetic tracking errors[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2009, 28(6):951-967. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.2008954 [5] SHAHRIARI N, HEKMAN E, OUDKERK M, et al.Design and evaluation of a computed tomography(CT)-compatible needle insertion device using an electromagnetic tracking system and CT images[J].International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology & Surgery, 2015, 10(11):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s11548-015-1176-3 [6] HARISH V, BAKSH A, UNGI T, et al.Measurement of electromagnetic tracking error in a navigated breast surgery setup[C]//Medical Imaging 2016: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling.Bellingham: International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2016: 1-8. [7] LUND K T, TANGEN G A, MANSTAD H F.Electromagnetic navigation versus fluoroscopy in aortic endovascular procedures:A phantom study[J].International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology & Surgery, 2016, 12(1):1-7. [8] VILLAGRAN C R T, IKEDA S, FUKUDA T, et al.Catheter insertion path reconstruction with autonomous system for endovascular surgery[C]//Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation, 2007.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 398-403. [9] TERCERO C, IKEDA S, UCHIYAMA T, et al.Autonomous catheter insertion system using magnetic motion capture sensor for endovascular surgery[J].The International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery, 2007, 3(1):52-58. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1478-596X [10] FU Y L, GAO A, LIU H, et al.The master-slave catheterisation system for positioning the steerable catheter[J].International Journal of Mechatronics and Automation, 2011, 1(3-4):143-152. doi: 10.1504/IJMA.2011.045271 [11] LIU H, FU Y L, ZHOU Y Y, et al.An in vitro investigation of image-guided steerable catheter navigation[J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H:Journal of Engineering in Medicine, 2010, 224(8):945-954. doi: 10.1243/09544119JEIM730 [12] FISCHER G S, TAYLOR R H.Electromagnetic tracker measurement error simulation and tool design[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Berlin: Springer, 2005: 73-80. doi: 10.1007%2F11566489_10 [13] IKITS M, BREDERSON J D, HANSEN C D, et al.An improved calibration framework for electromagnetic tracking devices[C]//Proceedings IEEE Virtual Reality 2001.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2001: 63-70. [14] TRAUB J, KAUR S, KNESCHAUREK P, et al.Evaluation of electromagnetic error correction methods[C]//Bildverarbeitung Für Die Medizin 2007.Berlin: Springer, 2007: 363-367. doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-540-71091-2_73 [15] HIMBERG H, MOTAI Y, BRADLEY A.Interpolation volume calibration:A multisensor calibration technique for electromagnetic trackers[J].IEEE transactions on Robotics, 2012, 28(5):1120-1130. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2012.2198929 [16] BOUTALEB S, RACINE E, FILLION O, et al.Performance and suitability assessment of a real-time 3D electromagnetic needle tracking system for interstitial brachytherapy[J].Journal of Contemporary Brachytherapy, 2015, 7(4):280-289. [17] KWARTOWITZ D M, RETTMANN M E, HOLMES D R, et al.A novel technique for analysis of accuracy of magnetic tracking systems used in image guided surgery[C]//Medical Imaging 2010: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling.International Society for Optics and Photonics.San Diego: SPIE Medical Imaging, 2010: 1-8. [18] GERGEL I, GAA J, MVLLER M, et al.A novel fully automatic system for the evaluation of electromagnetic tracker[C]//Medical Imaging 2012: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling.International Society for Optics and Photonics.San Diego: SPIE Medical Imaging, 2012: 1-10. [19] ATUEGWU N C, GALLOWAY R L.Volumetric characterization of the Aurora magnetic tracker system for image-guided transorbital endoscopic procedures[J].Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2008, 53(16):4355-4368. [20] BOOKSTEIN F L.Principal warps:Thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2002, 11(6):567-585. doi: 10.1109/34.24792 -








 下载:
下载: