Life prediction method of lithium battery based on improved relevance vector machine
-
摘要:
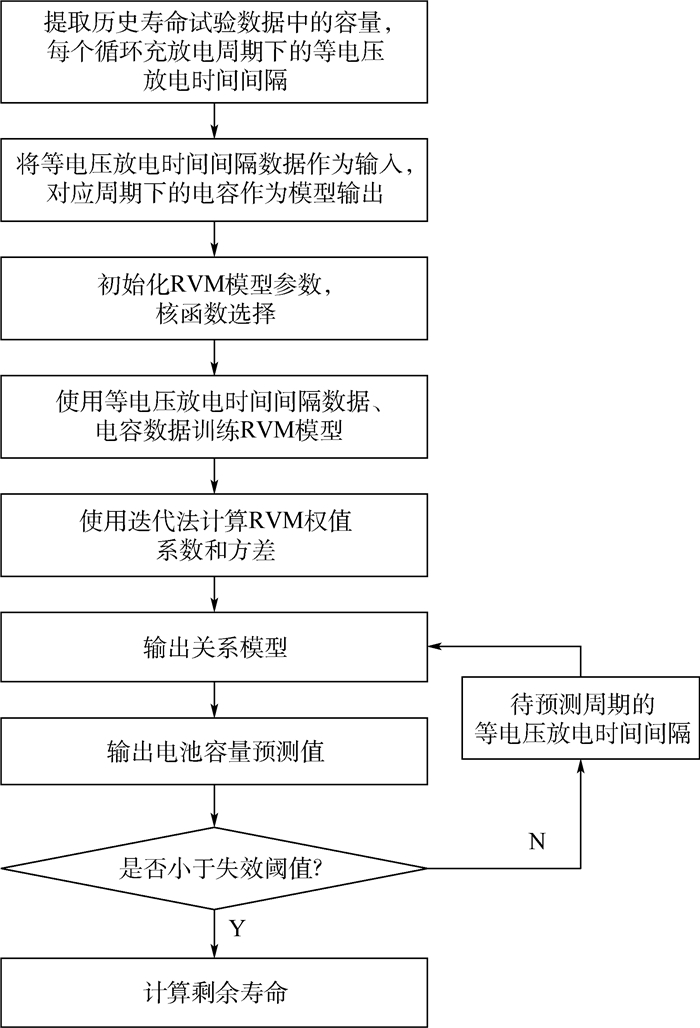
锂电池具有轻便安全、循环寿命长和安全性能好等优点,作为一个被广泛应用的储能电源,锂电池健康管理和寿命预测是国内外研究的热点。建立锂电池寿命预测方法和模型,基于实验历史数据,建立电池衰减模型从而对整个电池的工作状态进行评估,及时对设备进行维护和替换,以确保电池工作的稳定。对相关向量机(RVM)的核函数进行了组合改进,优化了RVM的性能,减小了锂电池寿命预测的偏差度,提高了预测精度。
-
关键词:
- 锂电池 /
- 剩余寿命 /
- 预测 /
- 相关向量机(RVM) /
- MATLAB
Abstract:Lithium batteries have the advantages of light weight and safety, long cycle life, and good safety performance. As a widely-used energy storage power supply, lithium battery health management and life prediction are hot topics both at home and abroad. Lithium battery life assessment methods and prediction models were established. Battery decay models were established based on experimental historical data to evaluate the working status of the entire battery, and the equipment was maintained and replaced in time to ensure stable battery operation. In this paper, the kernel function of the relevance vector machine (RVM) was mainly improved, the performance of the relevance vector machine was optimized, the lithium battery life prediction bias was reduced, and the prediction accuracy was improved.
-
Key words:
- lithium battery /
- remaining useful life /
- prediction /
- relevance vector machine (RVM) /
- MATLAB
-
表 1 B0005电池预测结果
Table 1. B0005 battery prediction results
预测方法 预测起点 偏差度 标准差 拟合程度 运行时间/s 组合核函数 70 0.003 365 5 0.013 604 0.979 43 3.221 高斯核函数 70 0.010 356 0.013 678 0.979 42 2.938 表 2 B0006电池预测结果
Table 2. B0006 battery prediction results
预测方法 预测起点 偏差度 标准差 拟合程度 运行时间/s 组合核函数 80 0.006 954 2 0.016 442 0.972 59 3.634 高斯核函数 80 0.008 217 0.017 83 0.967 837 3.718 表 3 B0007电池预测结果
Table 3. B0007 battery prediction results
预测方法 预测起点 偏差度 标准差 拟合程度 运行时间/s 组合核函数 80 0.000 959 2 0.010 576 0.974 3 3.71 高斯核函数 80 0.002 875 8 0.011 009 0.972 19 3.593 表 4 B0018电池预测结果
Table 4. B0018 battery prediction results
预测方法 预测起点 偏差度 标准差 拟合程度 运行时间/s 组合核函数 60 -0.000 522 0.008 783 0.975 64 2.188 高斯核函数 60 -0.026 622 0.029 332 0.777 98 1.954 -
[1] 张卓识.锂离子电池建模与故障预测方法研究[D].大连: 大连海事大学, 2016.ZHANG Z S.Study of lithium-ion battery modeling and prognostics method[D].Dalian: Maritime Affairs University of Dalian, 2016(in Chinese). [2] 朱亮标.基于数据驱动的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测模型及软件实现[D].广州: 华南理工大学, 2014.ZHU L B.Remaining life prediction model and Software implementation for lithium-ion battery based on data-driven[D].Guangzhou: Institutes of Technology of South China, 2014(in Chinese). [3] 艾力, 房红征, 于功敬, 等.基于数据驱动的卫星锂离子电池寿命预测方法[J].计算机测量与控制, 2015, 23(4):1262-1265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2015.04.059AI L, FANG H Z, YU G J, et al.Research on data-driven life prediction methods of satellite lithium-ion battery[J].Computer Measurement & Control, 2015, 23(4):1262-1265(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2015.04.059 [4] 郑方丹.基于数据驱动的多时间尺度锂离子电池状态评估技术研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学, 2017.ZHENG F D.Multi-time scale state estimation of lithium-ion batteries using data driven method[D].Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017(in Chinese). [5] 赵春辉, 张燚.相关向量机分类方法的研究进展与分析[J].智能系统学报, 2012, 7(4):294-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201112019ZHAO C H, ZHANG Y.Research progress and analysis on methods for classification of RVM[J].CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2012, 7(4):294-301(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201112019 [6] 杨树仁, 沈洪远.基于相关向量机的机器学习算法研究与应用[J].计算机技术与自动化, 2010, 29(1):43-47. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjsyzdh201001013YANG S R, SHEN H Y.Research on data-driven life prediction methods of satellite lithium-ion battery[J].Computer Measurement & Control, 2010, 29(1):43-47(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjsyzdh201001013 [7] TIPPING M.The relevance vector machine, 2000[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Cambridge: MIT Press, 2000: 652-658. [8] 黄海.锂离子动力电池老化特性研究与循环寿命预测[D].济南: 山东大学, 2016.HUANG H.Research on aging performances and cycle-life predictions of Li-ion battery[D].Jinan: Shandong University, 2016(in Chinese). [9] 王立昆, 杨新峰.一种基于RVM回归的分类方法[J].电子科技, 2011, 24(5):14-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkj201105005WANG L K, YANG X F.A classification method based on RVM regression[J].Electronic Science and Technology, 2011, 24(5):14-16(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkj201105005 [10] 周建宝.基于RVM的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测方法研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013: 20-23.ZHOU J B.Research on lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation with relevance vector machine[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013: 20-23(in Chinese). [11] 杨柳, 张磊, 张少勋, 等.单核和多核相关向量机的比较研究[J].计算机工程, 2010, 36(12):195-197. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjgc201012067YANG L, ZHANG L, ZHANG S X, et al.Comparison research of single kernel and multi-kernel relevance vector machine[J].Computer Engineering, 2010, 36(12):195-197(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjgc201012067 [12] 豆金昌.锂离子电池健康评估及剩余使用寿命预测方法研究[D].南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.DOU J C.Health assessment and remaining useful life prediction of Li-ion battery[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013(in Chinese). [13] 李晗, 萧德云.基于数据驱动的故障诊断方法综述[J].控制与决策, 2011, 26(1):1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdhxb201609001LI H, XIAO D Y.Survey on data fault diagnosis methods[J].Control and Decision, 2011, 26(1):1-9(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdhxb201609001 [14] 张金, 魏影, 韩裕生, 等.一种改进的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测算法[J].电子技术应用, 2015, 41(8):110-112. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzjsyy201508032ZHANG J, WEI Y, HAN Y S, et al.An improved particle filter algorithm for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction[J].Application of Electronic Technique, 2015, 41(8):110-112(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzjsyy201508032 [15] 李柱.锂离子电池寿命预测方法研究[D].淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2017.LI Z.Study on remaining useful life prediction method for lithium-ion batteries[D].Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [16] 杨丽.基于模型驱动的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测方法研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.YANG L.Research on lithium-ion battery rul model driven prognosis method[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: