Numerical simulation of near-field magnetic anomaly field for large-scale ferromagnetic objects
-
摘要:
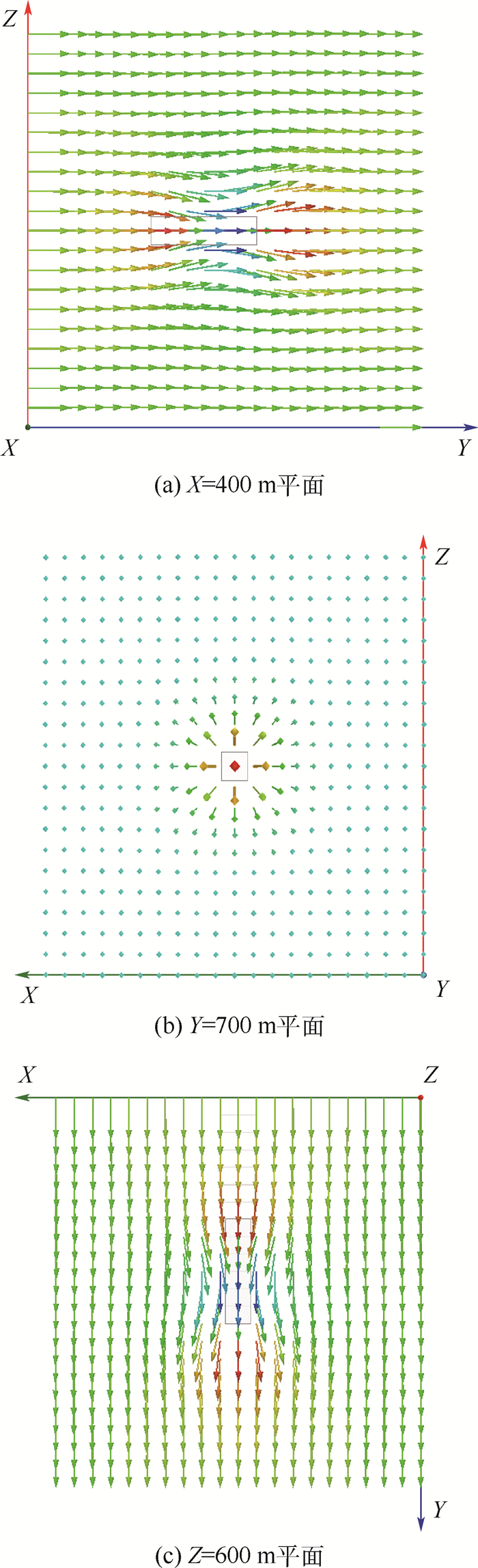
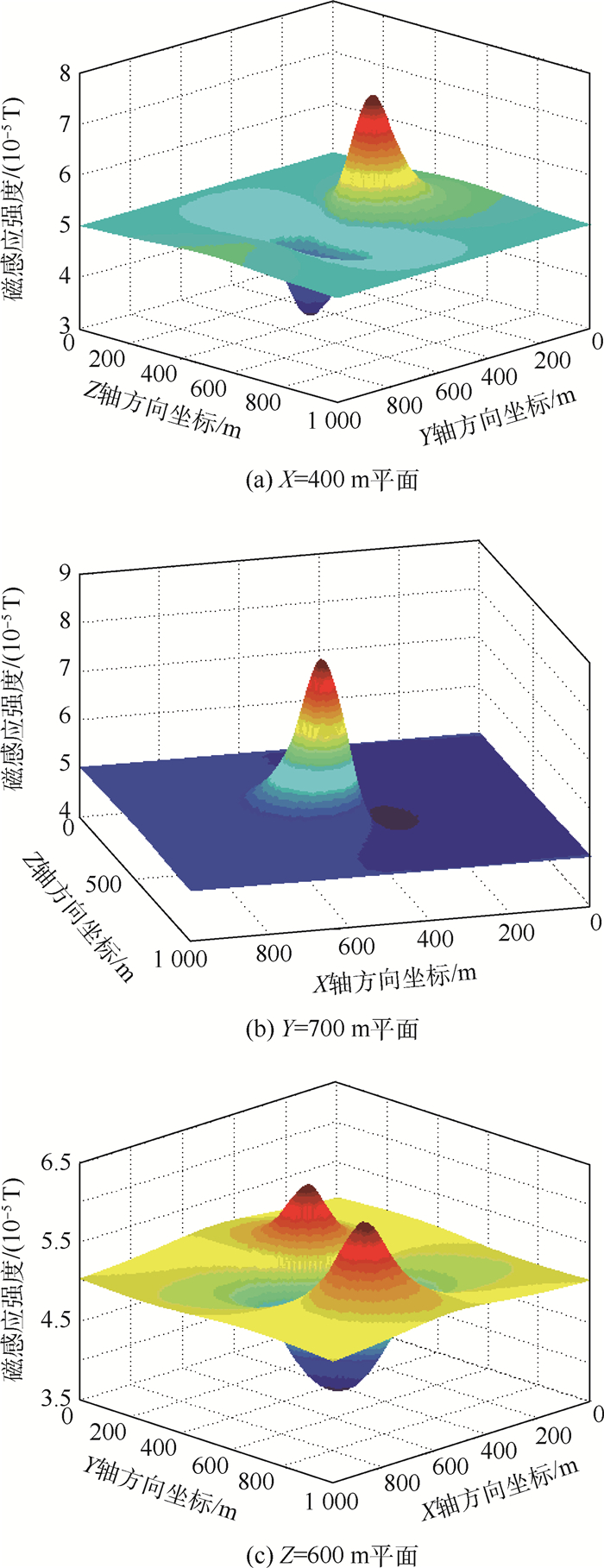
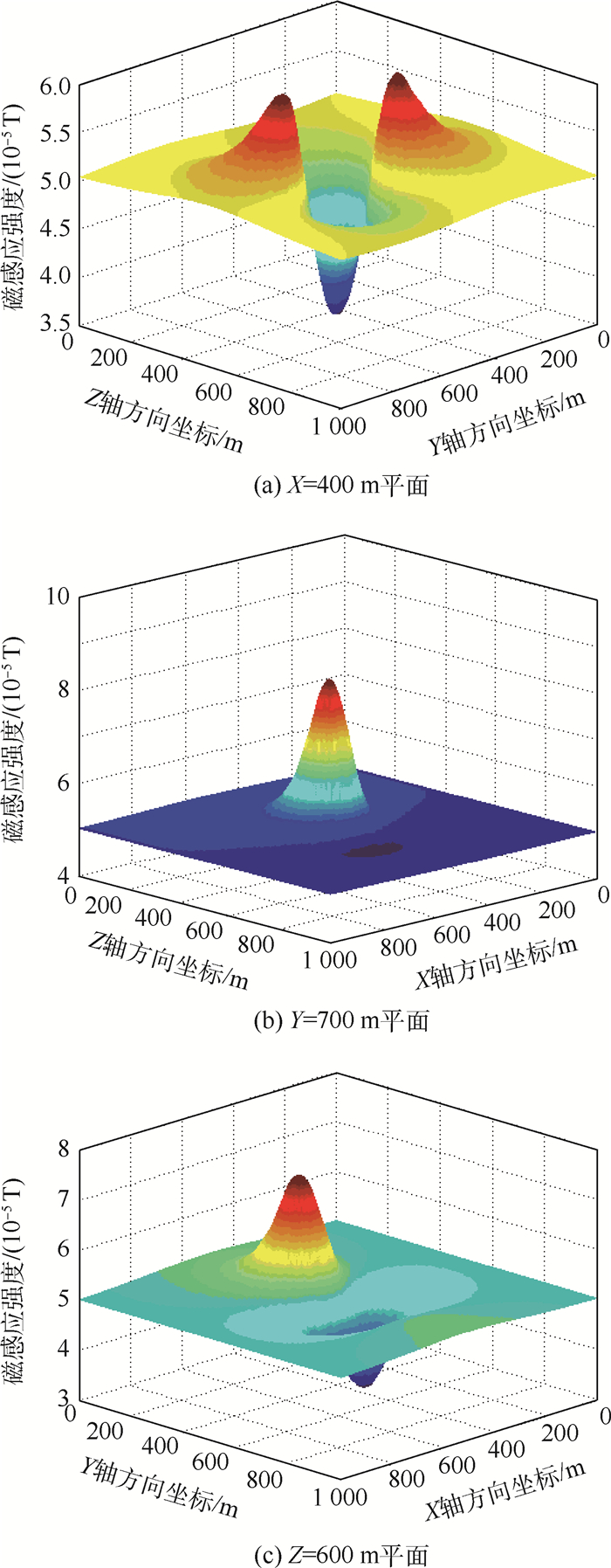
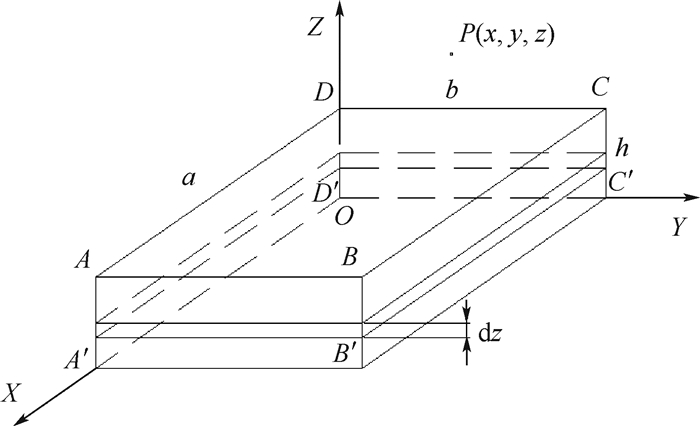
磁异常探测是一种在地球物理领域有着广泛应用的探测方法,磁异常场的空间分布规律信息是磁异常探测的主要理论依据。对矩形铁磁性物体空间磁场模型进行了推导,利用ANSYS Maxwell分析了大型铁磁性物体近场的磁异常场空间分布规律。针对不同地磁场方向条件,得到了近场空间磁感应强度总量分布及矢量分布规律,揭示了在不同条件下磁感应强度模量场和矢量场都具有普遍的对称性和规律性。通过对仿真模型进行缩比试验,测量了类似条件下模型近场的磁感应强度模量场和矢量场信息,验证了仿真得到的磁异常场空间分布规律的一致性和正确性。
Abstract:Magnetic anomaly detection is a widely used approach to detect ferromagnetic objects, which is mainly based on the spatial distribution of magnetic anomaly field. The spatial magnetic field model of rectangular ferromagnetic object is derived. The spatial distribution of the magnetic anomaly field in the near-field of the large-scale ferromagnetic target is analyzed using ANSYS Maxwell. For different geomagnetic field direction conditions, the laws of magnitude distribution and vector distribution of the magnetic induction in the near-field are obtained, which reveals a universal symmetry and regularity in magnetic induction modulus field and vector field. The shrinkage ratio experiment is conducted and the magnitude distribution and vector distribution of the magnetic induction in the near-field of model are measured in similar conditions, which validates the consistency and correctness of the spatial distribution law of magnetic anomaly field.
-
-
[1] LIU B, CAO Y, ZHANG H, et al.Weak magnetic flux leakage:A possible method for studying pipeline defects located either inside or outside the structures[J].NDT & E International, 2015, 74:81-86. [2] ZHANG M Y, WANG H, GE L, et al.Automatic search algorithms for near-field ferromagnetic targets based on magnetic anomaly detection[J/OL].Mathematical Problems in Engineering, (2018-07-05)[2018-07-06].https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2130236/. [3] EGE Y, KALENDER O, NAZLIBILEK S.Direction finding of moving ferromagnetic objects inside water by magnetic anomaly[J].Sensors & Actuators A Physical, 2008, 147(1):52-59. [4] 李泽林, 姚长利, 郑元满, 等.数据空间磁异常模量三维反演[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(10):3804-3814. doi: 10.6038/cjg20151030LI Z L, YAO C L, ZHENG Y M, et al.3D data-space inversion of magnetic amplitude data[J].Chinese Jourral of Geophysics, 2015, 58(10):3804-3814(in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg20151030 [5] ZALEVSKY Z, BREGMAN Y, SALOMONSKI N, et al.Resolution enhanced magnetic sensing system for wide coverage real time UXO detection[J].Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2012, 84(9):70-76. [6] 张恒磊, 胡祥云, 刘天佑.基于二阶导数的磁源边界与顶部深度快速反演[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(11):3839-3847. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.031ZHANG H L, HU X Y, LIU T Y.Fast inversion of magnetic source boundary and top depth via second order derivative[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(11):3839-3847(in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.031 [7] GADRE A S, STILWELL D J, DAVIS B.An information-theoretic approach to underwater magnetic dipole localization[C]//Proceedings of MTS/IEEE Oceans.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2005, 1: 703-710. [8] SHEINKER A, FRUMKIS L, GINZBURG B, et al.Magnetic anomaly detection using a three-axis magnetometer[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2009, 45(1):160-167. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2008.2006635 [9] LIU D, XU X, FEI C, et al.Direction identification of a moving ferromagnetic object by magnetic anomaly[J].Sensors & Actuators A Physical, 2015, 229:147-153. [10] NARA T, SUZUKI S, ANDO S.A closed-form formula for magnetic dipole localization by measurement of its magnetic field and spatial gradients[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(10):3291-3293. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.879151 [11] NARA T, ITO W.Moore-Penrose generalized inverse of the gradient tensor in Euler's equation for locating a magnetic dipole[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 115(17):17E504. doi: 10.1063/1.4861675 [12] BEIKI M, CLARK D A, AUSTIN J R, et al.Estimating source location using normalized magnetic source strength calculated from magnetic gradient tensor data[J].Geophysics, 2012, 77(6):J23-J37. doi: 10.1190/geo2011-0437.1 [13] 张恒磊, MARANGONI Y R, 左仁广, 等.改进的各向异性标准化方差探测斜磁化磁异常源边界[J].地球物理学报, 2014, 57(8):2724-2731.ZHANG H L, MARANGONI Y R, ZUO R G, et al.The improved anisotropy normalized variance for detecting non-vertical magnetization anomalies[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(8):2724-2731(in Chinese). [14] BLAKELY R J.Potential theory in gravity and magnetic applications[M].Cambrige:Cambrige University Press, 1996:75-79. [15] 刘宏娟.矩形永磁体三维磁场空间分布研究[D].北京: 北京工业大学, 2006: 4-11.LIU H J.Research of the three-dimensional magnetic field distribution around a rectangular permanent magnet[D].Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2006: 4-11(in Chinese). [16] 任来平, 谭美景, 李凯锋, 等.水下目标磁异常强度与质量磁化强度分析[J].海洋测绘, 2012, 32(2):7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2012.02.003REN L P, TAN M J, LI K F, et al.Analysis on magnetic anomaly strength and mass magnetization of underwater object[J].Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2012, 32(2):7-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2012.02.003 -







 下载:
下载: